Development and organization of the nervous system
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
CNS
Brain (perception and cognition) and Spinal Cord
PNS division I
Somatic / Autonomic (Sensory in/motor out)
Somatic
Controls voluntary actions like raising a hand or walking (PNS). Have one area of skin that correlates with with spinal nerves
Autonomic
Controls involuntary actions like breathing, heart beat (PNS)
Somantic nervous system division
(PNS - Somatic) Afferent nerves - 5 senses. Efferent nerves - skeletal motor (moving)
Autonomic nervous system division
(PNS-automatic) afferent nerves (sensory information from internal organs) and efferent nerves (carries motor information out that controls heartbeat, breathing),
Efferent Nerves in Autonomic nervous system
(PNS - Autonomic - efferent) divides into sympathetic - shifting of blood, when activities system is either fight or flight, and parasympathetic - Resting and Digesting state
Potency
the ability to develop into different types of cells
Totipotent
The ablilty of cells to be extracted and implanted to form another success for pregnancy.
Pluripotent / Multipotent
the Ability of cells to turn into a couple of other things
Unipotent
The ability to only turn into one thing
Zygote
egg and sperm meet, about 8-10 days time in between fertilization and implantation.
Morula
3 days into devolvement. Group of 16-32 cells that are virtually identical. CELLS ARE TATIPONENT

blustula
fluid filled cavity fills morula. Cells on the outside are destined to be support cells, and small group too the side are destined to be enbronyic stem cells (inner cell mass). Should be implanted in uterine lining now. CELLS ARE PLURIPONENT
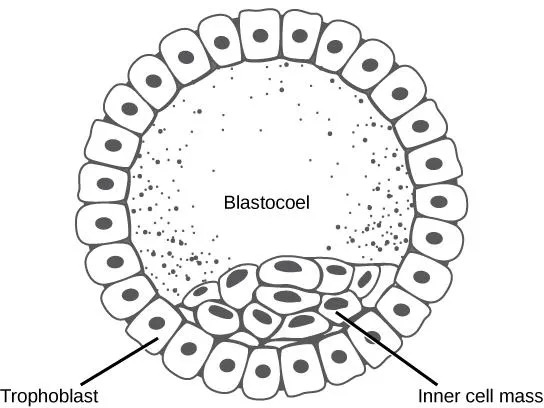
pluriponent
embryonic stem cells - cells that become the future you
Blastocyst
Ending position of embryo in germinal stage, baby is compacted into a disc.
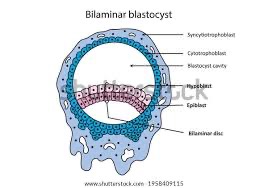
Multiponent
Cells that are able to become one of a few things; but not everything
