MGMT CH 9
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:52 PM on 4/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
leadership
process by which a person exerts influence over other people and inspires, motivates and directs their activities to achieve group or org goals
* influence > power
* influence > power
2
New cards
leader
individual able to exert influence over other people to help achieve goals
* effective leadership increases firms ability to meet new challenges
* effective leadership increases firms ability to meet new challenges
3
New cards
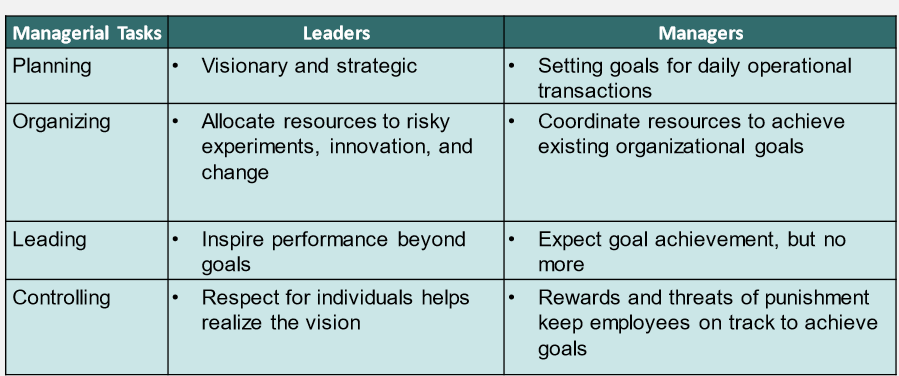
leadership vs management
4
New cards
personal leadership style
* specific ways a manager chooses to influence others and how they approach planning, organizing and controlling
* managers all levels have own leadership style
\
* managers all levels have own leadership style
\
5
New cards
difference between leadership and management
* managers promote stability
* leaders push for change
* managers implement vision and strat
* leaders provide it
* managers appointed
* leaders emerge organically
* leaders push for change
* managers implement vision and strat
* leaders provide it
* managers appointed
* leaders emerge organically
6
New cards
leadership styles
* emotional intelligence
* servant leadership
* indigenous leadership
* authentic leadership
* compassionate leadership
* discretionary leadership
* servant leadership
* indigenous leadership
* authentic leadership
* compassionate leadership
* discretionary leadership
7
New cards
sources of managerial power
* expert
* referent
* legitimate
* coercive - ability to infuence
* reward
* referent
* legitimate
* coercive - ability to infuence
* reward
8
New cards
emotional intelligence
ability to understand and manage one’s own emotions and others
9
New cards
servant leadership
desire to work for benefit of others; share power with followers
10
New cards
indigenous leadership
leadership as helping people
11
New cards
authentic leadership
being true, transparent, and thoughtful about ones response to leading
12
New cards
compassionate leadership
able to make difficult decisions in a humane manner
13
New cards
discretionary leadership
experts leading experts, immersion in details and collab
14
New cards
legitimate power
authority resulting from position in org heirarchy
15
New cards
reward power
ability to give or withhold tangible and intangible rewards
16
New cards
coercive power
ability to persuade someone to do something that they wouldn’t do otherwise
17
New cards
expert power
based on special knowledge skills and expertise of leader
18
New cards
referent pwoer
function of personal characteristics of the leader which earn workers respect, admiration and loyalty
19
New cards
early models of leadership
* trait model
* behavioural model
* behavioural model
20
New cards
trait model
* focused on identifying personal characteristics responsible for effective leadership
* effective leaders have certain personal qualities that set them apart from ineffective leaders
* effective leaders have certain personal qualities that set them apart from ineffective leaders
21
New cards
trait model characteristics
* intelligence
* knowledge and expertise
* dominance
* self confidence
* high energy
* tolerance for stress
* integrity and honesty
* maturity
* knowledge and expertise
* dominance
* self confidence
* high energy
* tolerance for stress
* integrity and honesty
* maturity
22
New cards
behavioural model
* two basic dimensions of leadership behaviours
* consideration (employee centered) behaviours
* initiating structure (production oriented) behaviours
* consideration (employee centered) behaviours
