AP Environmental Science - (Smedes Quizlet Sets)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/590
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:35 PM on 10/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
591 Terms
1
New cards
Symbiosis
A relationship in which two different species live in close association with each other in a long-term relationship
2
New cards
Ecosystem
All of the abiotic (non-living) and biotic (living) components of a given area
3
New cards
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit
4
New cards
Parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed. The parasite often lives inside of and using the host as an energy source, although not always.
5
New cards
Interspecific competition
competition between members of different species, such as lions and hyenas competing for food
6
New cards
Competition
A common demand by two or more organisms upon a limited supply of a resource; for example, food, water, light, space, mates, nesting sites. It may be intraspecific or interspecific.
7
New cards
Resource partitioning
The evolution of behavioral and physical adaptations that allow two species to reduce their competition for a shared resource
8
New cards
Coevolution
Process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other. Can often result in resource partitioning or mutualistic relationships
9
New cards
population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
10
New cards
community
All the different populations that live together in an area
11
New cards
biome
An area with a particular average temperature and precipitation (climate)
12
New cards
Terrestrial
relating to the land (not aquaitc, or water-based)
13
New cards
Climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
14
New cards
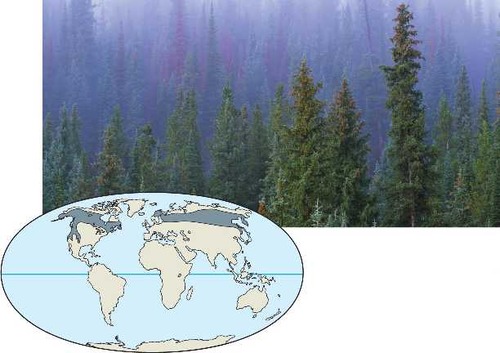
Taiga (boreal forest, northern coniferous forest)
Forests with mostly coniferous (cone-bearing) trees that can tolerate cold winters and short growing seasons. Needles of coniferous trees are adapted to tolerate freezing temperatures, so they stay on all year (evergreen).
Cold temperature, waxy, tough needles that don't break down easily both contribute to slow decomposition and low soil nutrient levels.
Cold temperature, waxy, tough needles that don't break down easily both contribute to slow decomposition and low soil nutrient levels.
15
New cards
Tundra
Flat, cold, treeless biome with permanently frozen soils in winter, and a short, 4 month growing season in the summer. Even in summer, deeper soil remains totally frozen (permafrost) preventing taller trees from establishing roots. Mostly shrubs, grasses, mosses, and lichens that can withstand shallow, waterlogged soil & cold temperatures.
Cold temp. = low decomp. = low soil nutrients
Cold temp. = low decomp. = low soil nutrients

