Community Health Exam 3 Communicable disease
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Epidemic
significant increase in a disease-above what is normally expected in a specific population or area.
Example-seasonal flu outbreaks.

Endemic
Usual number of cases of a disease within a population.
-a disease that is constantly present in a specific population or geographic area.
Example-malaria in certain regions of Africa.

Pandemic
Epidemics occurring around the globe.
Epidemic that has spread across countries affecting a large number of people.
Example: COVID-19

CDs that affect the respiratory system
•Chicken pox
•Diphtheria
•Rubella
•Influenza
§Vaccinations = decline in these diseases
Malaria
•Spread by the bite of an infected mosquito
•Found in subtropical areas
•Affects greater than one-half of the world's population

Diarrheal Disease
•Most common route for transmission is the fecal-oral route.
‒Good hand hygiene, especially hand washing, and soap alone can reduce the incidence of diarrheal disease by as much as 48%.
‒Efficient sanitary systems and safe drinking water also play a huge role in preventing diarrheal diseases.
-2nd leading cause of death for children under 5 yrs old.

Diarrheal disease causes & transmission
§Caused by
•Bacteria
•Virus
•Protozoa
§Mode of transmission
•Waterborne (for example, cholera)
•Foodborne/person to person (for example, Escherichia coli)

(WHO) Goals for TB
•Aim to have a 90% reduction in TB deaths and 80% reduction in TB incidence by 2030
The Cycle of Transmission
The epidemiological triangle is expanded to help disease researchers understand the cycle of transmission.
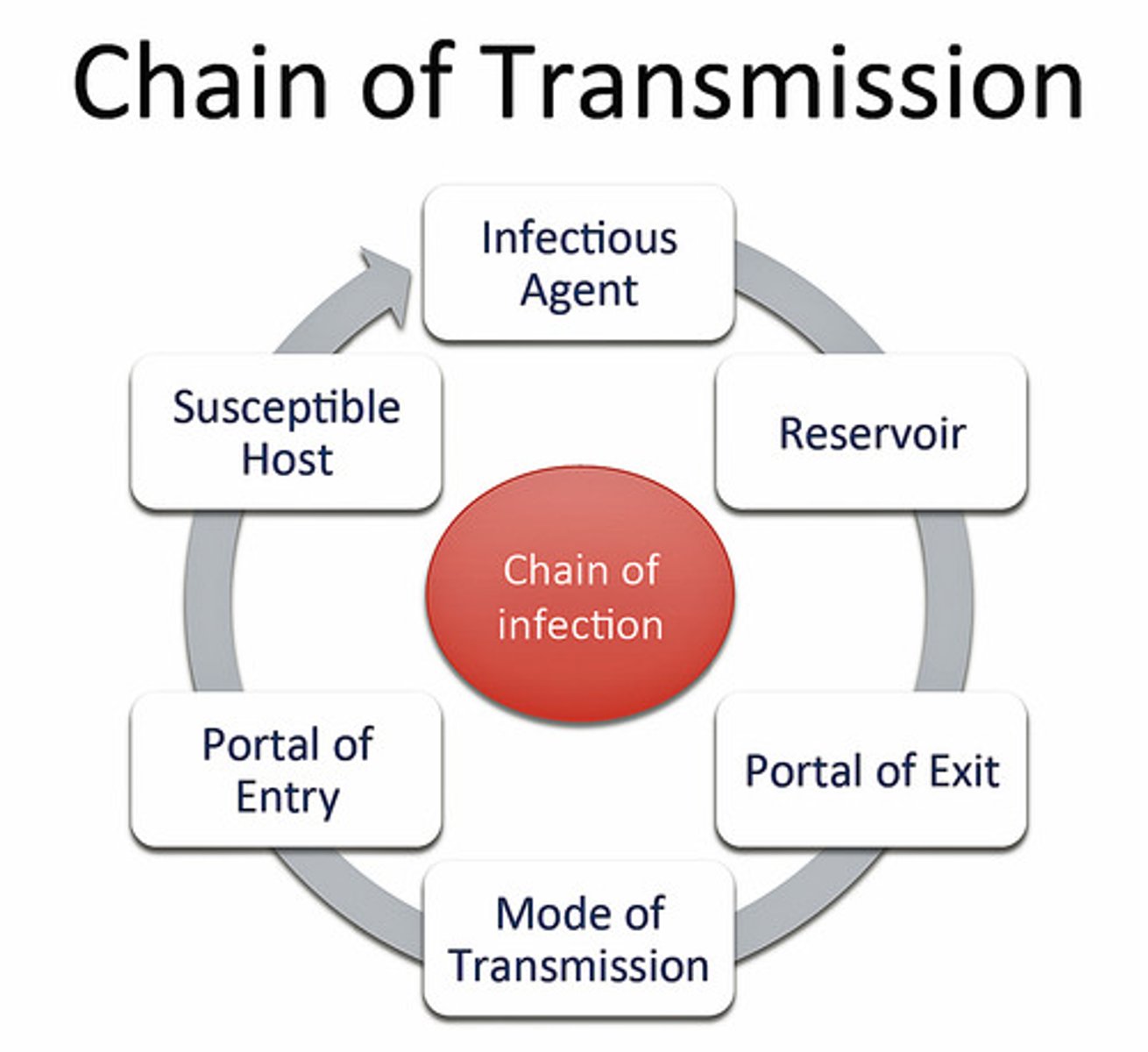
The key components needed in the transmission cycle are?
