Functional Human Anatomy Final (new material only)
1/499
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Rutgers Functional Human Anatomy Final, based on Rudy's study guide, contains endocrine system, urinary system, axial musculature, upper extremity skeleton, upper extremity musculature, lower extremity skeleton, lower extremity musculature, reproductive system, pregnancy + delivery
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
500 Terms
Endocrine System
this system secretes hormones into the bloodstream to maintain homeostasis
Hormones
chemical messengers that act upon effectors to regulate bodily functions
In order to create a response, a specific one must bind to a specific receptor
endocrine cells
located in a gland or gland-like structure; release and produce hormones
main endocrine organs
pituitary gland, hypothalamus, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, pineal gland, parathyroid gland, pancreas
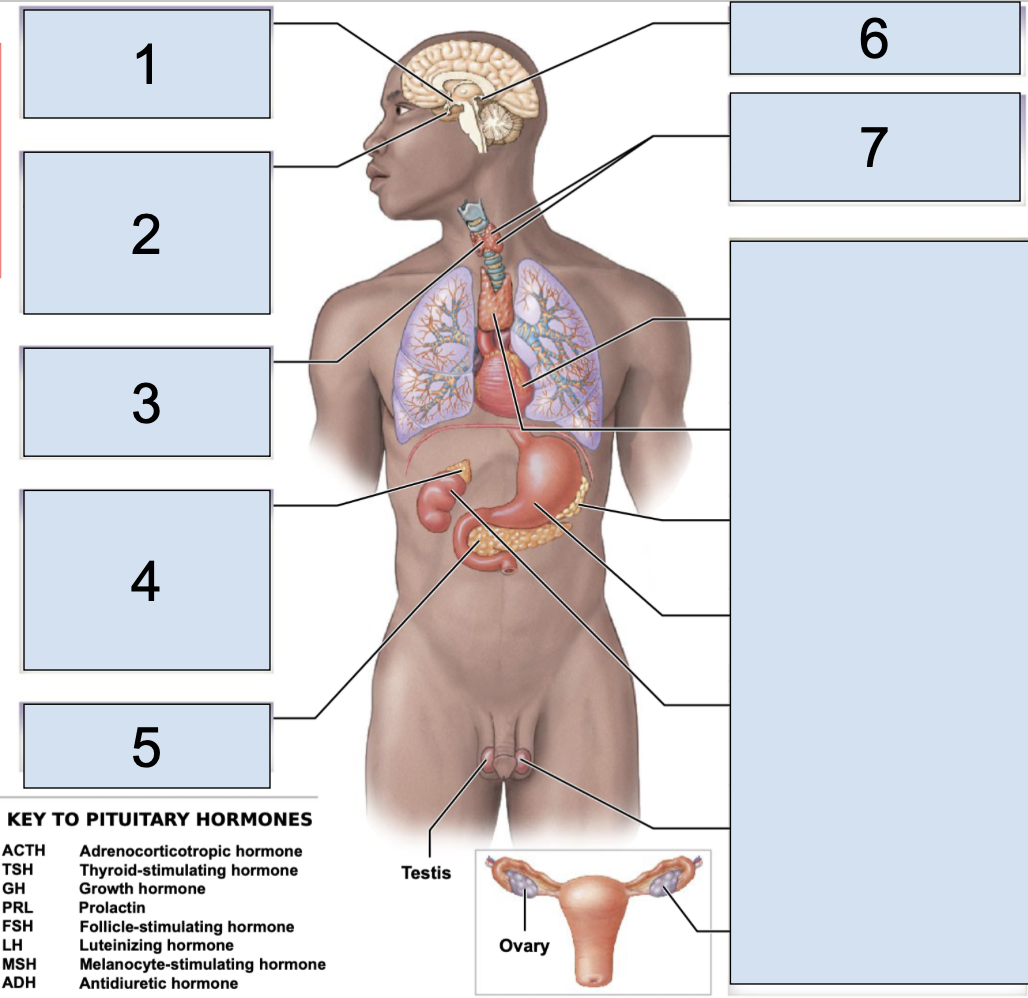
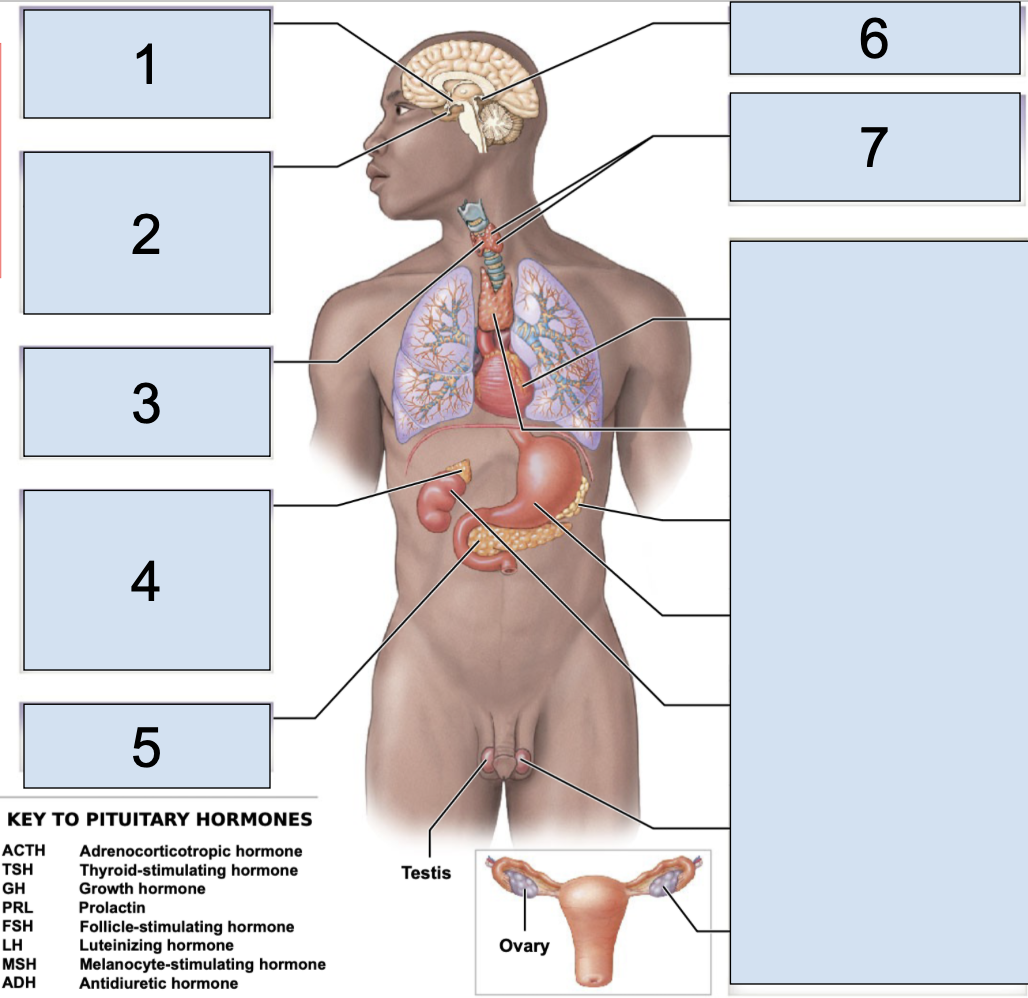
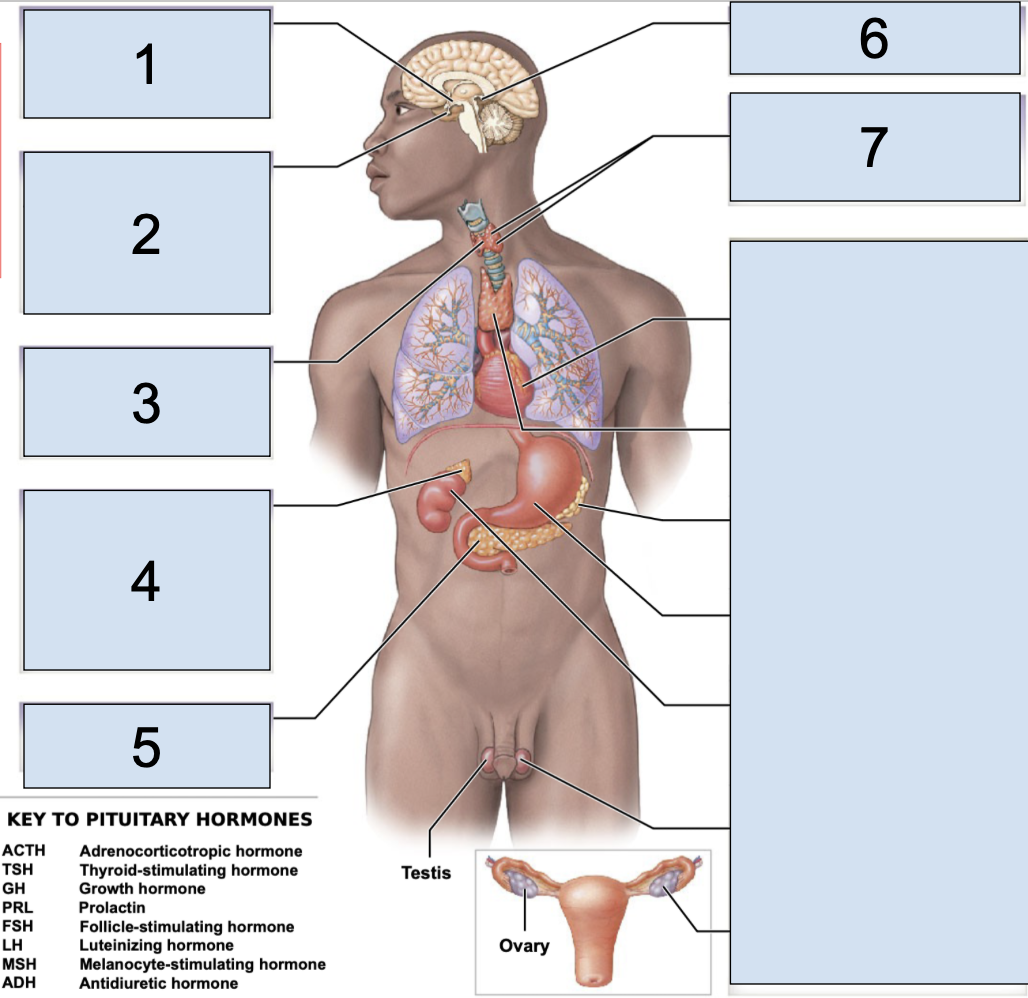
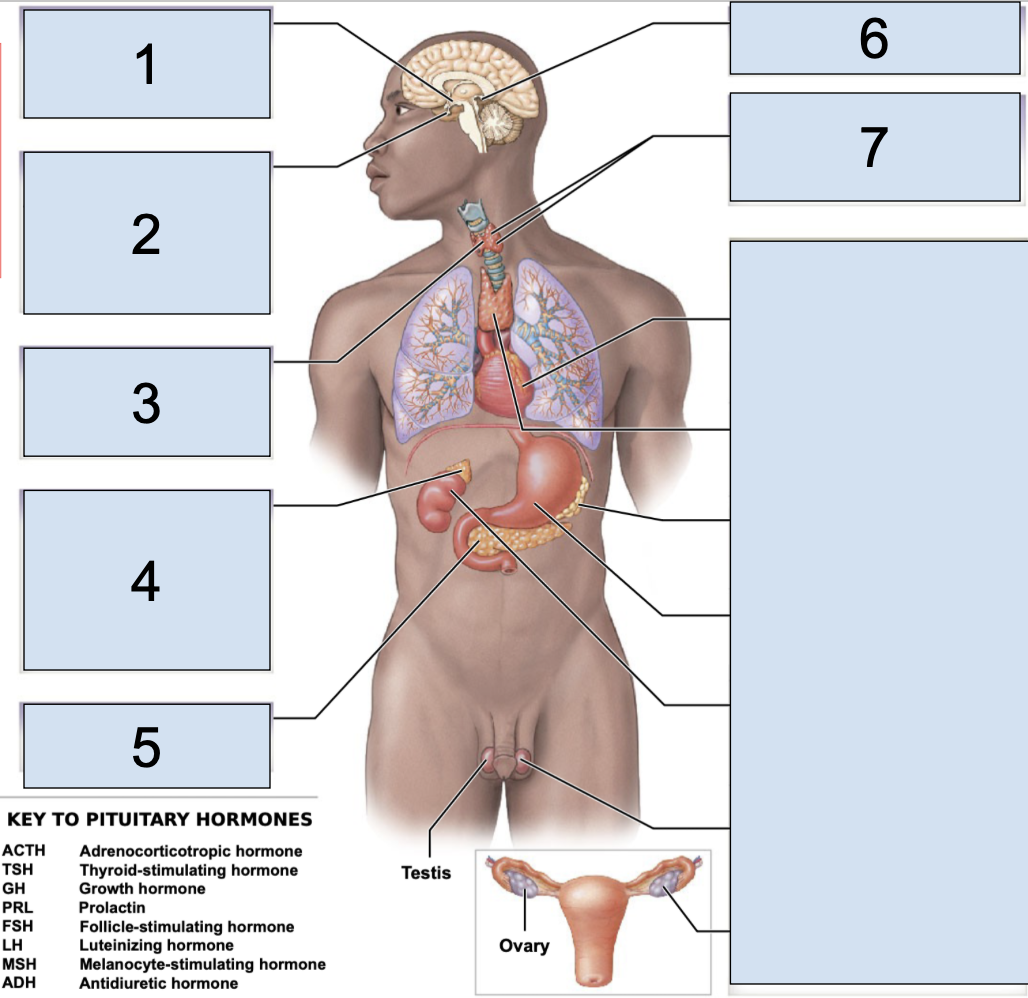
pituitary gland
main endocrine structure located in the brain inferior to hypothalamus
oxytocin + antidiuretic hormone produced by the hypothalamus are released HERE
(2)
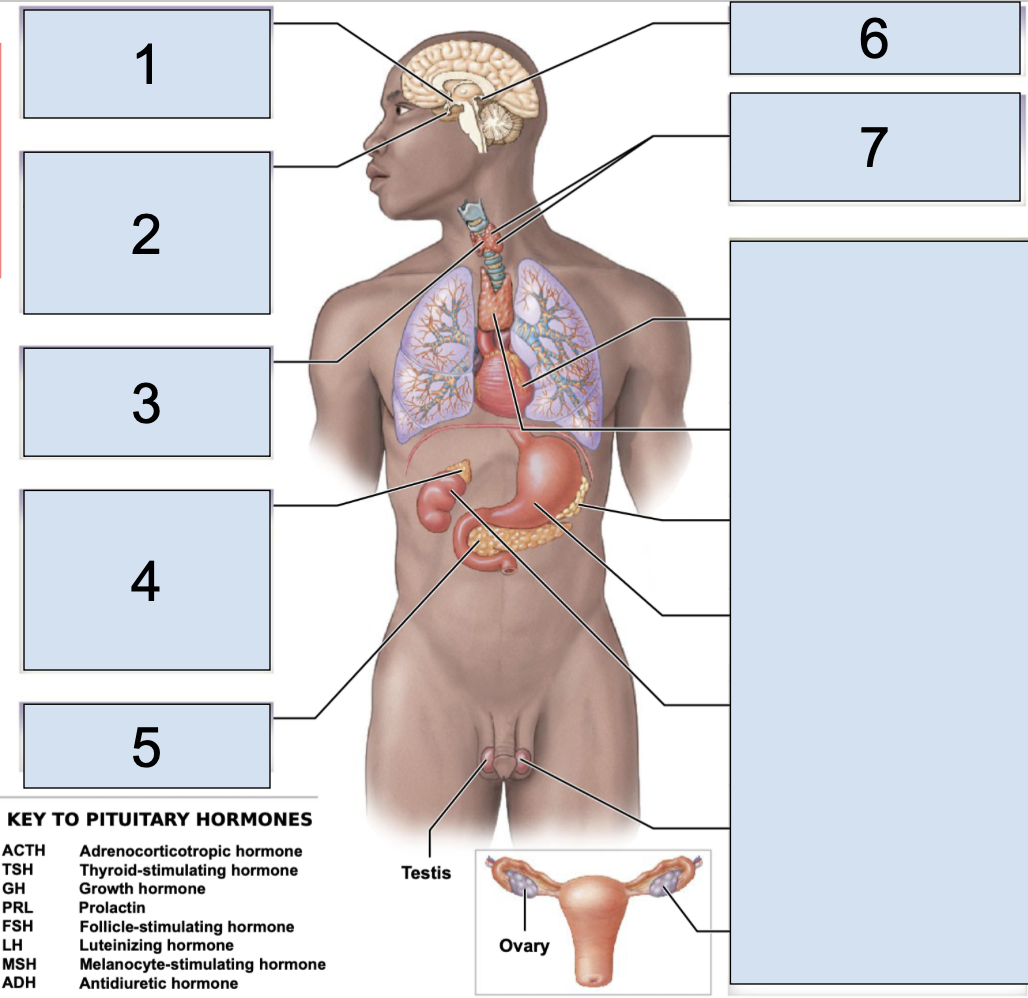
what does the pituitary gland secrete in the anterior lobe?
