Unit 1: Biochemistry - #3 Structure and Function of Macromolecules: Lipids (copy)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Lipids
Lipids are nonpolar biological molecules that provide long term energy storage, insulation, cushioning of internal organs and are the main component of the cell membrane
Lipids are the main structure of some hormones
All lipids are hydrophobic (do not dissolve in water)
Five Main Types of Lipids
Fatty Acids
Fats
Phospholipids
Steroids
Waxes
Fatty Acid
Consist of a long chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms with a terminal carboxyl functional group
Carboxyl gives its acidic properties
The longer the chain the more hydrophobic it becomes
What are the two types of Fatty Acids?
Saturated
Unsaturated
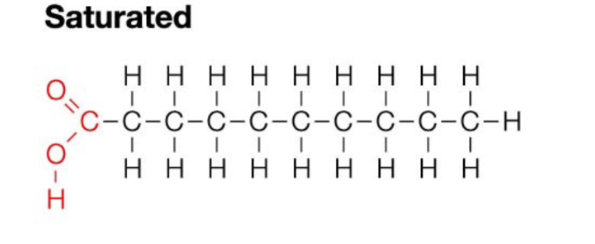
Saturated Fats
Contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms per carbon atom
No double bonds - a straight chain
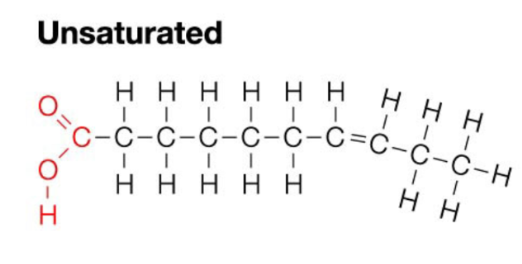
Unsaturated Fats
Contain a carbon double bond formed by removal of H from carbon skeleton - chain with a bend in it
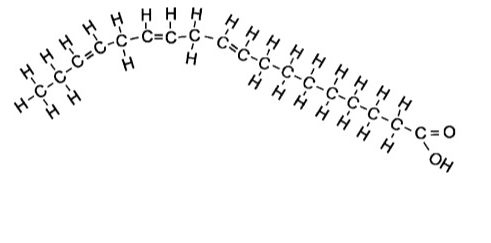
Polyunsaturated
Contains more than one carbon double bond
Fats
Energy storage molecule - more than 2x energy than carbohydrates
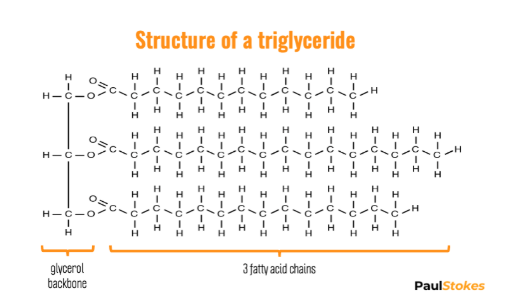
The most common fat is the triglyceride which contain 3 fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol backbone.
They are linked with a dehydration synthesis reaction and are held together with an ester linkage.
Phospholipids
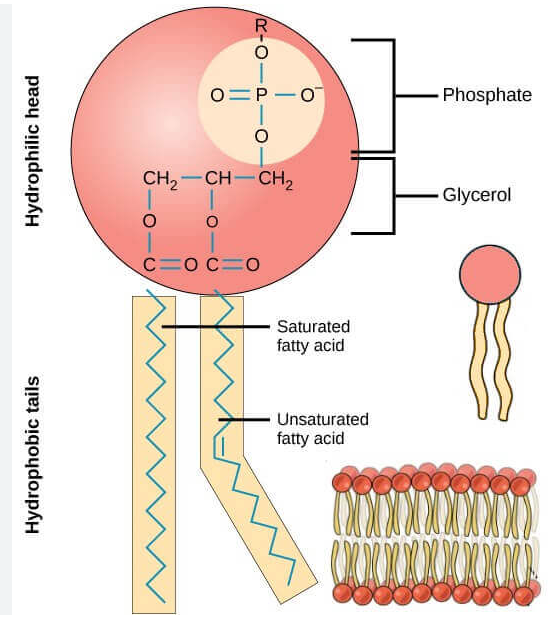
The main component of cell membrane
Composed of two main parts, a phosphate head and two fatty acid tails
Amphipathic: The phosphate head is polar and hydrophilic while the fatty acid chains are nonpolar and hydrophobic (similar to soap)
Steroids
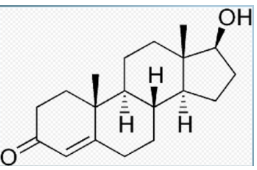
Consist of four linked carbon rings
Different steroids have different functional groups attached to the rings
Steroids rings are hydrophobic
Group of steroids Sterols, have a single polar -OH group at one end
Gives molecule dual solubility properties
Includes Cholesterol(component of the cell membrane), and sex hormones
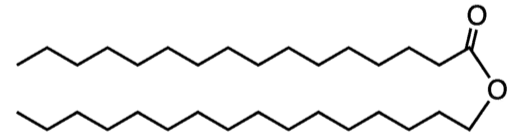
Waxes
Waxes are composed of long-chained fatty acids that are attached to an alcohol or a carbon ring
Waxes are hydrophobic, non-polar and are firm yet pliable
EX. Cutin: Water resistant coating on plants, bird feathers, and beeswax