1. Agent
2 Host
3. Environment
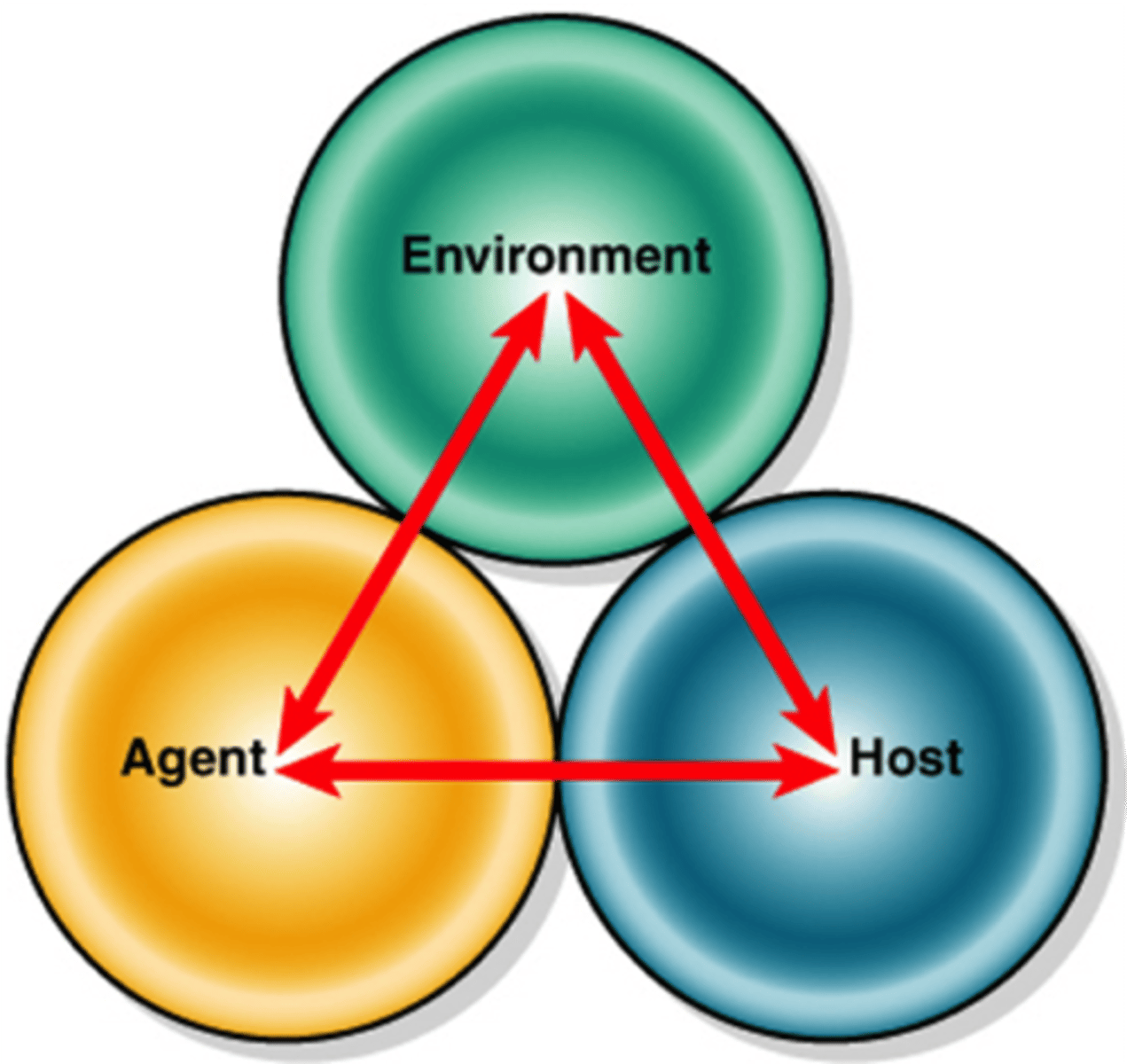
Six pathogens
Bacteria-TB or Strep.
Rickettsia-Typhus or rocky mountain spotted fever.
Viruses-HIV or influenza
Mycoses-Candida or fungal meningitis.
Protozoa-Malaria or giardia
Helminths- Lyme disease
infectivity of the agent
Capacity of an agent to enter and multiply in the host.
Pathogenicity
Capacity of the agent to cause disease in the human host
Virulence
How severe a disease is caused by an infectious agent.
-the ability of an infectious agent to cause disease and how severe that disease is.

Toxigenicity of a pathogen
The ability to release toxins that contribute to disease within the human host.

Antigenicity Agent Characteristics
The ability to produce antibodies in the human host.

Environmental characteristics
§Environment: conditions external to the host and agent associated with the transmission of the agent
§Reservoir: where the agent resides
•Human
•Animal
•Water, food, air, or soil
Incubating Carrier
Someone who has been infected but has not yet shown signs of the disease.
Convalescent Carrier
A person who is infected but no longer shows signs of acute disease.
-Person has recovered from the symptoms of a disease but still carries it and can spread it.