16
New cards
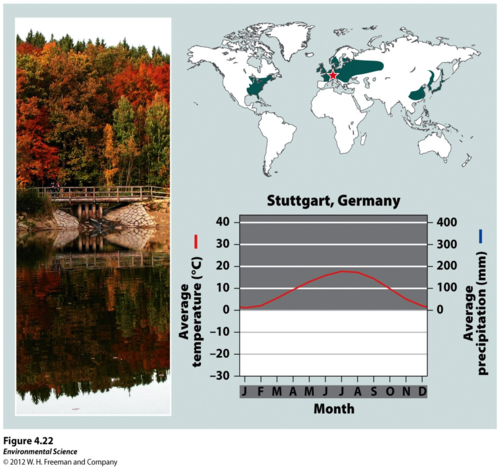
temperate seasonal forest
A biome with warmer summers and colder winters than temperate rainforests and dominated by deciduous (broadleaf - maples, oaks, etc.) trees.
High summer temp. = faster decomp.
Broadleaves easier to decomp. than needles = higher soil nutrients than boreal forests or temperate rainforests
High summer temp. = faster decomp.
Broadleaves easier to decomp. than needles = higher soil nutrients than boreal forests or temperate rainforests
17
New cards
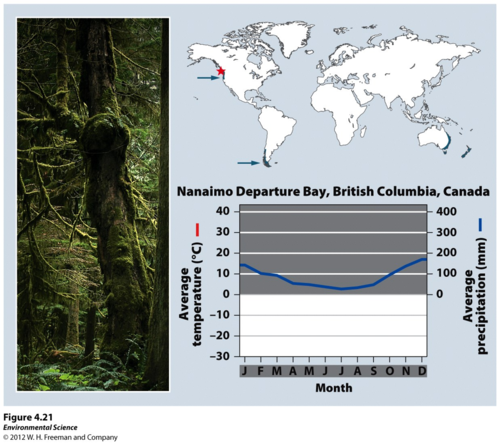
Temperate rainforest
Cool, rainy forests found along coasts, such as the northern Pacific. Water vapor from oceans keeps the temperature moderate and provides lots of moisture for high precipitation. Huge conifers like the red woods of California are found in these biomes.
Cooler temperature = slow decomp.
heavy rainfall & rapid absorption by large trees = low nutrient levels in soil
Cooler temperature = slow decomp.
heavy rainfall & rapid absorption by large trees = low nutrient levels in soil
18
New cards
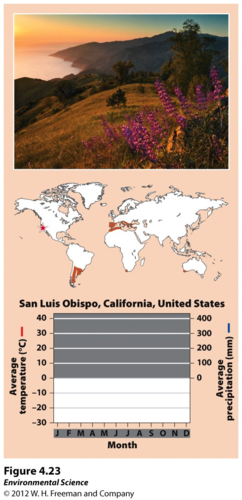
woodland/shrubland (chaparral)
Hot dry summers with mild, rainy winters. 12 month growing period, but relatively low precipitation in summer, and lower temperature in winter limit plant growth. Plants here must be adapted to both fires and drought (sagebrush, scrub oak, and shrubs).
High rain in winter = leaching of nutrients = low nutrient soil
High rain in winter = leaching of nutrients = low nutrient soil
19
New cards
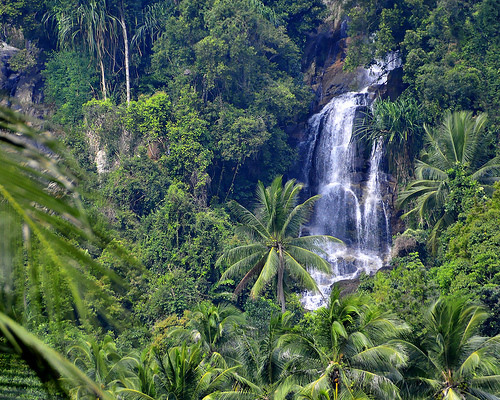
Tropical rainforests
Near the equator. Warm with lots of precipitation. Little seasonal temperature variation. Highly productive (high plant growth) terrestrial biome.
Hot temp. = rapid decomp. of organic matter
High plant growth = rapid absorption of nutrients
Low nutrient soils
Hot temp. = rapid decomp. of organic matter
High plant growth = rapid absorption of nutrients
Low nutrient soils

20
New cards
Savanna
Warm biome with distinct wet and dry seasons. Dominated by clustered trees and widespread grasses. Trees adapted to drought by dropping leaves in dry season.
Warm temperature = high decomp. = high soil nutrients
Warm temperature = high decomp. = high soil nutrients

21
New cards
Desert
Occur around 30 degrees N & S latitude. Very high temperatures and low precipitation levels limit plants to drought-resistant species like cacti & succulents. Needles are modified leaves to prevent water loss and most photosynthesis happens in the stem, to limit water loss.

