GGR321 - Quiz 1 + 2 questions
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Quiz questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
ModelBuilder is used to create, edit, and manage geoprocessing models that automate tools. It can also be thought of as a visual programming language for building workflows. True or False?
True
Variables
Are elements in a model that hold a value or a reference to data. 2 types: data and value variables
Geoprocessing tools
Perform various operations on geographic or tabular data
Groups
Are visual elements that group related tools together, can collapse or expand
Connectors
Connect data and values to tools, arrows show direction of processing. 4 types; data, environment, precondition, and feedback
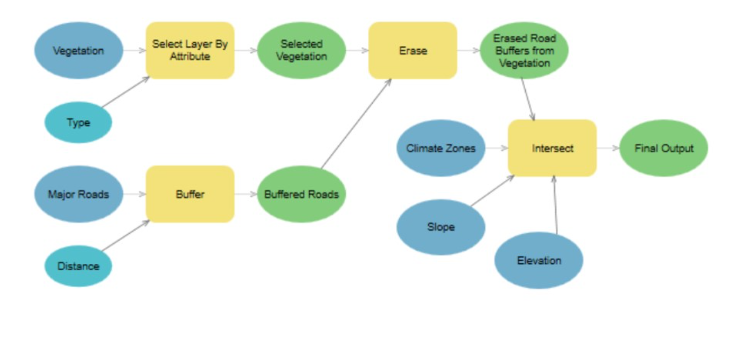
In the example of biodiversity conservation model discussed in class, the 'Vegetation' element is
Input data,
Derived Data
Derived Value
Input Value
... are special ModelBuilder-only tools that repeat the same operation or loop through a set of input data or values.
Iterators
Data Models
templates for data, a framework into which specific details of relevant aspects of the Earth’s surface can be fitted. It is a statement about how the world looks
Spatial Models
expressions of how the world is believed to work, how tasks are broken down in a sequence of operations; in other words they are expressions of process
Mammoth Cave protection model developed with application of ModelBuilder discussed in class and described in the recommended reading materials is an example of geospatial modelling for forest protection, T or F
False
All GIS transformations of rasters can be classified into four basic classes,
Local
examines rasters cell by cell
Focal
compares the values of each cell with its neighbours
Zonal
computes results for blocks of contiguous cells that share the same value
Global
Produces results that are true of the entire layer
Spatial models can be expressed visually as a flowchart (ModelBuilder) or as a script (Python, ArcPy) - True or False?
True, any model actually can be expressed as both
Cellular models represent the surface of the Earth as a combination of vector objects - True or False?
False
Multicriteria Decision Making (MCDM) is commonly used when stakeholders have different views on the weights of various factors, especially when modeling decisions related to environmental impacts and when decisions are controversial. T or F?
True, used when decisions are controversial
Which three of the following statements correspond to Raster Data Models?
Support the use of map algebra functions
Allow to conduct visibility (viewshed) analysis
Cannot effectively display linear features
Euclidean distance global operations assign to each cell in the output raster dataset its distance from the closest source cell. Tor F?
True
Line of sight analysis
essentially a point-to-point operation
Viewshed analysis
Is typically a point or point set to surface operation
Viewsheds are regions of visibility observable from one or more observation points. Typically the inputs for viewshed analysis include:
a surface raster or set of raster files
one or more observation points
offset values for the observation points
Which two extensions from the ArcGIS Pro Advanced Analysis products are the most suitable to conduct visibility and least-cost path analysis ?
3D Analyst
Spatial Analyst
The Least-Cost Analysis creates Euclidean distance surfaces to understand the straight-line distance from one location to another, or creates cost-weighted distance surfaces to understand the cost of getting from one location to another based on a set of input criteria. T or F?
True
Python as a cross-platform open-source programming language was created and developed by ____________ in late 1980s, Netherlands
Guido van Rossum
Scripting language
automating certain functionality within another program
Programming language
development of sophisticated multifunctional applications
A strength of Python is that it is:
both a scripting language and a programming language
A key feature of Python is that it
is interpreted; does not need conversion (binary code) before running it
ArcPy
a Python site package that provides a useful and productive way to perform geographic data analysis, data conversion, data management, and map automation.
Based on Python demo example in Lecture 6, please, fill out the text box below with a short script in ArcPy to run the Get Count geoprocessing tool located in the Data Management Tools toolbox for ambulances layer.
arcpy.management.GetCount("ambulances")
arcpy.management.GetCount('ambulances')