secretes ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone)
GH (growth hormone)
PRL (prolactin)
FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone)
LH (luteinizing hormone)
MSH (megalocyte-stimulating hormone)
what does the pituitary gland secrete in the posterior lobe?
secretes OXT (oxytocin)
ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
a hormone that targets your kidneys
it works to reabsorb water to increase blood volume and blood pressure
oxytocin (OXT)
a hormone that in females targets the mammary glands and the uterus causing milk ejection in the mammary gland + uterine wall contraction
in males it targets the prostate gland + ductus deferens leading to contractions of both of these structures
neurohypophysis
posterior pituitary gland
adenohypophysis
anterior pituitary gland
hypothalamus
main endocrine structure located in the brain inferior to thalamus and superior to pituitary gland
a key organ that serves as link between neural + endocrine system
oxytocin + antidiuretic hormone are produced HERE but then are released in the posterior pituitary gland
preganglionic neurons that start HERE synapse on the adrenal medulla
(1)
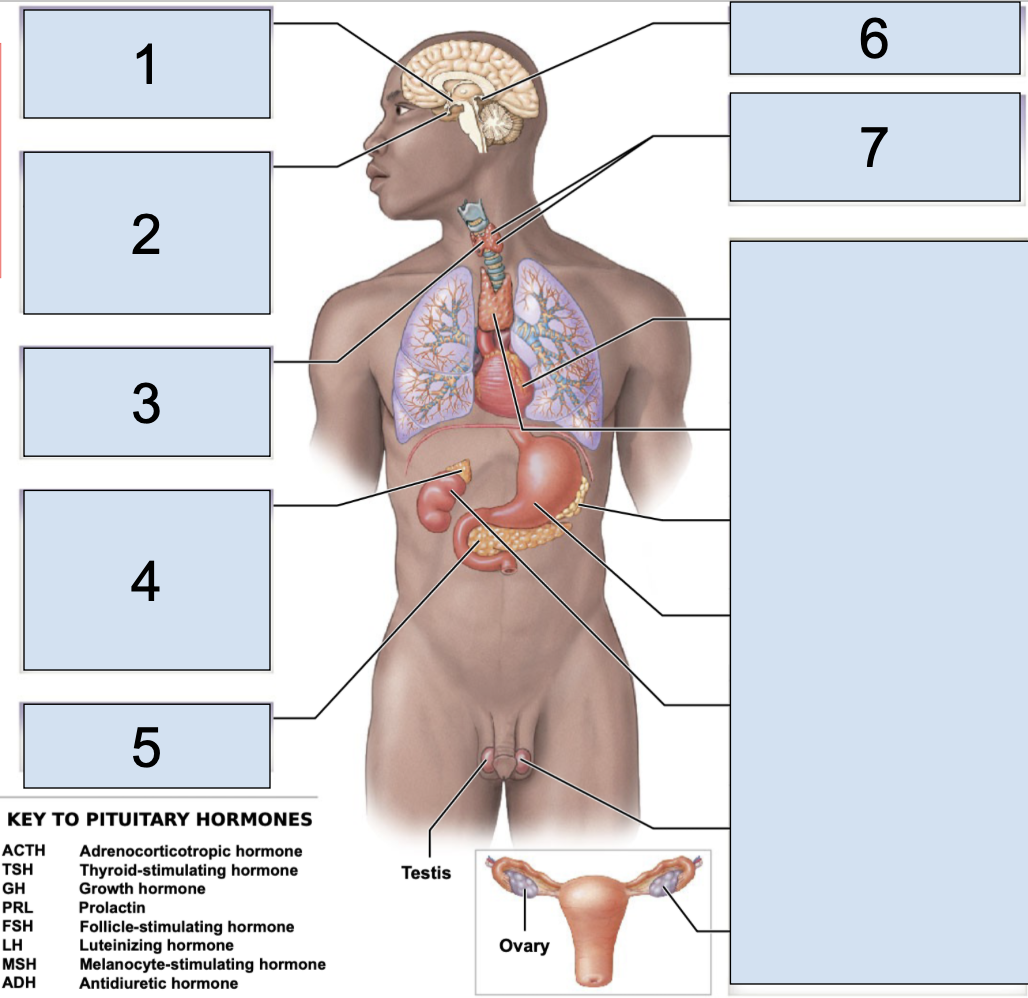
what does the hypothalamus secrete?
ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
OXY (oxytocin)
regulatory hormones
thyroid gland
main endocrine structure located on the anterior side of the neck (3)
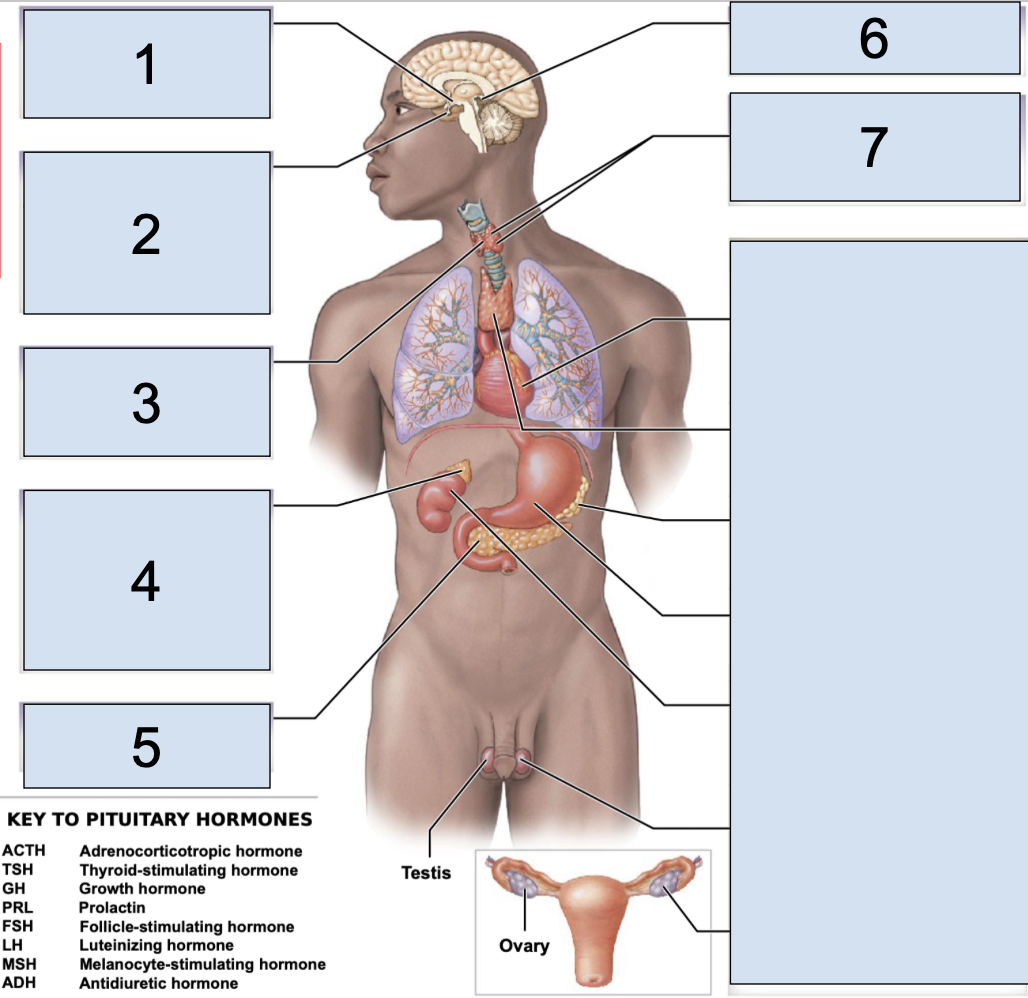
what does the thyroid secrete?
T4 (Thyroxine)
T3 (Trilodothyrine)
CT (Calcitonin)
T3 (Trilodothyronine) + T4 (Thyroxine)
these hormones influence metabolism
Calcitonin
a hormone that works to lower blood calcium levels
adrenal gland
main endocrine structure located on top of the kidneys
preganglionic neurons starting in the hypothalamus synapse HERE
have a pyramidal shape
(4)
adrenal cortex
outer portion of adrenal gland
adrenal medulla
inner portion of adrenal gland
what does the medulla of the adrenal gland secrete?
E (epinephrine)
NE (norepinephrine)
what does the cortex of the adrenal gland secrete?
Cortisol
Corticosterone
Aldosterone
Androgens
cortisol
a hormone that works to increase blood sugar so that we have energy to respond to internal + external stresses
aldosterone
a hormone that helps promote water retention to increase blood volume + blood pressure
androgens
these are sex hormones (estrogen + testosterone)
pineal gland
main endocrine structure located near the epithalamus in the brain (6)
what does the pineal gland secrete?
melatonin
parathyroid gland
main endocrine structure located on the posterior side of the neck, has 4 nodules (7)
what does the parathyroid gland secrete?
PTH (Parathyroid Hormone)
PTH (Parathyroid Hormone)
a hormone that works to increase blood calcium levels
pancreas
main endocrine structure located in the abdomen that relies on the bloodstream to move the hormones
it is also an exocrine gland that relies on the ducts to move its products within HERE
sits inside the curve of the duodenum (5)
what does the pancreas secrete?
insulin, glucagon
glucagon
a hormone that works to increase blood sugar levels
insulin
a hormone that works to decrease blood sugar levels
secondary endocrine organs
heart, thymus, adipose tissue, digestive tract, kidneys, gonads
kidneys
this secondary endocrine structure is located on either side of your spine below the ribcage; in the retroperitoneal space of abdominal cavity
regulates blood calcium levels
produces urine (start of urine flow)
most superior large structure of urinary tract
what does the kidneys secrete?
renin, erythropoietin (EPO)
renin
a hormone that stimulates a series of steps that ultimately lead to the production/release of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex, it works to increase sodium and water retention (response to low blood pressure)
How Does the Body Respond to Low Blood Pressure?
(1) The kidneys secrete renin
(2) renin stimulates steps
(3) production/release of aldosterone by adrenal cortex
(4) increases sodium + water retention
erythropoietin (EPO)
a hormone that stimulates the creation of more red blood cells so that we can carry more oxygen in the body
how does the body respond to low calcium?