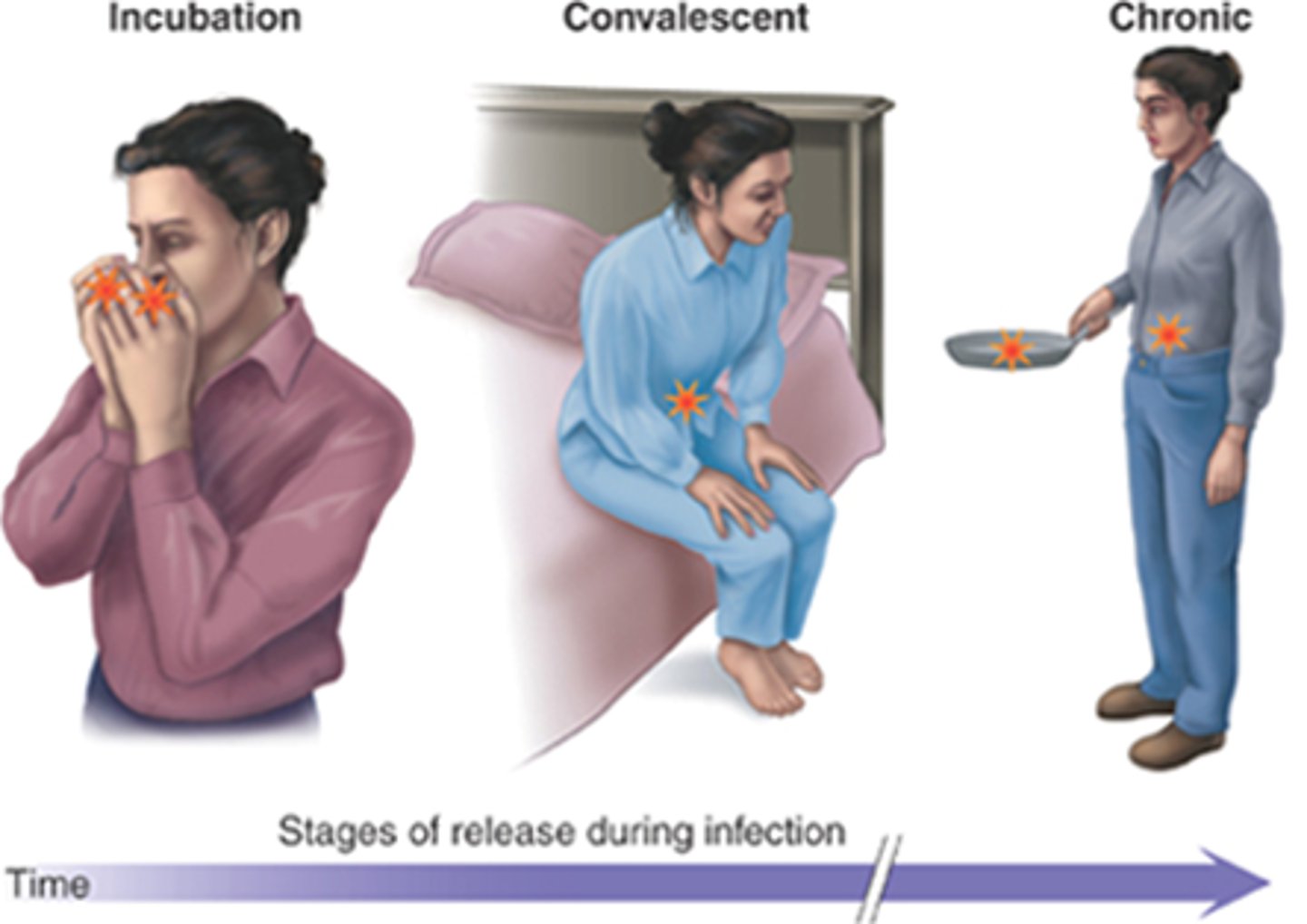
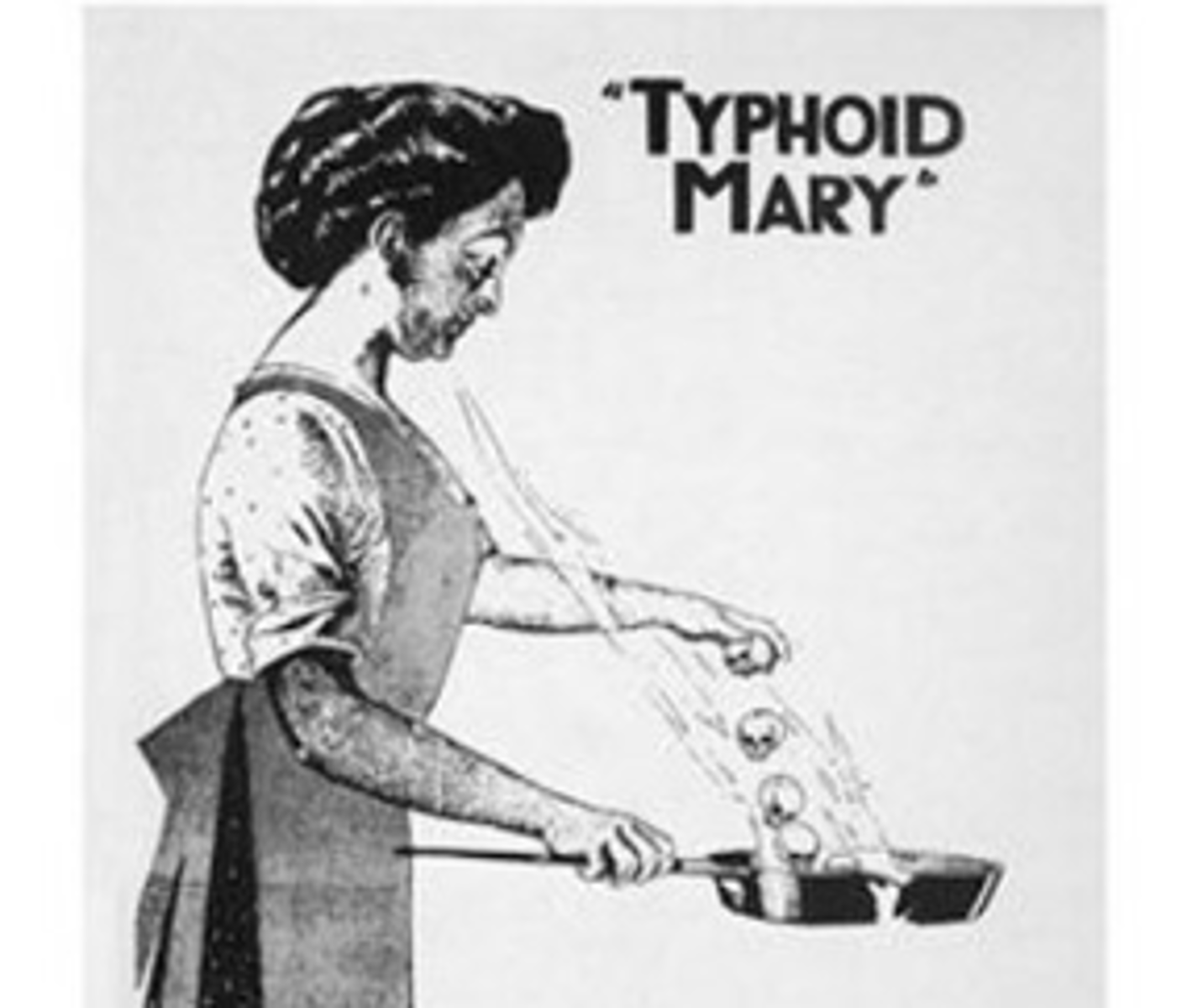
Chronic Carrier
Infected with the agent with no sign of disease for a long period of time (Typhoid Mary)

Mode of Transmission
§The method through which the agent leaves its reservoir and enters its host
•Water, food, air, vectors, fomites, unprotected sexual contact, or penetrating trauma
‒Vectors are usually insects that carry the disease from the reservoir to humans.
