7. Management of Peptic Ulcer
1/41
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Define and describe peptic ulcer.
An ulcer of the alimentary tract mucosa, usually stomach or duodenum, rarely in lower esophagus, where mucosa is exposed to gastric acid secretion
A localized loss of gastric as well as duodenal mucosa leads to the formation of peptic ulcer
Common disorder affecting millions worldwide
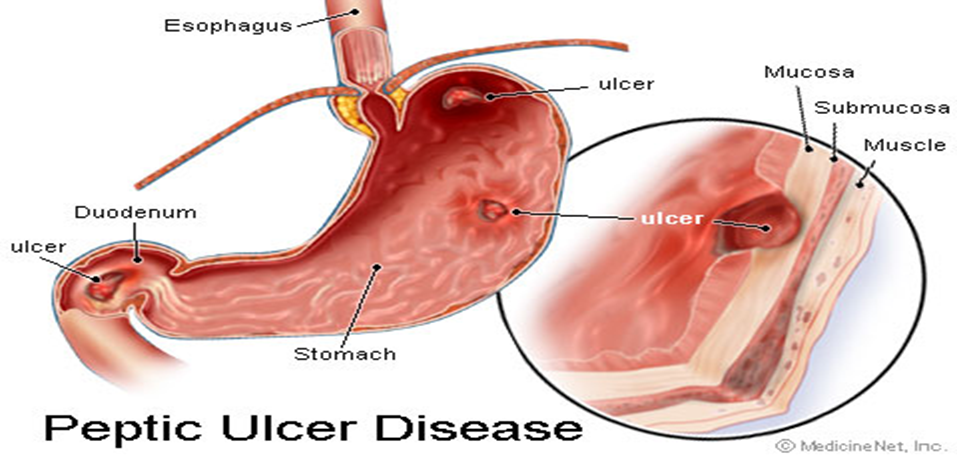
How do peptic ulcers come about?
When normal mucosal defense mechanisms (mucus, mucosal blood flow, formation of HCO3- and PGE2) are impaired
When normal mucosa is overpowered by damaging factors (acid, pepsin, NSAIDs, and H. pylori)
Ulcers occur 5 times more commonly in
duodenum
Gastroduodenal mucosal integrity is determined by __________ (defensive) and ________ (aggressive) factors.
protective
damaging
List protective/defensive factors that determine gastroduodenal mucosal integrity.
Gastric mucus
Prostaglandins
Bicarbonate
Mucosal blood flow
Local nitric acid
List aggressive/damaging factors that determine gastroduodenal mucosal integrity.
Acid
Pepsin
H. pylori
Bile
NSAIDs
Tobacco
Alcohol
Emotions (stress and anger)
Mechanism of Acid Secretion
Gastric acid is secreted by ________ cells in the gastric mucosa. They contain receptors for 3 main stimulants: _________, _______, and _____________. _________ binds to H2 receptors. Gastrin and ACh exert their effects by increasing _________ ____. They stimulate acid secretion through ___ ______ (______ ____).
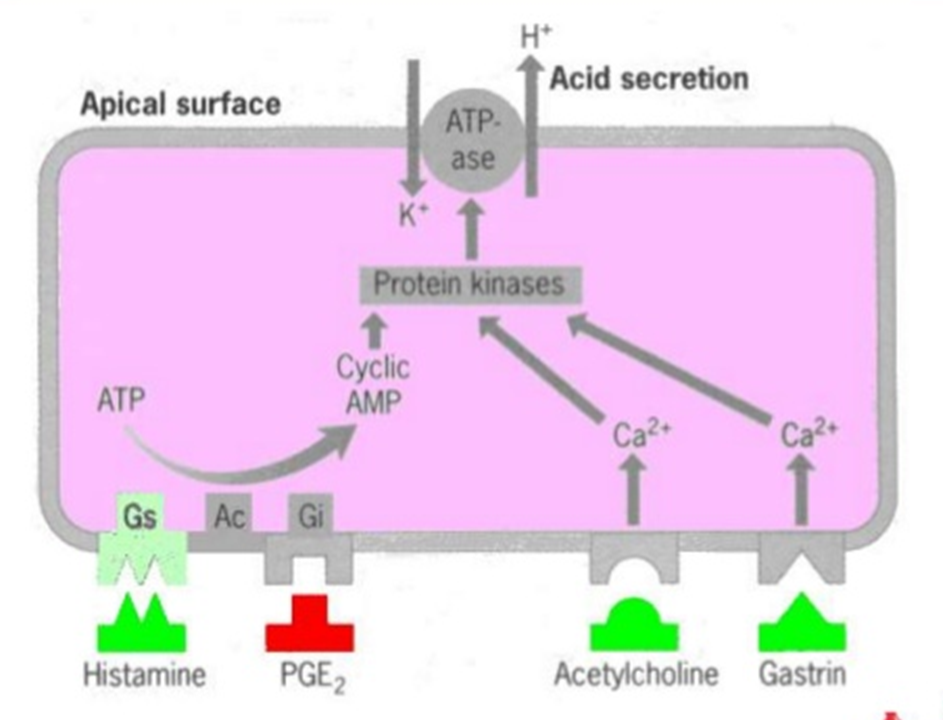
parietal
histamine
gastrin
acetylcholine
Histamine
cytosolic Ca2+
H+/K+ ATPase (proton pump)
List the 3 classes of drugs used to treat peptic ulcers.