(1) sunlight converts a hormone into inactive vitamin D3
(2) parathyroid hormone targets the kidneys
(3) kidney cells convert Vitamin D3 into its active form
(4) active vitamin D3 is released + causes the small intestine to absorb more calcium ions into the bloodstream
target cells
they contain hormone receptors
maintaining electrolyte and fluid balance
function of urinary system
eliminating wasters from the body
function of urinary system
regulating blood volume + blood pressure
function of urinary system
maintaining acid/base balance in the body
function of urinary system
structures in the urinary tract
kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra
1st Urine Flow Location
kidney
2nd Urine Flow Location
Ureter
3rd Urine Flow Location
urinary bladder
4th Urine Flow Location
Urethra
1st Urine Flow Location in Kidney
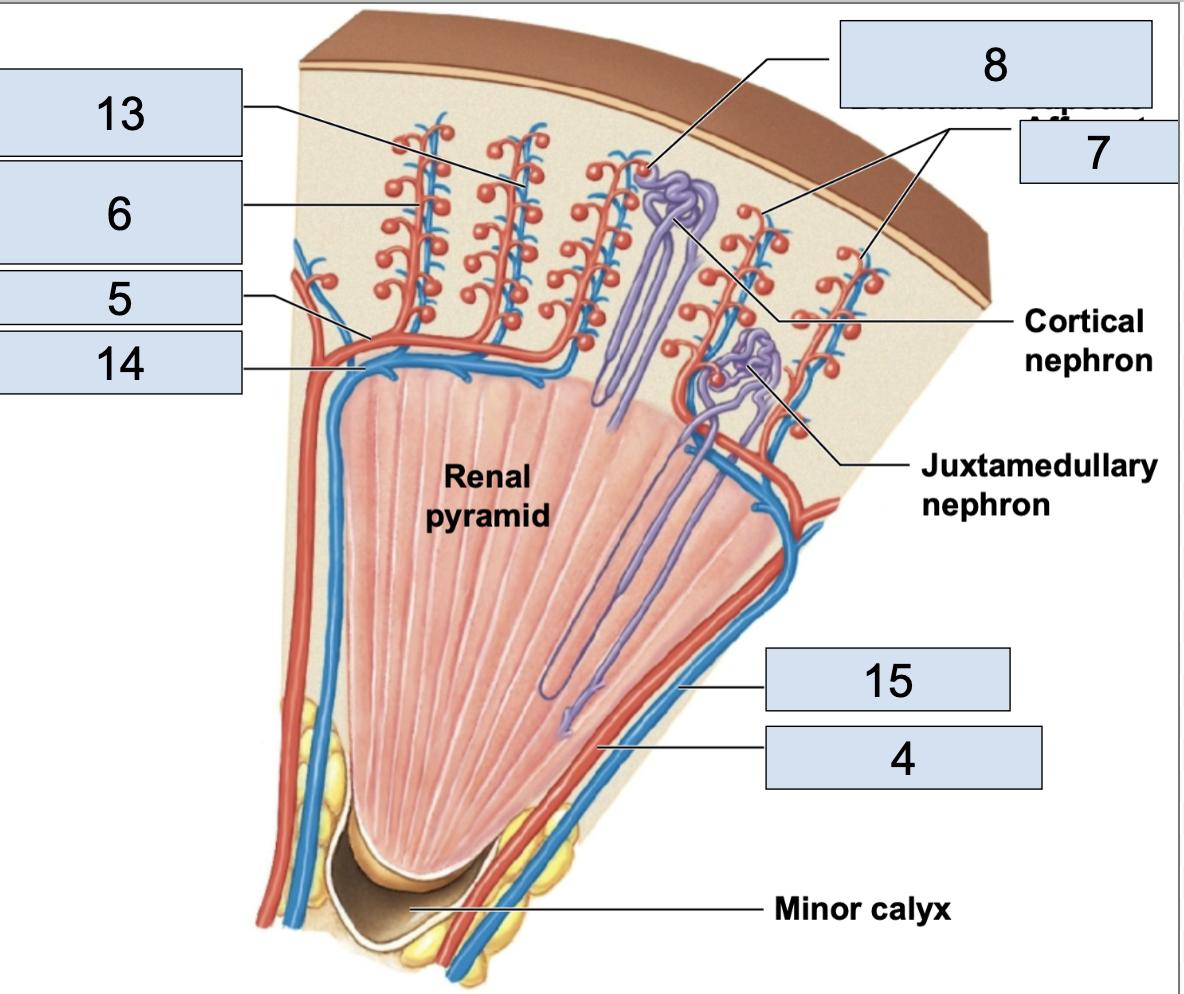
minor calyx
2nd Urine Flow Location in Kidney
major calyx
3rd Urine Flow Location in Kidney
renal pelvis
