Humerus + Shoulder Girdle
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
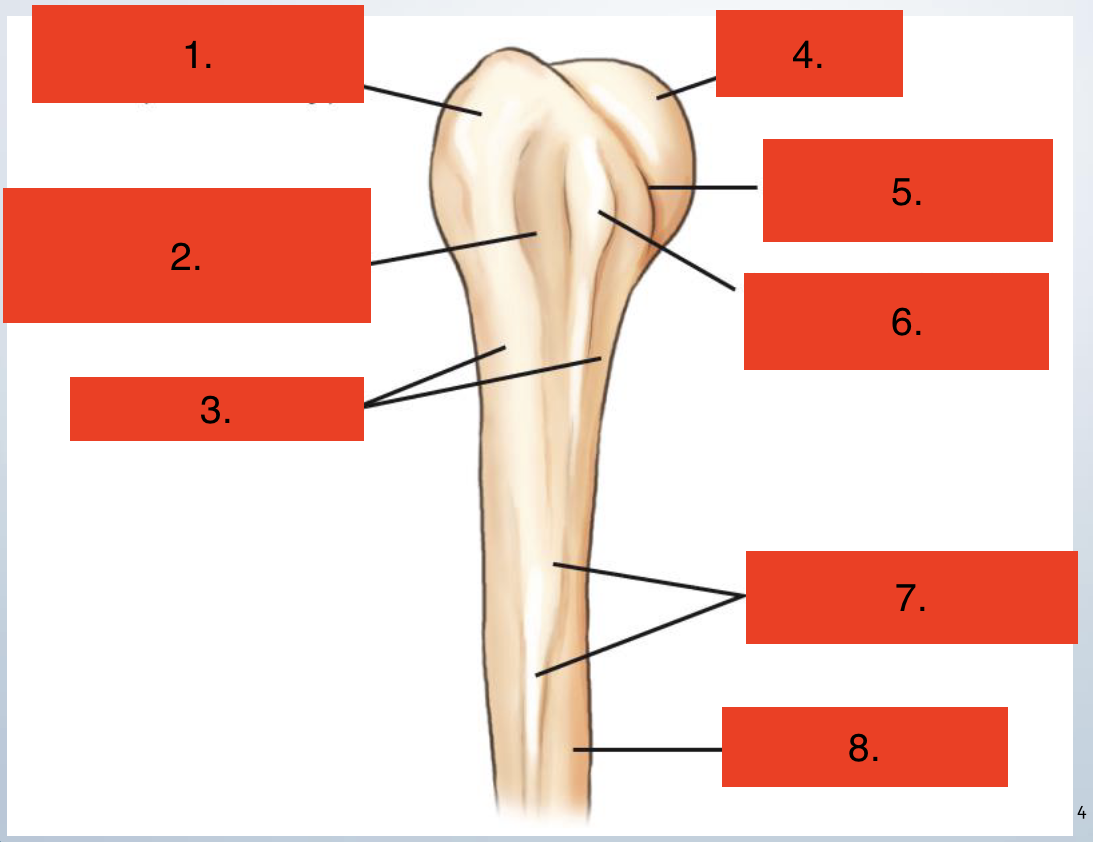
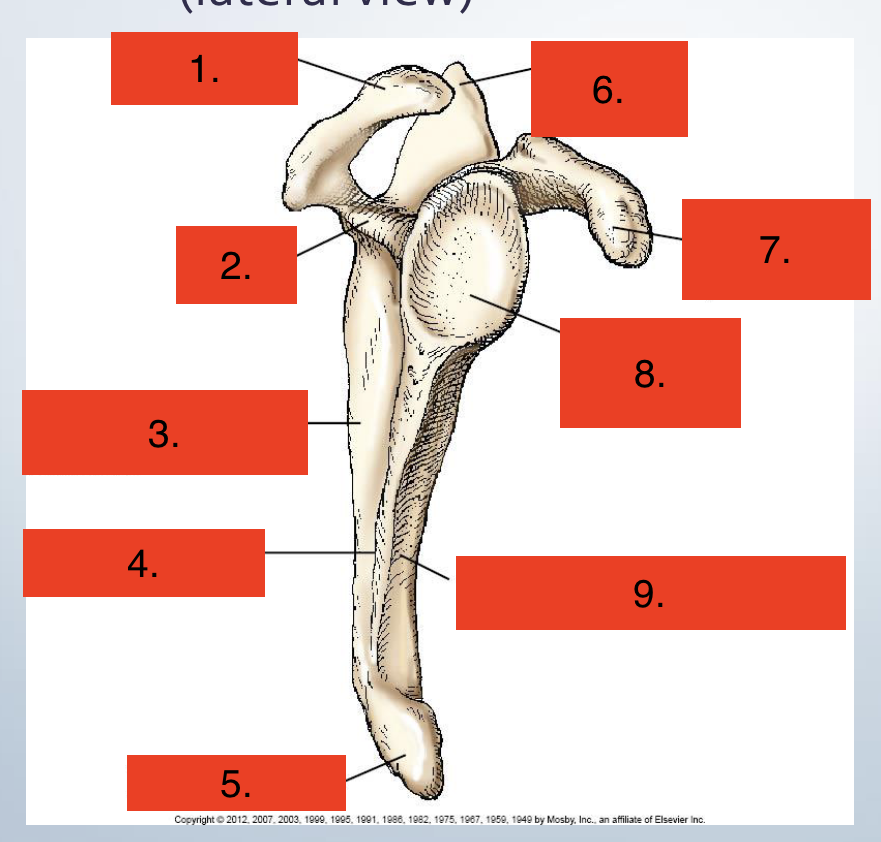
Proximal Humerus
Greater Tubercle
Intertublar groove
Surgical neck
Head
Anatomic neck
Lesser tubercle
Deltoid Tuberosity
Body
Shoulder Girdle
What is part of it?
What does it articulate with?
Scapula and clavicle
Humerus is not a true part
Articulates with - Head of humerus (shoulder joint), Manubrium of sternum (sternoclavicular joint), Clavicle to scapula (acromioclavicular joint)
-Functions to connect the upper limb to the trunk of the body
Scapulohumeral joint
Ball and socket (greater freedom of movement)
Sternoclavicular joint
