Nervous system and homeostasis
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
1
New cards
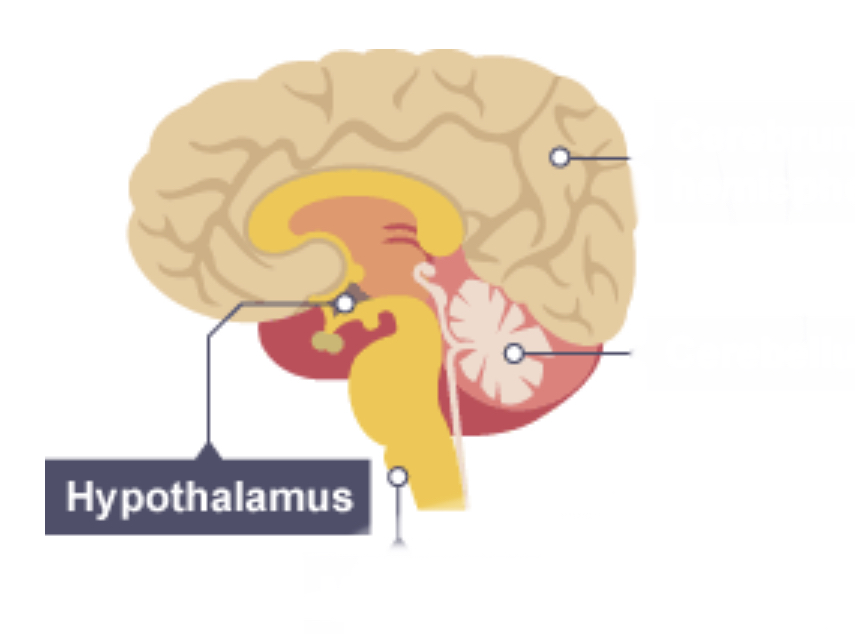
Hypothalamus
Regulates body temperature and water balance in the body
2
New cards
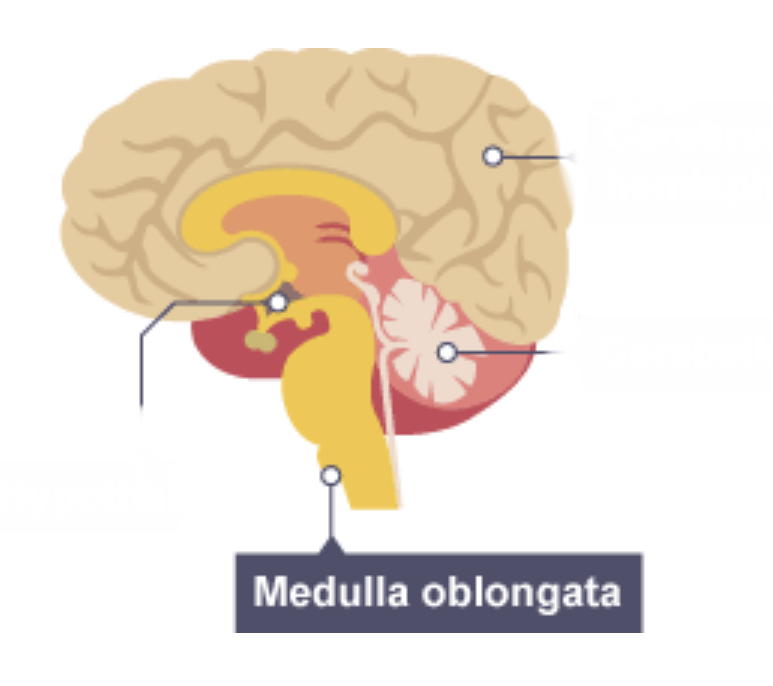
Medulla
Controls unconscious activities eg heart rate and breathing
3
New cards
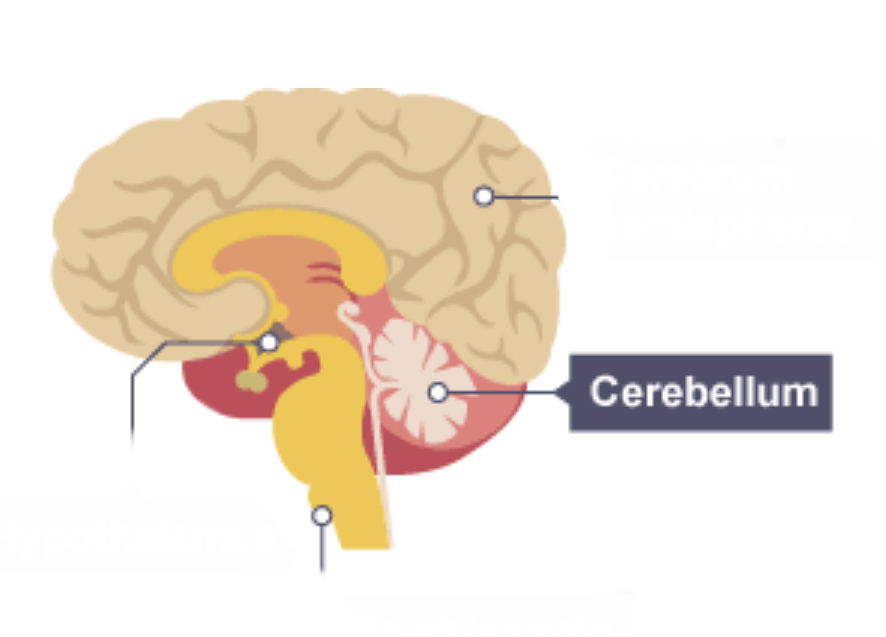
Cerebellum
Controls balance, co-ordination of movement and muscular activity
4
New cards
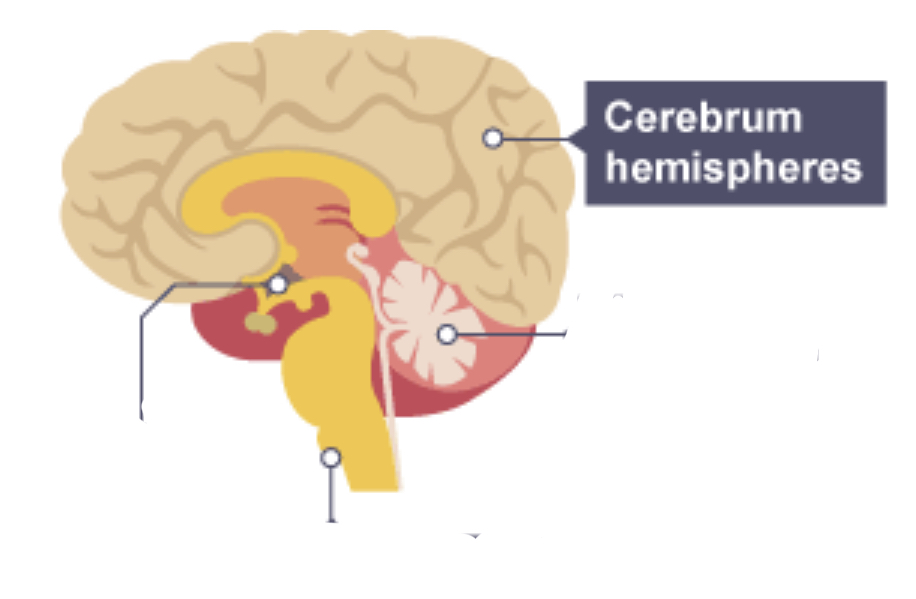
Cerebrum
* Outer layer = cerebral cortex
* Controls intelligence, personality, conscious thought, and high level functions eg language/ memory
\
* Controls intelligence, personality, conscious thought, and high level functions eg language/ memory
\
5
New cards
Motor neurones
Send electrical impulses to an effector
6
New cards
Effector
Produces a response to the stimulus
7
New cards
Stimulus
Change in environment
8
New cards
Sensory neurone
Sends electrical impulses to the relay neurone
9
New cards
Relay neurone
Located in the spinal chord, they connect the sensory and motor neurones
10
New cards
Synapse
* Spaces between neurones when the electrical impulses are turned into a chemical messengers
* they can ‘diffuse’ across the neurones and bind to the specific neurotransmitters
* these stimulate the next neurone to transmit the electrical impulse
* they can ‘diffuse’ across the neurones and bind to the specific neurotransmitters
* these stimulate the next neurone to transmit the electrical impulse
11
New cards
Neurotransmitters
A chemical involved in passing nerve impulses from one nerve cell to the next (across a synapse)
Neurones bind to SPECIFIC neurotransmitters
Neurones bind to SPECIFIC neurotransmitters
12
New cards
Electrical stimulation
* A non invasive procedure, the brain is stimulated by a small electric current,
* depending on the patients response, scientists can locate which part of the brain was stimulated
* Eg. If the patient makes an involuntary movement, the motor area has been stimulated
* Done with EEGs
* depending on the patients response, scientists can locate which part of the brain was stimulated
* Eg. If the patient makes an involuntary movement, the motor area has been stimulated
* Done with EEGs
13
New cards
MRI (brain scan)
* Use strong magnetic fields and radio waves
* Shows details of brain structure and function
* If a person carries out tasks while under an MRI scan, scientists can see which parts of the brain are active as the task is carried out.