‒Fomite is an inanimate object.

Innate immunity
Body's first line of defense against pathogens, that is always ready to respond.
Adaptive Immunity
The body's second line of defense that is tailored to recognize and remember specific pathogens.
Active Immunity
-Acquired through exposure to the agent. Either pathogen or vaccine.
-Can be acquired natural (when you get infected with a disease like chickenpox), or Artificial (through vaccinations like flu vaccine).
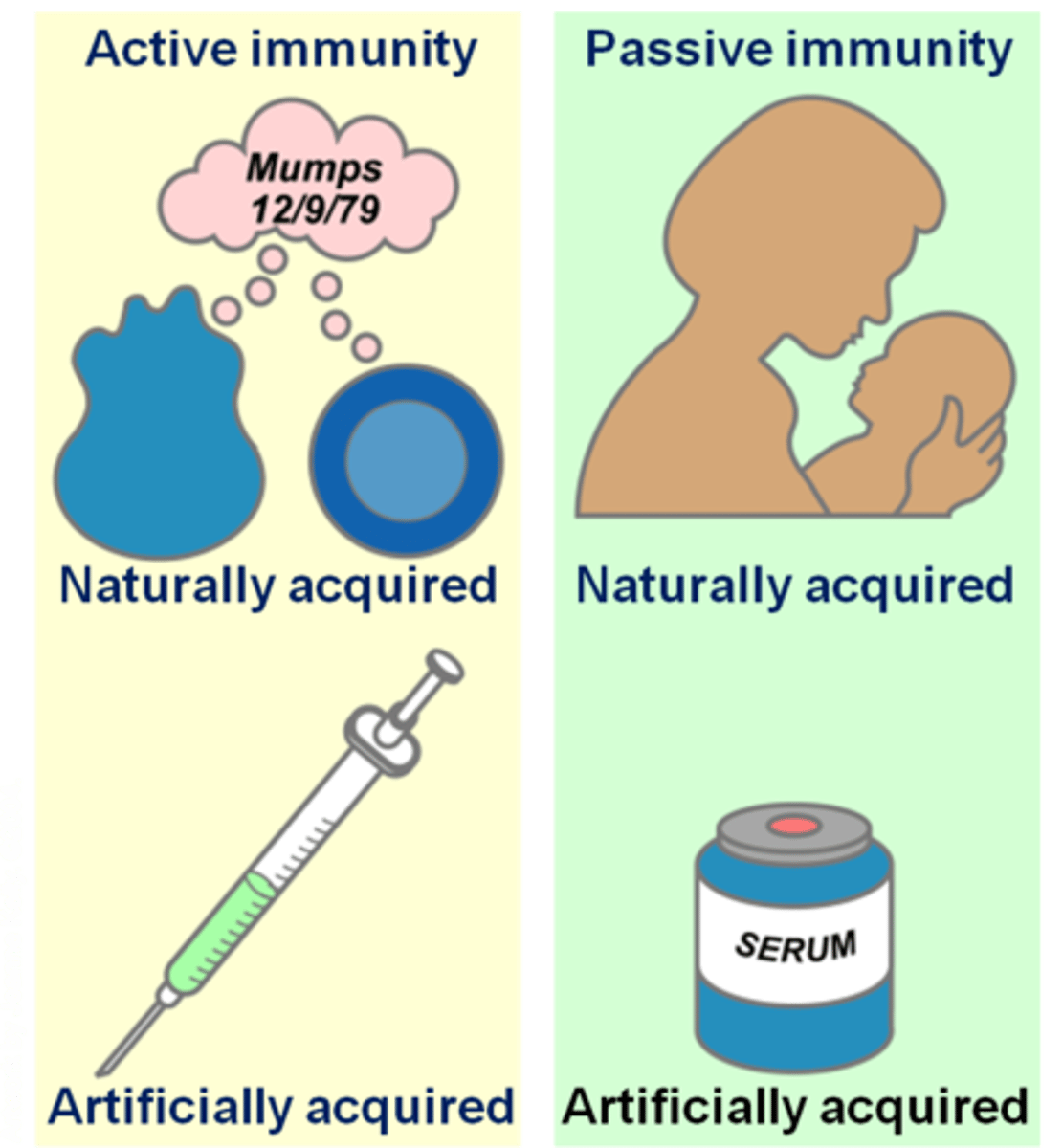
Passive Immunity
Acquired by receiving antibodies from another source, rather than producing them on your own.
Natural-from mothers' milk to baby.
Artificial-By receiving antibody injections like immunoglobulin.
Host characteristics: defense mechanisms.
Avoidance-skin helps prevent exposure its a barrier.
Resistance-resists disease by inherited or acquired immunity
Tolerance-host body enhance tissues to fix damage by pathogen.