Gliding
Acromioclavicular joint
Gliding
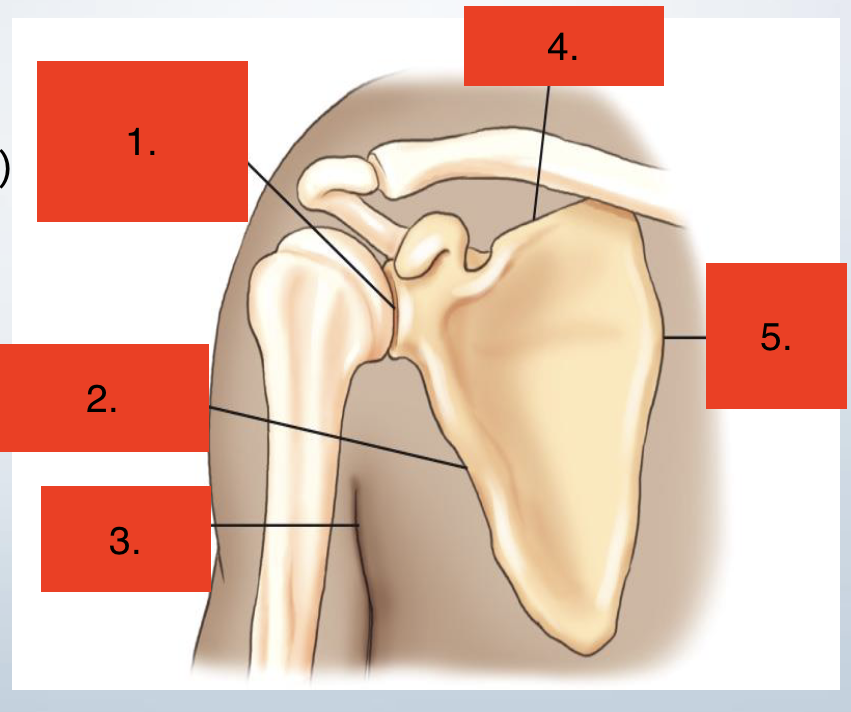
Scapulohumeral joint
Lateral (axillary) border
Axilla
Superior border
Medial (vertebral) border
Name the 3 borders and 3 angles of scapula
Borders
Superior
Medial (vertebral)
Lateral (axillary)
Angles
Superior
Inferior
Lateral/Head
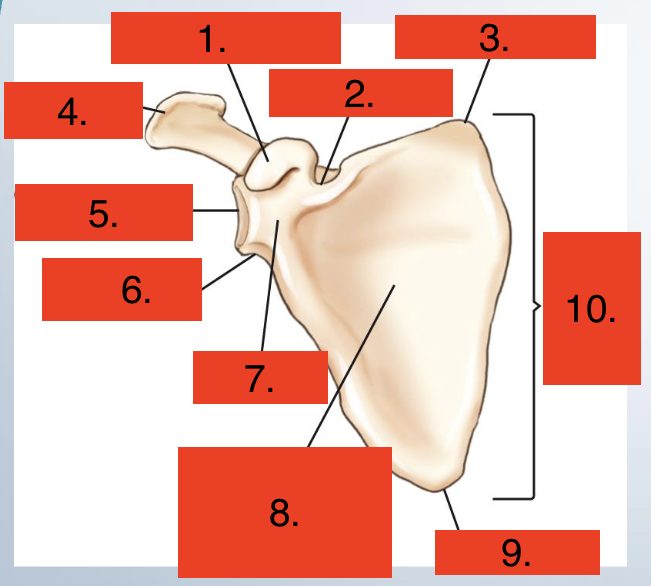
Scapula anterior view
Coracoid Process
Scapular notch
Superior angle
Acromion
Glenoid cavity
Lateral angle (head)
Neck
Costal surface, subscapular fossa
Inferior angle
Body (blade, wing, ala)
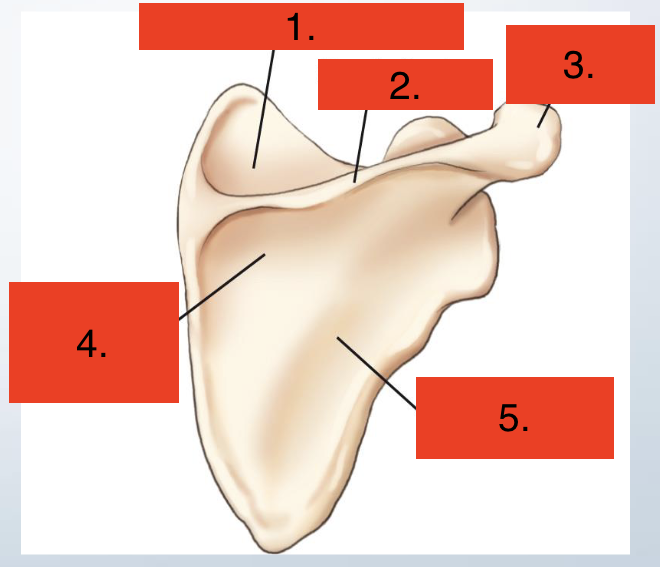
Scapula posterior view
Supraspinous fossa
Crest of spine
Acromion
Infraspinous fossa
Dorsal surface