22
New cards
Latitude
distance north or south of the Equator, measured in degrees
23
New cards
Altitude
Elevation (height) above sea level
24
New cards
Permafrost
permanently frozen layer of soil beneath the surface of the ground, particularly in tundra biomes. Thaws out in the winter to produce standing water and water-logged soils that further restrict plant growth in tundra biomes.
25
New cards
temperate grassland/cold desert
Great plaines (prairie) biome with cold, harsh winters and hot, dry summers restrict plant growth to mostly grasses and non-wood plants like wild flowers. Deep roots can reach water in droughts and store energy for quick regrowth after frequent fires due to such dry conditions.
High temperature & long growing season = rapid decomp. = high soil nutrients
High temperature & long growing season = rapid decomp. = high soil nutrients
26
New cards
Salt Marsh
An estuary marsh, found along the coast in temperate climates. Mix of fresh and salt water. Highly productive breeding grounds for many fish and shellfish species.

27
New cards
Aquatic
relating to water
28
New cards
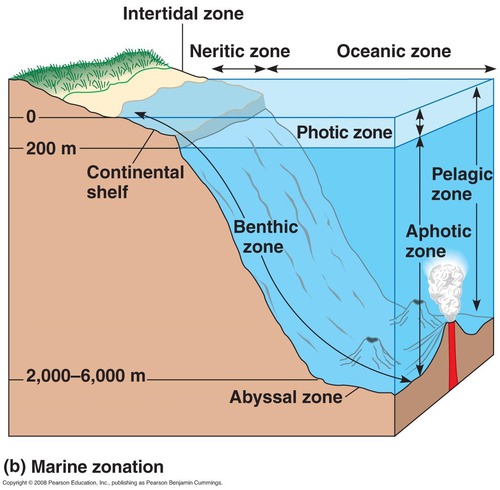
benthic zone
bottom of an aquatic ecosystem; consists of sand and sediment and supports its own community of organisms
29
New cards
Open Ocean
Deep, salty aquatic biome. Largest boime on earth. Algae in this biome produce a significant portion of earth's oxygen via photosynthesis
30
New cards
Coral reef
Shallow, warm, ocean biome featuring the symbiotic relationship between coral and algae. Coral supply the calcium-carbonate reef for algae to live in, as well as nutrients and CO2. The algae use nutrients and CO2 for photosynthesis and release sugar for the coral to use as energy.

31
New cards
Mangrove swamps
A swamp biome that occurs along tropical and subtropical coasts, and contains salt-tolerant trees with roots submerged in water. Roots provide organic matter and habitat for many fish & shellfish species as well as stabilizing the shoreline from erosion.

32
New cards
Estuary
A habitat in which the fresh water of a river meets the salt water of the ocean. High levels of organic matter term-50are deposited by the river, making them high nutrient, highly productive ecosystems.
33
New cards
Algae
a very simple plant without stems or leaves that grows in or near water.
34
New cards
Salinity
A measure of the amount of dissolved salts in a given amount of liquid.

35
New cards
Turbidity
A measure of how cloudy water is (higher turbidity = more cloudy). Sediments like sand and leaf litter increase turbidity.

36
New cards
Freshwater Wetlands
An aquatic biome that is submerged or saturated by water for at least part of each year, but shallow enough to support emergent vegetation such as trees and cattails. Plants must have adaptations to allow them to survive water-logged soil.

37
New cards
Salt Marsh
An estuary marsh, found along the coast in temperate climates. Mix of fresh and salt water. Highly productive breeding grounds for many fish and shellfish species.