Gastrulation
-2 to 3 weeks into pregnancy. Cells push against each other and submerge creating 3 layers. Cells are said to be MULTIPONENT
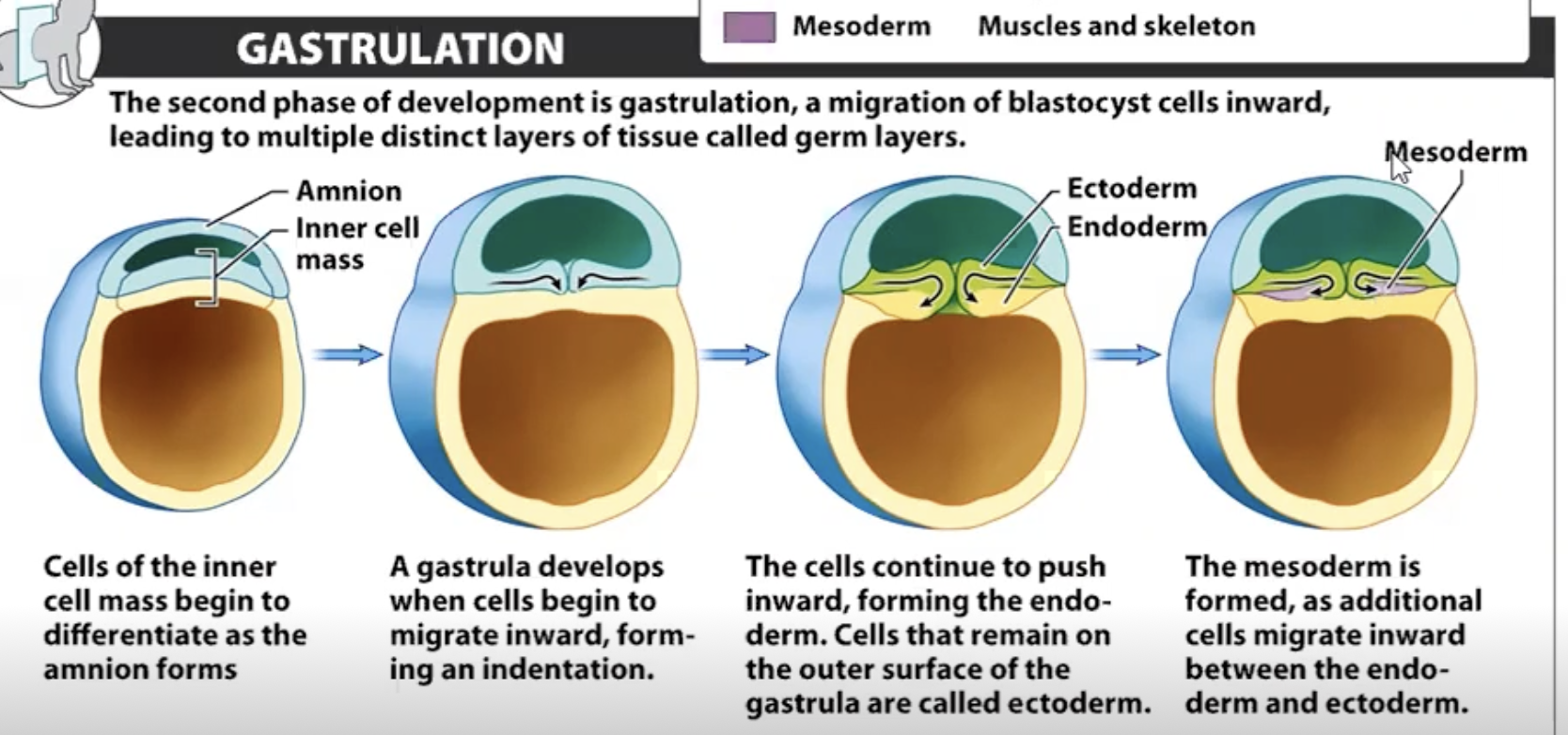
Gastrulation top layer
Ectoderm -Skin and Nervous system CELLS ARE MULTIPONENT
Gastrulation middle layer
Mesoderm - Muscles and Skeletons CELLS ARE MULTIPONENT
Gastrulation bottom layer
Endoderm - internal organs CELLS ARE MULTIPONENT
Neurulation - Ectoderm
HappeCells in the middle of the ectoderm are destined to be the foundation of the nervous system. Forms into a neural plate and then cells on the edge of the plate begin to curl up and form the neural tube
Neural tube
CNS brains and spinal cord, filled with fluid cavities that turn into ventricles and the spinal cavity. CELLS ARE UNIPOTENT.
Cells that don’t make it into the neural tube
squeezed out on top of neural tube, becomes neural crest PNS
Cells around the neural tube
Somites - mesoderm, middle layer. Cells around the neural tube turn into bone that surrounds the CNS.
Neurulation
Point at which nervous system develops, at the end cells are unipotent
neural proliferation
happens from about 3 week to 40 week. Neural tube creates about 4000 cells per second to change the shape of the Neural tube. End of the tube enlarges and the bottom narrows to become spinal cord. 3 Bumps into 5 Bumps (5 major divisions of the brain).
Neural Migration and Aggregation
neurons move from middle to the edge of the neural tube to begin forming there sutures via cell vel crows (sticky protein, if they match cells group). Then they “aggregate” (group) and form structures
Neural Stem cells
Radial glial cells
radical Neural cell migration
cells climb the rope to the outside of the neural tube
Tangential neural cell migration
cells travel down the and around the neural tube to achieve the outside
Axon Growth and Synapse formation
Once positioned neurons extend figures that smell chemicals to call. These figures will ultimately become axon dendrites. “Growing tip” - called growth cone.