Scapula lateral view
Acromion
Spine
Dorsal surface
Lateral border
Inferior angle
Superior angle
Coracoid process
Glenoid surface
Costal surface
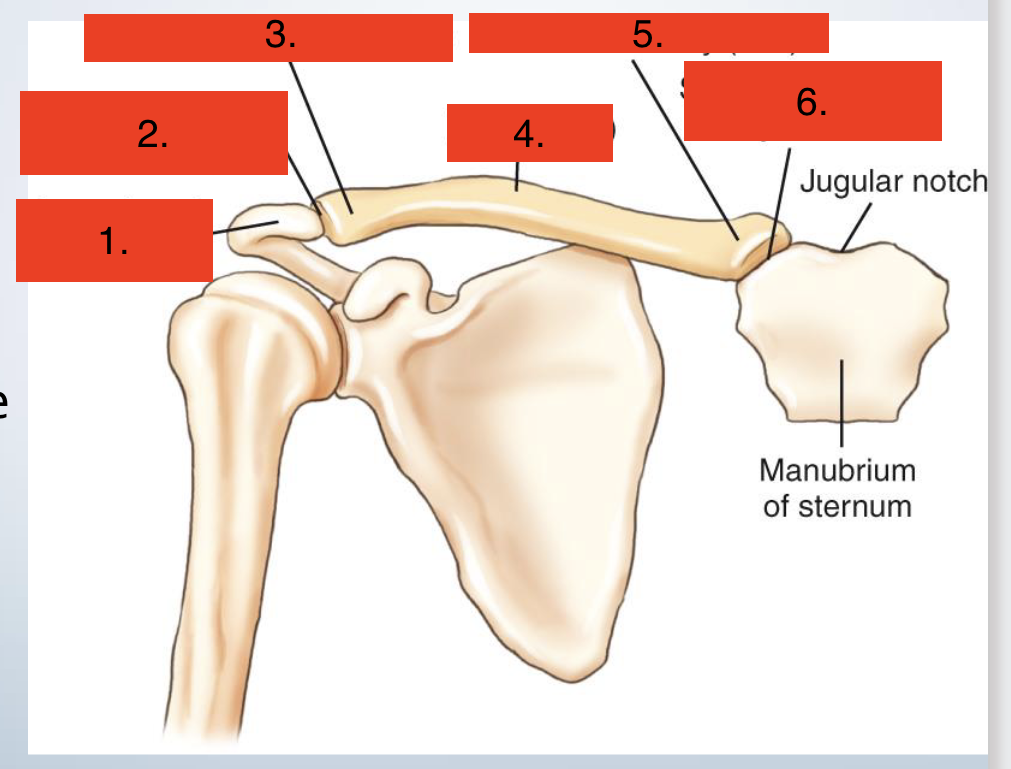
Clavice
Females clavicle is shorter and less curved than male
Acromion of scapula
Acromioclavicular joint
Acroomial extremity (end)
Body
Sternal extermity (end)
Sternoclavicular joint
Label -
Neutral, External, Internal
1 - External
2 - Internal
3 - Neutral
Shoulder girdle technical factors
KVP - 75-85
Grid
Small focal spot
40 SID
Turn head away from side of interest
Remove necklaces, clothing in area
Suspend respiration to elimate motion
can be done erect or recumbent
AP Humerus
Include both shoulder + elbow joints
