Genetics - Lecture 9: Introduction to Molecular Genotyping
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Synthetic oligonucleotide primers
can be made in an automated way for replication of a target gene
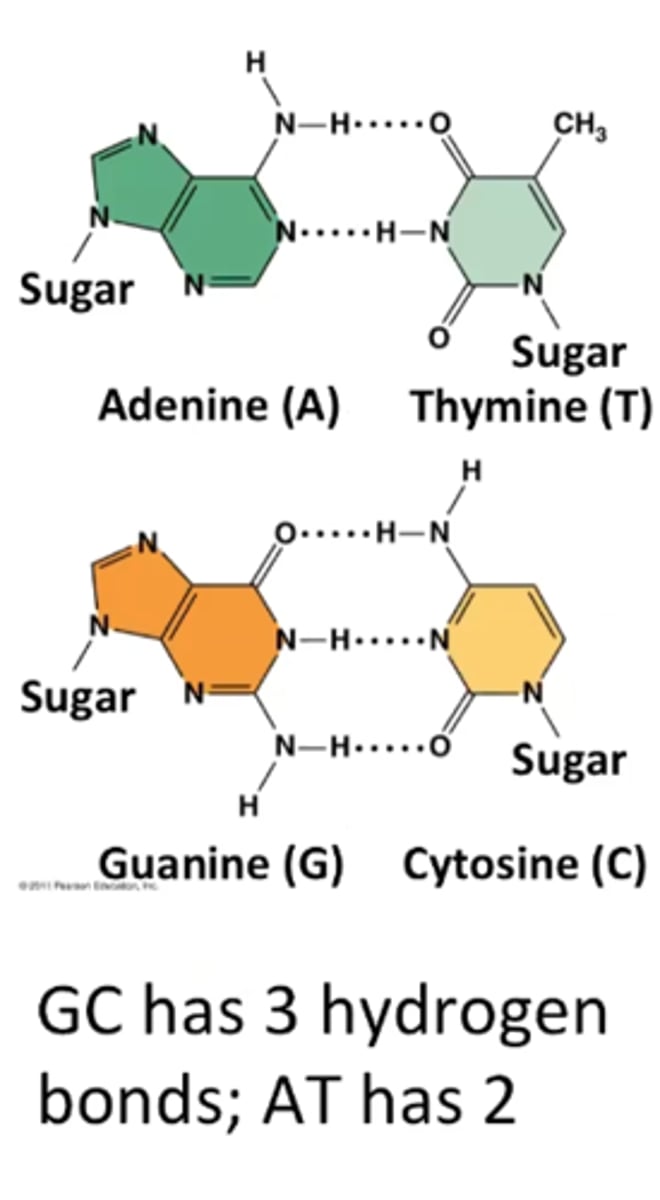
Having more of which, GC or AT, increased melting point of DNA molecule? Why?
GC because it has 3 H bonds and AT only has 2
General primer guidlines