38
New cards
Aquatic
relating to water
39
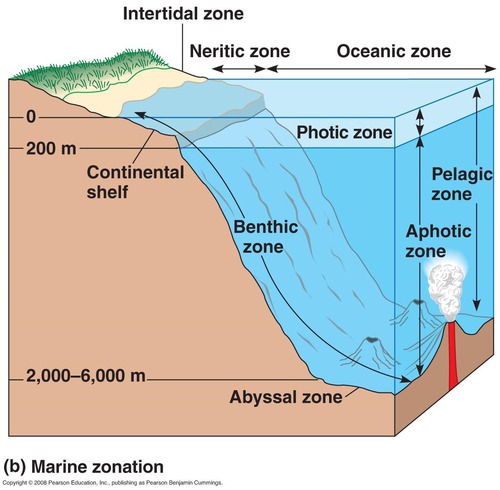
New cards
benthic zone
bottom of an aquatic ecosystem; consists of sand and sediment and supports its own community of organisms
40
New cards
Open Ocean
Deep, salty aquatic biome. Largest boime on earth. Algae in this biome produce a significant portion of earth's oxygen via photosynthesis
41
New cards
Coral reef
Shallow, warm, ocean biome featuring the symbiotic relationship between coral and algae. Coral supply the calcium-carbonate reef for algae to live in, as well as nutrients and CO2. The algae use nutrients and CO2 for photosynthesis and release sugar for the coral to use as energy.

42
New cards
Mangrove swamps
A swamp biome that occurs along tropical and subtropical coasts, and contains salt-tolerant trees with roots submerged in water. Roots provide organic matter and habitat for many fish & shellfish species as well as stabilizing the shoreline from erosion.

43
New cards
Estuary
A habitat in which the fresh water of a river meets the salt water of the ocean. High levels of organic matter term-50are deposited by the river, making them high nutrient, highly productive ecosystems.
44
New cards
Algae
a very simple plant without stems or leaves that grows in or near water.
45
New cards
Salinity
A measure of the amount of dissolved salts in a given amount of liquid.

46
New cards
Turbidity
A measure of how cloudy water is (higher turbidity = more cloudy). Sediments like sand and leaf litter increase turbidity.

47
New cards
Freshwater Wetlands
An aquatic biome that is submerged or saturated by water for at least part of each year, but shallow enough to support emergent vegetation such as trees and cattails. Plants must have adaptations to allow them to survive water-logged soil.

48
New cards
Carbon reservoirs
Relatively stable, short-term stores of carbon on earth.
Ex: fossil fuels, soils and sediments, plant and animal biomass, and the atmosphere
Ex: fossil fuels, soils and sediments, plant and animal biomass, and the atmosphere
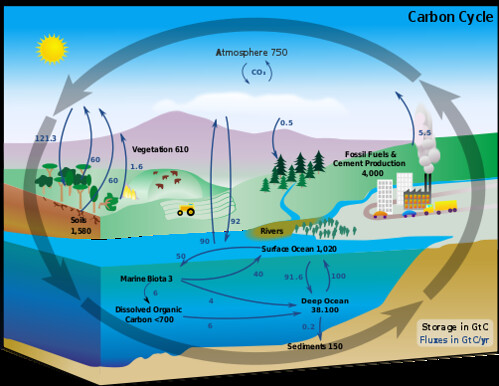
49
New cards
Carbon sinks
Relatively long-term stores that can take in more carbon dioxide than they produces
Ex: Plants, ocean, soils, sedimentary rock (can be either reservoirs or sinks, depending on their depth & time)
Ex: Plants, ocean, soils, sedimentary rock (can be either reservoirs or sinks, depending on their depth & time)

50
New cards
Photosynthesis
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into sugars and oxygen. Removes CO2 from atmosphere.
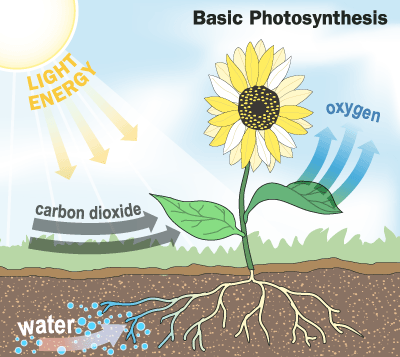
51
New cards
Cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and releasing CO2 into atmosphere
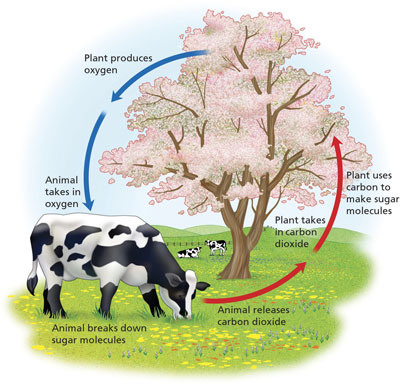
52
New cards
Decomposition
A chemical proc done by soil bacteria that breaks down organic matter and stores carbon in the soil and releases it into the atmosphere as CO2 and methane (CH4)