CR - midhumerus
Arm in anatomical position
Epicondylar plane parallel to IR
Entire humerus
Greater tubercle in profile laterally
Medial and lateral epicondyles in profile distally
Lateral Humerus
Can be done lateromedial or mediolateral
Epicondylar plane perpendicular to IR
CR to midhumerus
both joints
Lesser tubercule in profile medially
Epicondyles superimposed distally
Shoulder AP external rotation
Epicondyles parallel to IR
CR- 1 inch inferior to coracoid process
Same position as AP humerus
Greater tubercule in profile laterally, lesser tubercule superimposed head of humerus
Scapulohumeral joint centered
Proximal humerus, upper scapula, clavicle visualized
AP shoulder Internal rotation
Epicondyles perpendicular to IR
CR - 1 inch inferior to coracoid process
Looks like lateral humerus
Lesser tubercule in profile medially, greater tubercule superimposed over head
Scapulohumeral joint centered
Proximal humerus, upper scapula, and clavicle visualized
AP Scapula
Breathing techinque - blurr ribs, rapid short in and out breaths, long exposure time
CR - midscapula, 2 inches inferior to coracoid process
Move scapula laterally off the ribs - raise arm
Entire scapula
Lateral border of scapula free of ribs and lungs
Scapular Y Lateral
Lateral Scapula
Scapula in lateral position, perpendicular to IR
Center at vertebral border with patient in anterior oblique
RAO=LPO 40-60 degree
