NEURO DEGENERATIVE DISORDERS
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
definition of NDD
Occur when nerve cells in the brain (with/without peripheral nervous system involvement) lose function over time and ultimately die
what happened in NDD
irreversible loss of neurons with age
protein deposition & aggregation in the neurons
altered physicochemical properties in the brain and in peripheral organs
Common conditions under NDD
Alzheimer’s disease
Lewy Body Dementia
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Prion disease
Huntington disease
Spinocerebellar ataxia
Parkinson disease
Frontotemporal Dementia
Neuronal loss in general in NDD
Abnormal protein aggregatioan and inflamation in the brain
cause cell death
due to Oxidative stress, Mitochondria dysfunction, Excitotoxicity, Neurotransmitter depletion, Abnormal ubiquitination, BBB pathology
Classification of NDD
PATHOGENESIS - Protein-based classification – protein processing pathways
CLINICAL FEATURES- Predominant signs and symptoms
clinical feature of NDD
dementia
movement disorders
what is the Pathogenesis of AD
Extracellular beta-amyloid deposits- senile plaques
Intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFT)- tau-containing NFTs
Non modifiable risk factor of AD
genetics
APP, ApoE4, Presenilin 1&2
aging - >75 years old
gander- male > female
Modifiable risk factor of AD
Lifestyle and mental health
diet, personal trait, education, depression, sleep disturbance, physical activity
comorbidities and life events
Cerebrovascular disease, Type 2 diabetes, Hypertension, Hypercholestrolemia
clinical hallmark of AD
Cognitive impairment
list sign & symptoms or clinical feature AD
Withdrawal from society activities
confusion with time and location
difficulty completing familiar tasks
misplacing items
difficulty solving problems
memory loss (short term memory)
difficulty in words
physical feature of AD
• Loss of balance or coordination
• Stiff muscles
• Shuffling gait
• Trouble standing or sitting up in a chair
• Weak muscles and fatigue
• Sleep disturbances
• Trouble controlling bladder or bowels.
• Seizures and uncontrollable movements
What to expect in the late-stage dementia
loss of facial expression
Problem with everyday activities like bathing, dressing, eating
bedround, requires around the clock care
unable to speak
unable to walk or sit up without assistance
loss long term memory
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) vs Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
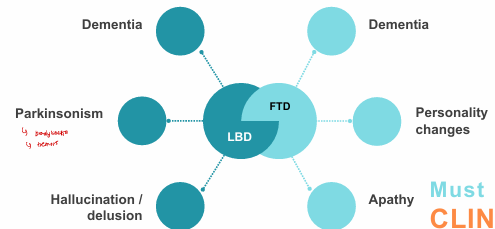
treatment of Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) vs Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
acethyl colinesterase inhibitors
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
upper and lower motor weaknesses
Asymmetrical weakness at first, then affecting all limbs and trunk,
Presence of significant wasting with hyperreflexia
Pseudobulbar palsy and difficulty breathing Incurable (cant breath, swallow, speak) mesti ada ventillation
life expectancy less than 2 years with riluzole
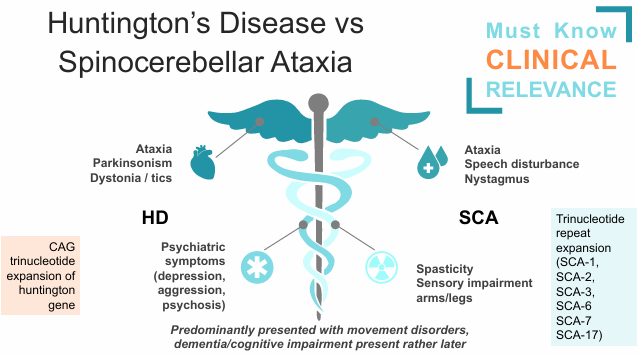
Huntington’s Disease vs Spinocerebellar Ataxia
prion disease / Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies or TSEs
A group of rare, fatal brain diseases that affect animals and humans.
They are caused by an infectious agent known as a prion
Prions – misfolded proteins with ability to transmit misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein.
spread to humans by infected meat products
Rapid deterioration of symptoms – death within 4 months to 2 years
Clinical features of prion disease
• loss of intellect and memory.
• changes in personality.
• loss of balance and coordination.
• slurred speech.
• vision problems and blindness.
• abnormal jerking movements.
• progressive loss of brain function and mobility