53
New cards
Carbon sequestration (storage)
The act of removing carbon from the atmosphere and storing it. Plants sequester, or store carbon from the atmosphere.
54
New cards
Direct exchange
Movement of carbon dioxide gas directly between the ocean and atmosphere.
Happens at a relatively stable rate, although excess atmospheric carbon will increase the level of CO2 in the ocean
Happens at a relatively stable rate, although excess atmospheric carbon will increase the level of CO2 in the ocean
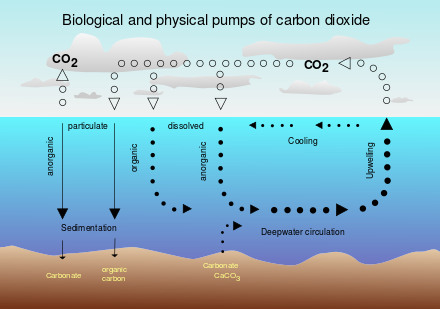
55
New cards
Sedimentation
The process of soil particles and decaying organic matter building up in layers on the ground or at the bottom of the ocean.
Over time, pressure from water or rock layers above compresses sediments into sedimentary rock (limestone) or FFs
Over time, pressure from water or rock layers above compresses sediments into sedimentary rock (limestone) or FFs
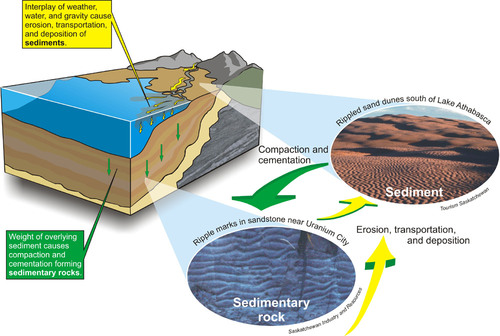
56
New cards
Burial
The formation of sedimentary rock like limestone, or fossil fuels, as layers of sediments are compressed under the ocean or overlying rock layers.
57
New cards
Extraction
Removal of fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) from the ground, usually by mining or drilling.
A very rapid process compared to the sedimentation and burial required to form fossil fuel
A very rapid process compared to the sedimentation and burial required to form fossil fuel

58
New cards
Combustion of fossil fuels
Burning of fossil fuels (primarily in cars and power plants) to release energy
Releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere very rapidly, acting as a carbon source
Releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere very rapidly, acting as a carbon source

59
New cards
Reservoir
A place on earth that stores a relatively stable amount of (water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus)

60
New cards
Sink
A place on earth that can store an increasing amount of water, carbon, nitrogen, or phosphorus, usually for a long period of time
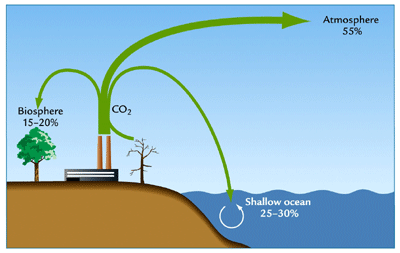
61
New cards
Source
An action that returns carbon, or water to the atmosphere. Ex: burning fossil fuels like gasoline releases CO2 into the atmosphere