Colonization
infected with agent but no sign of disease
can spread disease
example-MRSA
Case Fatality Rate
•Determines severity of the outbreak
•Represents number of fatal cases divided by the number of cases

Epidemic Curve
•Plotted on graph
•Shows number of cases on the Y axis
•X axis placed by date
•Shows time elapsed from exposure to clinical symptoms
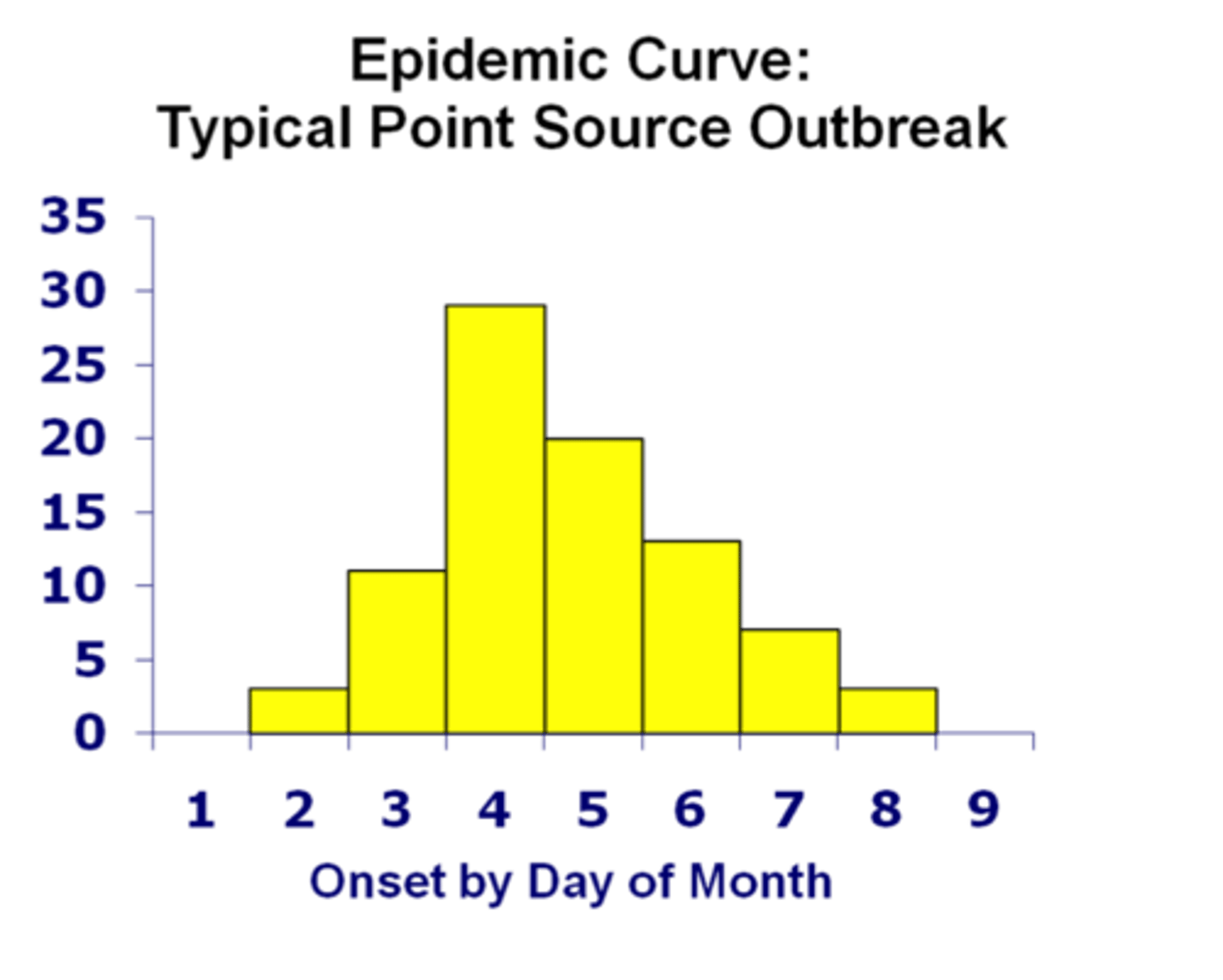
Epidemic Curve what is it?
§Graph also helps determine if you have
•Point source
‒Exposure at one point in time
•Intermittent source
‒Exposure comes and goes
