Wound care skin anatomy
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what is the most common cell of the epidermis?
Keratinocytes
What are the cells of the epidermis?
keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans and Merkle cells
Melanin serves as what protection?
UV radiation absorption
Transepidermal water loss (TEWL)
water lost through skin under non-sweating conditions
Dark skin contains more fibroblasts that are larger than those in white people this results in what?
heightened risk for keloids
hypertrophic scar formation (more raised and thickened scars)
who has higher TEWL compared to white people?
Blacks and Aisians
subcutaneous tissue
loose connective tissue below the dermis.
Binds skin to tissue
characteristics of subcutaneous tissue?
pale yellow, waxy , globular, oily and glistens
Bones contain what percent of the bodies calcium?
99%
Red Blood Cell lab range normal
Normal Range:
Male: 4.7-6.1 million cells/microliter (µL)
Female: 4.2-5.4 million cells/µL
Hemosiderin staining
capillaries leak hemoglobin into the extracellular space . Iron stains purple on the skin
Pitting edema
indentation on the skin when finger is firmly pressed for 5 seconds
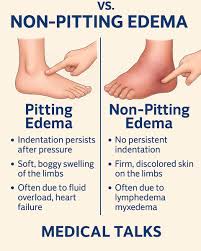
pitting vs non pitting edema
How can you distinguish ligaments from tendons?
Ligaments are broader, flatter, and more loosely woven than tendons and the striations feel like tape with embedded threads.
What causes dark skin to be thicker compared to light skin?
The presence of more compact collagen bundles in higher amounts and a longer BMZ
What is the function of the fibroblast?
Develop connective tissue and produce collagen and elastin
What effect does a higher TEWL in dark skin have?
Compromises the epidermal barrier function making the skin more susceptible to irritants and possibly drier
What is the largest component of the dermis and what is its function?
Extracellular matrix Provides structural support, regulates cellular functions, lubricates cells, and provides a transport system for nutrients and waste products
What is the function of subcutaneous tissue?
Stores energy, supports blood vessels and nerves, cushions the body, and protects against cold
Protection from UV rays
What is the function of melatin