62
New cards
Organic
of, relating to, or derived from living matter, contains carbon
63
New cards
Lithosphere
The rocks and soil that make up earth's "land" surface or crust
64
New cards
Hydrosphere
All of the water reservoirs on earth (ocean, lakes, groundwater, streams, water vapor in the atmosphere)

65
New cards
Biosphere
All living things (or organic matter from living things) on earth

66
New cards
Atmosphere
the layer of gases surrounding Earth
67
New cards
Primary productivity
rate at which organic matter is created by producers (via photosynthesis) in an ecosystem
68
New cards
GPP (gross primary productivity)
The total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time
69
New cards
NPP (net primary productivity)
The energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire
70
New cards
Trophic levels
The hierarchical levels of the food chain through which energy flows from primary producers to primary consumers, secondary consumers and so on.
71
New cards
Conservation of matter
the principle stating that matter is not created or destroyed during a chemical reaction
72
New cards
Omnivore
A consumer that eats both plants and animals
73
New cards
Carnivore
A consumer that eats only animals.
74
New cards
Herbivore
A consumer that eats only plants.
75
New cards
First law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
76
New cards
second law of thermodynamics
when energy is changed from one form to another, some useful energy is lost as heat
77
New cards
Energy pyramid
Shows the amount of energy that moves from one trophic level to another in a food web
78
New cards
10% rule
Only 10% of the total energy produced at each trophic level is available to the next level. The amount of energy passed up to the levels of the trophic pyramid decreases as you go up.
79
New cards
producers (autotrophs)
organisms that make their own food by using a primary energy source (such as sunlight or heat) to conduct photosynthesis or chemosynthesis
80
New cards
Primary consumers
animals that feed on producers; ex. herbivores like rabbits or deer
81
New cards
secondary consumers
carnivores that eat herbivores; ex wolves, lions
82
New cards
tertiary consumers
carnivores that eat secondary consumers; ex large birds of prey
83
New cards
heterotrophs
An organism that obtains organic food molecules by eating other organisms or their by-products. (basically consumers like animals)
84
New cards
Biodiveristy
the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem. Three types: ecosystem, species, genetic
85
New cards
species biodiversity
represents the number of different species living in an area
86
New cards
genetic biodiversity
the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species (higher gen. biodiversity makes populations more resistant to disturbance)
87
New cards
ecosystem biodiversity
refers to the variety of ecosystems found in a given area
88
New cards
habitat
the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism.
89
New cards
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment. (abiotic + biotic)
90
New cards
specialist species
Species with a narrow ecological niche. They may be able to live in only one type of habitat, tolerate only a narrow range of climatic and other environmental conditions, or use only one type or a few types of food. (pandas)
91
New cards
generalist species
Species with a broad ecological niche. They can live in many different places, eat a variety of foods, and tolerate a wide range of environmental conditions. (cockroaches, mice, rats, and human beings)
92
New cards
biodiversity hotspots
Relatively small areas of land that contain an exceptionally high number of species and are at high risk from human activities
93
New cards
ecosystem services
Important environmental benefits, such as clean air to breathe, clean water to drink, and fertile soil for growing crops, that ecosystems provide (have a monetary value to humans)
94
New cards
provisioning services
Benefits of biodiversity that humans use, including lumber, fur, meat, crops, water, and fiber
95
New cards
regulating services
the service provided by natural systems that helps regulate environmental conditions (trees removing carbon from atmosphere and roots filtering ground water)
96
New cards
supporting services
the basic ecosystem processes, such as nutrient cycles and soil formation, that are needed to maintain other services like agriculture (bees, moths pollinating agricultural crops)
97
New cards
cultural services
ecosystems provide cultural or aesthetic benefits to many people (tourists willing to pay to visit nature, or scientists conducting research that leads to new knowledge)
98
New cards
Anthropogenic
caused by humans
99
New cards
ecological
relating to or concerned with the relation of living organisms to one another and to their physical surroundings.
100
New cards
island biogeography theory
explains how species come to be distributed among oceanic islands