Energy Changes
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Law of conservation of energy / mass
Energy is conserved and cannot be made or destroyed, only transferred.
→ The amount of energy at the end of a chemical reaction is the same as before the reaction takes place.
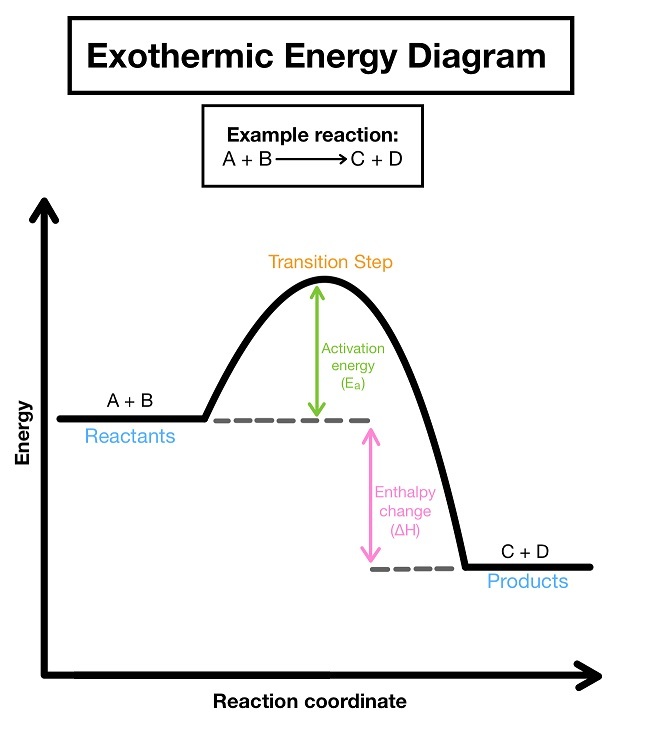
Exothermic reaction and examples
A reaction where energy is transferred to the surroundings.
→ surroundings temperature increases
Examples:
combustion, oxidation reactions and neutralisation (acid + alkali) reaction, hand warmers
Endothermic reaction and examples
A reaction where energy is taken in from the surroundings
→ surroundings temperature decreases
Examples:
thermal decomposition, photosynthesis, neutralisation, sports injury packs
Activation energy
Minimum amount of energy needed for a reaction to take place.
Reaction profile
Graph which shows the relative energies of reactants and product, as well as activation energy and energy change of the reaction.
Bond energies in chemical reactions
Energy is supplied to break bonds and energy is released when bonds are made.
Bond energies in Exothermic reactions
Energy released from forming bonds is greater than that needed to break the bonds.
Bond energies in Endothermic reactions
Energy released from forming bonds is less than that needed to break the bonds.
Equation for energy change
Energy of reaction = sum of bonds broken - sum of bonds made
Rechargeable cells
Chemical reactions are reversed when an external current is supplied.
Non-rechargeable cells
Reactants are used up, reactions cannot be recharged.
Fuel cell
Fuel cells are supplied by fuel and oxygen to oxidise the fuel to generate electricity.
Overall reaction in hydrogen fuel cell
Cathode: 2 H2 → 4 H+ + 4 e−
Anode: O2 + 4 H+ + 4 e−→ 2 H2O
Overall: 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O.
Advantages of hydrogen fuel cells
no pollutants
no recharging
Disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells
flammable
Hydrogen difficult to store / transport
fossil fuel production
toxic chemicals
expensive production of hydrogen by electrolysis
Rechargeable cells characteristics
Fuel doesn’t need to be constantly supplied
Hard to dispose of → non-biodegradable
eventually stops working