•Continuous source
‒Exposure is ongoing
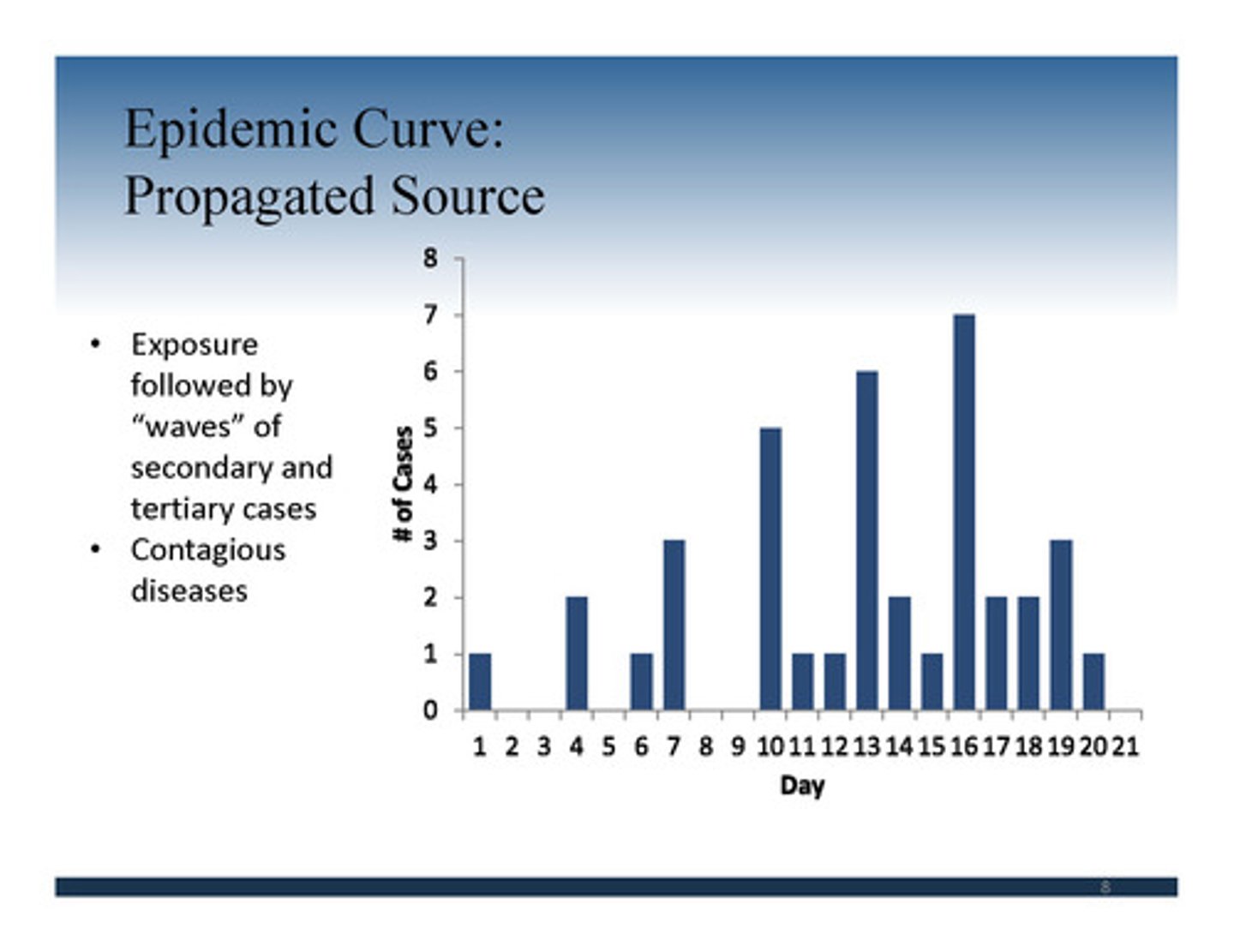
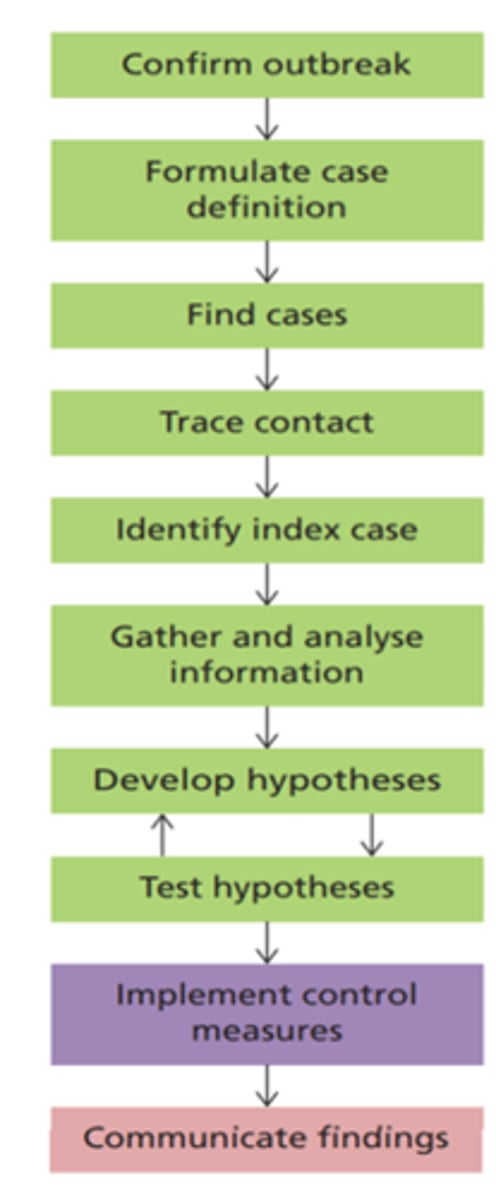
Managing an Outbreak
§Management of epidemic
•Identify source
•Isolate source
•How best to break the cycle
§Incubation period
•Exposure to onset of symptoms
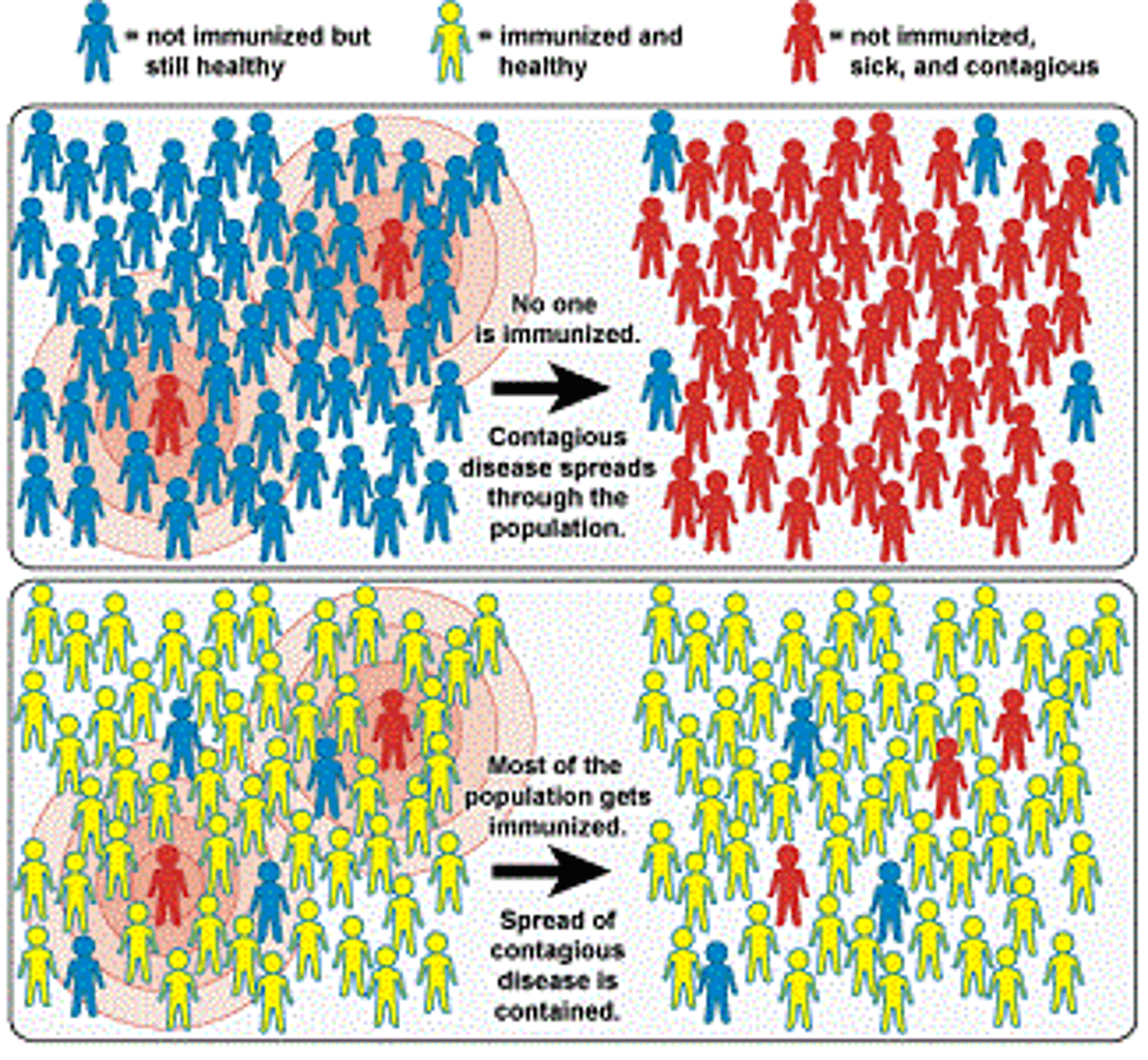
§Herd immunity
•Greater population protected (vaccine)
•Protects those who cannot be vaccinated or choose not to be
Incubation period
§The incubation period for the pathogen is the period of time between exposure and first signs of disease.
