Radiographic Exposures - Beam Limitation and Filtration
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
The equipment is designed with my devices that radiologists and technologist can use to do what?
- optimize the quality of the image
- reduce radiation exposure for patients undergoing various imaging procedures
Why have multiple features been built into new x-ray producing machines by their manufacturers?
to ensure radiation safety
Why have some extra characteristics have also been included into the equipment?
to meet enhanced federal regulations
What are the accessories available to do?
lower radiation dose for the patient
Measures must be taken to ensure that radiographic equipment operates safely in order to protect whom?
patients and all personnel
What 2 things does every diagnostic imaging system need to have?
- protective tube housing
- correctly functioning control panel
What is a radiographic examination table, as well as other devices and accessories, designed to do?
reduce the patient's radiation dose
What is a lead-lined metal diagnostic-type protective tube housing required to do?
protect the patient and imaging personnel from off-focus, or leakage radiation by restricting the emission of x-rays to the area of the useful, or primary, beam
How should the x-ray tube housing be constructed?
so that if radiation leaks through any portion of the housing, it leaks away from the useful beam
- measured at a distance of 1-m from the x-ray source
- does not exceed 1 mGya/hr (100 mR/hr) when the tube is operated at its highest voltage at the highest current that allows continuous operation
The x-ray tube is constructed in such a way that when the tube is operated at its highest voltage at the highest current that allows continuous operation it does not exceed what?
1 mGya/hr (100 mR/hr)
Where is the control panel or console located?
behind a suitable protective barrier that has a radiation-absorbent window that permits observation of the patient during any procedure
What must the control panel or console indicate?
the conditions of exposure and provide a positive indication when the x-ray tube is energized
What does the control panel or console have that permits the operator to assess exposure conditions?
visible mA and kVp digital readouts
What happens when the exposure begins?
a tone is emitted, and the sound stops when the exposure terminates
What does the audible sound indicate?
that the x-ray tube is energized and ionizing radiation is being emitted
How strong must the radiographic examination table be?
strong enough to adequately support patients whose weight is in excess of 300 pounds
What does a radiographic examination table frequently have? Why?
a floating table top; makes it easier to maneuver the patient during an imaging procedure
What should the radiographic examination table be in regards to thickness?
uniform thickness
Why must the radiographic examination table be as radiolucent as possible?
to absorb only a minimal amount of radiation, thereby reducing the patient's radiation dose
What is the radiographic examination table, frequently made of?
carbon fiber material
SID
Source to Image Receptor distance
What does the Source-to-Image Receptor Distance (SID) Indicator do?
provides a way to measure the distance from the anode focal spot to the image receptor (IR) to ensure that the correct SID is maintained
Is there a manual way to measure the SID?
yes, frequently a simple device such as a tape measure is attached to the collimator or tube housing so that the radiographer can manually measure the SID
What is another way to measure the SID?
lasers
How accurate does the distance and centering indicators have to be?
within 2% and 1% of the SID
How should the primary x-ray beam be adequately collimated?
so that it is no larger than the size of the IR being used for the examination
What is the light-localizing variable-aperture rectangular collimator used for?
to adjust the size and shape of the x-ray beam either automatically or manually
What is currently the predominant x-ray beam limitation device?
collimator
What do the x-ray beam limitation devices do?
confine the useful, or primary beam before it enters the area of clinical interest, and thereby limits the surface area of body tissue irradiated.
What is another thing the x-ray beam limitation devices do?
reduce the amount of scatter radiation in the tissue and prevent unnecessary exposure to tissues not under examination
What are the benefits of restricting x-ray field size to include only the anatomic structures of clinical interest?
- significant reduction in patient dose because less scatter radiation is produced
- improves the overall quality of the radiographic image
What are the light-localizing variable-aperture rectangular collimators?