20-200 bases
~50% GC
Avoid repeats of bases
Gel electrophoresis
separates DNA fragments by size
molecules are sorted into bands on the gel by size
Dye used in agarose gel
intercalating dyes which insert themselves into DNA molecules
Ladder mixture (gel electrophoresis)
bands are compared to ladder mixture containing DNA of known sizes
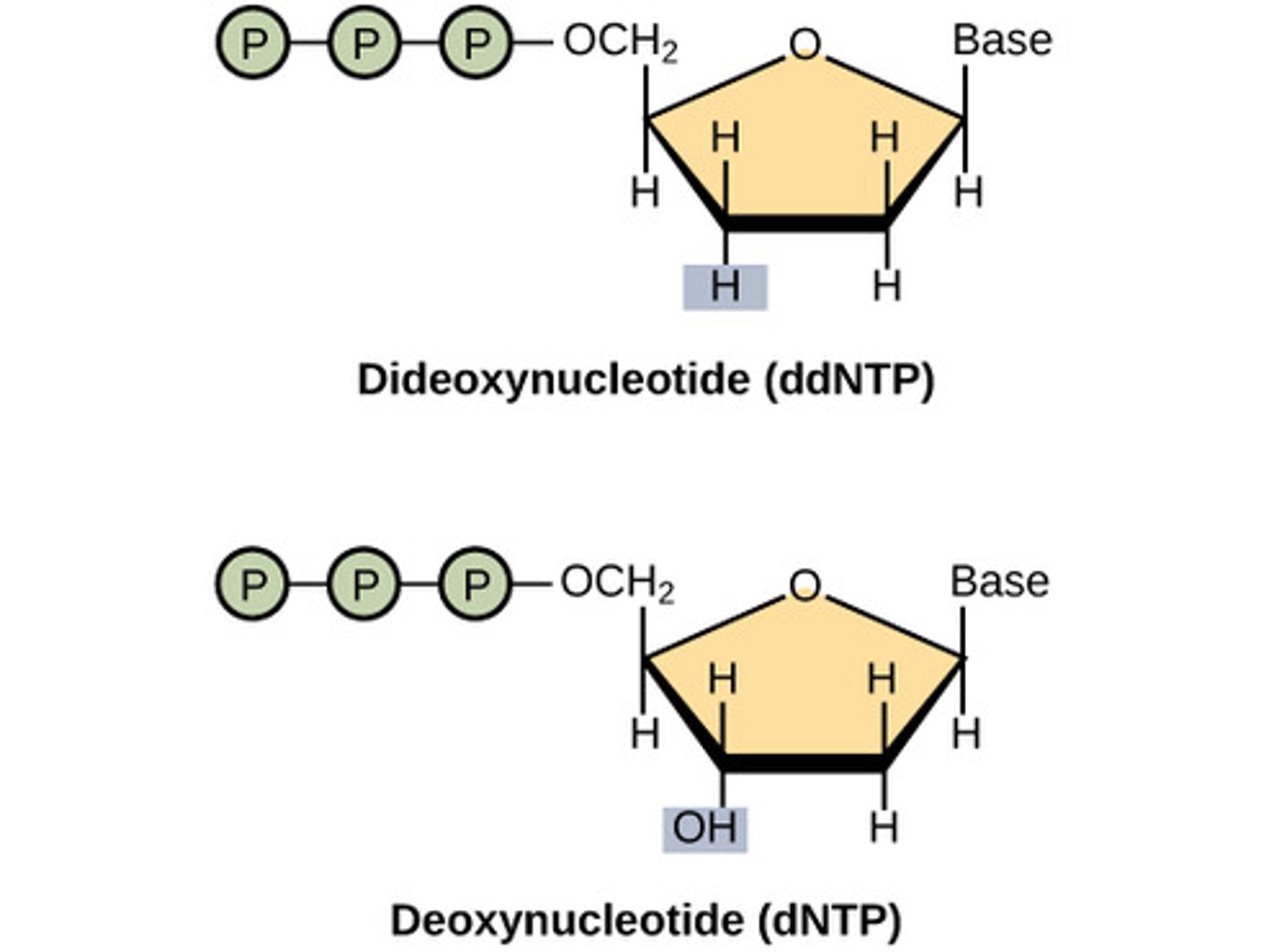
Dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs)
a nucleotide used in DNA sequencing that is missing the 3'-OH group. If a dideoxyribonucleotide is incorporated into a DNA strand, it stops any further growth of the strand.
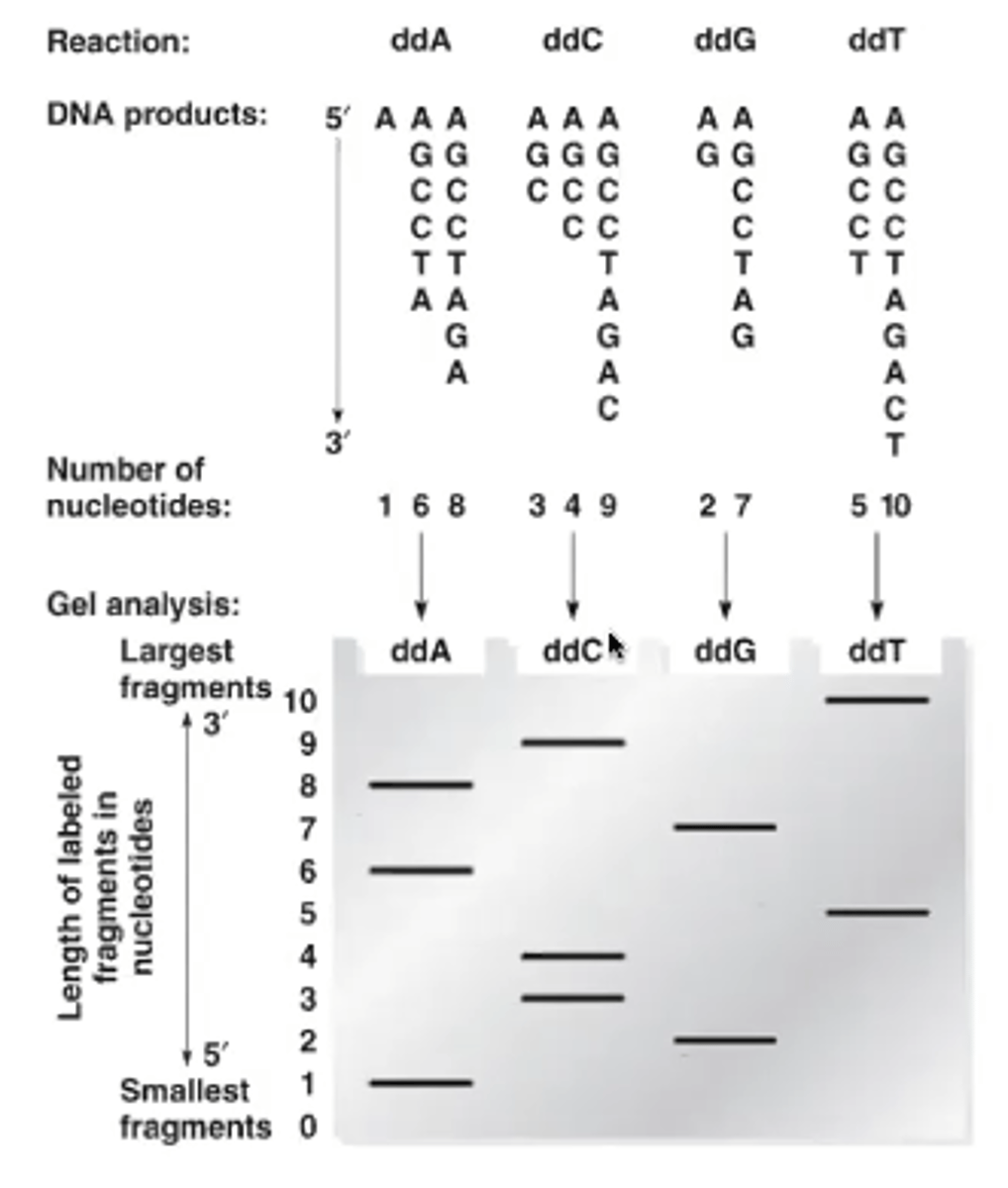
Old school Sanger sequencing
radiolabelled primer anealled just above target sequence
four rxns, each containing primer, dNTPs, and trace levels of single ddNTPs
