Topic 6: Inheritance, Variation & Evolution
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What does DNA stand for?
DNA - Deoxyribonucleic acid
What is a chromosome?
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part the genetic material of an organism
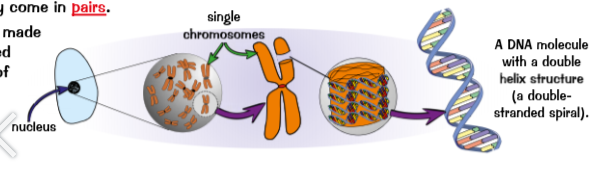
Where in a cell are the chromosomes located?
The nucleus
How many chromosome are there in a typical human cell?
46
How many pairs of chromosomes are there in a typical human cell?
23 pairs
What is the basic structure of DNA?
DNA is a polymer made up of two strands wrapped around each other to form a double helix
What are sex chromosomes?
Sex chromosomes are the 23rd pair of chromosomes. They determine whether and individual is male or female.
What sex chromosomes do females have?
XX
What sex chromosomes do males have?
XY
What is a gene?
A gene is a small section of DNA on a chromosome. Each gene codes for a particular sequence of amino acids, to make a specific protein.
What is the "genome“ of an organism?
The genome of an organism is the entire genetic material of an organism
How could understanding the human genome help science?
1) It will allow scientists to search for genes linked to different diseases
2) It could help understand and treat inherited disorders
3) It also could be used for tracing human migration patterns from the past
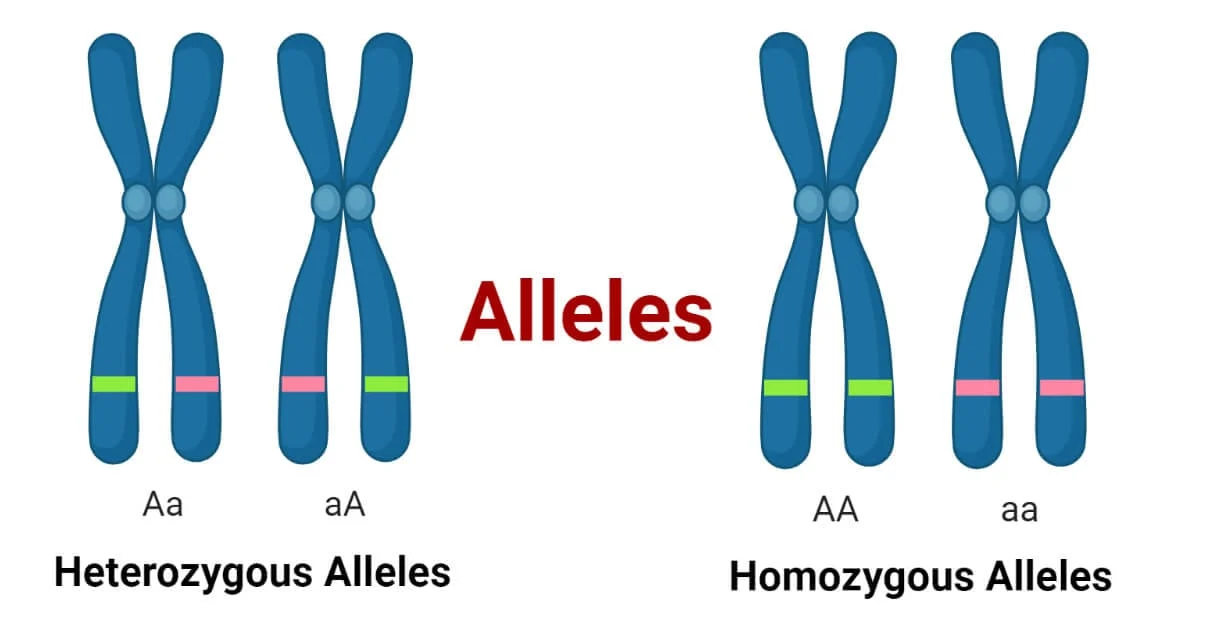
What is an allele?
Alleles are the different versions of a particular gene
How many alleles of each gene does an individual have?
2
What does it mean to be “homozygous“ for a particular gene?
Both alleles of that gene are identical
What does it mean to be “heterozygous“ for a particular gene?
The two alleles of that gene are different
What is the dominant allele?
A dominant allele is one which is always expressed, even if there is only one copy of that allele
What type of allele is one which is only expressed if there are two copies of it?
recessive allele
What does “genotype” mean?
The term genotype can be difficult to understand because it has multiple meanings.