* Shows details of brain structure and function
* If a person carries out tasks while under an MRI scan, scientists can see which parts of the brain are active as the task is carried out.
14
New cards
Risks of investigating and treating the brain
* some conditions, such as tumours, may require surgery, this could cause more damage/ side effects
* Risks need to be weighed against benefits in order for it to be ethical and practical
* Risks need to be weighed against benefits in order for it to be ethical and practical
15
New cards
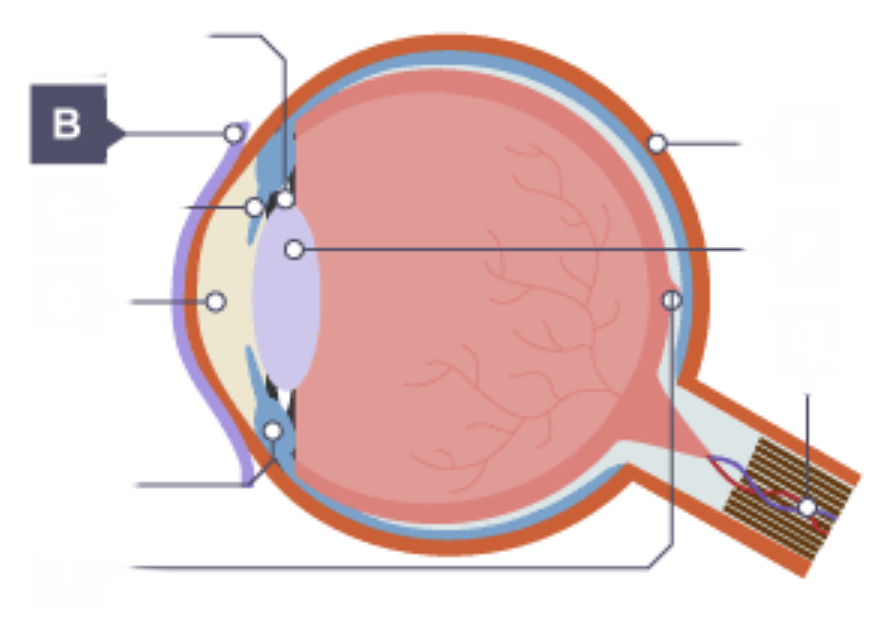
Cornea
Transparent and curved, lets light in and refracts it so that it is focused onto the retina
