2.3 Carbon Compounds
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Building blocks of life
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Organic: carbon forms framework
Organic
Carbon form’s their framework
Characteristics of carbon
4 valence electrons
4 covalent bonds
Carbon bonds to
carbon
oxygen
nitrogen
sulfur
hydrogen
phosphorus
Carbon backbone
Carbon atoms join to form carbon-based molecules
MUST include multiple carbons
Ex: Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆)
Anabolisim
Add
energy→complex molecules
consumes energy
Catabolisim
Cut
Break down comples→usuable energy
Macromolecules
Very large molecules made of thousands of smaller molecules
Not all macromolecules are polymers
Polymer
Long chain of REPEATING monomers
Monomer
Single subunit making up polymer’s
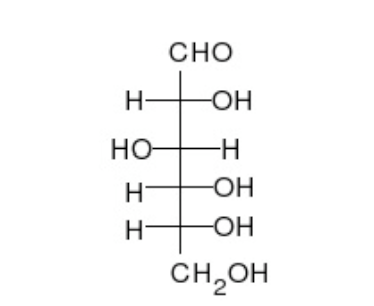
Polymer: Carbohydrates
Monomer: Sugar (Saccharide)
Short-term energy
C, H, O
C(H2O); 1:2:1
Polymer: Lipid
Monomer: Fatty acid chain
Long-term energy
Cushion for organs
C, H, O
Func. group: Carboxyl (-COOH)

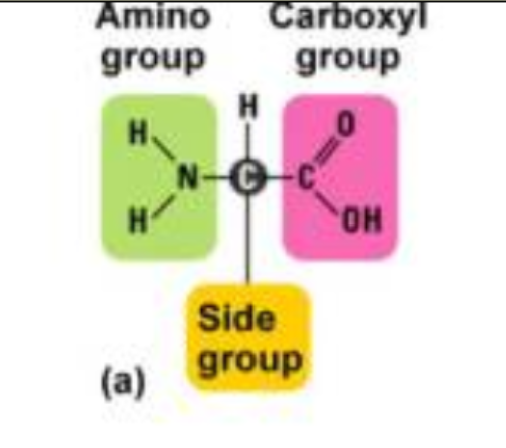
Polymer: Protein
Monomer: Amino Acid
Rebuilds muscle
C, H, N, O, S
Func. group: Amino (-NH2), Carboxyl (-COOH)
Amino Acid Composition:
R group (variable side group)
determines the type of amino acids
Amino Group: -NH2
Carboxyl Group: -COOH
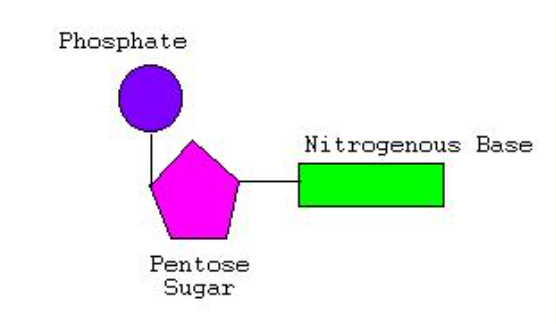
Polymer: Nucleic Acid
Monomer: Nucleotides
Stores genetic info
C, H, N, O, P
3 components
Func. group: Phosphate group (p)
Pentose (5-C) sugar
Nitrogen-containing base
adenine
guanine
cytosine
thymine
uracil
Synthesis
Smaller molecules join together to form larger molecules
Polymerization
Synthesis of monomers to make polymers
Type of synthesis reaction
Condensation Polymerization
Dehydration synthesis
Type of synthesis reaction
Joins monomers to make a polymer
Releases water as byproduct
Monosaccharide
Type of carbohydrate
One saccharide
Simple sugar
Building block
Ex: Glucose
Disaccharide
Type of carbohydrate
Two monosaccharides
Ex: Glucose + fructose = sucrose + H2O
Oligosaccharide
Type of carbohydrate
3-10 monosaccharides bonded together
Polysaccharide
Type of carbohydrate
Many monosaccharides
Long sugar chain
Structure:
Cellulose (think celery)
Chitin
Storage
Glycogen
Starch
Lipids
Consists of glycerol molecule + fatty acid chain
chain: methyl (-CH) units
Carboxyl group (-COOH) at one end
Hydrophobic: Water-fearing
Does not bond with water well
Water=polar
Lipids=non-polar
clumps together due to polarity
Triglyceride
Glycerol Molecule + 3 Fatty Acid Chains
Saturated
No double bonds exist
Maximum # of hydrogen bonds exists
Solid
Unsaturated
Molecule has at least one double bond
Isn’t maximum # of hydrogen bonds
Liquid
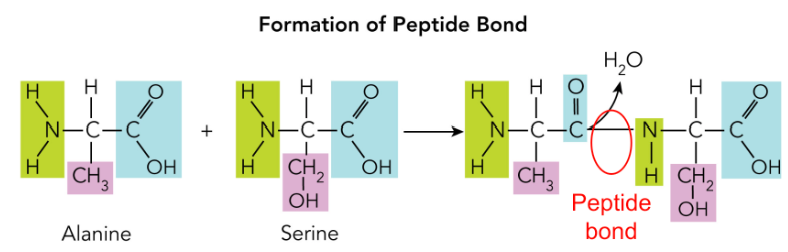
Peptide bond
Involves (Polymer: Protein)
Covalent bond between amino group of one amino acid another carboxyl group of another amino acid
Summary: Holding two amino acids
Polypeptide bond
Involves (Polymer: Protein)
Holding many bonds between amino acids