Infectious period
§The infectious period is the period during which an infected person can transmit the infection to another susceptible host.
The threshold of immunity
•This refers to the percentage of the population that must be immune to achieve herd immunity to a specific agent.
•Even if a few members of the community become infected, the population as a whole is protected from an outbreak.
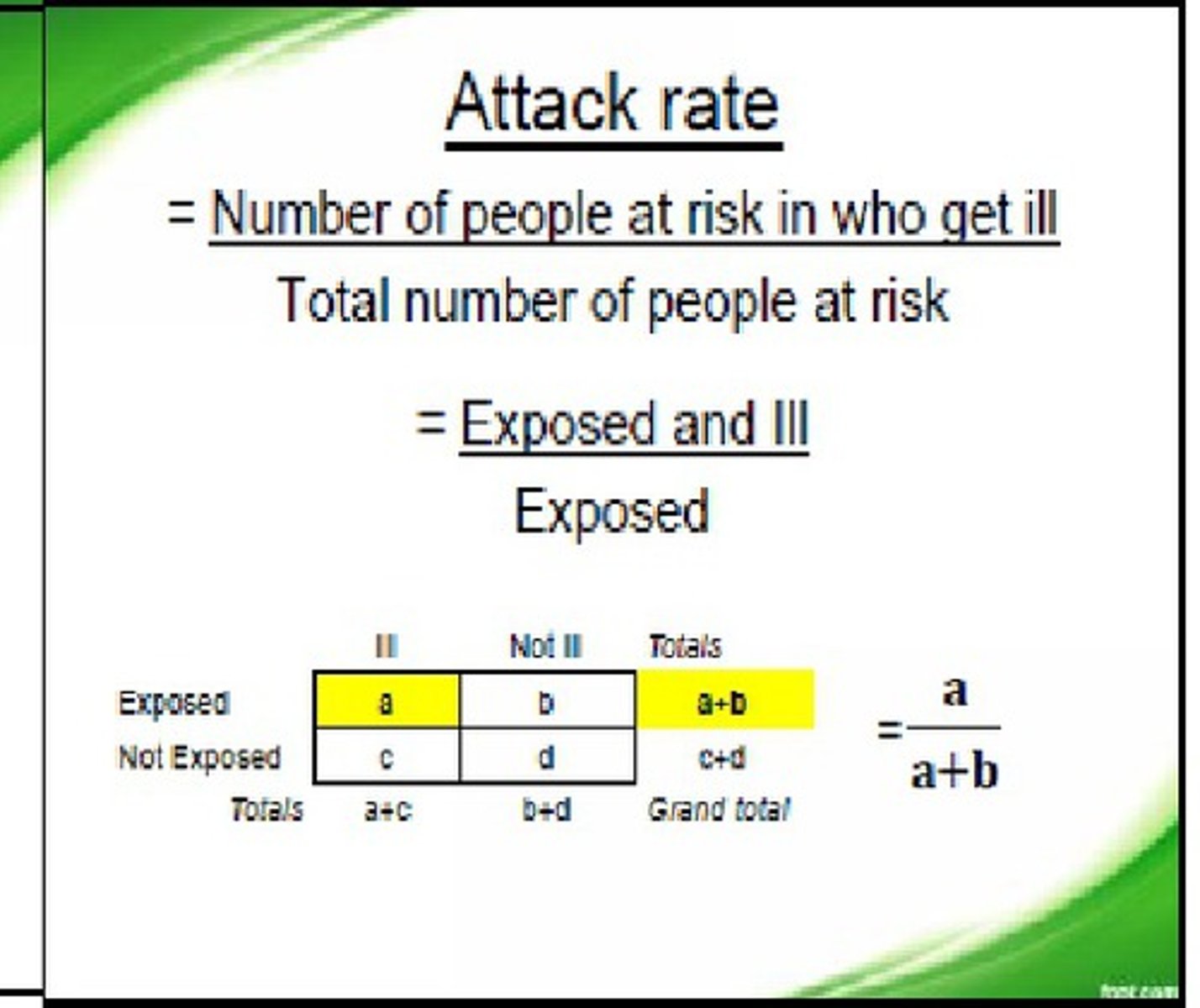
Attack Rate
The number of persons who are ill divided by the total population (ill+sick).