4th Urine Flow Location in Kidney
urethra
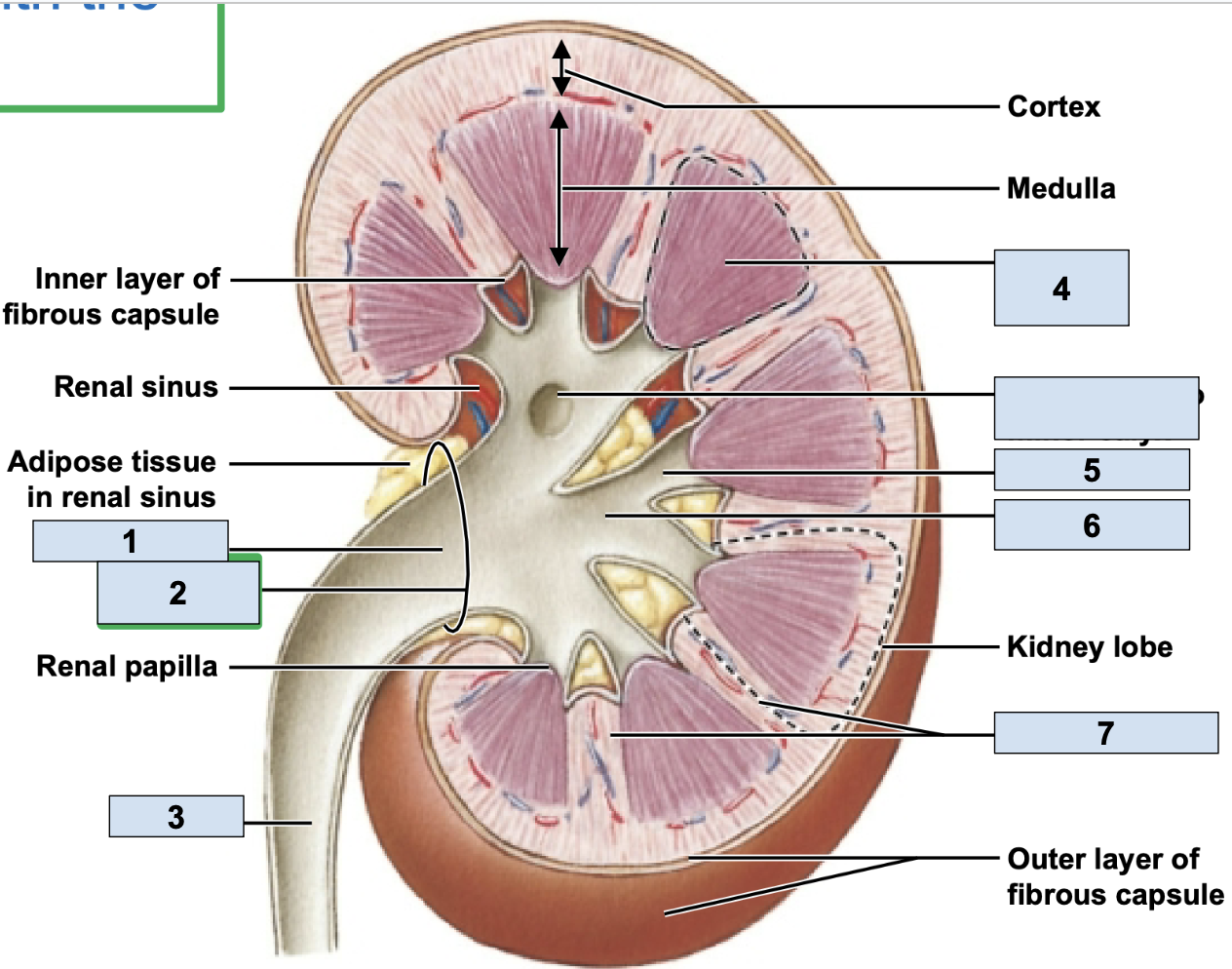
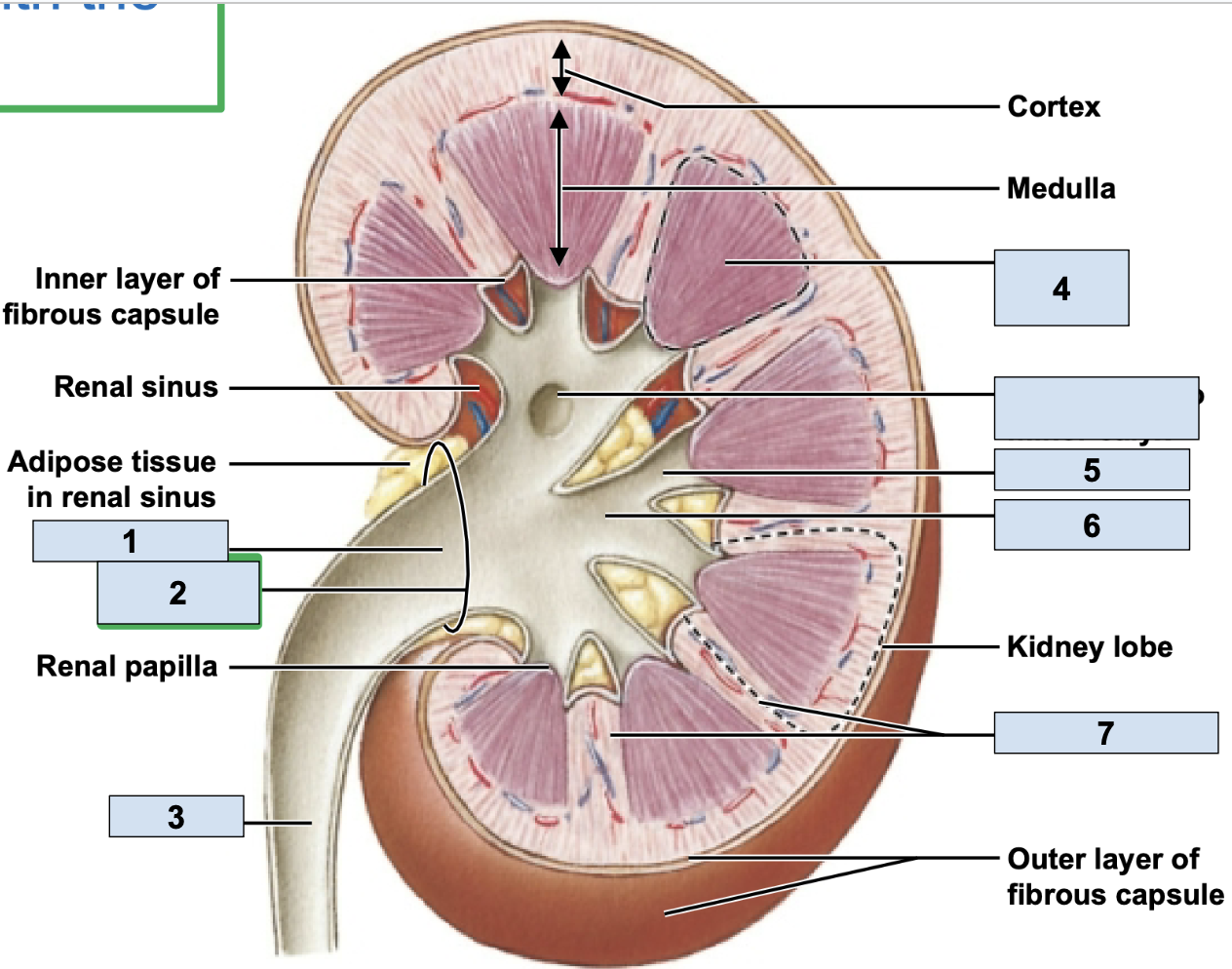
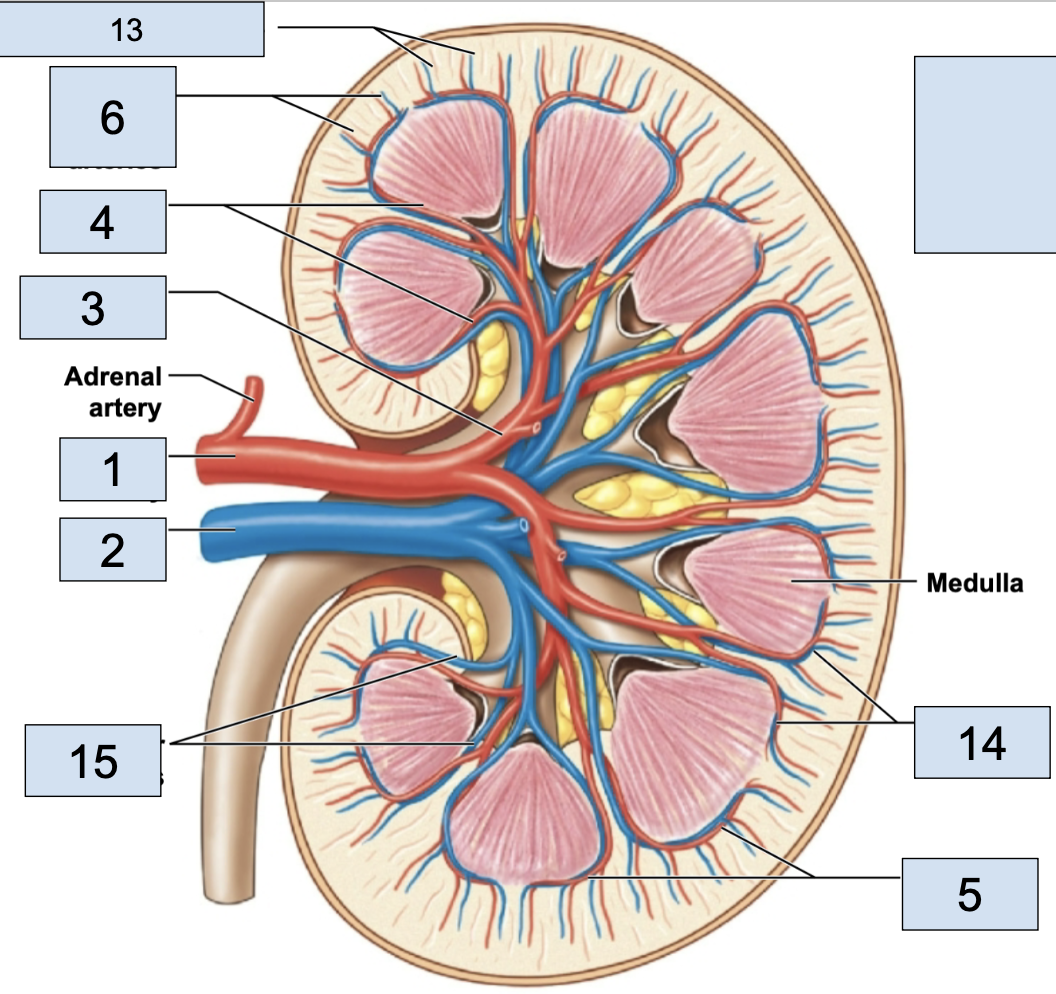
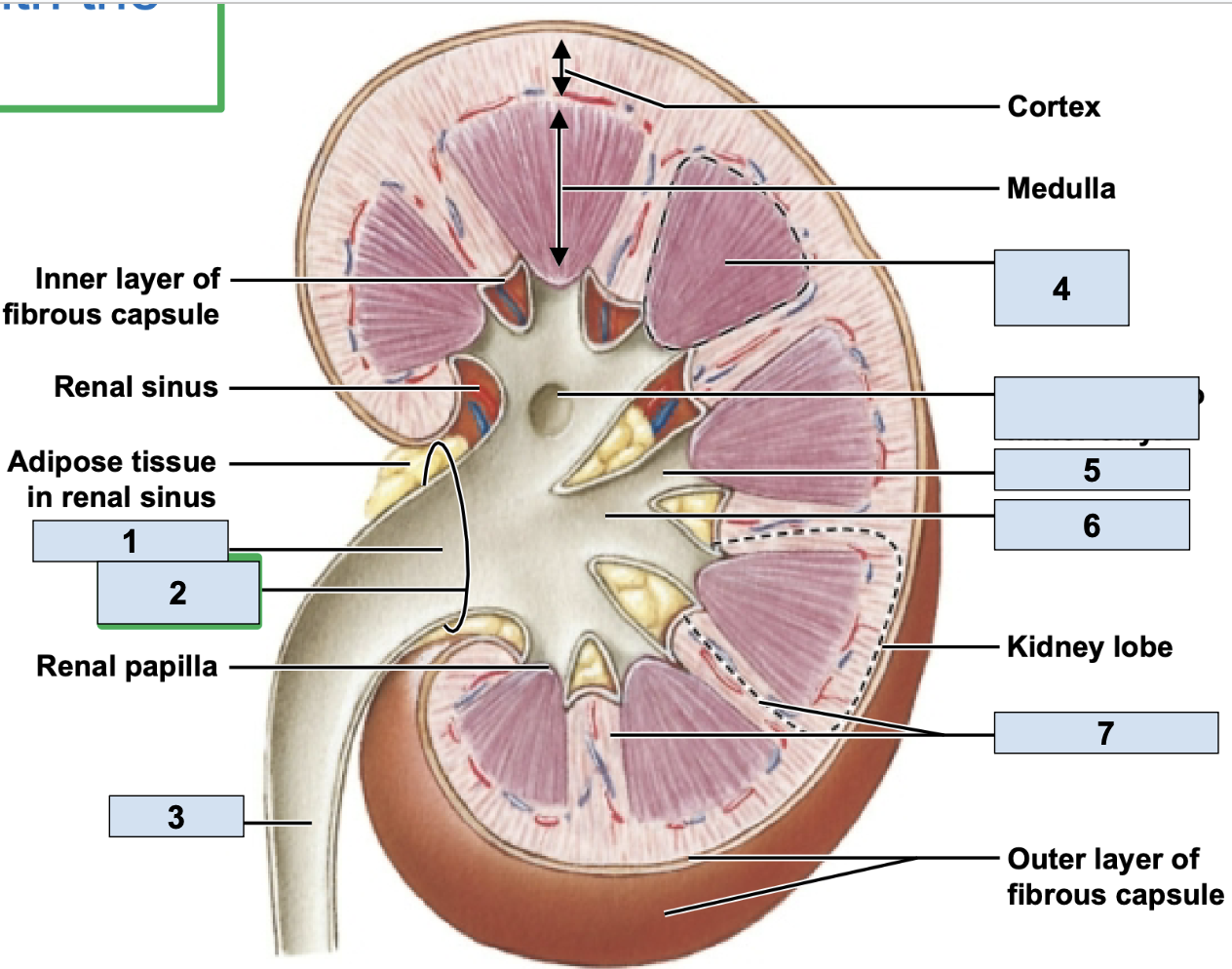
renal/fibrous capsule
innermost protective layer of kidney
Perirenal Fat
middle of kidney protective layer
adrenal fascia
outermost kidney protective layer
renal artery
brings oxygenated blood to kidney (1)
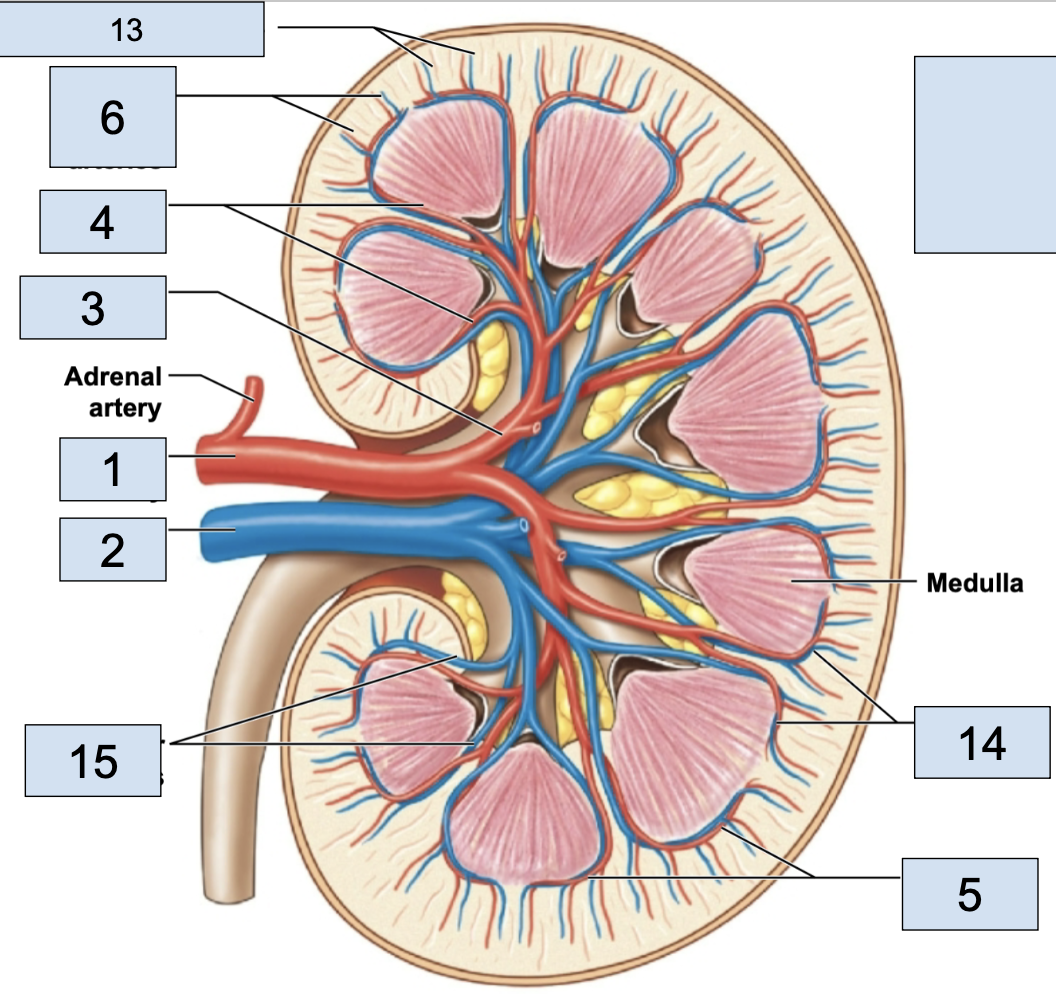
renal vein
brings deoxygenated blood away from kidney (2)
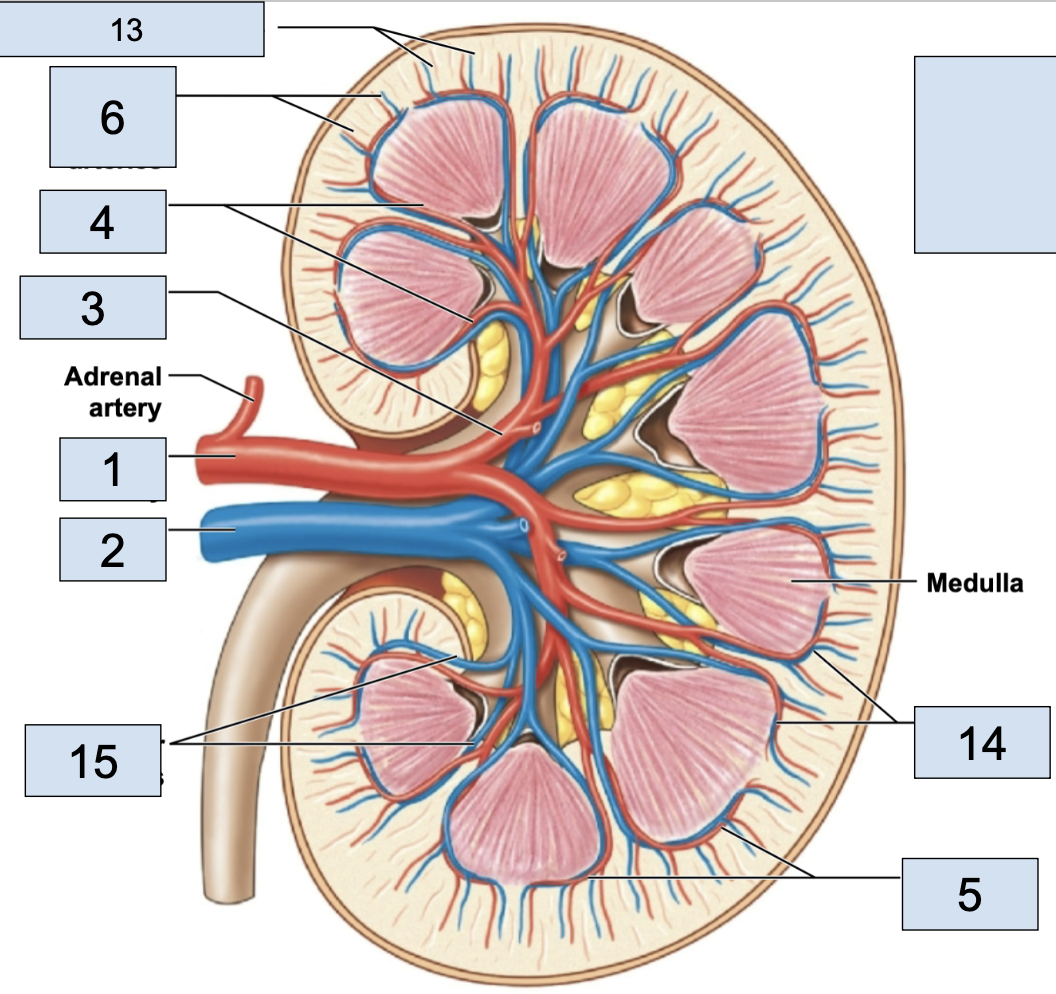
hilum
where the renal artery, renal vein, and ureter physically link up with the kidney (2)
minor calyx
smallest branch in the kidney, urine enters here first in kidney (5)
major calyx
bigger branch in the kidney, urine enters her after minor calyx in kidney (6)
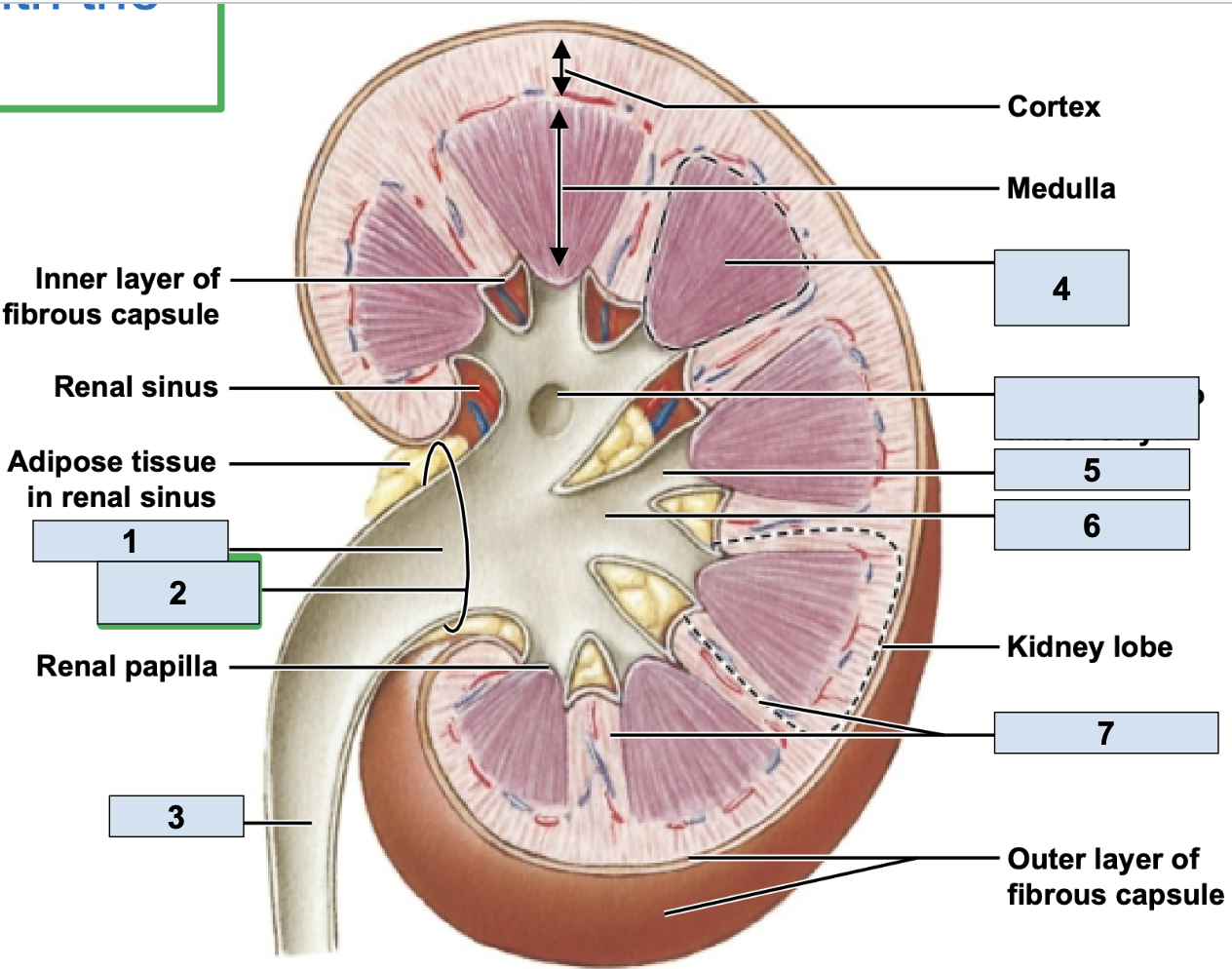
renal pelvis
big trunk branch in the kidney leading to ureter, urine enters here after major calyx and passes it to ureter (1)