- construction
- components
- reduction of off-focus, or stem, radiation
- confinement of the radiographic beam
- skin sparing
- minimizing skin exposure to electrons produced by photon interaction with the collimator
- luminescence
- coincidence between the radiographic beam and the localizing light beam
- positive beam limitation (PBL)
- alignment of the x-ray beam
Light-Localizing Variable-Aperture Rectangular Collimators: construction
box shaped and contains beam defining system
Light-Localizing Variable-Aperture Rectangular Collimators: components
- 2 sets of adjustable lead shutters mounted with in the device at different levels
- a light source to illuminate the x-ray field
- a mirror to deflect the light beam toward the patient to be imaged
Where is the first set of adjustable lead shutters?
near the tube window
What does the first set of adjustable lead shutters do?
eliminate off focus radiation
What is off focus radiation?
x-rays emitted from parts of the tube other than the focal spot and at various angles from the x-ray tube window
Where is the second set of collimator shutters mounted?
below the light source and mirror and further confine beam to area of interest
What is skin sparing?
reduce skin exposure to electrons produced by photon interaction with collimation
What should the SSD be for skin sparing?
at least 15 cm below the collimator for fixed radiographic equipment
SSD
Source to Skin Distance
What should the collimator light provide?
enough luminescence to adequately outline the margins of the radiographic beam
What should the light field be?
within the 2% SID with the corresponding beam
PBL
positive beam limitation
What is positive beam limitation?
automatic collimators that restrict the beam to be no larger than the size of the image receptor
What should the PBL be?
within 2% of the actual exposed field
What must the radiographer ensure with the PBL?
that collimation is adequate by collimating the radiographic beam so that it is no larger than the IR
What is the x-ray beam limitation device called a cone used for?
radiographic examinations of specific areas such as the head?
What does the cone look like?
flared metal tubes and straight cylinders
When could the beam-defining cone be used?
dental radiography
What is filtration?
the removal of low energy photons from the beam
Types of filtration
inherent and added
What is the purpose of filtration?
- increase the mean (average) energy of the beam
- fewer photoelectric interactions
- markedly reduces patient dose
What is the downside to filtration?
fewer photoelectric interactions
What is inherent filtration?
always present
What are the components of inherent filtration?
- glass envelope encasing the x-ray tube
- insulating oil surrounding the tube
- glass window in the tube housing
- equivalent to .5 mm aluminum
What are the components of added filtration?
- thin sheets of aluminum (or equivalent)
- added outside of glass window above the shutters
What is the minimum aluminum equivalent required for total filtration for fixed radiographic units operating at above 70 kVp?
2.5 mm aluminum equivalent
Why is aluminum selected as a filter material for filtration for general diagnostic radiology?
it effectively removes low-energy x-rays from a heterogeneous x-ray beam without severely decreasing the x-ray beam intensity
In filtration for general diagnostic radiology, what must a diagnostic x-ray beam always be?
adequately filtered
HVL
half-value layer
What is the half-value layer?
the thickness of a designated absorber required to decrease the intensity of the primary beam by 50% of its initial value
Why must the HVL be measured?
to verify that the x-ray beam is adequately filtered
How often should a radiologic physicist obtain the HVL measurement?
at least once a year and also after an x-ray tube is replaced or repairs have been made on the diagnostic x-ray tube housing or collimation system
How is HVL expressed?
millimeter of aluminum
HVL is a measure of ________ quality, or effective energy of the x-ray beam.
beam
A minimal HVL is required at a given ______.
kVp
What does increasing the amount of tube filtration do to the x-ray beam? Why?
increases the x-ray beam quality because there is a greater percentage of x-rays that have high energy than low energy, and it decreases the quantity of x-rays or x-ray emission
What are the compensating filters made of?
aluminum, lead-acrylic, or other suitable materials
What are the compensating filters used for?
to accomplish dose reduction and uniform imaging of body parts that vary considerably in thickness or tissue composition
How do compensating filters work?