Four different ddNTPs
ddATP, ddCTP, ddGTP, and ddTTP
The bands on the gel in the Sanger sequencing correspond to...
one of the four different bases in a 5'---> 3' direction (top to bottom of the gel)
Each of the four Sanger reactions are run through polyacrylamide gel and read in which direction?
5'---> 3'
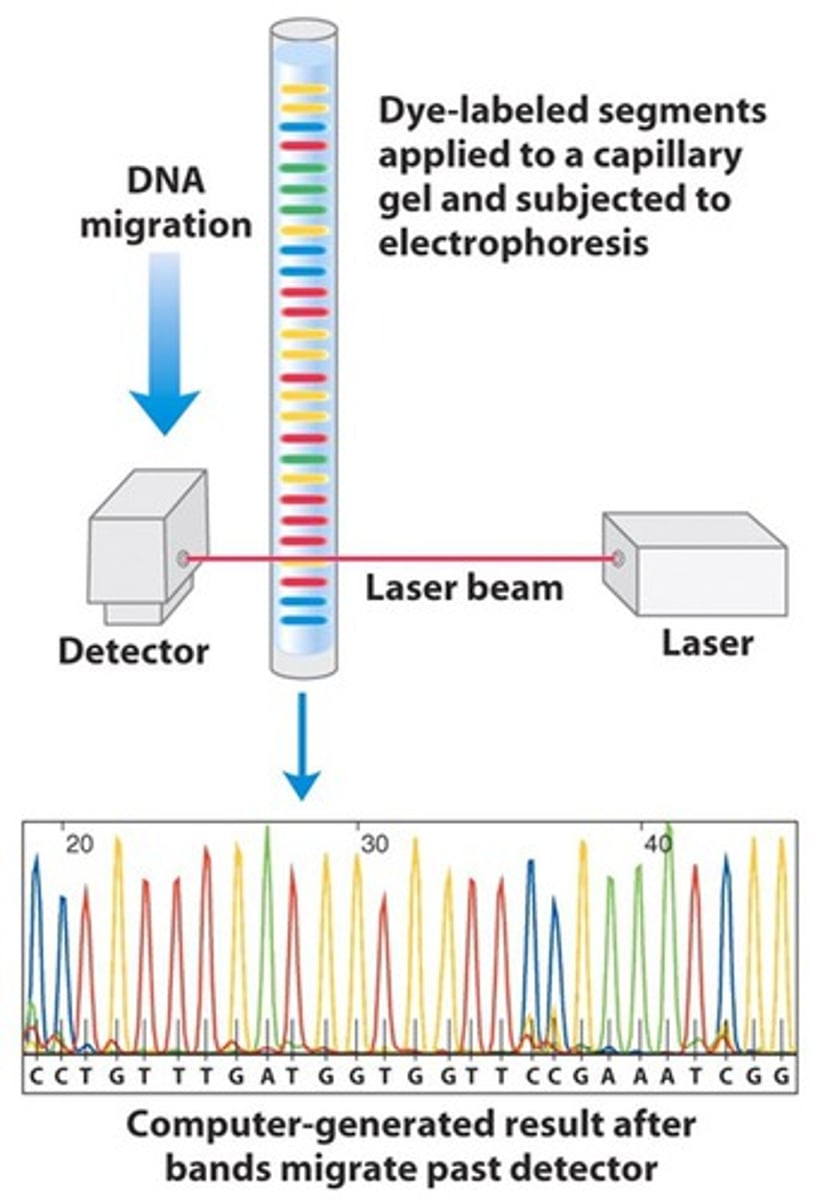
Modern Sanger sequencing