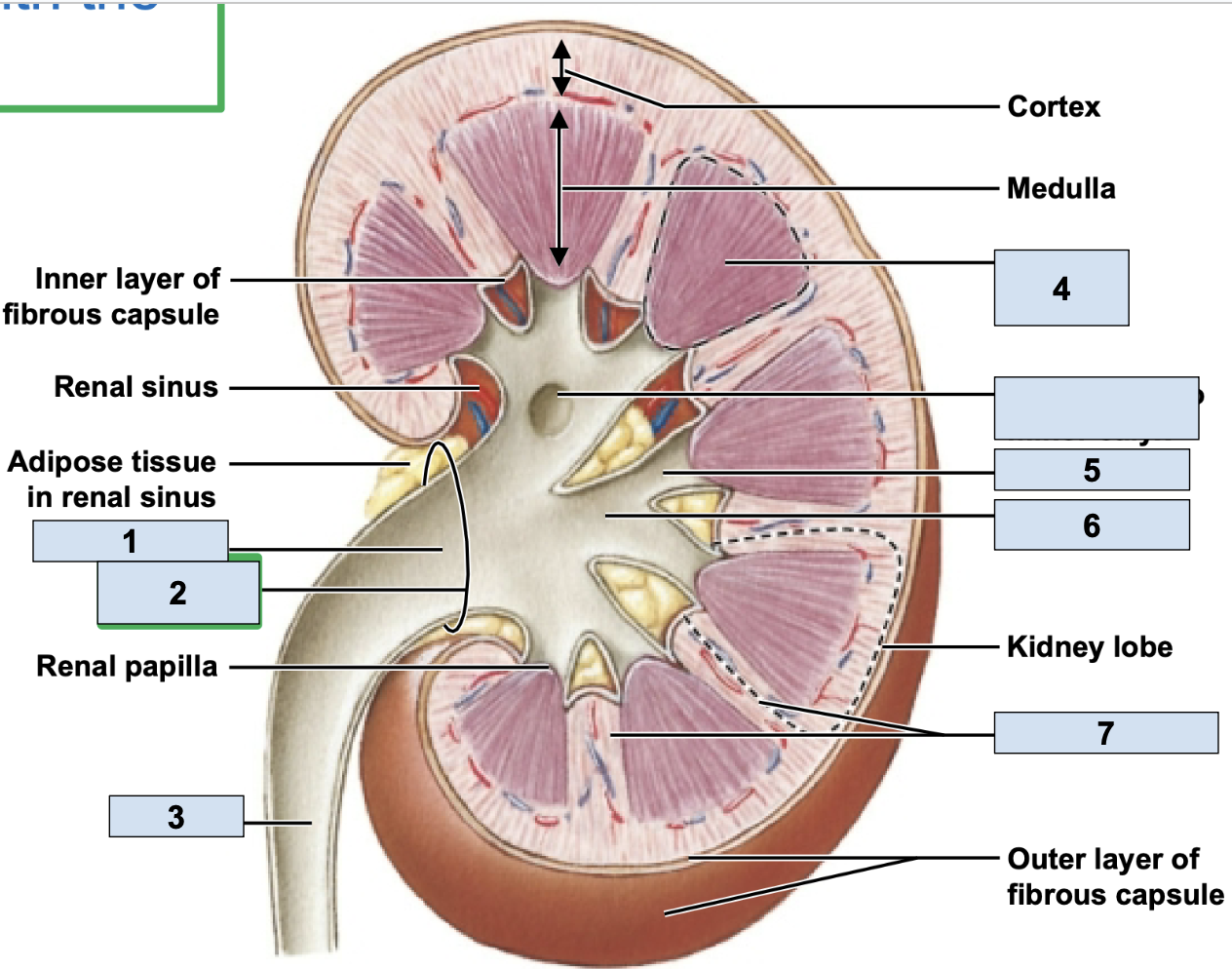
renal pyramid
triangle structures in kidney (4)
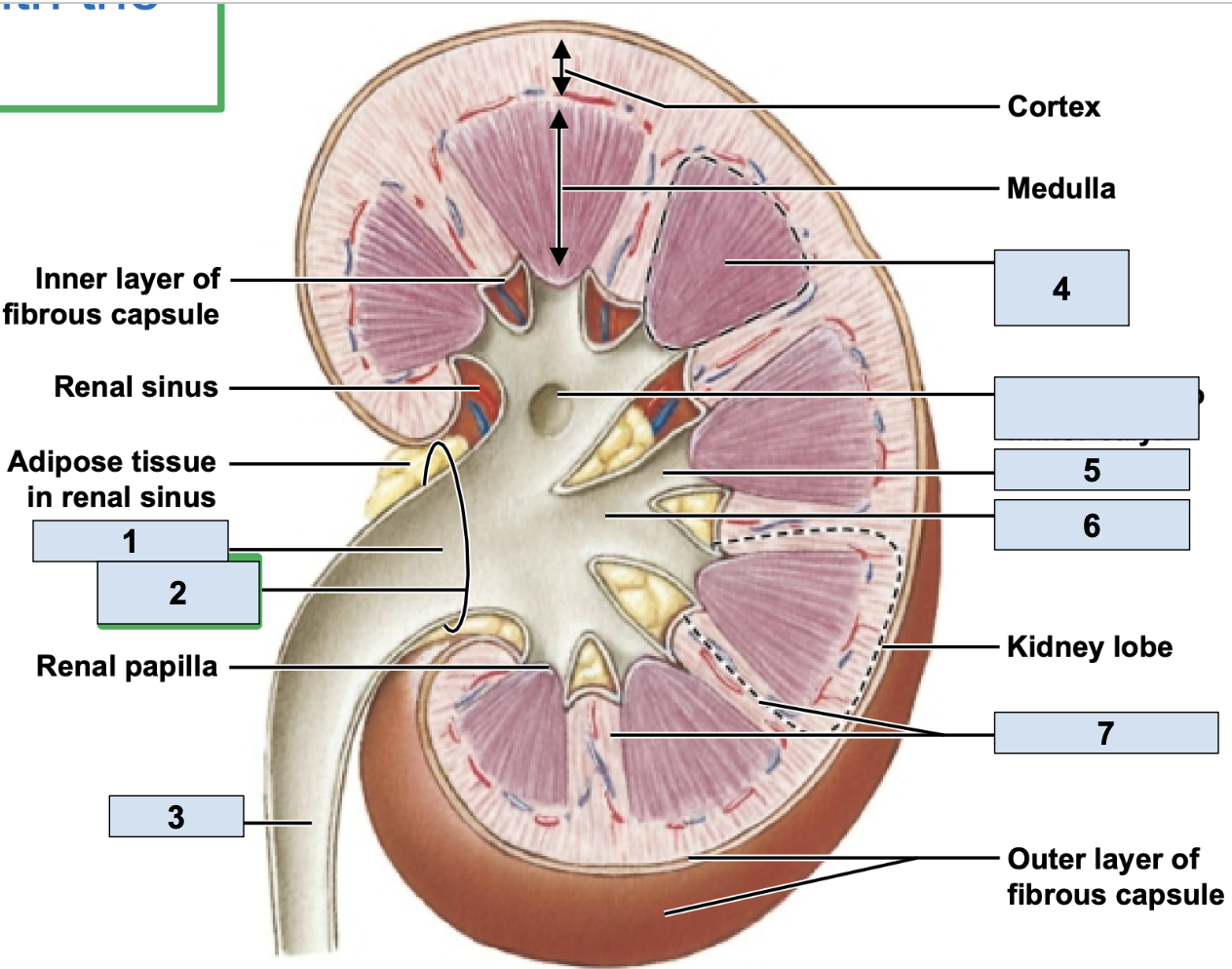
renal column
area between renal pyramids (7)
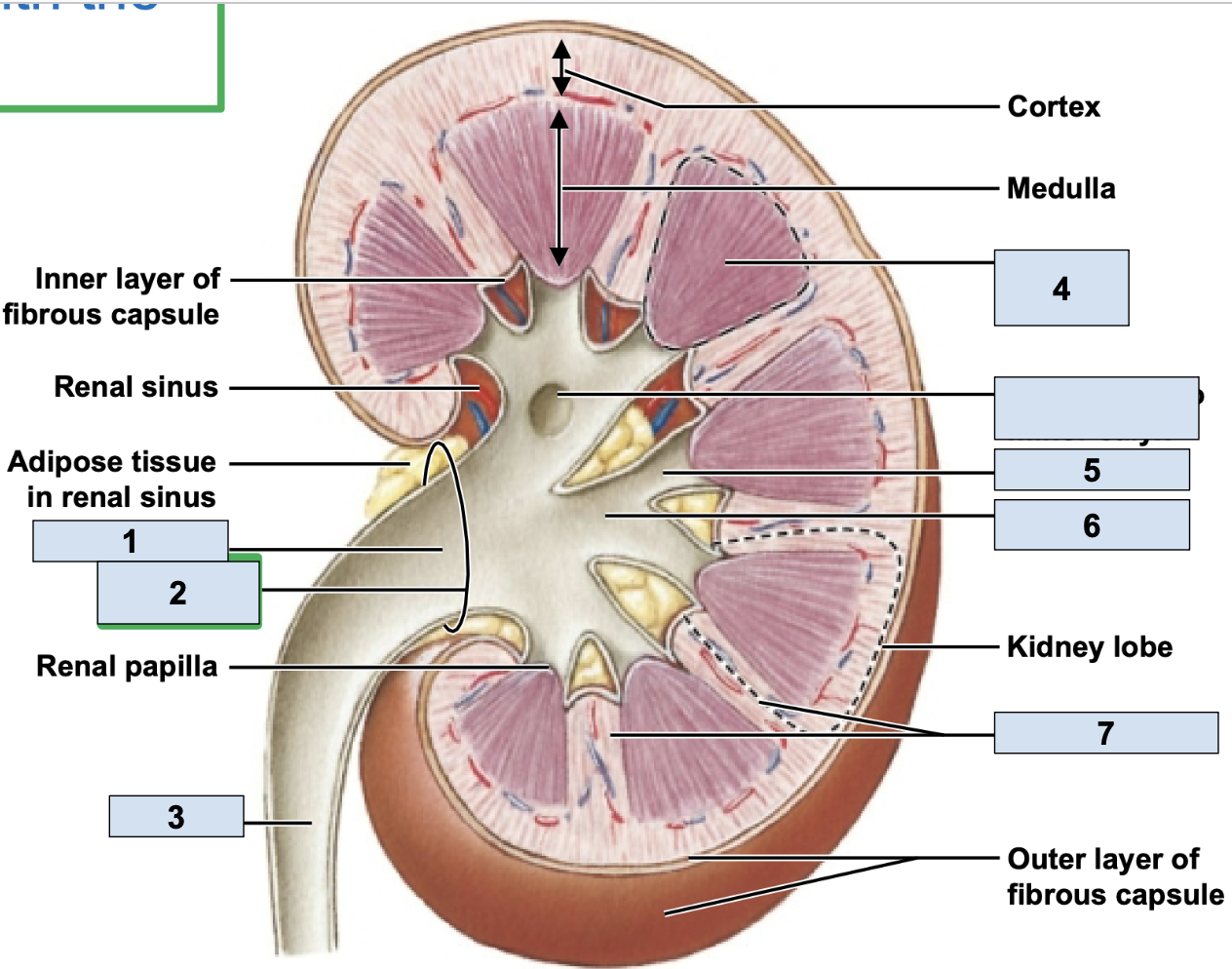
segmental arteries
the branch off renal arteries (3)
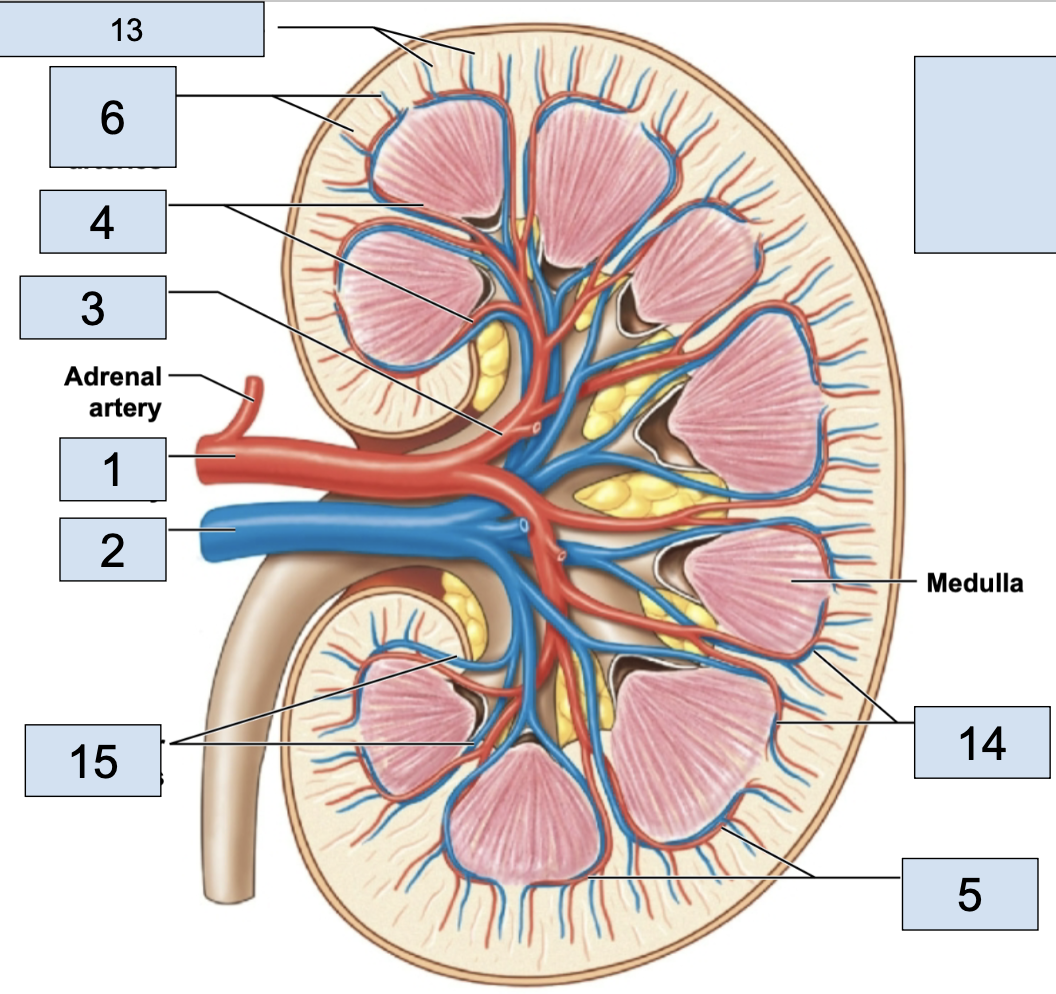
interlobar arteries
the arteries that curve around the renal pyramids from the segmental arteries (4)
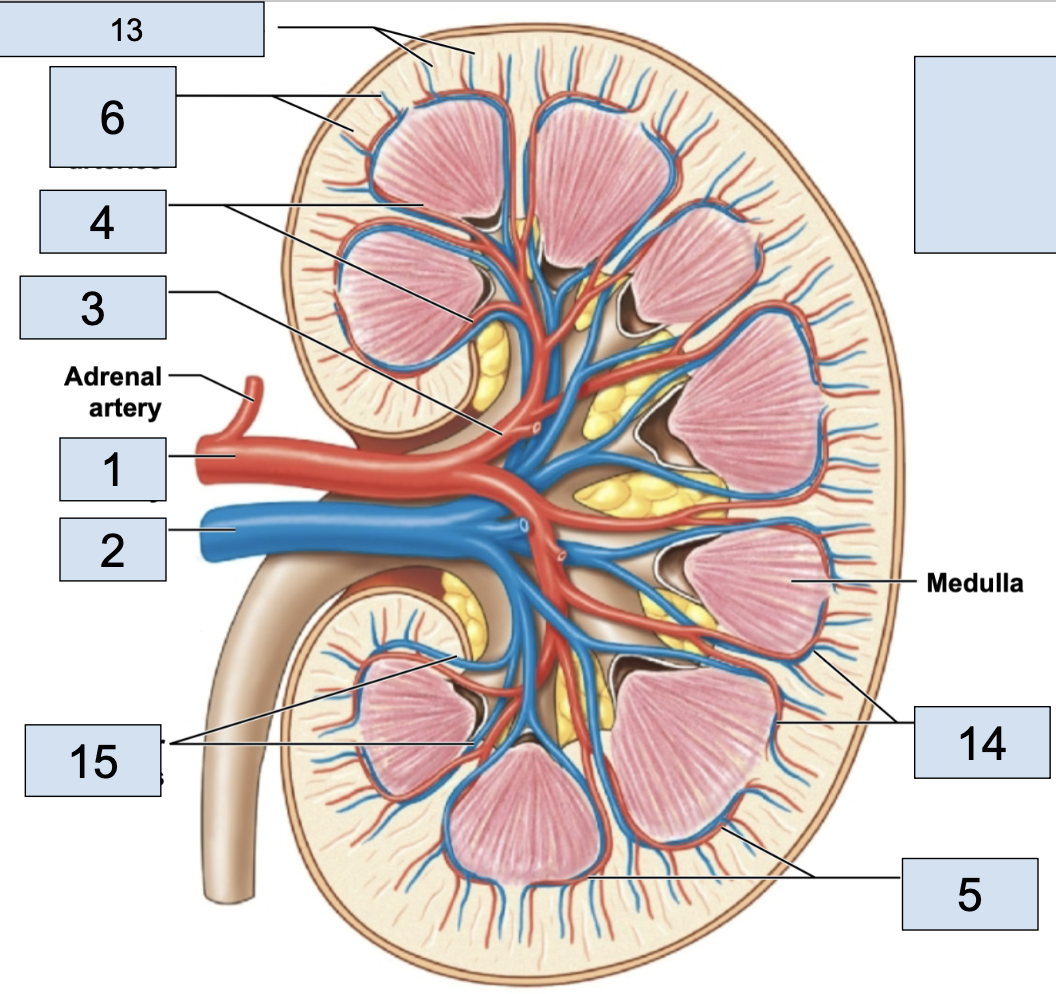
arcuate arteries
the vessels that branch after the interlobar arteries (5)
cortical radiate arteries
thin vessels branching from arcuate arteries (6)
afferent arterioles
the tiny stems branching from cortical radiate arteries; in nephron (7)
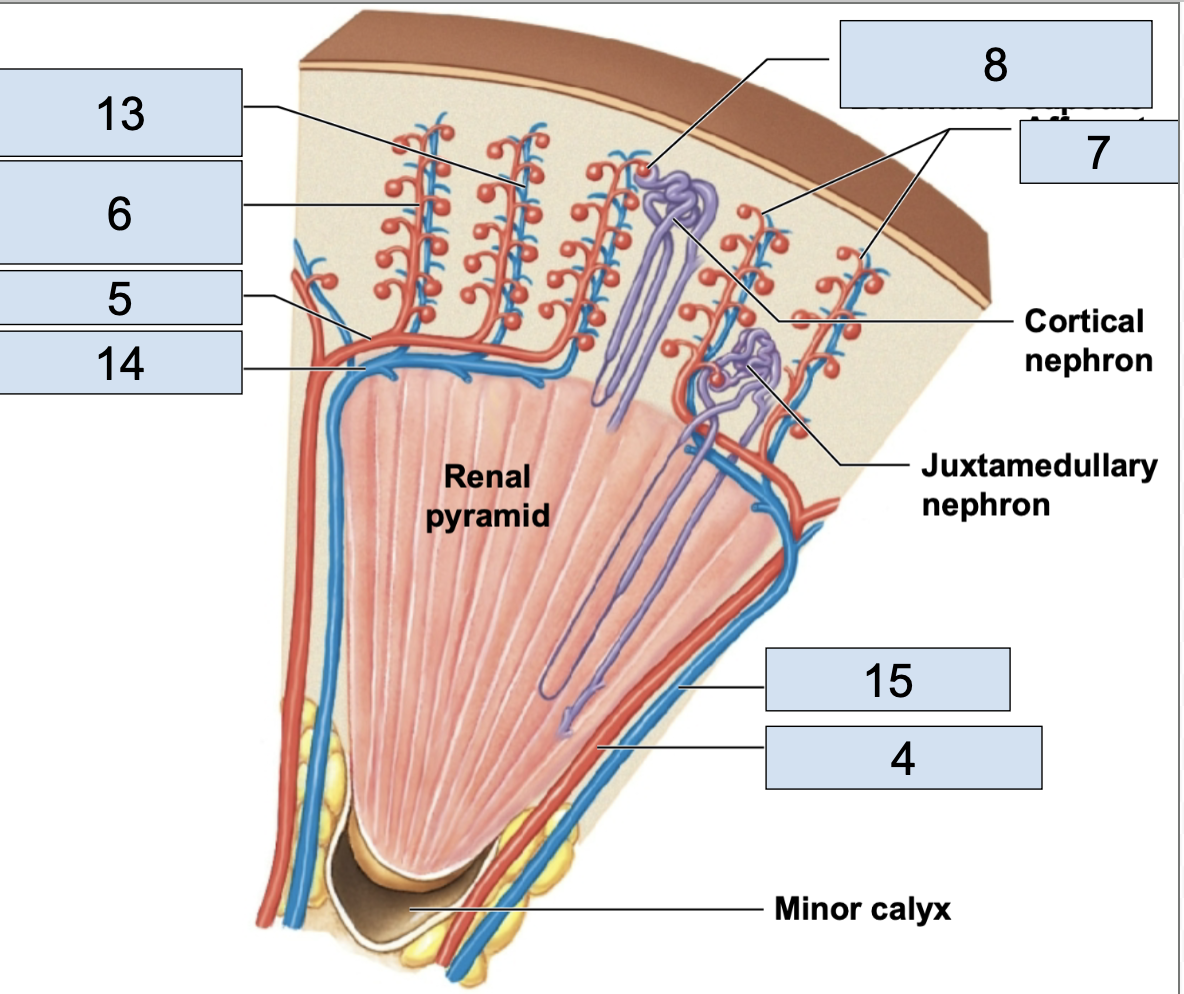
efferent arterioles
stem from glomerus; in nephron
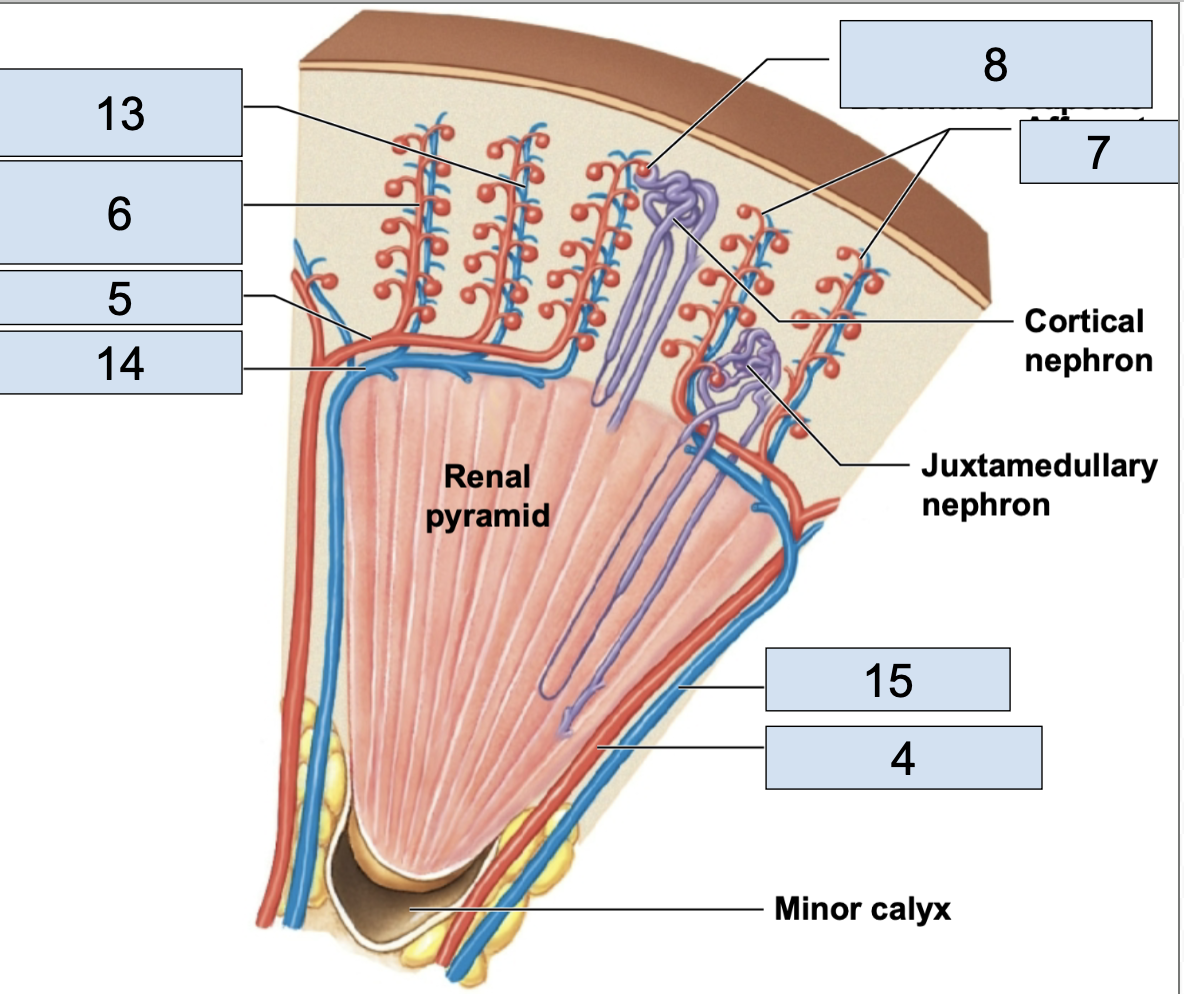
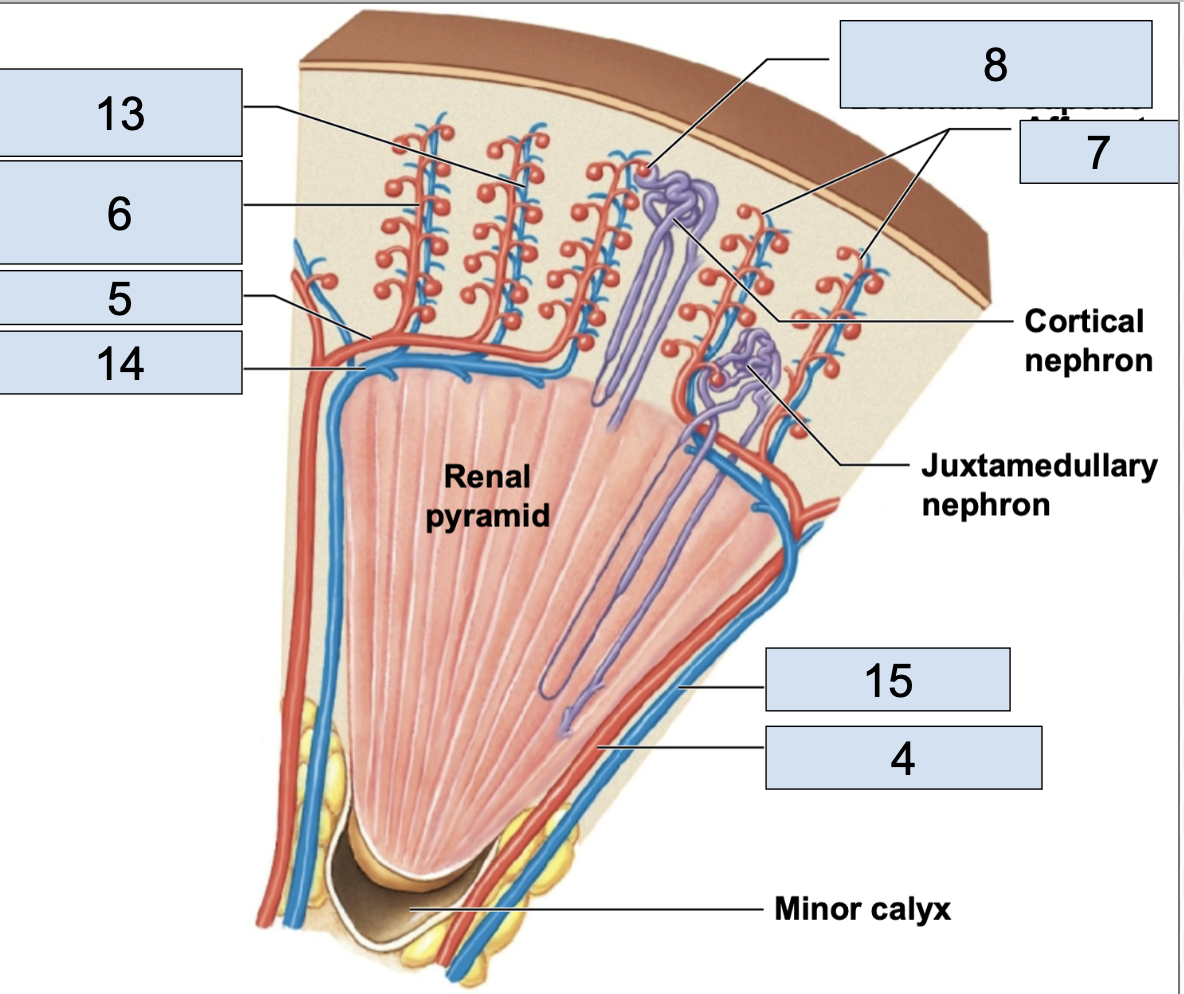
peritubular capillaries
stem from efferent arterioles; where nutrient exchange happens; in nephron
venules