Synapse Refinement
Nuerial cells call way to many cells over so they have to go through a process of getting rid of them. Cells release chemicals and if they receive one back they get to become a match. Cells that don’t match die.
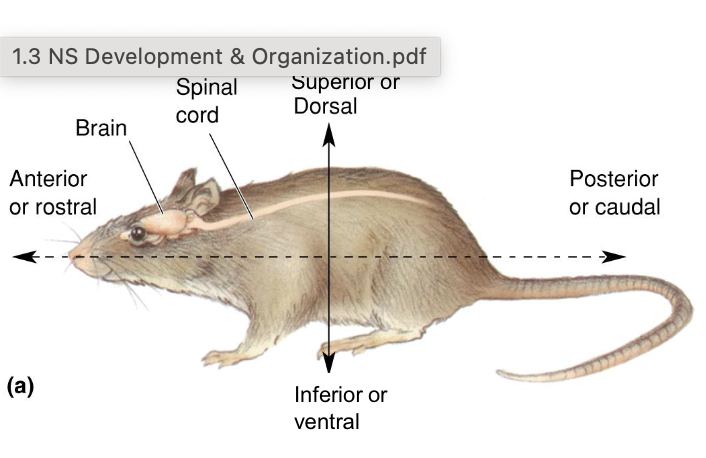
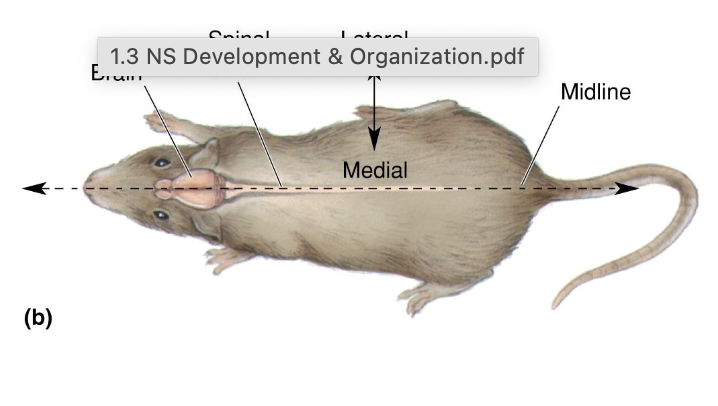
Anterior/rostral
Towards the front nose
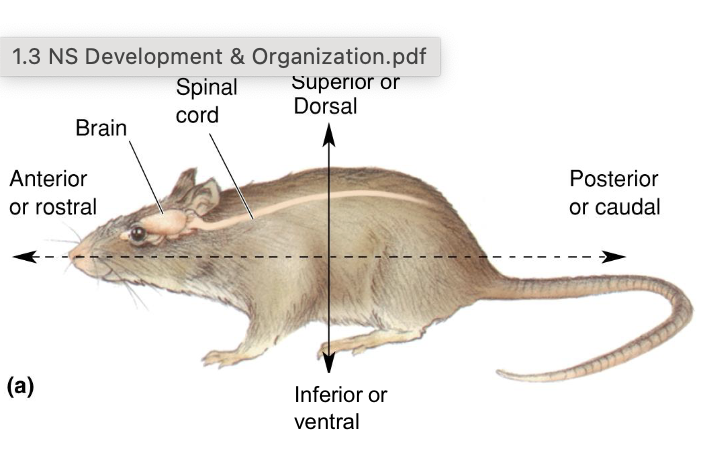
posterior/caudal
towards the back/tail
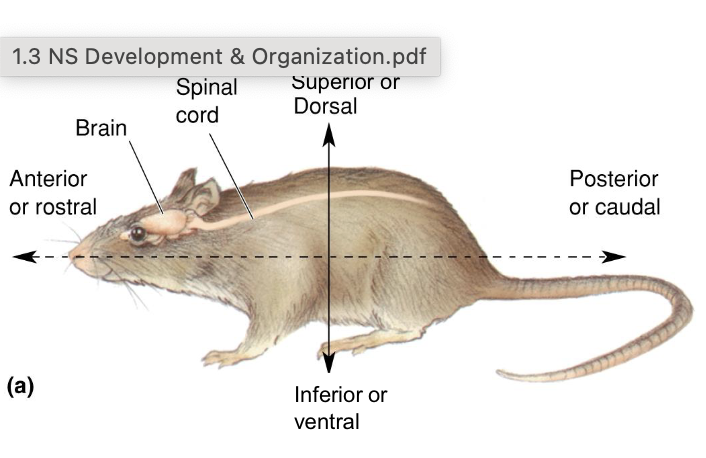
dorsal/superior
towards the top
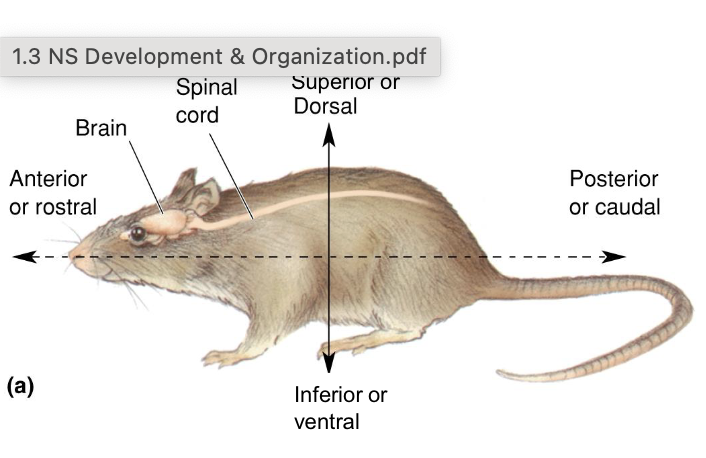
ventral/inferior
towards the bottom
Medial
towards the middle
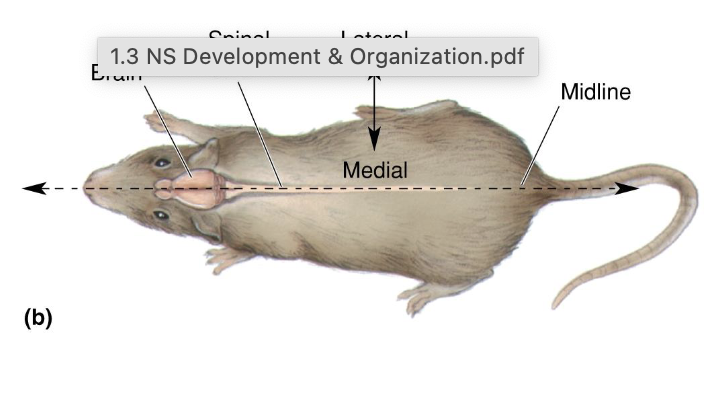