Borders(lateral and medial) of scapula superimposed
Free of superimposition by ribs
Arm elevated
Humerus not superimposing scapula
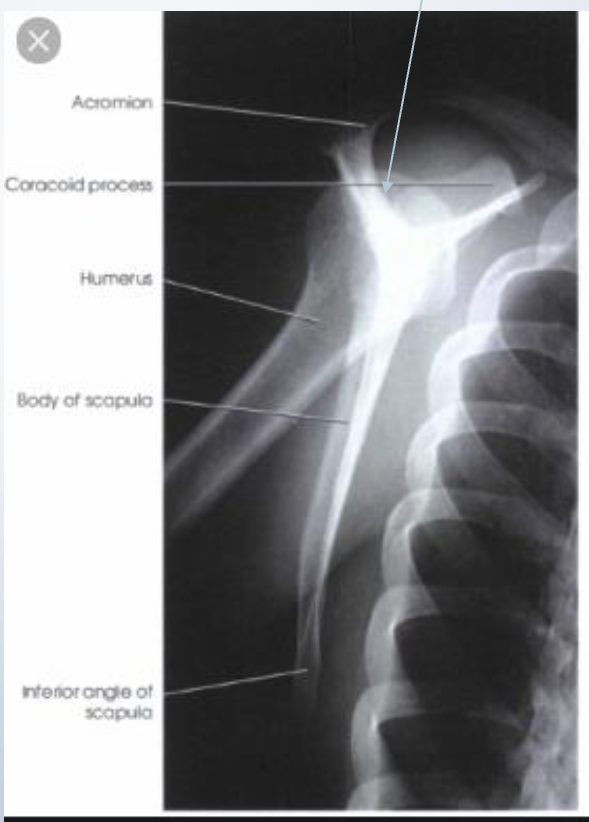
AP clavicle
CR perpendicular + midclavicle
AP Axial clavicle
CR- 15 to 30 degree angle cephalad
Asthenic - 25 to 30 angle
Hyperstenic - 15 to 20 angle
CR to midclavicle
Clavicle superior to apices
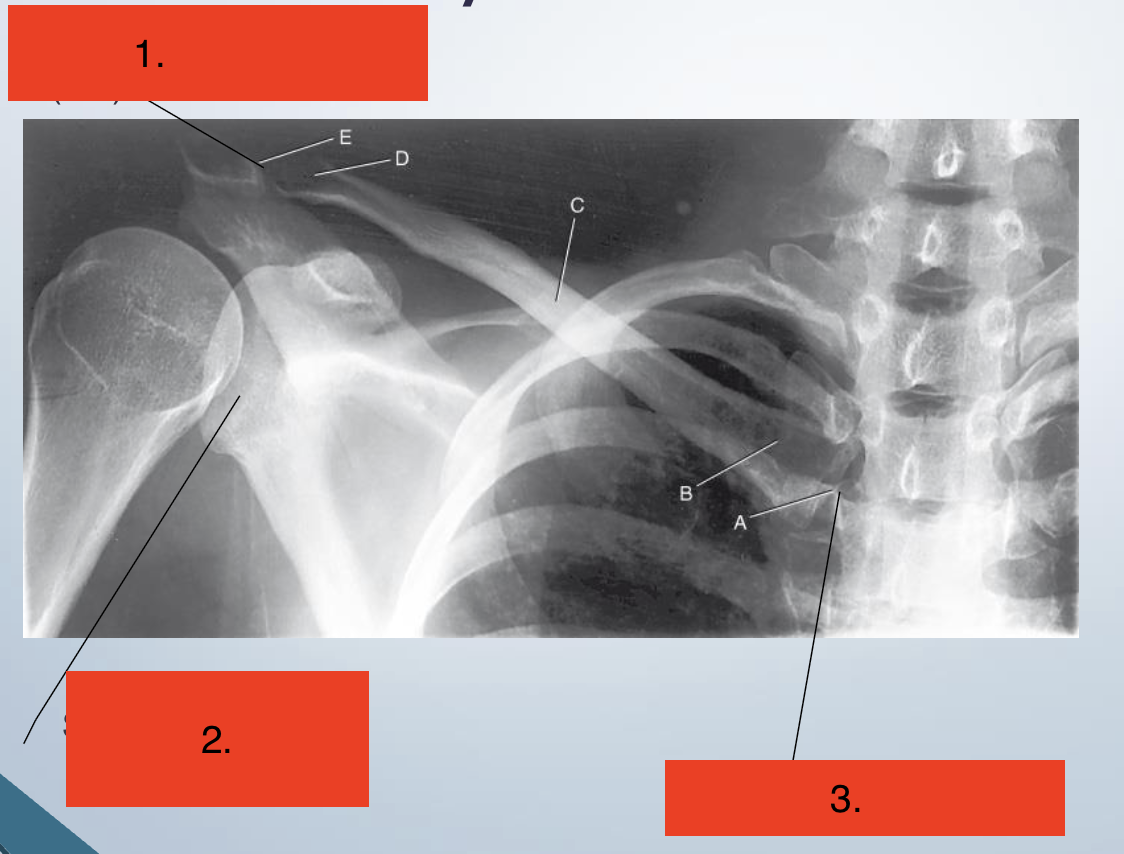
Label the joints
Acromioclavicular (AC)
Scapulohumeral
Sternoclavicular (SC)
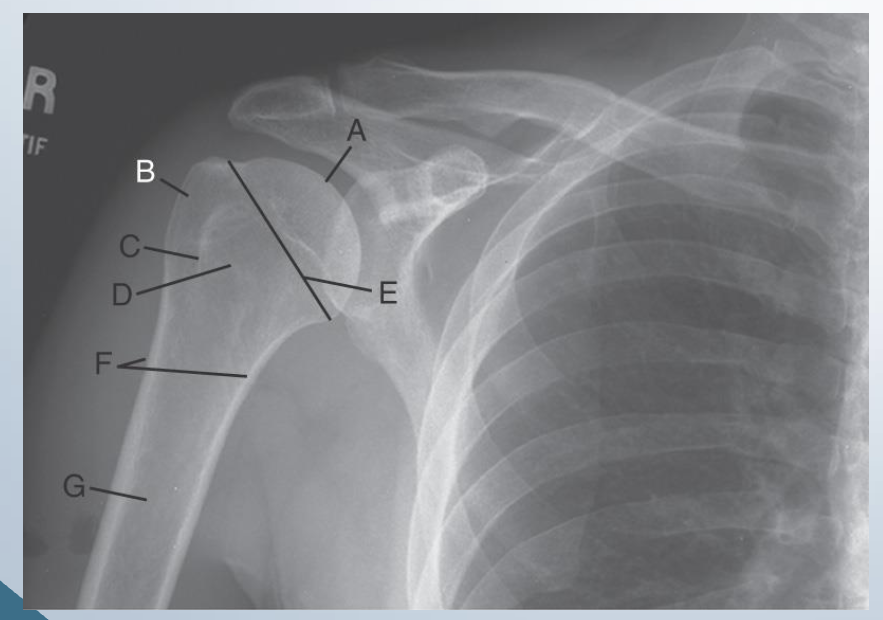
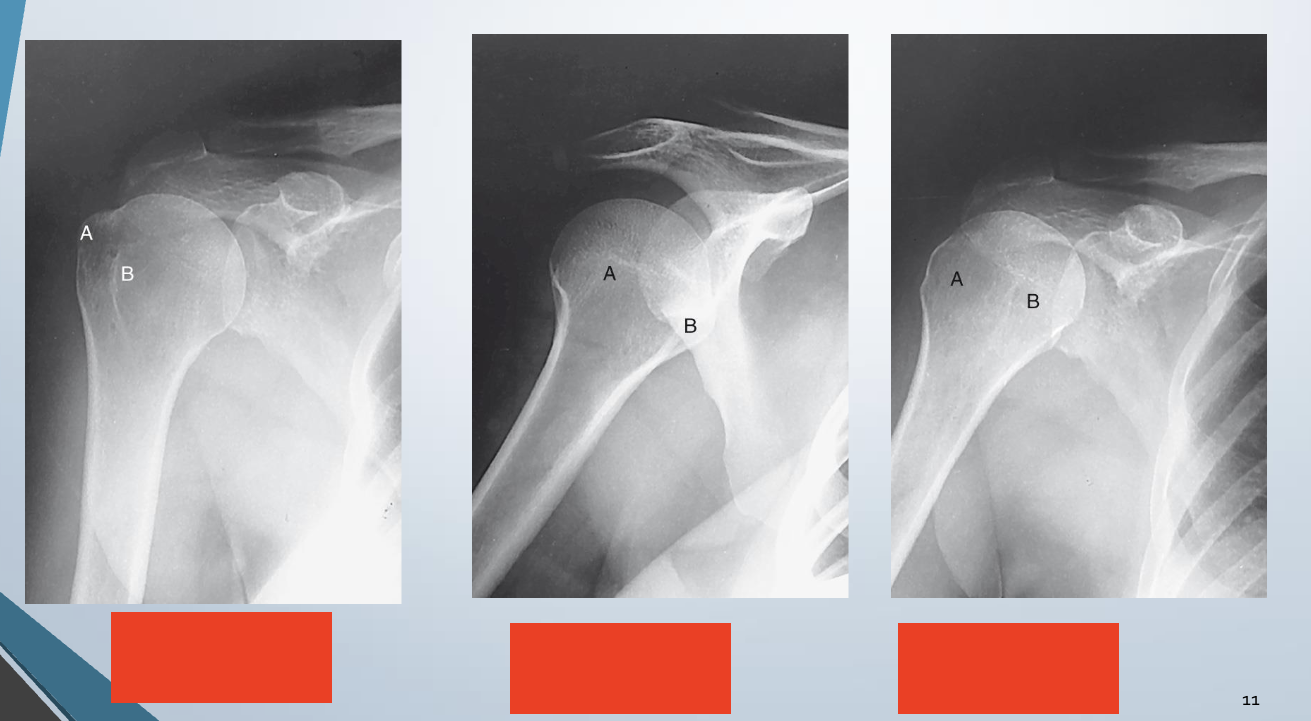
AP external rotation
LABEL
A. Head of humerus
B. Greater Tubercule
C. Intertubercular sulcus
D. Lesser tubercule
E. Anatomic neck