dNTPs + polymerase + trace amounts of flourescently labeled ddNTPs
How is modern Sanger sequencing read?
capillary electrophoresis
Why is PCR so useful?
allows us to look at one specific piece of DNA by making many copies of ONLY that piece of DNA
Requirements for PCR
-DNA template
-dNTPs
-DNA polymerase
-complimentary primers - RNA in vivo, DNA in vitro
-Mg2+ (for polymerase activity)
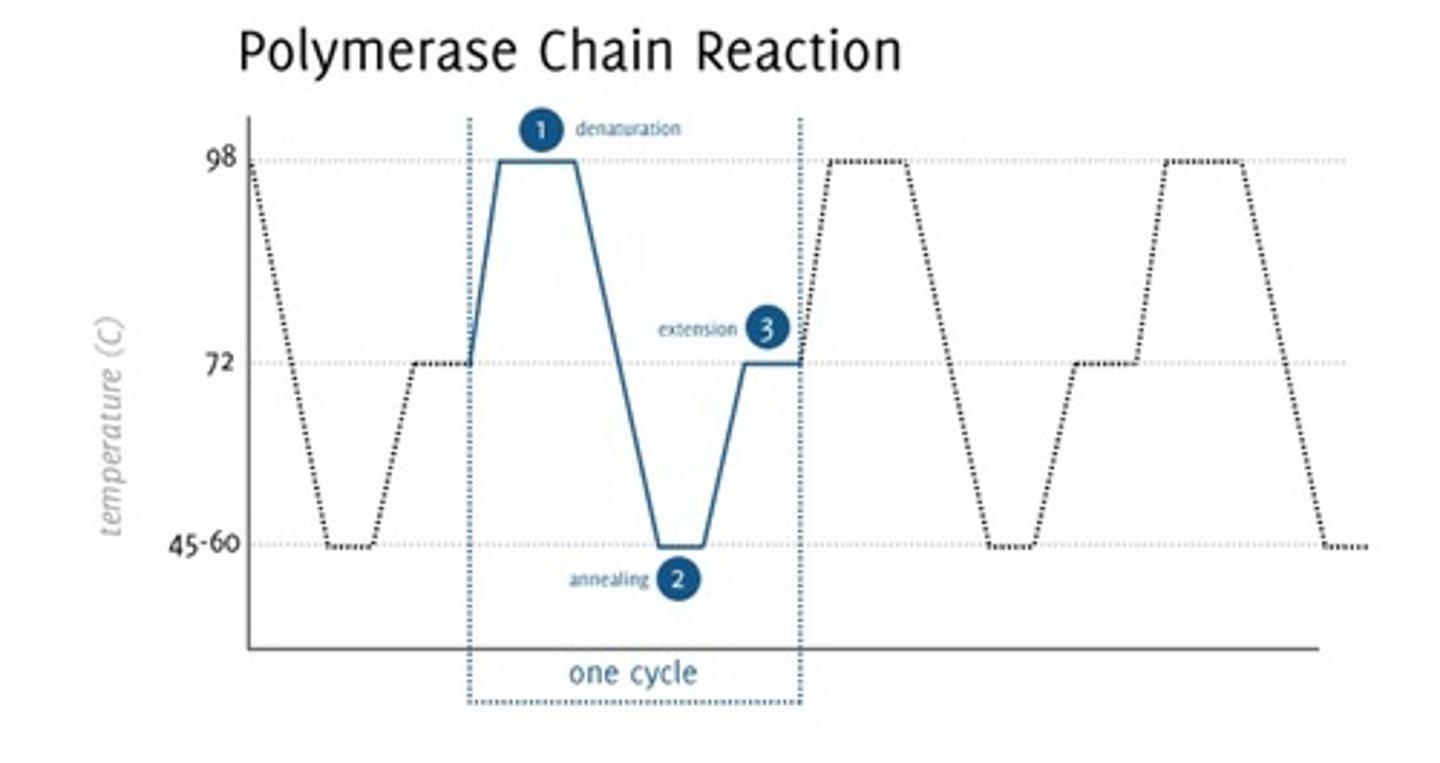
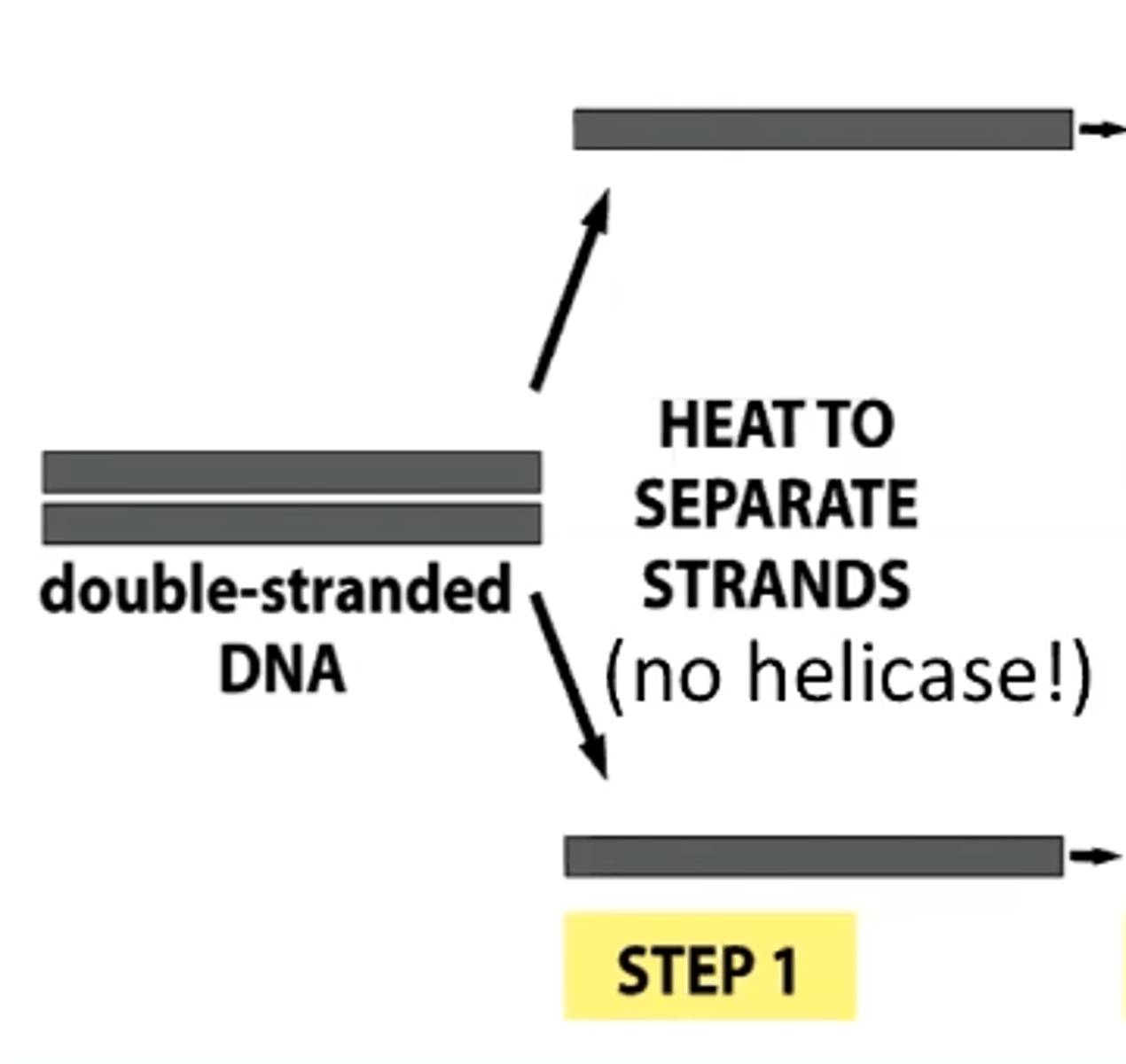
Step 1 PCR
heat DNA (denaturing)
Step 2 PCR
annealing of primers - both foward and reverse
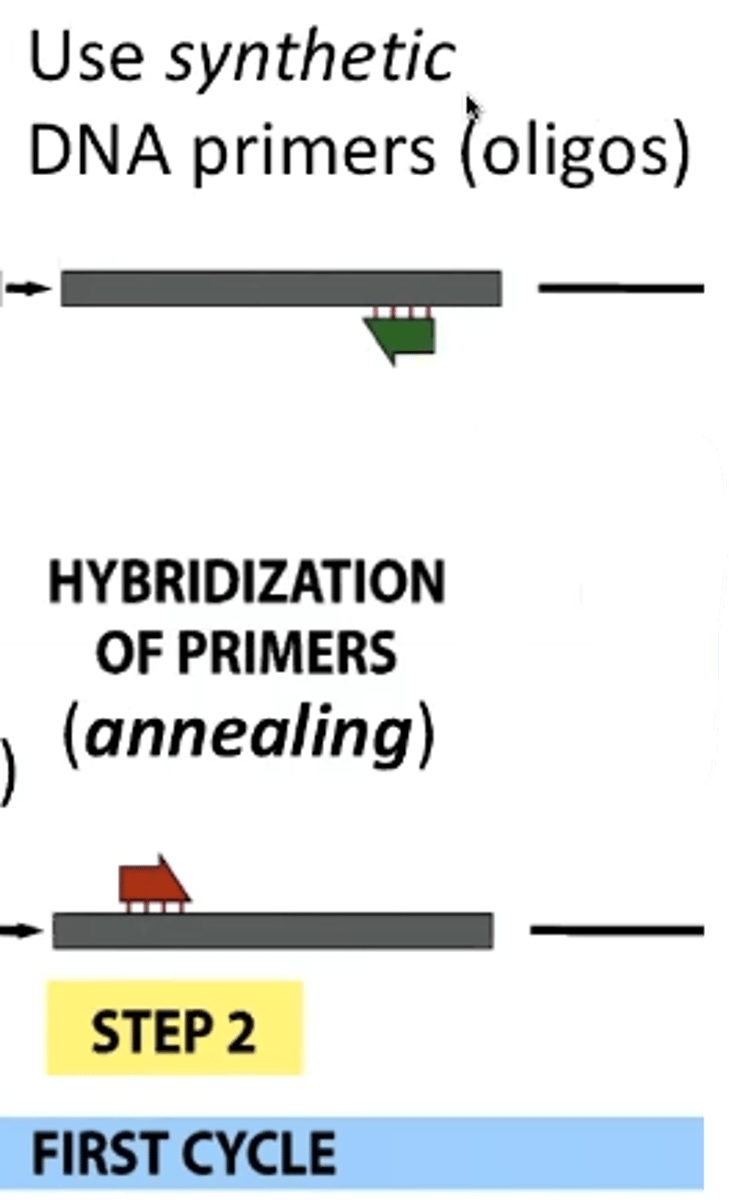
Step 3 PCR
Extension-primers build new DNA (free nucleotides) in 3' to 5' direction

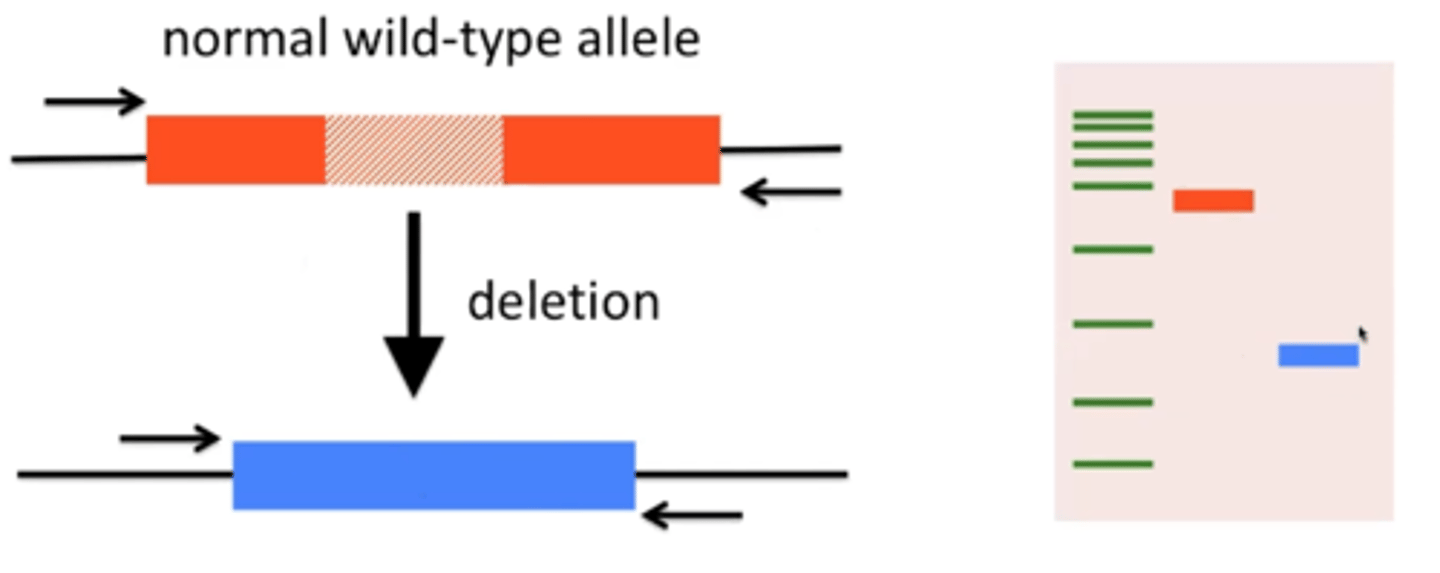
PCR and genotyping (indels)