1) One definition describes a genotype as: "an individual’s collection of genes”
2) But more common definition in this course is: “the two alleles present for a particular gene“
In either case, the term genotype refers to the specific genes or alleles that an individual has.
What does phenotype mean?
The characteristics an organism has a result of their genotype (and environment)
Are most characteristics determined by: a single gene, a combination of multiple genes or the combination of multiple genes and the environment?
Most characteristics are determined by the combination of multiple genes and the environment
Is DNA a monomer or polymer?
Polymer
What are the monomers that combine to form DNA
Nucleotides are the monomers that form DNA (a polymer)
What are the names of the 4 bases that make DNA?
1) Adenine (A)
2) Thymine (T)
3) Guanine (G)
4) Cytosine (C)
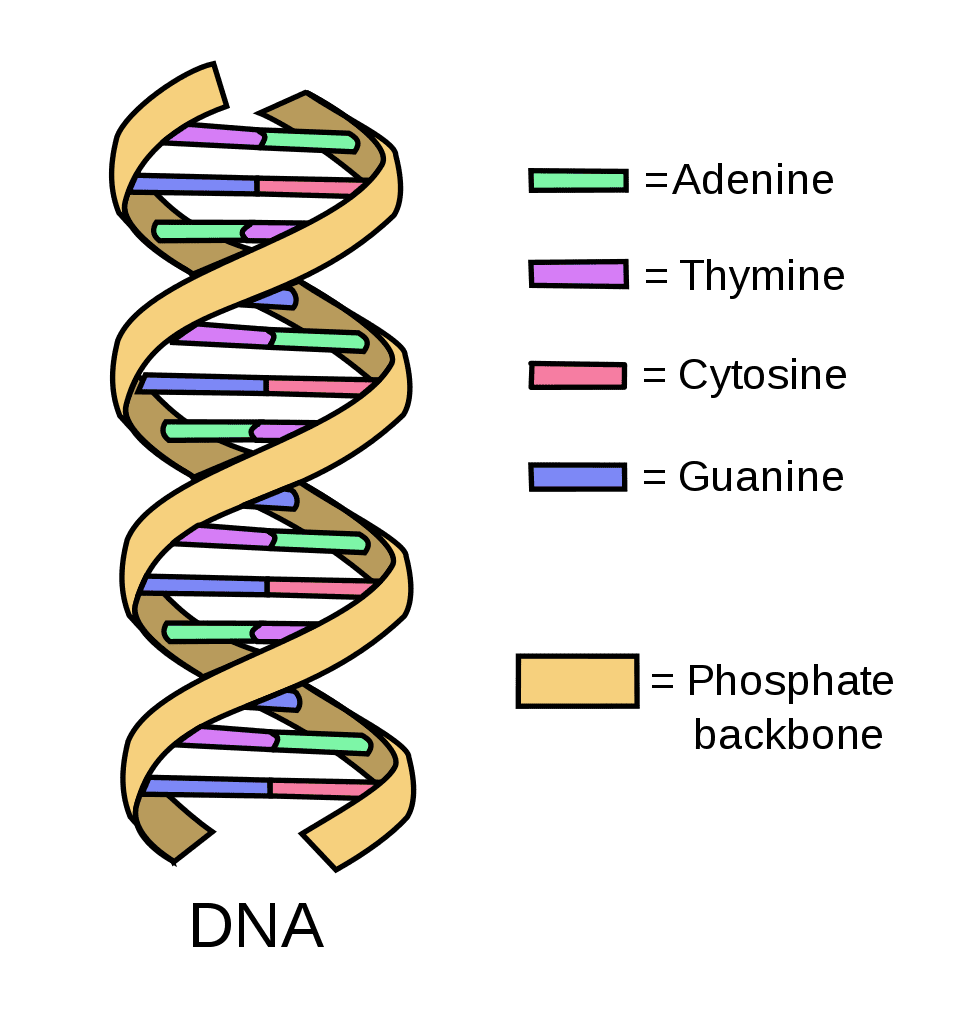
What is complementary base pairing?
Complementary base pairing is the idea that DNA bases always pair up in a similar way
Which base will adenine always pair?
Adenine (A) always pairs with Thymine (T)
Which base will guanine (G) always pair with?
Guanine (G) always pairs with cytosine (C)
How many bases are required to code for an amino acid?
3 bases are needed to code for an amino acid
What do we call a set of all 3 bases, which code for an amino acid?
A “triplet” or “codon“
Give 3 uses of proteins
1) Enzymes
2) Hormones
3) Structural proteins
(there are many more tho)