F. Surgical neck
G. Body
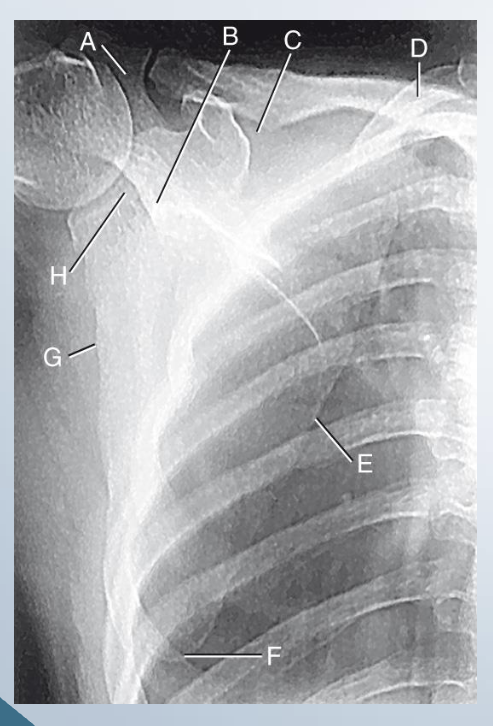
AP scapula
LABEL
A. Acromion
B. Neck of scapula
C. Suprascapular notch
D. Superior angle
E. Medial border
F. Inferior angle
G. Lateral border
H. Glenoid cavity
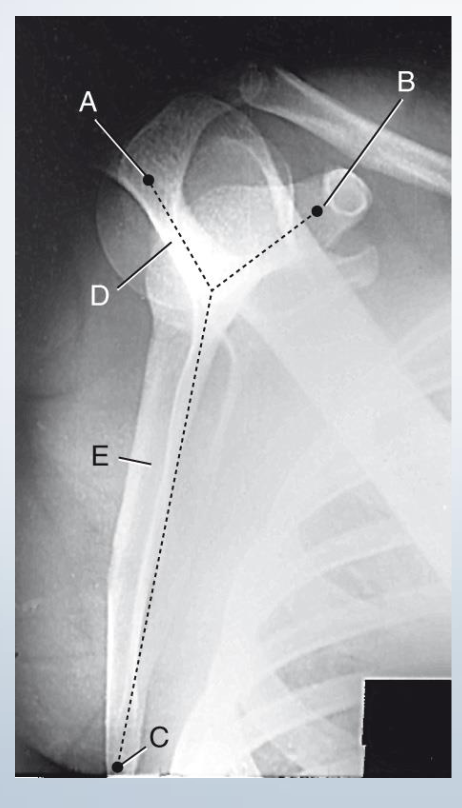
Spapular Y Lateral
A. Acromion
B. Coracoid Process (always closest to ribs)
C. Inferior Angle
D. Spine of scapula
E. Body of scapula
Breathing techinque
Orthostatic breathing
blurr ribs, rapid short in and out breaths, long exposure time 3-5 secs
AP scapula, Transthoracic lateral for humerus, Transthoracic lateral for shoulder
AC joint seperation
Trauma in upper shoulder resulting in a partial or complete tear of the AC.