Used to recognize certain mutations that give rise to different-sized PCR products (usually indels)
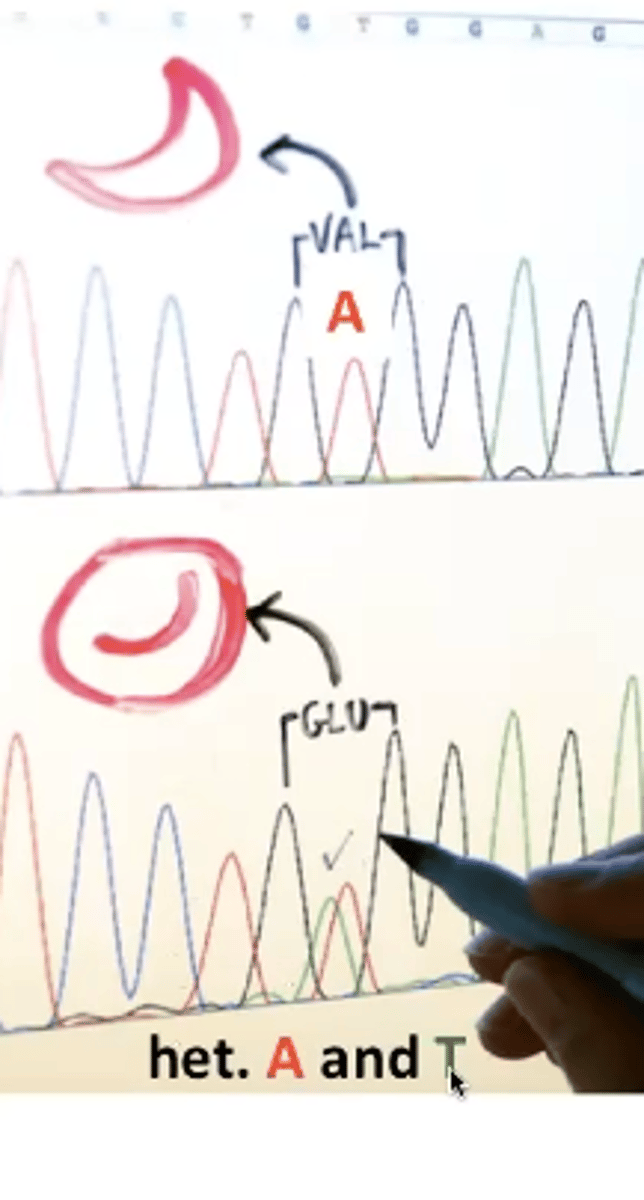
PCR and Sanger sequencing
The region around a known mutation can be PCR-amplified and sequenced directly
Two peaks at a specific base Sanger
heterozygous individual
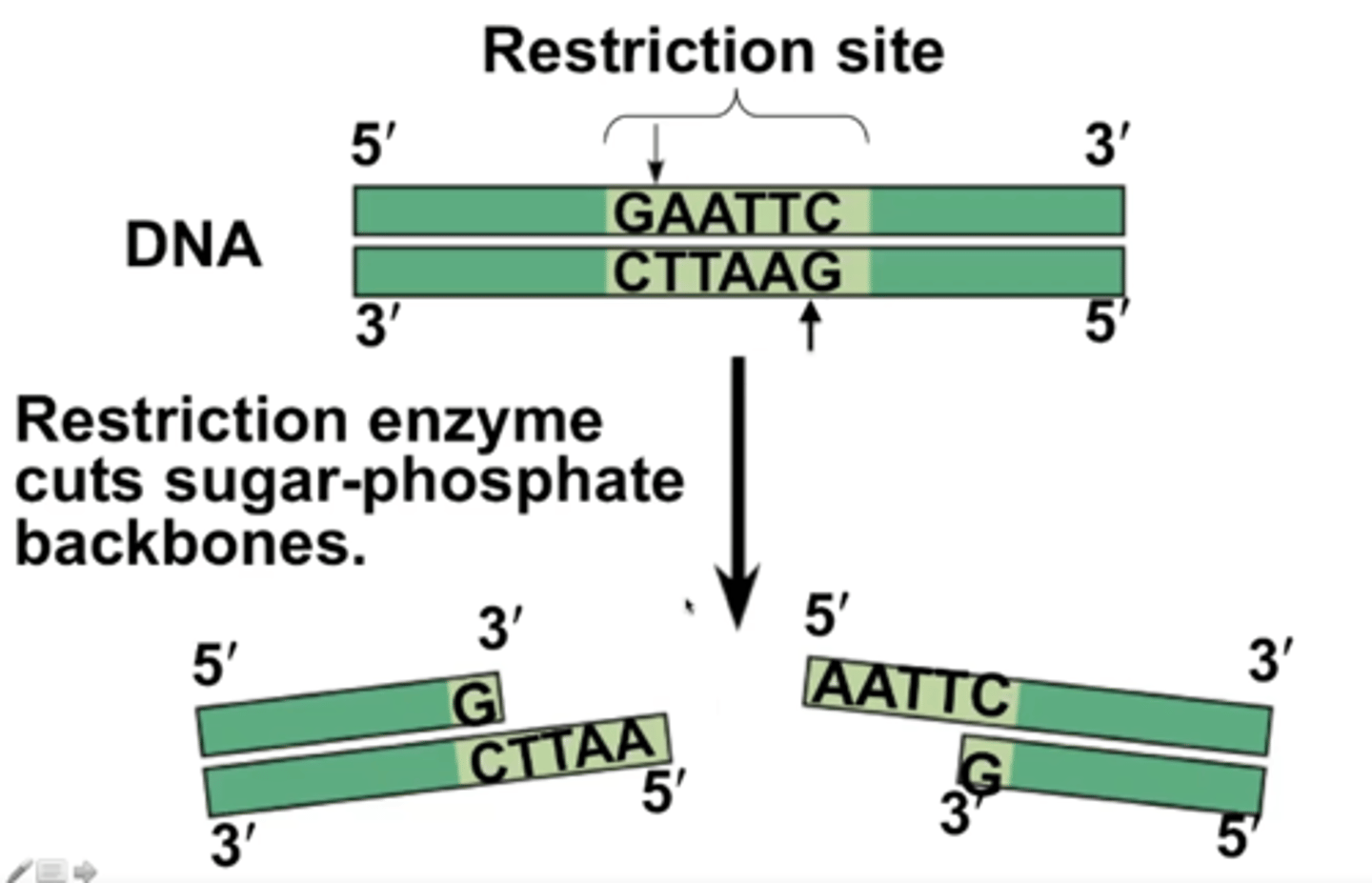
RFLP
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
Restriction enzyems in RFLP
recognize and cleave specific DNA sequences
What do the restriction enzymes do in RFLP?
cut the sugar-phosphate backbone at the restriction site
Mutations can remove restriction sites in a gene which...
changes the sizes and number of bands produced when the PCr product is run through the gel

Southern Blot
transfer DNA onto filter paper
add radioactively labeled probes for gene and observe autoradiography