-Can be calculated based on a particular risk factor.
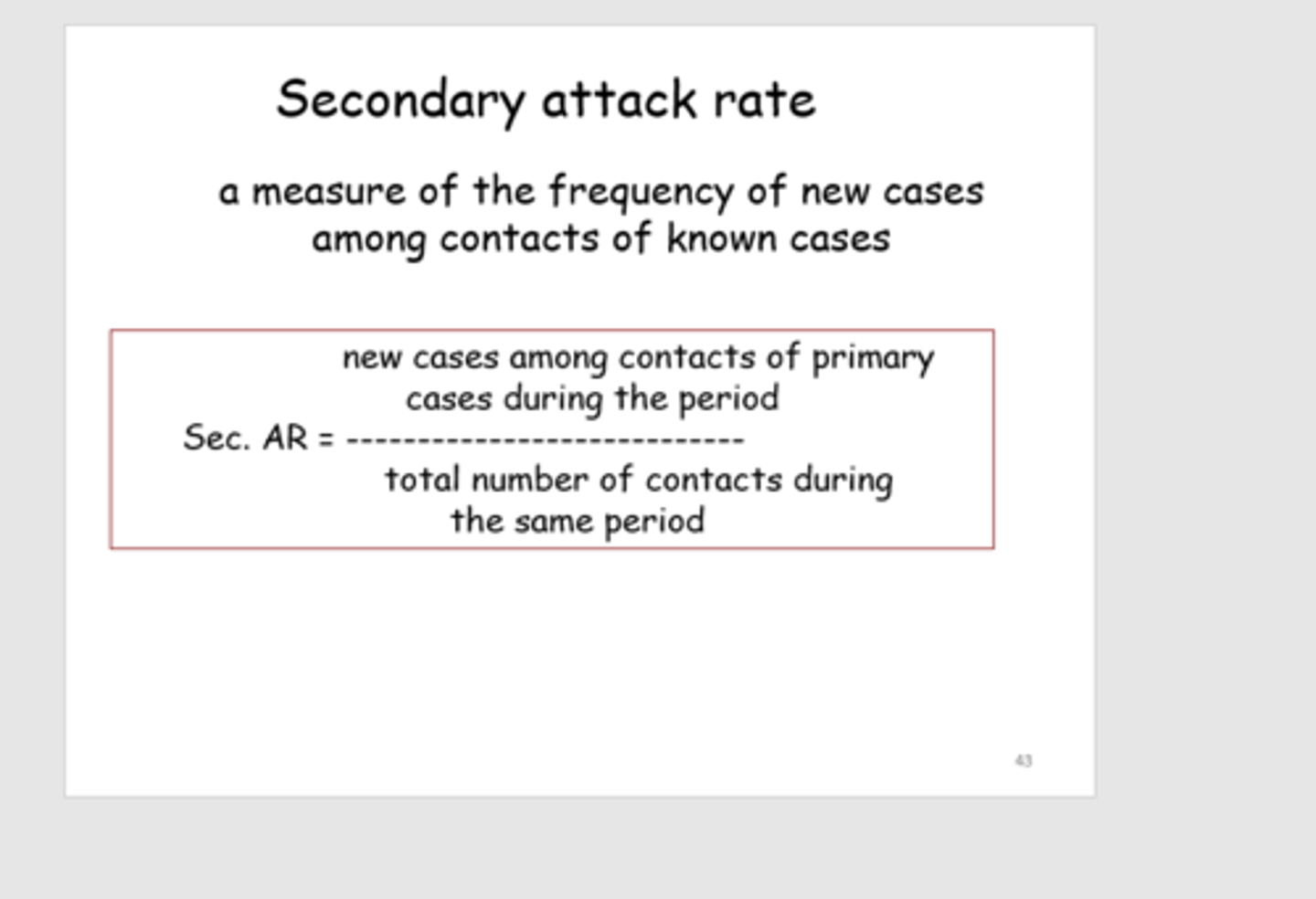
Secondary attack rate
§the total number of new cases among contacts divided by the total number of contacts
•Contacts: those in contact with persons who became ill following exposure to the initial source
sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Transmitted through sexual contact and exchange of bodily fluids.
-preventable disease
-25 infectious agents
§May cause serious illness and disability
•Reproductive health problems
•Fetal and perinatal health problems
•Cancer
Notifiable STIs in the U.S.
Federally funded control programs-healthcare workers must report.
1. Chlamydia
2. Gonorrhea
(can cause PID & Pass on to baby during delivery)
3.Syphilis (can be passed on during pregnancy or delivery.
STIs Risk Factors
1. Unprotected sex
2. Gender
3. Ethnicity
4. sexual orientation
5. socioeconomic factors
6. Not reporting it
7. Access to care
HIV & AIDS
Can go 15 years after exposure before developing AIDS.
-25- to 29-year-old have the highest rate
-Gay men, Black, and Hispanic highest rate
-increasing in older adults.
UNAIDS 95-95-95
Treatment for AIDS
§In 2020:
•84% of all people living with HIV knew their HIV status.
•73% of all people with diagnosed HIV infection were on sustained antiretroviral therapy.
•66% of all persons in treatment were virally suppressed.
3 Main approaches to controlling communicable diseases
1.Changing the environment
‒Altering or eliminating the reservoir, controlling the vector, applying personal measures of hygiene, and using aseptic technique
2.Deactivating the agent
‒ Use of physical and chemical agents
3.Increasing host resistance
‒Active or passive immunity
‒Includes use of vaccine for training the immune system