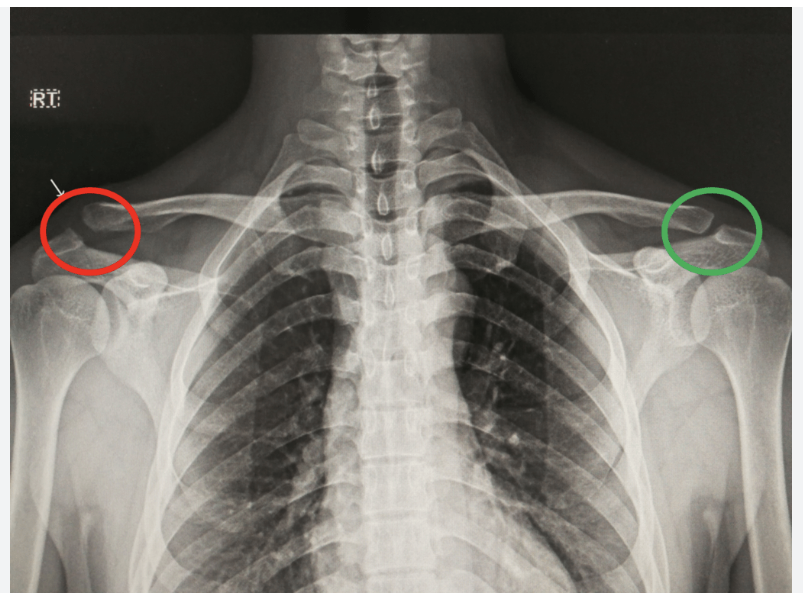
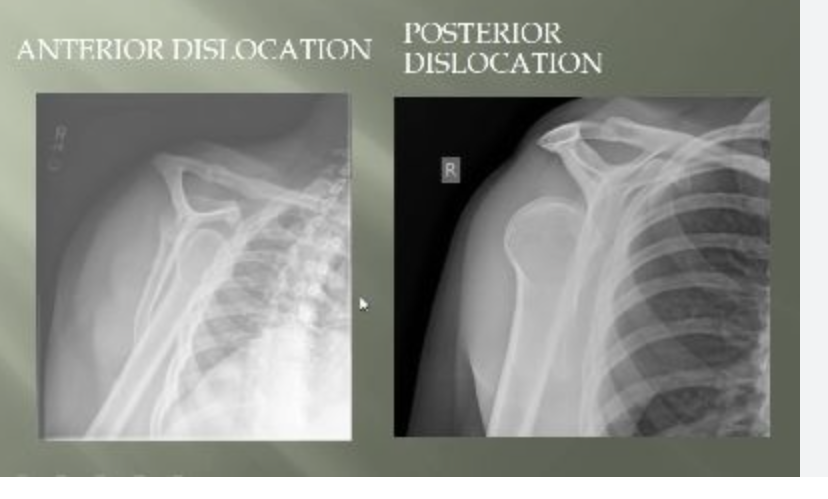
Dislocation
when bones at a joint separate from their normal positions, often caused by trauma, leading to intense pain, swelling, deformity, and inability to move the joint