Applied Physio lecture 27, 28 and 29 (exam 3)
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key terms and definitions related to ECG, cardiac contractility, and related physiological concepts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Atrial Depolarization
Represented by the P wave in an ECG.
PR segment
Represents the AV nodal delay, allowing for atrial contraction.
QRS complex
Represents sequential depolarization of the ventricles.
T wave
Indicates repolarization of the ventricles.
Asystole
Absence of electrical activity in the heart.
Excitation-Contraction Coupling
The process by which electrical excitation leads to muscle contraction. Calcium activates the contractile proteins , allowing cross-bridge cycling between actin and myosin filaments for contraction. Calcium induced Ca2+ release (CICR)
Cardiac Output
The volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute.
CO = SV (stroke volume) x HR (heart rate)
Pulse Pressure
The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure.
Afterload
pressure in arteries. pressure against which the heart pushes. increased afterload causes more energy for left ventricle to open aortic valve. increasing afterload decreases SV
Preload
pressure at which the heart fills. SV effected by degree of stretch of the ventricles It is the initial stretching of the cardiac muscle fibers at the end of diastole, directly related to ventricular filling. increasing preload increase SV
Skeletal Muscle vs cardiomyocytes
Skeletal muscle fibers are long, cylindrical, and multinucleated cells responsible for voluntary movements and have short action potentials, while cardiomyocytes are branched, striated cells with a single nucleus that function involuntarily to pump blood with long action potentials
Stenosis
Narrowing of a blood vessel or valve.
Frank-starling law of the heart
increasing right atrial pressure increases SV of both ventricles
Pressure volume curves
Area of the PV loop is the work done by the heart, length across is stroke volume. bounded by passive and active tensive curves
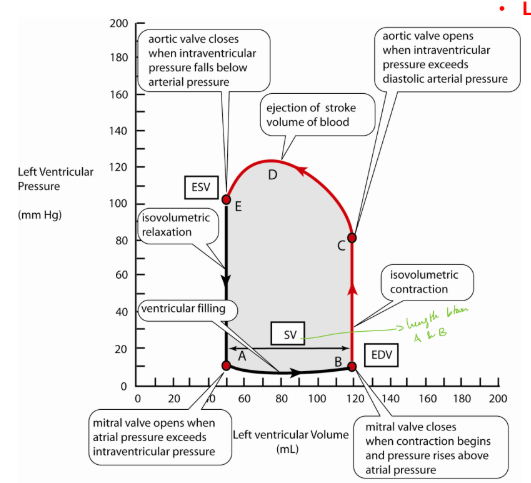
Contractility
ability to produce force at any stretch. can be altered by changing the amount of calcium releasing and the myofilament sensitivity to calcium. increasing contractility increases SV
Average Velocity equation
V - Qv (flow)/ A (cross sectional area)
Compliance with elasticity
High compliance means it can fit more volume per change in pressure, stretch easily. Low compliance means it can fit less volume per change in pressure, stiff. Depends on the makeup of the vessel. Drives blood flow
BP equation
systolic pressure/diastolic pressure
Pulse pressure equation
systolic - diastolic pressure
Mean arterial pressure (Pa) equation
P diastolic + (systolic - diastolic pressure)/3
or
CO x TPR
Blood vessels
they branch, reducing their diameter but increasing their overall area allowing for efficient delivery of blood to the cells throughout the body
Flux equation
Js = P (permeability) x change in concentration
Flow equation
Qs = A (area) x P (permeability) x change in concentration
Flow = flux/Area
driving force is the concentration difference
How to increase capillary solute diffusional transfer
increase blood flow (Qv)
Increase the effective area for diffusion (S)
increase the gradient for diffusion (Ca (arterial concentration)-Ci (interstitial fluid concentration)