* initiating structure (production oriented) behaviours
23
New cards
consideration behaviours
managers show care, trust, and respect towards subordinates
* emphasis on well being of employees and interpersonal relations
* emphasis on well being of employees and interpersonal relations
24
New cards
initiating structure (production oriented) behaviours
leaders define and structure their role and the roles of their subordinates in order to achieve org goals
* emphasis on task related and goal achievement behaviours, including technical aspects of job
* emphasis on task related and goal achievement behaviours, including technical aspects of job
25
New cards
contingency models of leadership
* leadership depends/contingent on the situation
* effective leadership is result of interaction between the managers, what they do, and the situation
* effective leadership is result of interaction between the managers, what they do, and the situation
26
New cards
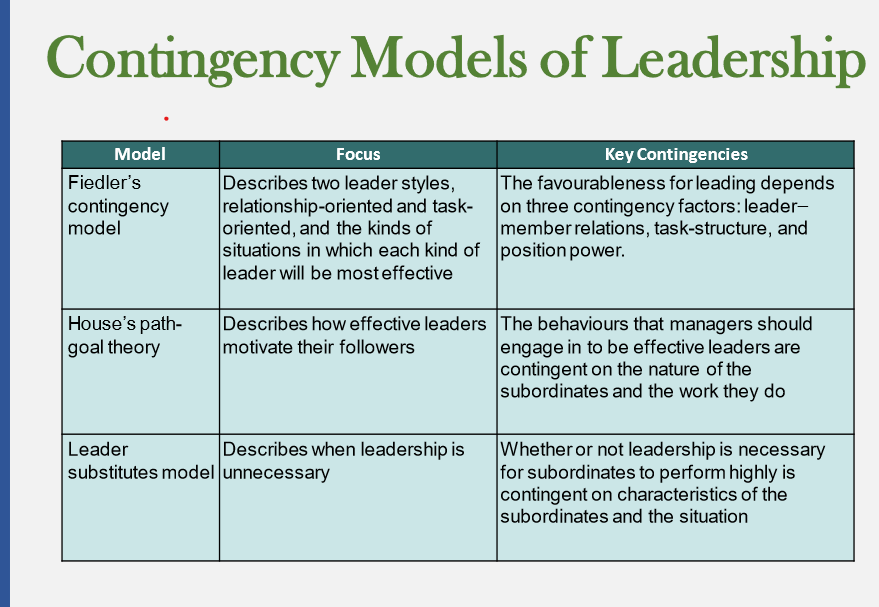
4 prominent contingency models
* Fiedler’s contingency model
* Evans-House’s path goal theory’
* leader sibstitues model
* Evans-House’s path goal theory’
* leader sibstitues model
27
New cards
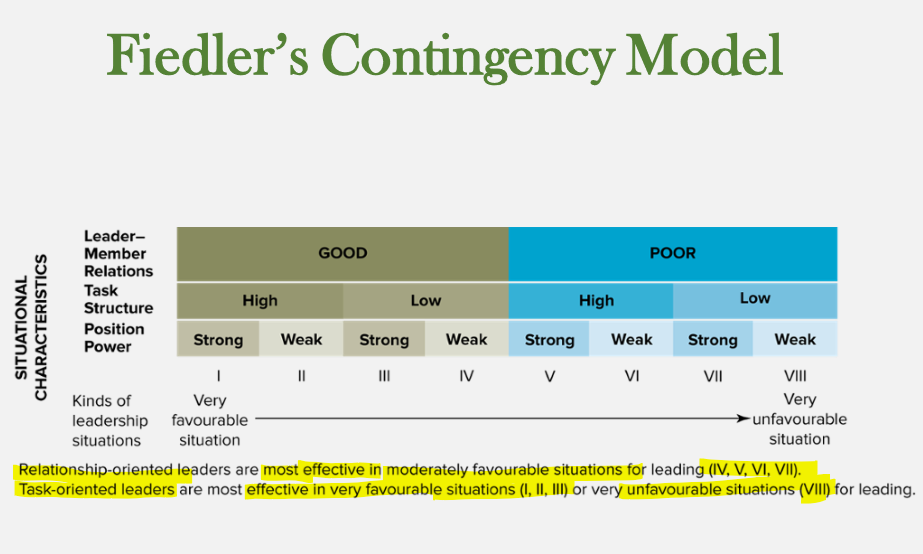
Fiedler’s contingency model
* effective leadership depends on characteristics of the leader and situation
* leader style
* manager’s characteristic approach to leadership
* identified two basic leader styles
* relationship oriented
* task oriented
* leader style
* manager’s characteristic approach to leadership
* identified two basic leader styles
* relationship oriented
* task oriented
28
New cards
Fiedler’s contingency model situational characteristics
important determinants of how favourable a given situation is for leading to occur
* leadership member relations
* extent to which followers like, trust and are loyal to their leader
* task structure
* extent to which work to be performed is clear cut so that workers know what needs to be accomplished and how to go about doing it
* position power
* amount of legitimate, reward, and coercive power leader has due to their position within an org
* leadership member relations
* extent to which followers like, trust and are loyal to their leader
* task structure
* extent to which work to be performed is clear cut so that workers know what needs to be accomplished and how to go about doing it
* position power
* amount of legitimate, reward, and coercive power leader has due to their position within an org
29
New cards
path goal theory
* based on expectancy theory of motivation
* find out what outcomes your subordinates are trying to obtain from their jobs and the org
* reward subordinates for high performance and goal attainment with the outcomes they desire
* clarify the paths to goal attainment for subordinates, remove any obstacles to high performance, and express confidence in subordinates capabilities
* find out what outcomes your subordinates are trying to obtain from their jobs and the org
* reward subordinates for high performance and goal attainment with the outcomes they desire
* clarify the paths to goal attainment for subordinates, remove any obstacles to high performance, and express confidence in subordinates capabilities
30
New cards
path goal theory behaviours
* behaviours that leaders can use to motivate subordinates
* directive behaviours
* setting goals, assigning tasks, showing subordinates how to compete tasks, and taking concrete steps to improve performance
* supportive behaviours
* expressing concern for subordinates and looking out for their best interests
* participative behaviours
* give subordinates a say in matters and decisions that affect them
* achievement oriented behaviours