stems from peritubular capillaries; blood is officially deoxygenated
cortical radiate veins
stems from venules, vessels getting bigger (13)
arcuate veins
stem from cortical radiate veins, on the end of the renal pyramid (14)
interlobar vein
stems from arcuate veins, all around renal pyramid (15)
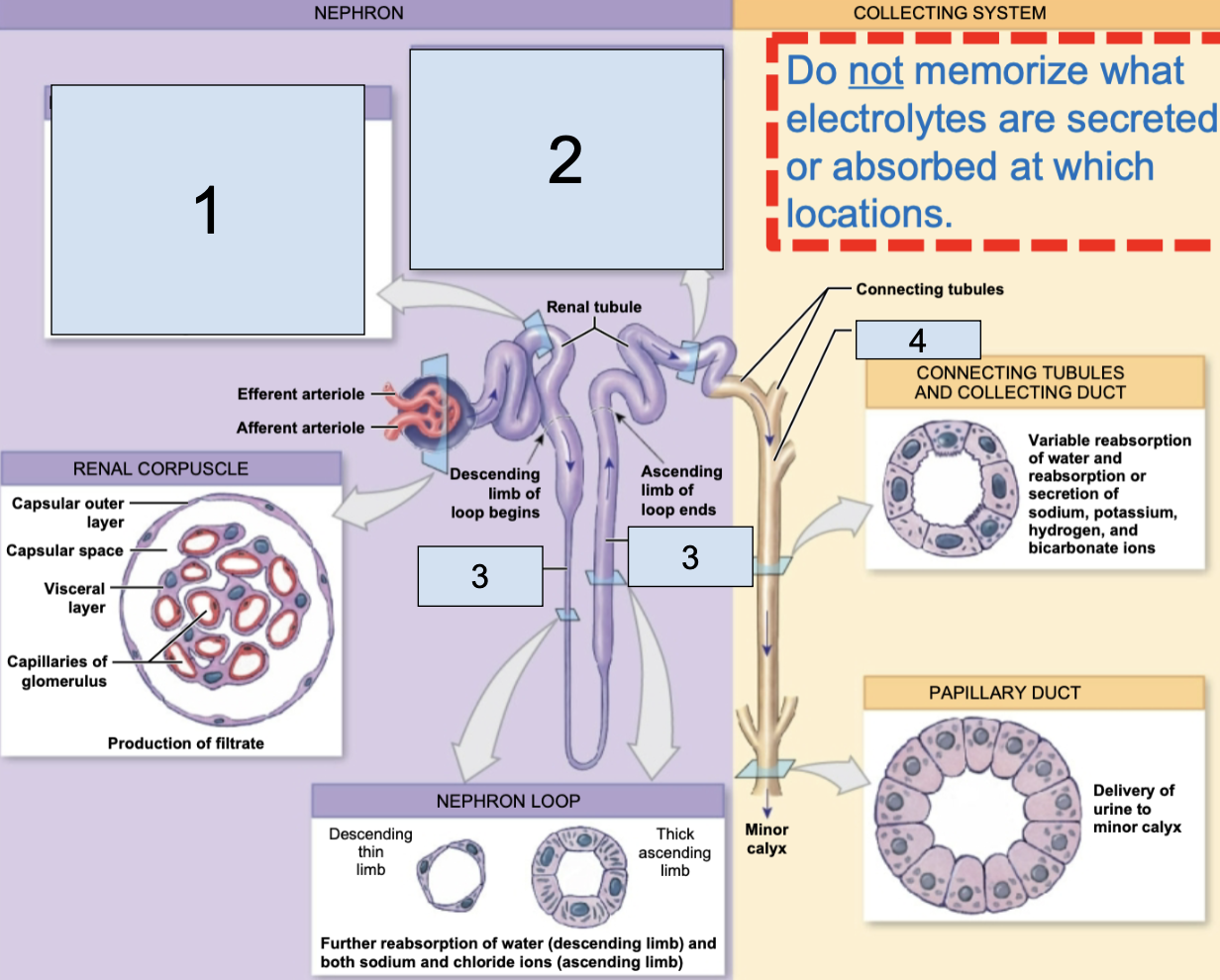
nephron
fundamental filtering unit of a kidney, leads into the collect system
renal corpuscle
in nephron, consists of glomerular capillaries + glomerular capsule
glomerulus/Bowman’s capsule
a small capillary bed in close proximity to the Bowman’s capsule of the nephron (8)
afferent arteriole brings oxygenated blood here
efferent arteriole takes deoxygenated blood away from her
renal tubule
in nephron, consists of proximal convoluted tubule, nephron loop, distal convoluted tubule, collecting duct
proximal convoluted tubule
the first part of the renal tubule (1)
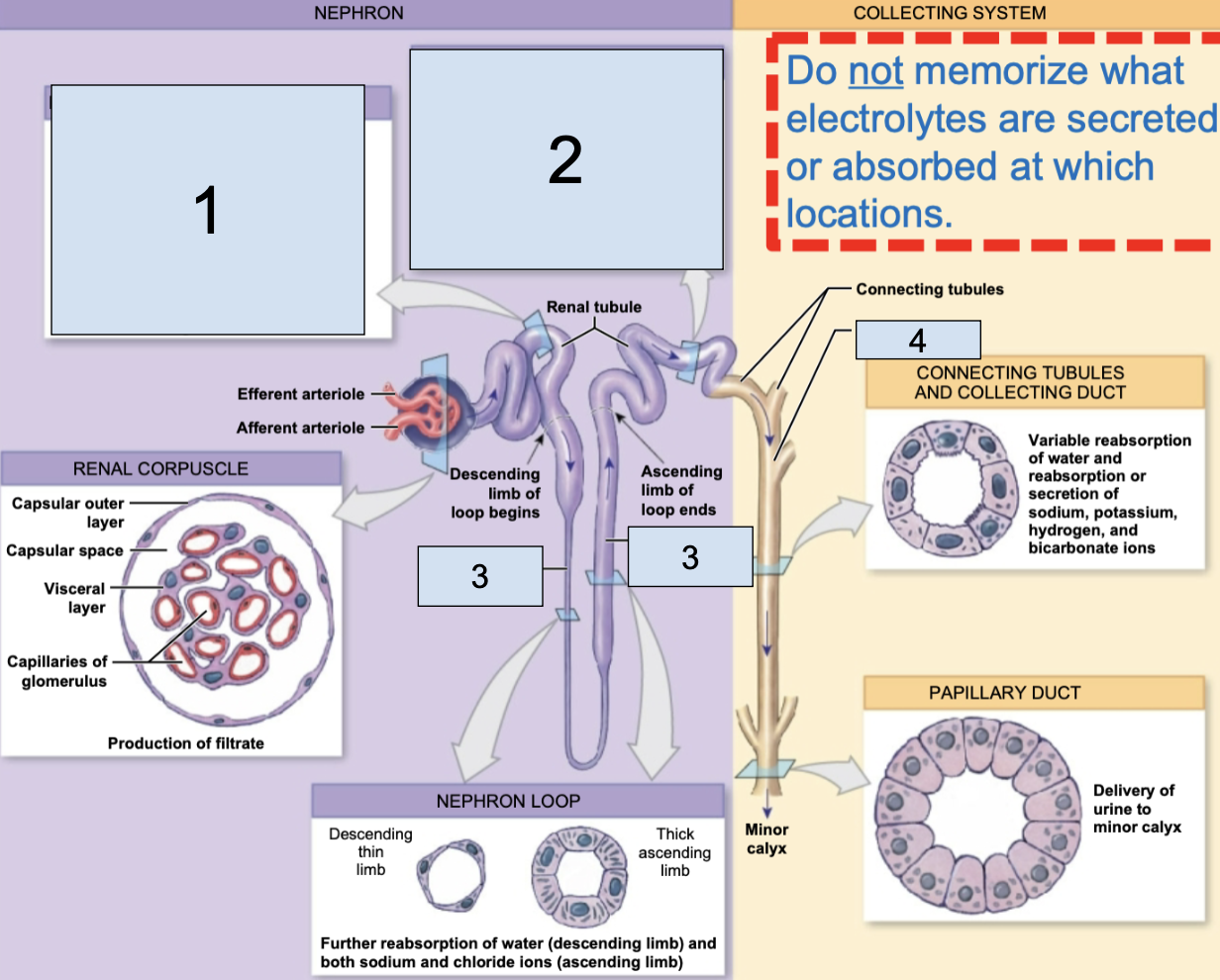
descending/ascending limbs of nephron loop