16
New cards
Iris
Controls how much light is let into the pupil, it is the coloured part of the eye that contains muscles that contract and relax
17
New cards
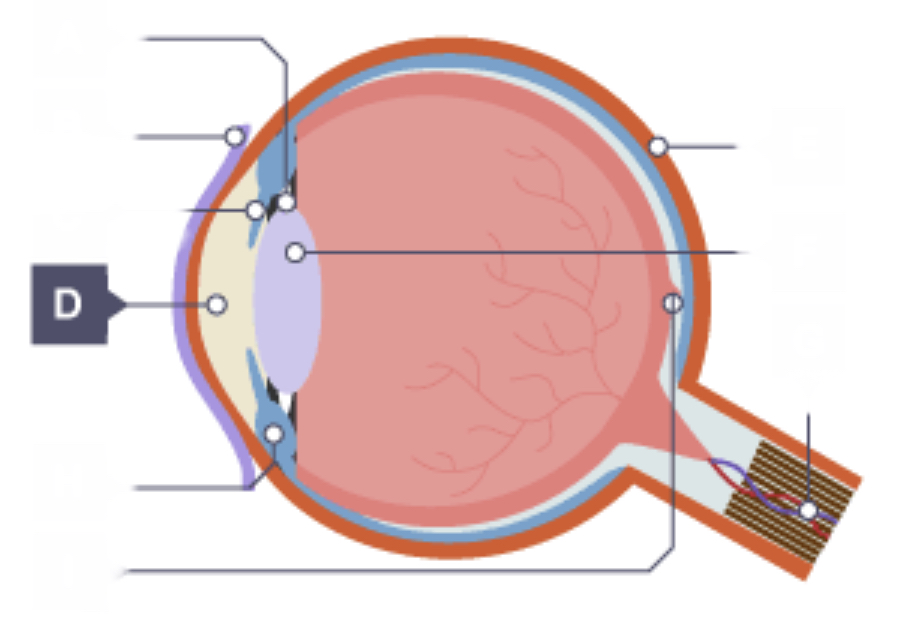
Pupil
Hole that lets in light
18
New cards
Sclera
Tough white outer layer that protects the eye
19
New cards
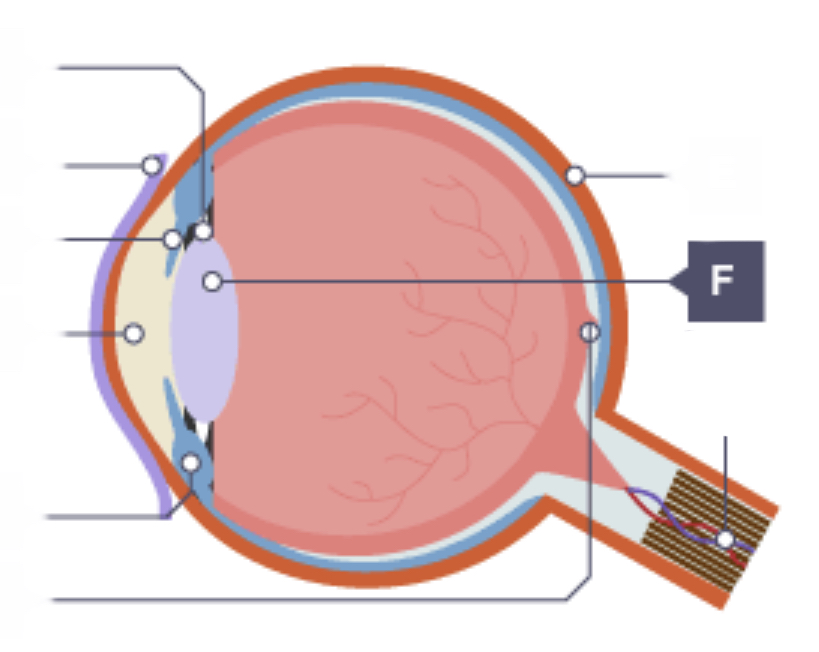
Lens
Sits behind pupil and focuses light onto the retina
20
New cards
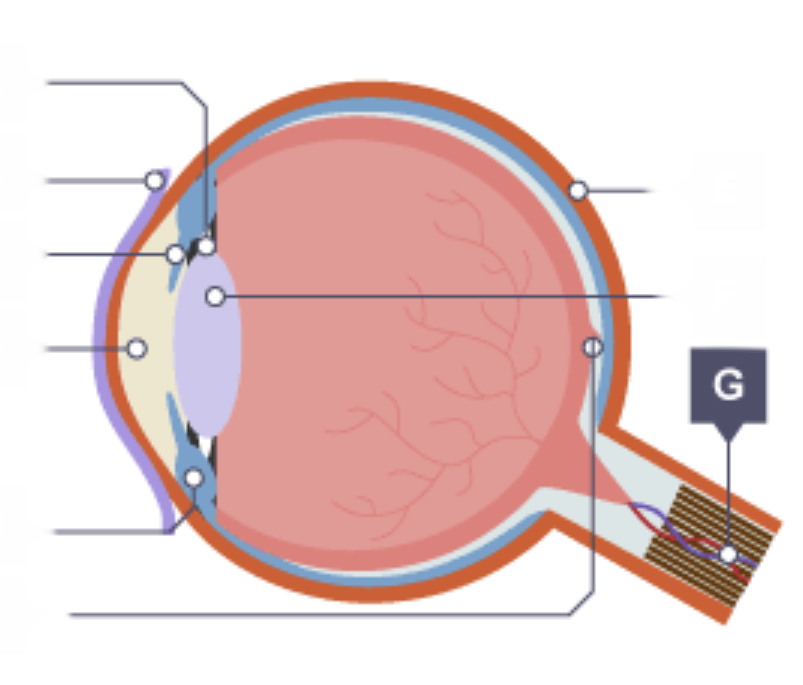
Optic nerve
Nerve that carries impulses between the eye and the brain
21
New cards
Ciliary muscle and Suspensory ligament
Contracts and relaxes to change the shape of the lens