they partially attenuate x-rays that are directed toward the thinner, or less dense area while permitting more x-radiation to strike the thicker, or more dense, area
Types of compensating filters
- wedge filter
- trough, or bilateral wedge filter
Wedge compensating filter
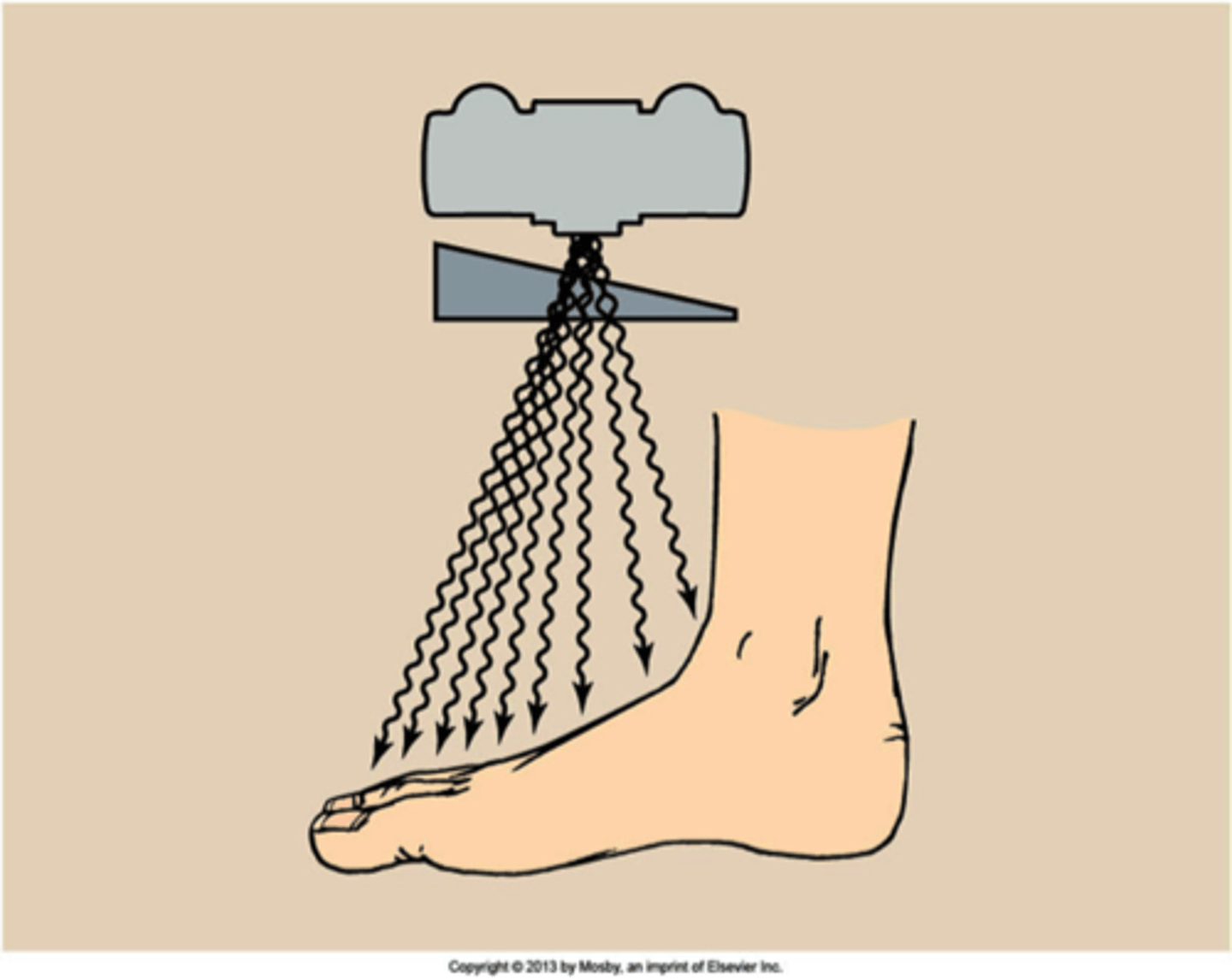
Trough, or bilateral wedge compensating filter
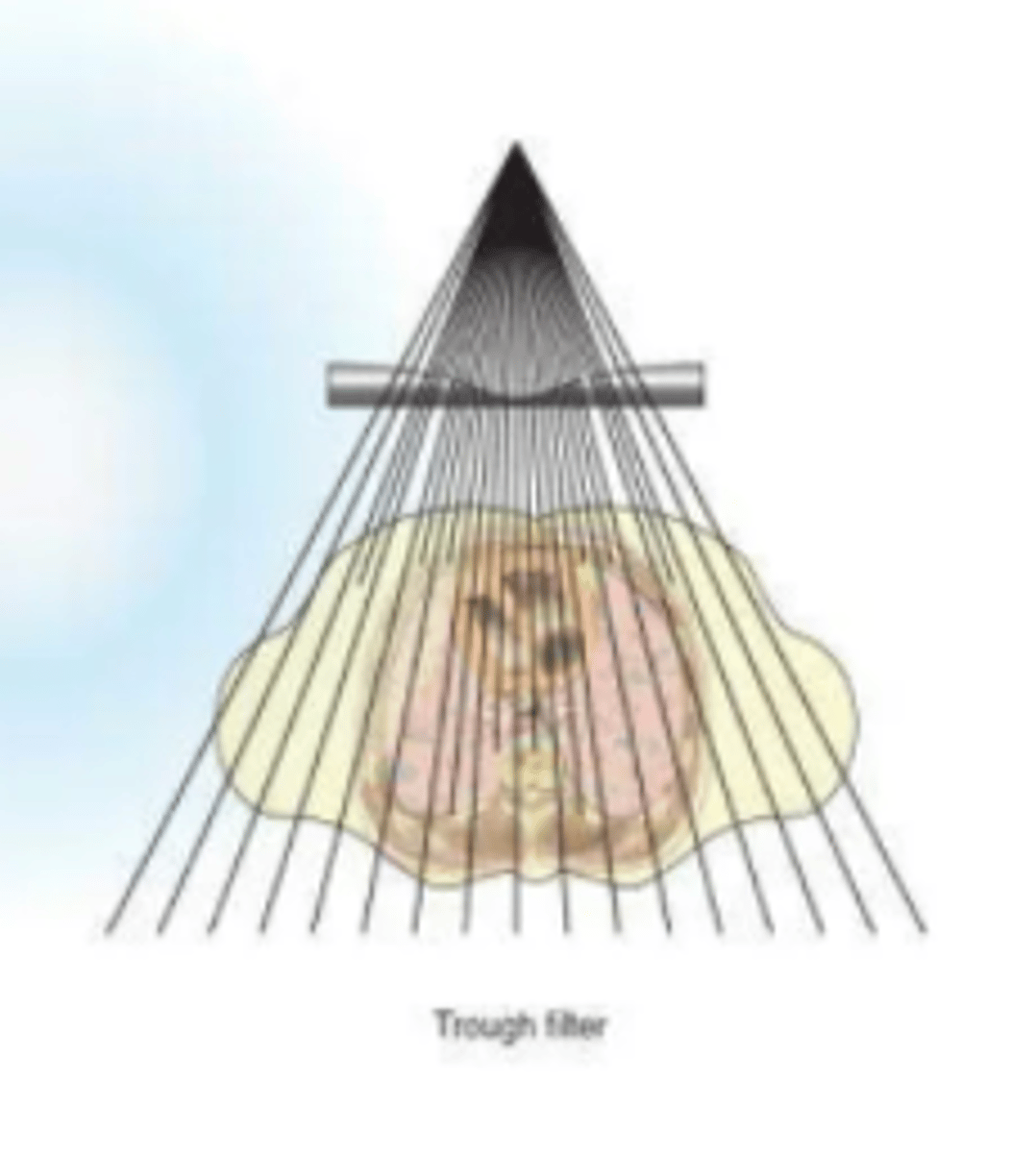
What is exposure reproducibility?
consistency in output in radiation intensity for identical generator settings from one individual exposure to subsequent exposures
What should the variance be for exposure reproducibility?
5% or less is acceptable
How might exposure reproducibility be verified?
by using the same technical exposure factors to make a series of repeated exposures and then, observing with a calibrated ion chamber, how radiation intensity varies
What is exposure linearity?
consistency in output radiation intensity at selected kVp settings when generator settings are changed from one mA and time combination to another
What is linearity?
the ratio of the difference in mSv/mAs or mR/mAs values between two successive generator stations to the sum of these mSv/mAs or mR/mAs values; must be less than 0.1
How much can the linearity vary when the settings are changed from one mA to a neighboring mA station?
the most that linearity can vary is 10%