the middle part of the renal tubule (3)
distal convoluted tubule
the last part of the renal tubule before the collecting duct (2)
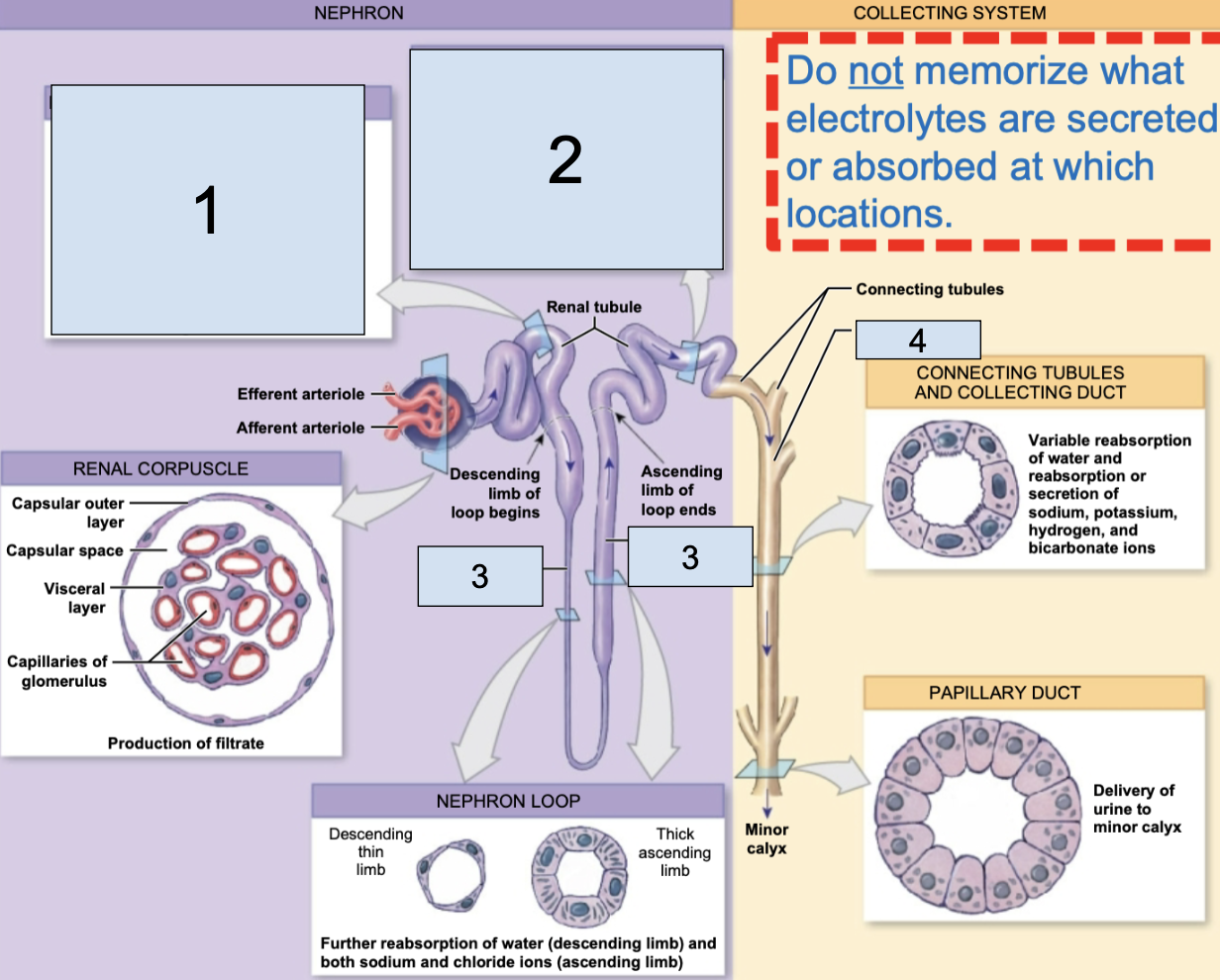
collecting duct
apart of collecting system, multiple of these channel urine toward a minor calyx (4)
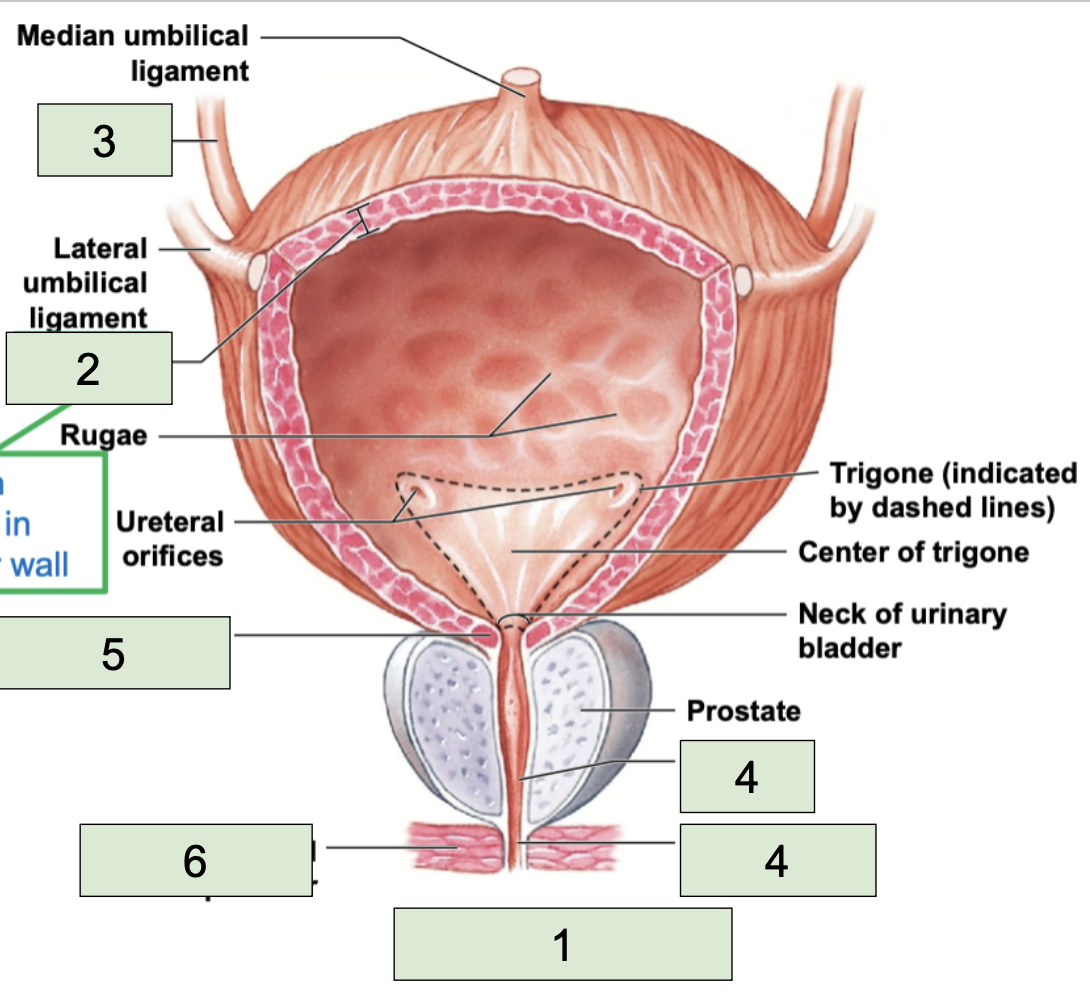
ureter
second most superior large structure of urinary tract; transports urine toward the urinary bladder (3)
urinary bladder
second most inferior structure of urinary tract, located superiorly to public symphysis; temporarily stores urine prior to elimination (1)
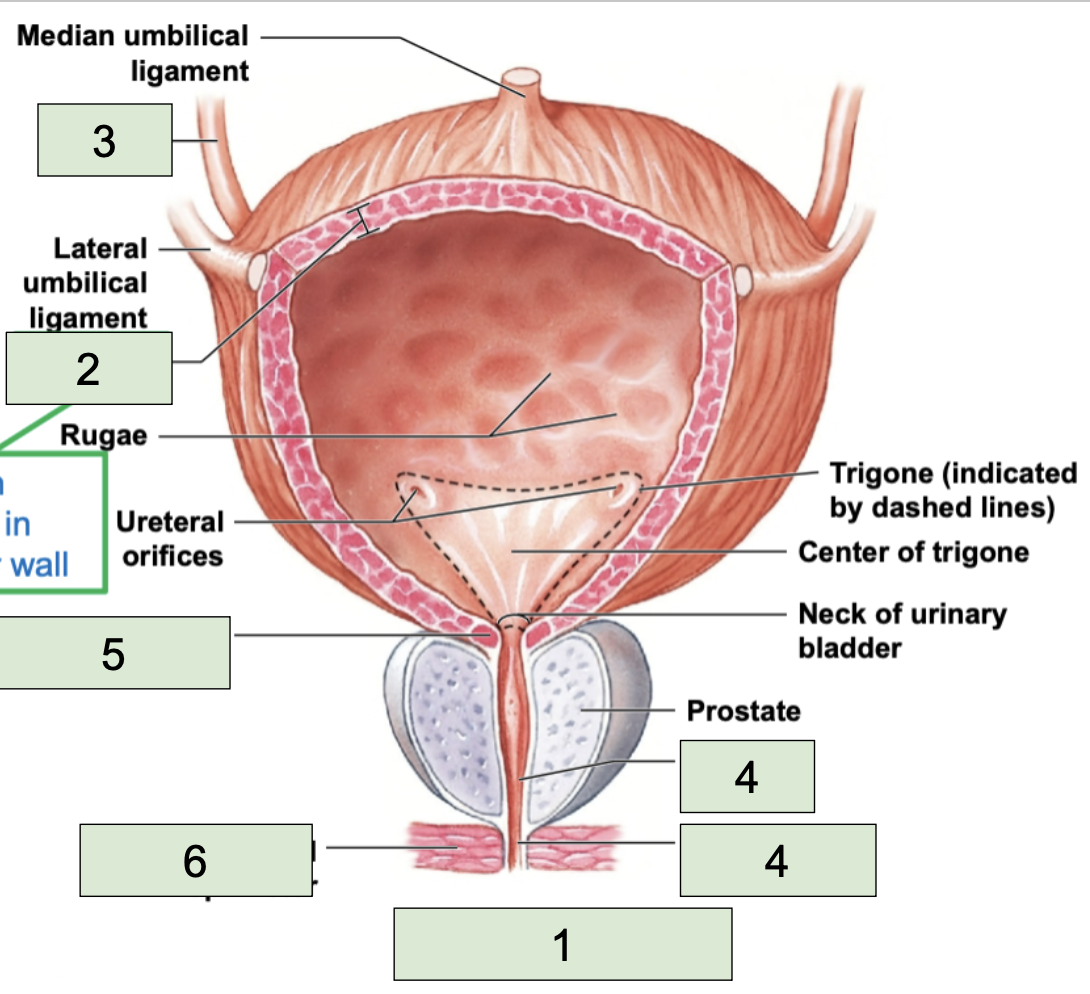
detrusor
smooth muscle found in the wall of the urinary bladder (2)
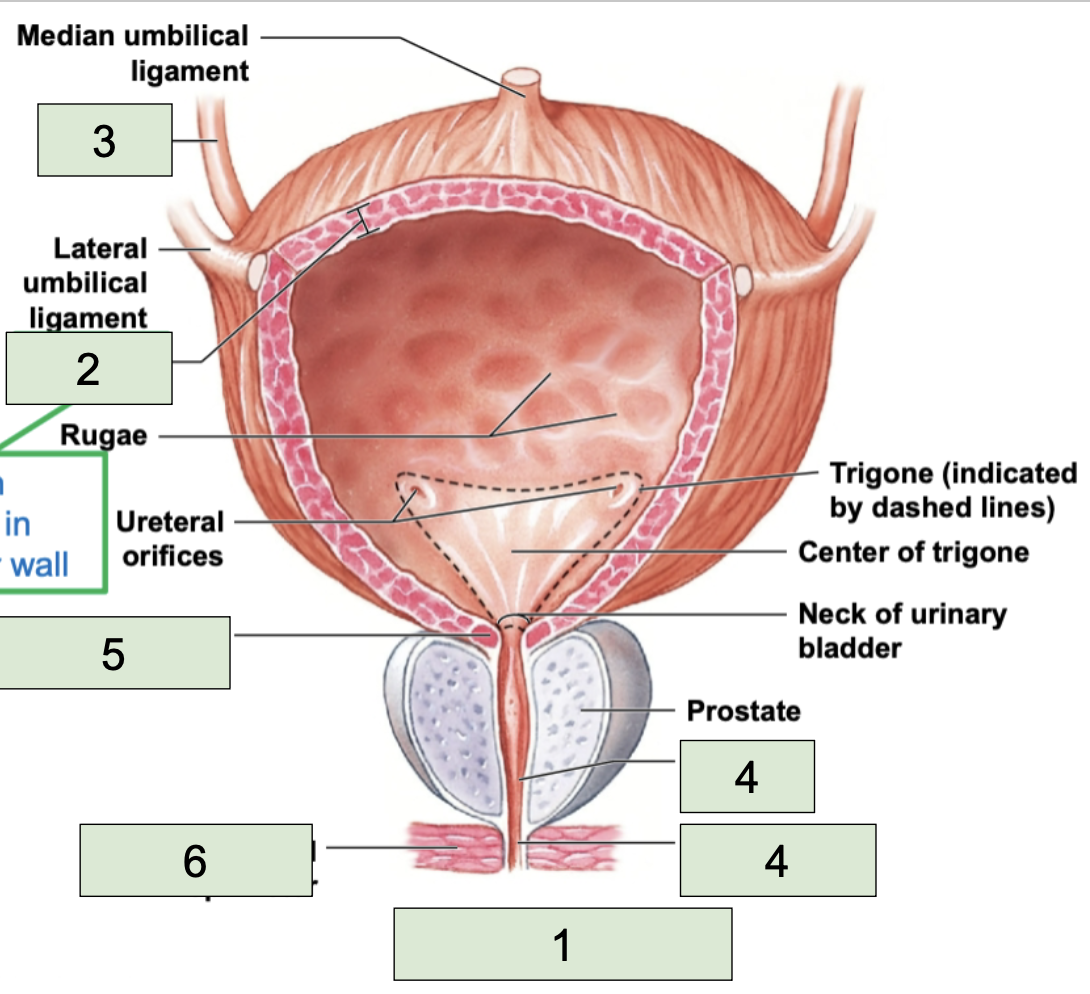
urethra
most inferior structure of urinary tract; conducts urine to exterior (semen too in males) (4)
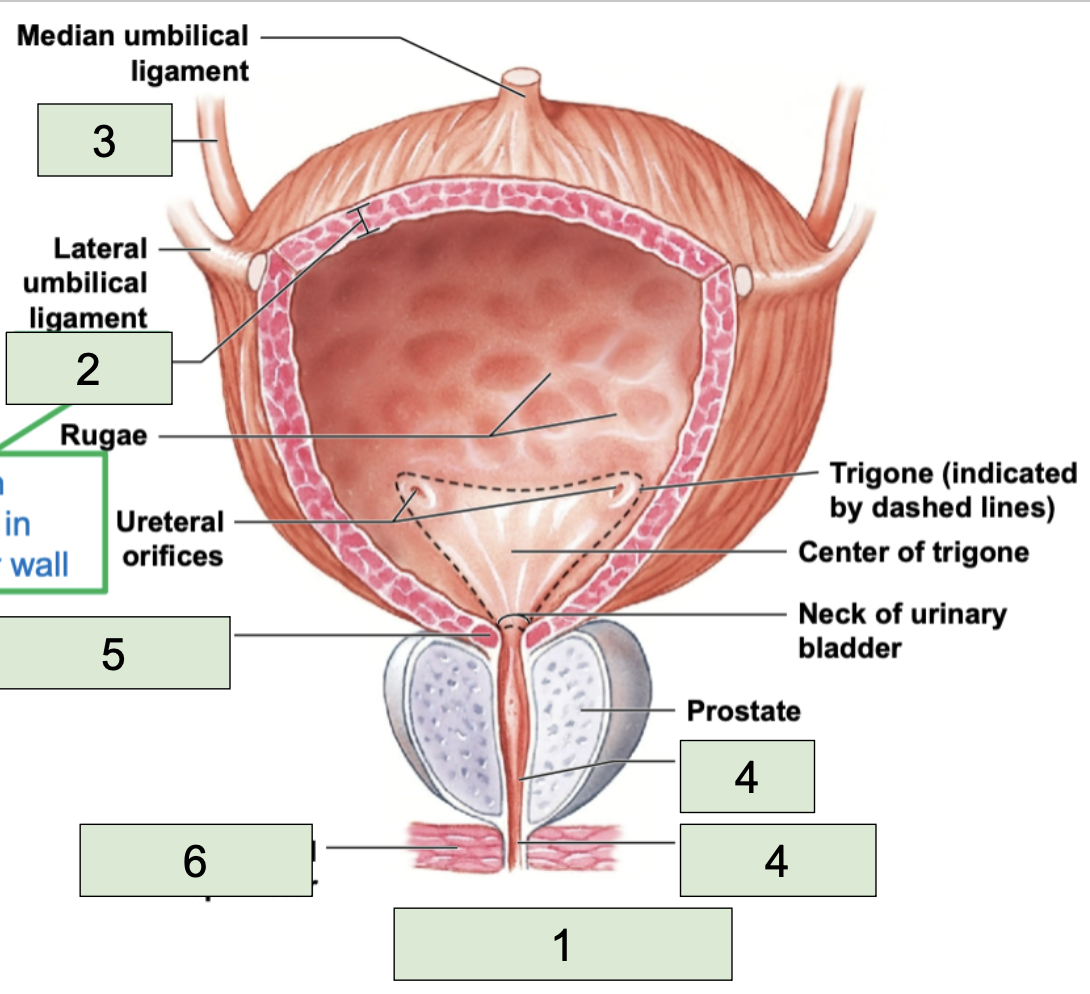
internal urethral sphincter
made of smooth muscle, involuntary contacts to stop urine flow (5)
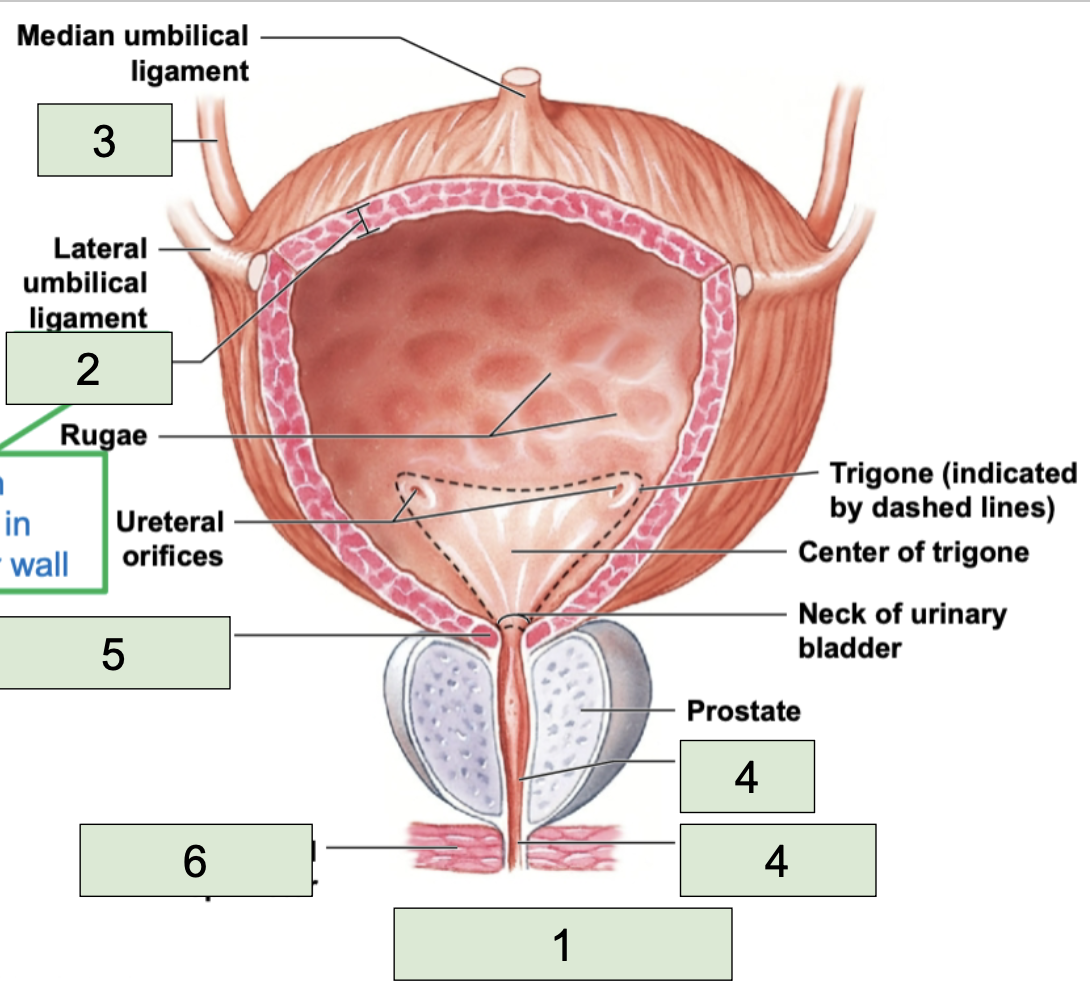
