32. intro to fungi and antifungal drugs
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
in what forms do fungi grow?
molds and yeasts
some are dimorphic → can grow as mold or yeast
what is the general structure of fungal cell walls?
multi-layered — polysaccharide subunits
chitin
glucans
mannans
protein fibrils
what is a major source of fungi?
soil (found everywhere)
how do molds grow?
growth as filaments (hyphae)
septate hyphae (crosswalls)
aseptate hypahe (no crosswalls)
how do fungi obtain nutrients?
get carbon from organic sources
hyphal tips release enzymes → enzymatic breakdown of substrate
products diffuse back into hyphae
how do molds reproduce?
asexually
spores or fragmentation of hyphae
usually seen in diagnostic labs
sexually (specialized spores)
important for taxonomy but not usually seen in infected animals or diagnostic lab
how do yeasts grow? how do they reproduce?
single-cell growth
reproduce by budding
microscopic fungi ID
direct microscopy
look for fungal elements in tissue or fluid
stain with new methylene blue, giemsa
gram stain not helpful
histopathology — need to use special stains to visualize fungal elements (not H&E)
silver stain
PAS
how are fungi cultured?
many fungi grow on blood agar, but usually use fungal media
molds often grow better at room temp than incubator temp
what makes fungi difficult to treat?
antibiotics don’t work → target bacterial molecules
similarity of fungal and mammalian cells pose toxicity problems
few effective antifungal drugs available
in general, therapy is prolonged, expensive, and can have significant side effects
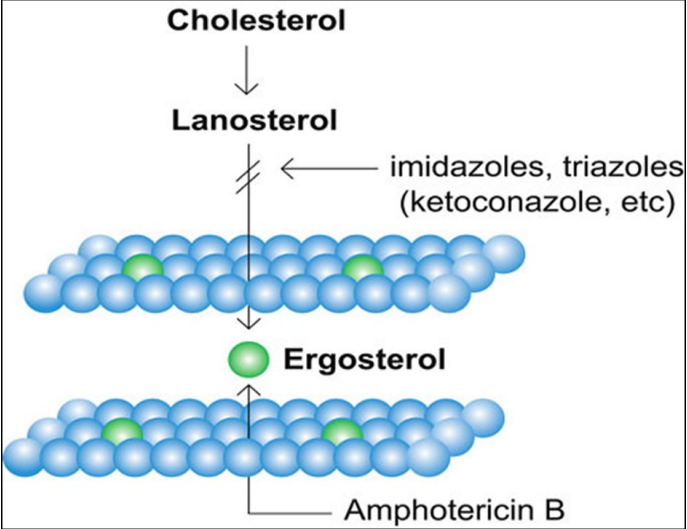
what is the mechanism of action for azole drugs?
inhibit enzyme* required for ergosterol synthesis (part of fungal cell wall)
*lanosterol 14a-demethylase = P450 enzyme known as CYP51
CYP51 found in fungi, animals, plants, and mycobacteria
some also inhibit aromatase (P450 enzyme involved in synthesis of estrogens vs. androgens)
side effects of azole drugs
usually minor (more with ketoconazole) → liver, inappetence, pruritis
inhibit certain P450 dependent pathways (i.e. CYP3A4)
can cause significant drug interactions with other drugs that are metabolized by CYP3A4
what are examples of polyene drugs?
amphotericin B, nystatin
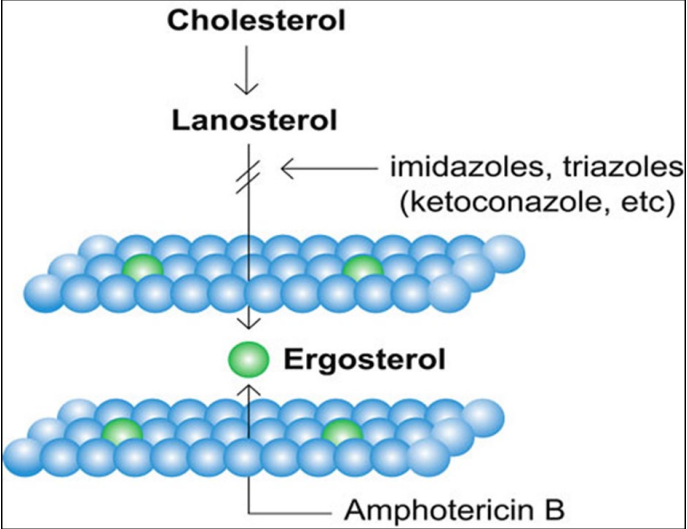
what is the mechanism of action for polyene drugs?
binds to ergosterol in fungal cell membrane; increase permeability
how are polyenes administered? what are the side effects?
poorly soluble; slowly infuse IV
toxicity → absorbs to renal tubules → loss of renal function
greater efficacy and less side effects with liposomal versions
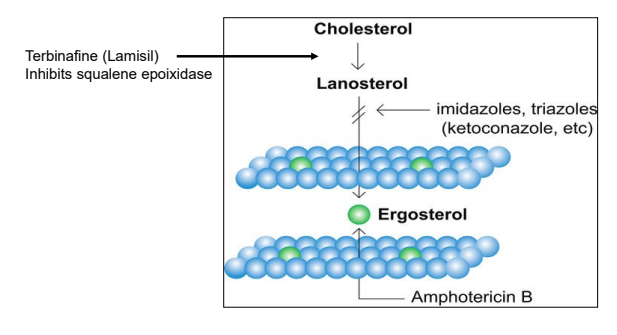
what is the mechanism of action for terbinafine (lamisil)?
inhibits squalene epoxidase (enzyme involved in ergosterol synthesis pathway)
how are iodides used in fungal treatment?
KI given orally or NaI by IV injection
effective for various chronic granulomatous infections (sporotrichosis, mycetoma)
mechanism unknown
cause iodide toxicity, but is reversible
low cost → used in large animals
is susceptibility testing a routine part of fungal treatment?
no → very difficult, especially for hyphal fungi
antifungal resistance
some fungi naturally resistant
some acquire resistance to azole drugs
genetic → point mutation in 14a-demethylase (i.e. CYP51)
phenotypic → greater efflux of azole drugs out of fungal cell
increasing resistance in certain aspergillus species
CYP51 mutation