ACFI231 - Lecture 11 paying for acquisitions and defences against takeovers
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Principal methods of payment for acquisitions
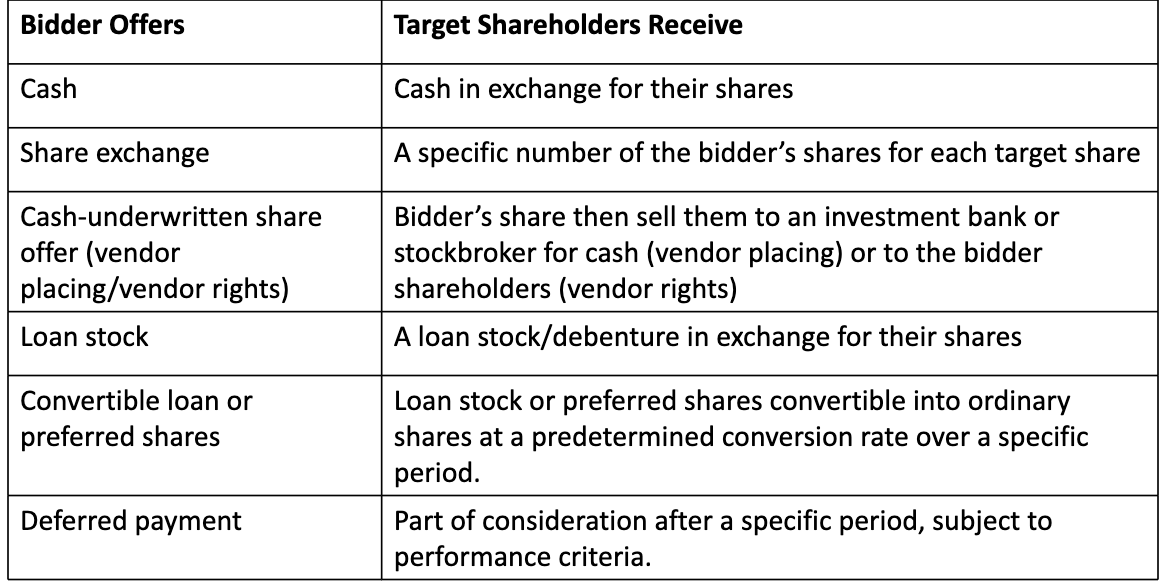
Number of shares post-acquisition
Number of shares post-acquisition = number of existing shares of bidder + number of shares issued to target shareholder
value of combined firms
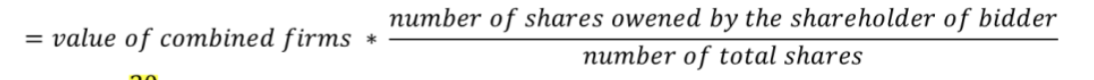
Factors influencing choice among acquisition financing methods
Risk and valuation considerations
Maximising tax benefits
Corporate control considerations
Deal execution considerations
Capital market conditions
Bid strategy
Bid strategy is a plan to acquire another company in order to achieve the predetermined business and corporate objective
being a first mover in bid strategies
Being a first mover you can:
Cherry pick the best target
buy at a lower price than follow on buyers
prevent competitors from accessing the buying targets resources
being a second mover in bid strategies
• A second mover may have advantages in new and fast-evolving industries, where
the true value of a target is difficult to access in both strategic and financial term.
• The second mover can also take the time to counter the first mover effectively
through strategies other than acquisitions, e.g., a joint venture.
Showstoppers
Firms must look for any potential ‘showstoppers’ or ‘deal-killers’ that can thwart the
bid.
• Antitrust regies: Office of Fair Trading (in the UK); Federal Trade Commission and
Justice Department (in the US); European Commission (in the EU).
• Litigation initiated by the target.
• Contracts between a target and its suppliers or customers.
• Bond covenants.
• Trade unions representing employee or employees themselves
Getting the board on board
A bid strategy must command the wholehearted support of all bidder directors.
Similarly, the strategy must also have the support of the large and influential
shareholders.
Where board is divided, the bidder team will find it very difficult to sell the deal to the
target board and its shareholders, and to other stakeholders.
Bid resistance motives
managers may resist takeovers as they believe remaining independent best serves the interest of shareholders, fear of loss, or waiting for the best time to extract maximum bid premium for shareholders
manager bid acceptance motives
best option available
secures a better deal in the post acquisition dispensation
Pre Bid defences
The best form of defence is being prepared. Pre-bid defences fall into two board
categories. Internal defences are decisions/actions to alter the internal structure or
nature of operations of the firm. External defences are actions taken to influence
outsiders’ perceptions of the firm, and to provide early warning signals about
potential predators.
Post offer defences
First response and pre emption letter
defence doc
profit forecaste
promise higher future dividends
asset revaluation
share support campaign