CAL: Feline injection site sarcomas
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Give an example of an adjuvant
AI(OH)3 id a common vaccine adjuvant
What is the aetiology of injection site sarcomas
injection→ inflammatory reaction
Transition zones from inflammation to neoplasia
Microscopic foci or sarcoma located in areas of granulomatous inflammation
Other tumours resulting from chronic inflammation
feline intraocular sarcoma, post-trauma or chronic uveitis
Bone tumours in areas of previous implants
describe the paracrine production of growth factors
Chronic inflammation can lead to cell mutation
Tumour microenvironment is rich in fibroblast like cells and inflammatory cells
cytokines and growth factor release
Tumour infiltrating lymphocytes can produce platelet derived growth factors (PDGF)
ISS cells have growth factor receptors
What is the typical history and clinical signs for injection site sarcomas
Present with a mass in the area of vaccination or other SQ injection
Generally non painful
Adhered to underlying tissue
what do injection site sarcomas look like
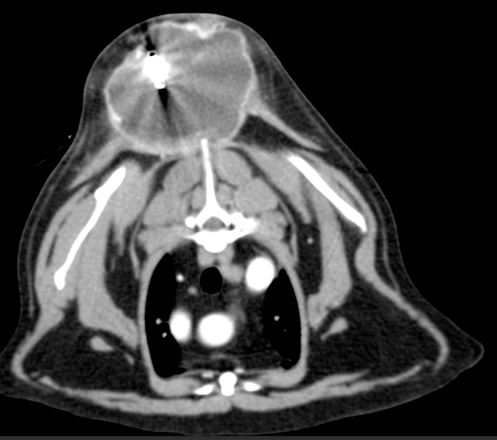
What is the most common type of injection site sarcoma
fibrosarcoma
Highly locally invasive and v infiltrative
Can be cystic
How are injection site sarcomas diagnosed
Physical exam and history
Location
Injection site
Cytology
Histopathology
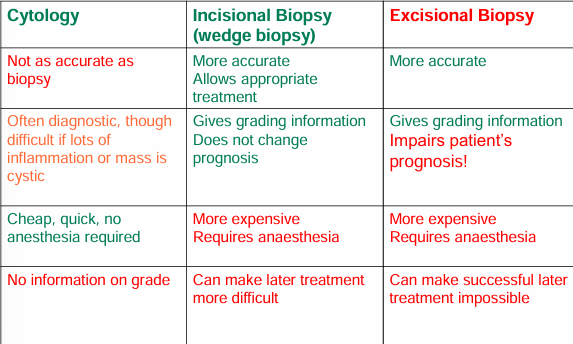
What are the pros and cons of cytology, incisional and excisional biopsy
When do you consider an incisional biopsy
It increases in size after 1 month post vaccine
>2cm diameter
mass persists >3 months
How do you stage injection site sarcoma
Thoracic radiographs
CT scan
Necessary to define extent of disease, and ca check for metastasis at the same time
What is the typical biological behaviour of injection site sarcomas
10-25% metastatic rate to lungs
Potentially curable in >75% with aggressive therapy
Local disease is the main cause of death
Recurrence
Unresectable
What are some prognostic factors of injection site sarcomas
Marginal resection
conservative surgery: disease free interval 2 months
Aggressive surgery: DFI 11-14 months
>16m with complete resection
More than 1 surgery
if surgery is performed by a non referral surgeon
Recurs in 2 months vs 9 months
Recurrence is possible after surgery despite clean margins
Who should perform injection site sarcoma surgery
outcome is better than the first surgery is performed by a referral surgeon
why is a second surgery less likely to be successful
Why is a second surgery less likely to be successful
Original anatomy has been altered
the surgical site will be altered
seeding through tissue planes
Harder to assess by imaging
harder to assess at surgery
Previously clean tissue considered contaminated
biopsy tracts, drains= contaminated
At time of first surgery there has been less time to metastasize
What is surgery for treating injection site sarcoma
Poor local control with 2-3cm
Histopathologically clean margins <50%
35% disease free at 1 year, 9% at 2 years
Amputation if possible
± dorsal spinous processes, dorsal scapula
Wide and deep surgical margins (3cm minimum and fascial plane)
3 cm: 28-45% recurrence
4-5cm and 2 fascial planes
select cases but:
Histopathologically clean in 97%
only 14% recurred
Anatomical resection of muscle compartment containing the tumour
cases also received chemo
14% recurrence
What do you do after surgery
Adjuvant radiation therapy after section
wait 10-14 days post op, as DFI/ST decreases the longer the wait
Surgery + RT: 40% cured
RT protocols
Hyperfractionated (definitive, small doses more frequently)
ST 3.5 years, disease free period 3 years
Hypofractionated (palliative, large doses weekly)
ST 2 years, disease free period 10 months
Pre operative RT
Very select cases as increased risk of wound dehiscence and RT more effective against microscopic disease
When do you consider chemotherapy for injection site sarcomas
Consider cytotoxic chemo if high grade, aggressive behaviour or metastatic disease
What protocol do you use for chemotherapy for injection site sarcomas
AC protocol (3 week cycle)
Doxorubicin 1mg/kg IV
40-50% response rate though short lived
Cyclophosphamide 200-250 mg/m2 PO
Carboplatin
250 mg/m2 IV q 3 weeks
4-6 cycles
What are some types of targeted therapy
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
metronomic chemotherapy
COX inhibitors
Metronomic chemotherapy
What do injection site sarcomas express
PDGFr
What are some treatments for ISS that are up and coming
Electrochemotherapy
Intratumoural chemo (bleomycin) + electropulsation
Tumour recurred in 12-19 months vs 4 months
When recurred, some responded when treated again
Immunotherapy (IL-2)
As vaccine or intratumoural
How can injection site sarcomas be reduced
use common sense: dont over vaccinate
avoid multiple vaccines in the same site and at the same time
use single dose vials and non-adjuvant vaccines
administer SQ in extremities as distal as possible or at base of tail
Where do you put rabies, FeLV, FVRCP ±C
Rabies- distal right hindlimb
FeLV- distal left hindlimb
FVRCP±C- distal right forelimb