* motivate subordinates to perform at the highest level possible
* directive behaviours
* setting goals, assigning tasks, showing subordinates how to compete tasks, and taking concrete steps to improve performance
* supportive behaviours
* expressing concern for subordinates and looking out for their best interests
* participative behaviours
* give subordinates a say in matters and decisions that affect them
* achievement oriented behaviours
* motivate subordinates to perform at the highest level possible
31
New cards
leader substitutes model
* in some situations, leadership is unnecessary because of leader substitutes - something that acts in the place of the influence of leader
* managers do not always need to directly influence over subordinates
* worker empowerment or self managed teams free up leaders time for other important activities
* managers do not always need to directly influence over subordinates
* worker empowerment or self managed teams free up leaders time for other important activities
32
New cards
visionary models of leadership
* leaders are not only expected to perform supervisory tasks but also need to focus on vision setting activities
* three visionary models of leadership
* transformational leadership
* charismatic leadership
* turnaround leadership
* three visionary models of leadership
* transformational leadership
* charismatic leadership
* turnaround leadership
33
New cards
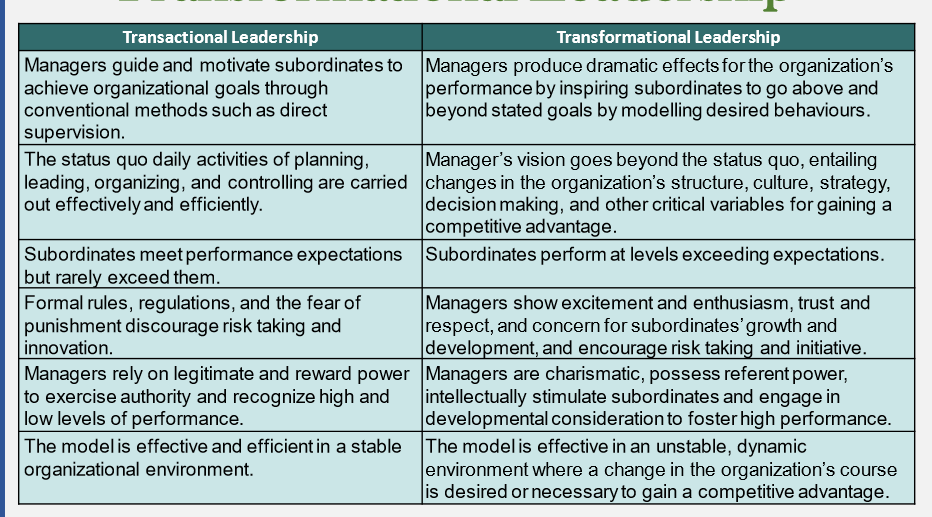
transformational leadership
* **transactional leadership**
* managers motivate their subordinates in direction of established goals
* employees generally meet (not exceed) expectations
* **transformational leadership**
* makes subordinates aware of the importance of their jobs and performance to the org
* provides a compelling vision and sense of mission
* inspires subordinates to exceed standards
* stimulates the intelligence of subordinates
* shows consideration for personal growth needs of subordinates
* managers motivate their subordinates in direction of established goals
* employees generally meet (not exceed) expectations
* **transformational leadership**
* makes subordinates aware of the importance of their jobs and performance to the org
* provides a compelling vision and sense of mission
* inspires subordinates to exceed standards
* stimulates the intelligence of subordinates
* shows consideration for personal growth needs of subordinates
34
New cards
transformational leadership changes
1. subordinate have increased awareness of the importance of thier jobs and high performance to the org as a whole
2. subordinates are made aware of their own needs for growth, development, and accomplishment
3. subordinates work for the good of the org as a whole not just for own personal gain or benefit
35
New cards
transactional vs transformational leadership
36
New cards
charismatic leadership
* enthusiastic, self confident leaders who are able to clearly communicate their vision of the org should operate
* key characteristics
* vision and articulation
* personal risk
* environmental sensitivity
* sensitivity to follower needs
* unconventional behaviour
* key characteristics
* vision and articulation
* personal risk
* environmental sensitivity
* sensitivity to follower needs
* unconventional behaviour
37
New cards
turnaround leadership
* leading a company that requires turning around
* dialogue with customers and employees
* refocus strat
* add value for customers
* be honest and realistic
* create an inspiring identity
* promote human value
* increase info flow
* dialogue with customers and employees
* refocus strat
* add value for customers
* be honest and realistic
* create an inspiring identity
* promote human value
* increase info flow