external urethral sphincter
made of skeletal muscle, voluntary contracts to stop urine (6)
pleyogram
a diagnostic medical image showing the main urinary structures
It can help visualize blockages + narrowing along parts of the urinary tract
female body urinary structures
short urethra, bladder is anterior to uterus + vagina, ureter pass near cervix
male body urinary structures
long urethra, bladder is anterior to the rectum, ureter is posterior to vas deferens
LOSE
Urethral sphincters _____ muscle tone as we age.
INCREASES
The risk of infection _____ as we age due to urine retention
bones of axial skeleton
skull, sternum, ribs, vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx
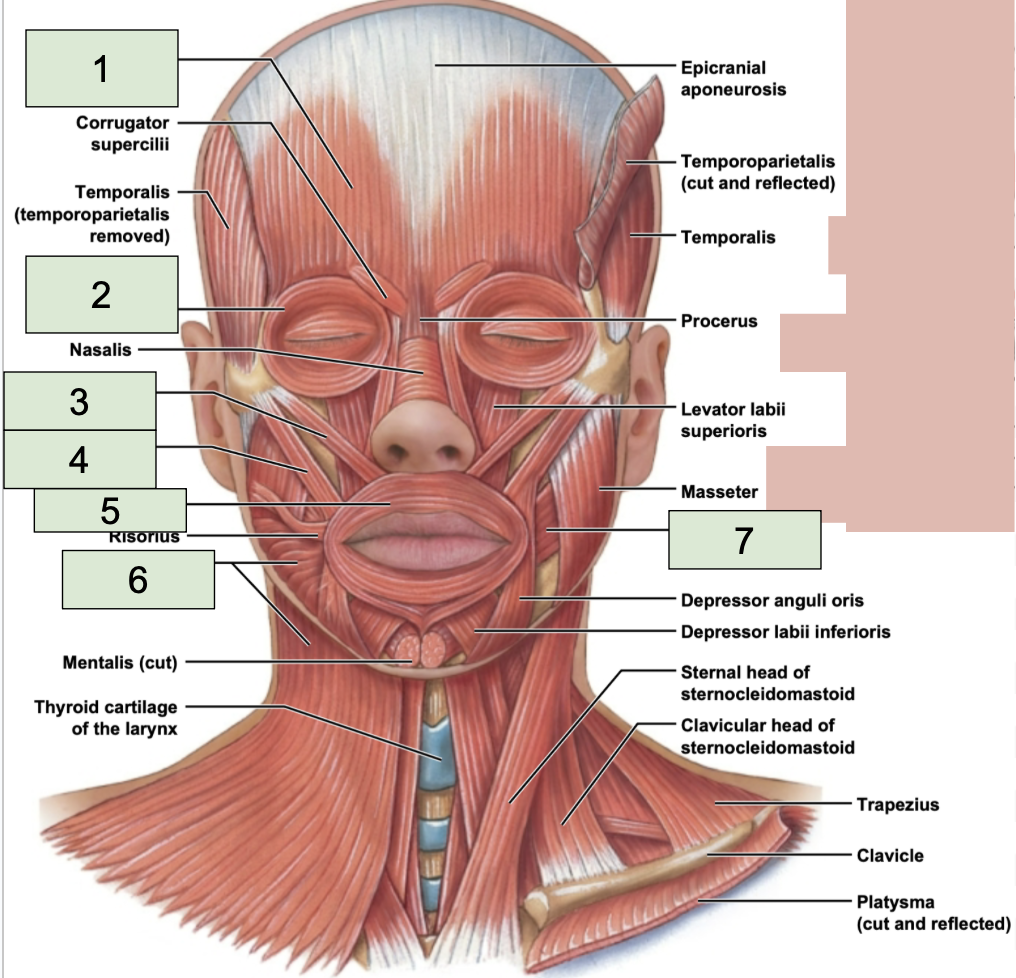
occipitofrontalis location
located from the forehead over top of the head to the back (1)
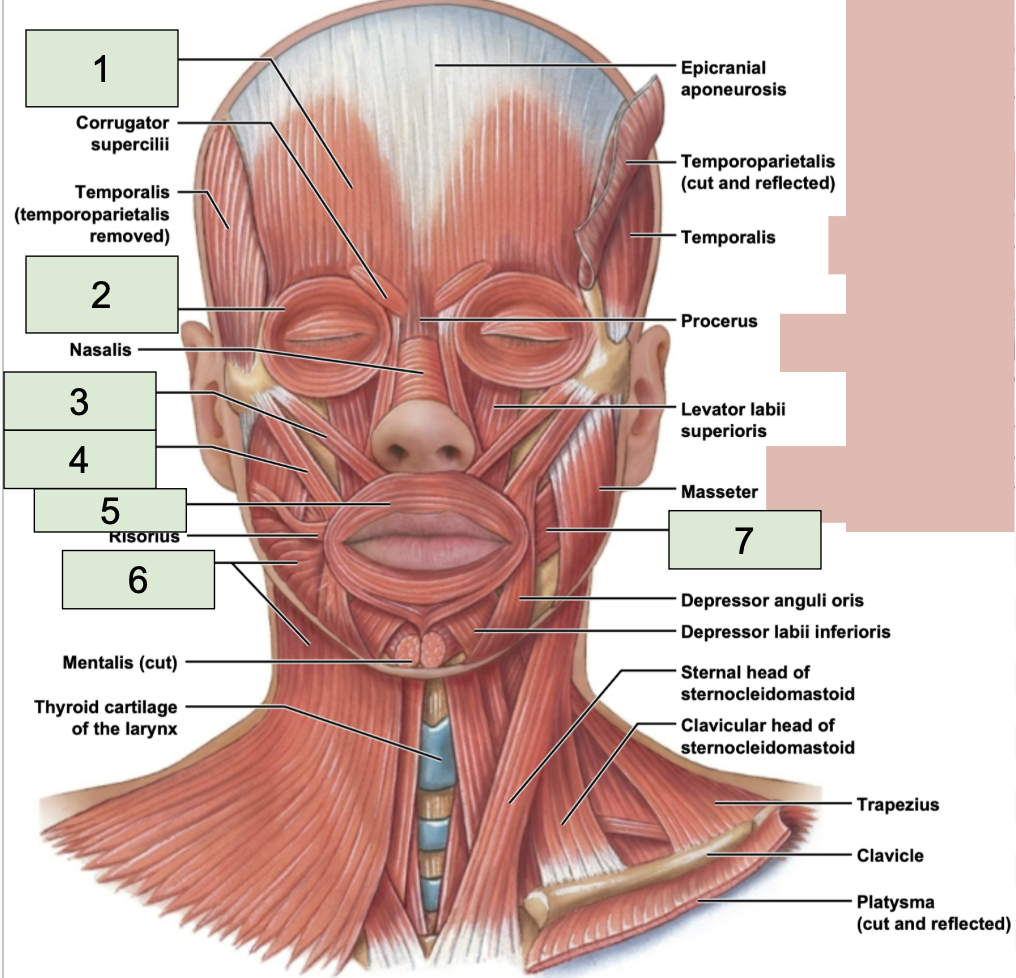
occipitofrontalis function
raise eyebrows, wiggle scalp + ears
orbicularis oculi location
around the eyes (2)