lateral
towards the side
Structures on the same side
ipsilateral
structures on opposite sides
contralateral
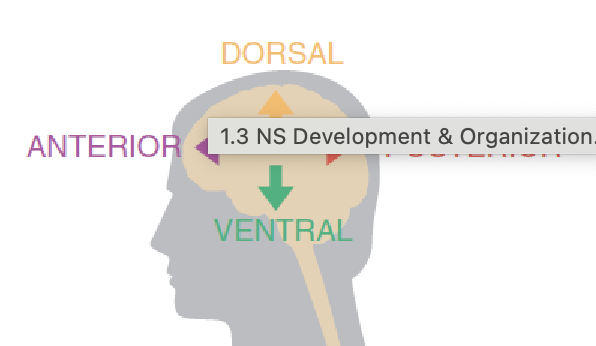
IN HUMANS Anatomical direction for head
(looking at human from the side) anterior - pointing to face, dorsal - pointing to top of the head (hair), posterior - pointing to back of the head/neck, ventral - pointing to the feet
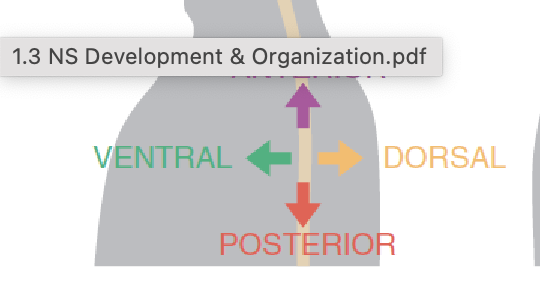
IN HUMANS Anatomical direction for body
(looking at human from the side) anterior - pointing to the top of the head (hair), ventral - pointing to the chest, posterior - pointing to the ground, dorsal - pointing to back.
IN HUMANS MEDIAL
towards spinal cord
IN HUMANS LATERAL
towards neck
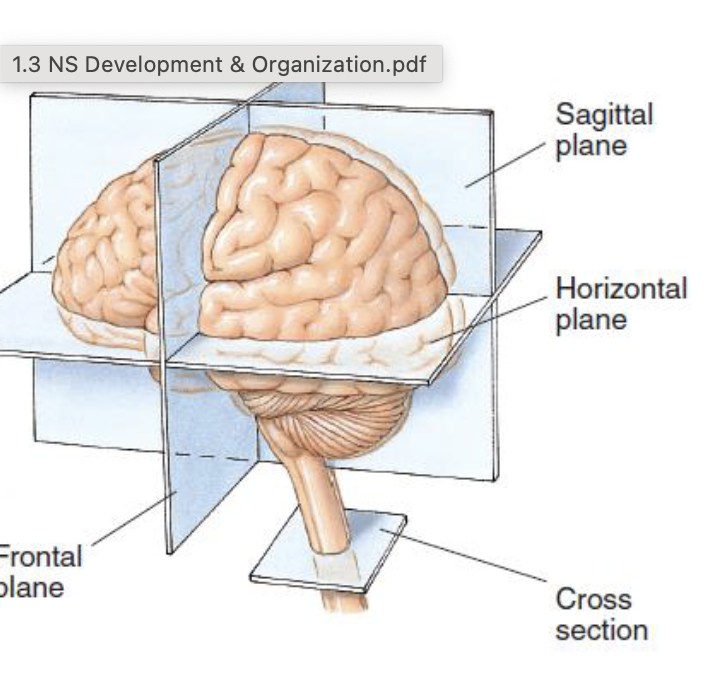
Sagittal plane
midsagittal cut, splits brain right in half
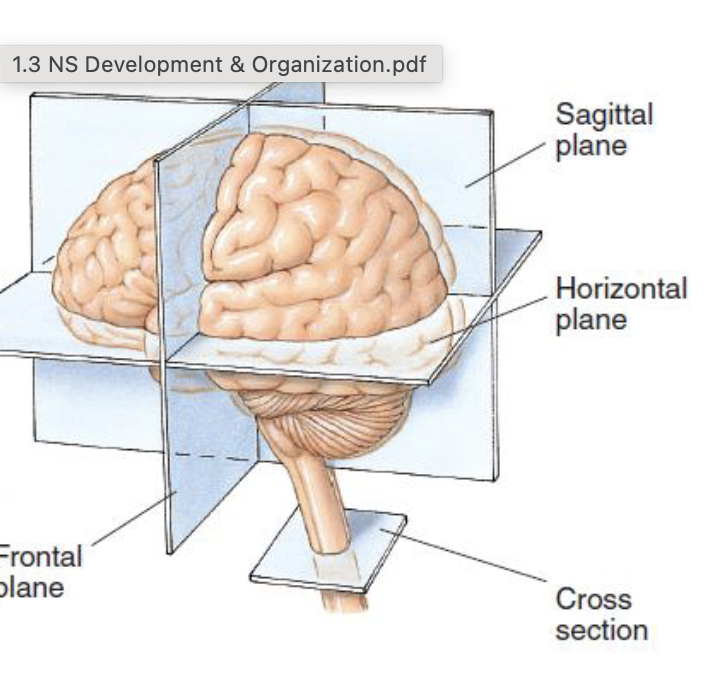
Horizontal place
cuts brain in half but horizontally. at about the ears
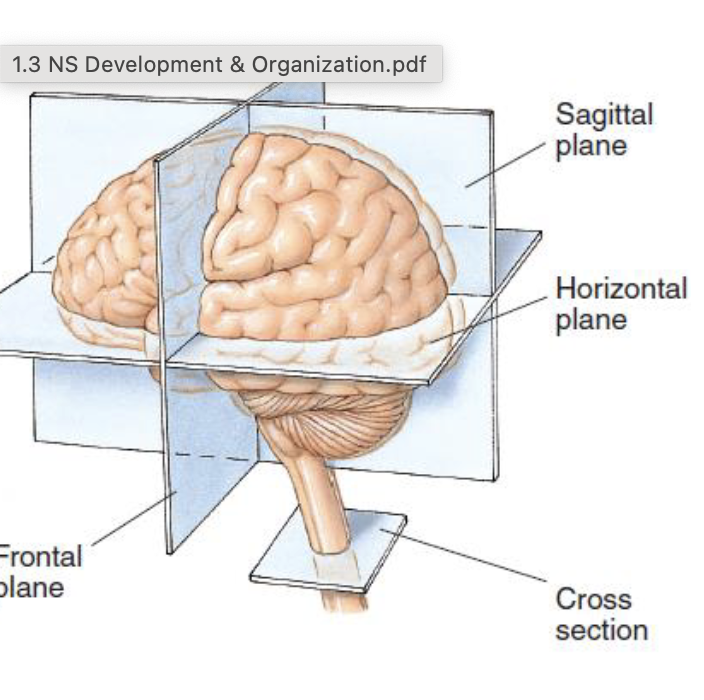
Frontal plane
cuts brain in half from the vertical way (like beats headphones).
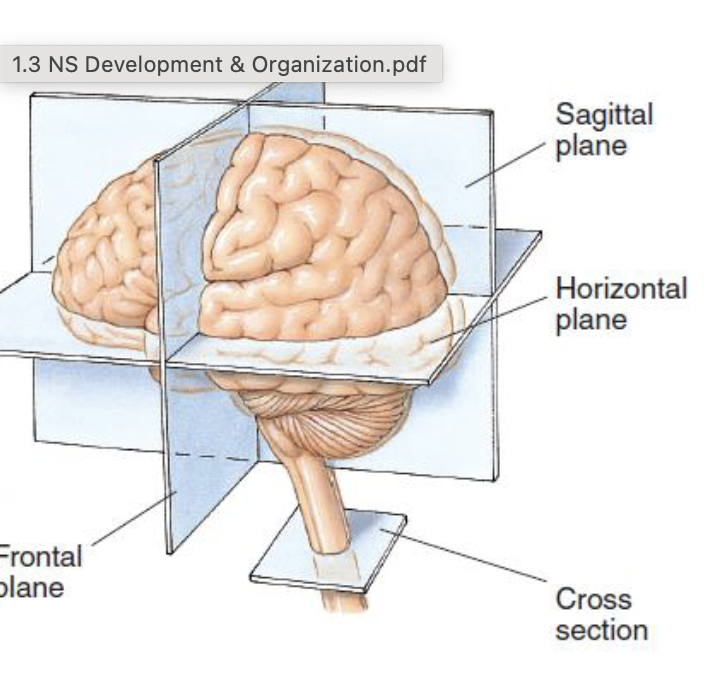
Cross section
ONLY in spinal cord at an angle
The cerebrum
top majority of the brain, Biggest part consists of telencephalon. Split into 2 hemispheres that receive sensory imput and control motor output to the opposite sides of the body.
Corpus Callosum
connects two hemispheres of the brain
cerebellum
Motor control center - “lets do it well”
brain stem/spinal cord
PNS - performs basic functions like heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. Main way information get out. 31 pairs of nerves that control different movements. (top nerves control arms and fingers, bottom ones control feet and legs)
Dorsal root
brings sensory information to the brain
ventral root
brings motor information out,
Brain blood barrier
CNS - blood will kill brain, but it needs it to function. enters through tight capillaries. Brain floats in blood that has been scrubbed of nutrients
Autonomic nervous system spinal nerves
middle spinal nerves are for fight or flight and the end and beginning of spinal nervous are for rest and digest.
Cranial nerves
information goes straight to the brain, touch on face, head or neck. hearing, seeing, smell ect.