Drugs which reduce gastric acid secretion
Mucosal/ulcer protective agents
Anti-H. pylori drugs
List the 4 categories of drugs which reduce gastric acid secretion.
H2 receptor antagonists
Proton-pump inhibitors
Anticholinergics
Prostaglandin analogues
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
List H2 receptor antagonists used to treat peptic ulcers.
Cimetidine
Ranitidine
Famotidine
Roaxitidine
Ioxatidine
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
List proton-pump inhibitors used to treat peptic ulcers.
Omeprazole
Pantoprazole
Rabeprazole
Lansoprazole
Esomeprazole
Dexlansoprazole
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
List anticholinergics used to treat peptic ulcers.
Pirenzipine
Propantheline
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
List prostaglandin analogues used to treat peptic ulcers.
Misoprostol
Enprostil
List mucosal/protective agents used to treat peptic ulcers.
Sucralfate (aluminum salt of sulfate sucrose)
Colloidal Bismuth Subcitrate (CBS)
List anti-H. pylori drugs used to treat peptic ulcers.
Amoxicillin
Clarithromycin
Metronidazole
Tetracylin
Tinidazole
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
How do H2 receptor antagonists work?
They block histamine-induced gastric acid secretion.
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
Describe the mechanism by which H2 receptor antagonists work.
Competitively inhibit H2 receptors on parietal cells and suppress basal and food-stimulated acid secretion
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
List the uses of H2 receptor antagonists.
Duodenal and gastric ulcers
NSAIDs-induced ulcer (PPIs preferred if NSAIDs have to be continued)
Prevention of stress-related gastric bleeding and gastritis
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
List the adverse effects of H2 receptor antagonists.
Safe drugs
Headache
Fatigue
Constipation (rare)
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
How are H2 receptor antagonists administered?
Cimetidine, slow infusion should be given
Rapid IV injection may cause bradycardia, arrythmia/cardiac arrest
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
Describe proton pump inhibitors (PPI) and their mechanism of action.
Most widely used, good efficacy, safe
Prodrugs requiring activation in acidic environment
Activated form binds irreversibly to H+/K+- ATPase enzyme system (proton pump) and inhibit it
Dose-dependent suppression of gastric acid secretion, powerful inhibitor of gastric acid; can fully abolish HCl secretion (basal/food stimulated)
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
How are the PPIs esomeprazole, lansoprazole, and pantoprazole administered?
IV
Lists the uses of PPIs.
Duodenal and gastric ulcers
Bleeding peptic ulcers
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
H. pylori associated ulcers
List the adverse effects of PPIs.
Quite safe
Diarrhea
Headache
Abdominal pain
Reduction in oral Vitamin B12 absorption occurs with prolonged therapy
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion - Anticholinergics (M1/M3)
Describe pirenzipine and list its adverse effects
M1 anticholinergic
Gastric secretion reduced by 40-50%
Effectively heal and prevent recurrence of duodenal ulcers
Dry mouth
Blurred vision
Constipation
Urinary retention
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion - Anticholinergics
Which anticholinergic is 25 times more potent than pirenzipine?
Telenzepine
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion - Anticholinergics
Which anticholinergic drug has intolerable adverse effects?
Propantheline
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
Prostaglandin (PG) analogues play an important role in
gastric defense mechanism
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
Which PG is produced by the gastric mucosa? List its functions.
PG-E
Inhibits secretion of acid
Stimulates secretion of mucus and bicarbonate
Cryoprotective effect
Enhances blood flow
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
What is misoprostol? What is it used for? What is it contraindicated in and why?
Analog of PGE1
Approved for healing of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers and in chronic heavy smokers
Contraindicated in pregnancy, since it can stimulate uterine contraction and cause miscarriage
Drugs Which Reduce Gastric Acid Secretion
List the adverse effects of PG.
Diarrhea
Colic pain
Uterine bleeding
Abortion
Needs multiple daily doses (short t1/2)
Patient acceptability is poor (PPIs are preferred)
List and describe the mechanisms of mucosal protective drugs.
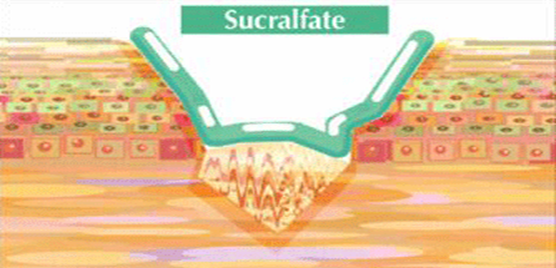
In acidic pH (<4), polymerizes by cross-linking of molecules; forms sticky gel, which acts as acid-resistant physical barrier
Dietary and mucosal proteins get deposited on this coat, forming another protective layer
Stimulates PGE2 synthesis and HCO3- secretion
Promotes healing of both duodenal and gastric ulcers by binding to epithelial and growth factors
List the uses of mucosal protective drugs.
Gastritis
Bile Reflux
Prophylaxis of stress ulcers
Mucosal Protective Drugs
List and describe the mechanisms of colloidal bismuth subcitrate (CBS).
Form acid-resistant protective coating over ulcer base
Stimulate PGE2
Mucus and bicarbonate secretion
Dislodges H. pylori from surface of gastric mucosa
Has antimicrobial activity
Used in H. pylori treatment
Mucosal Protective Drugs
List the adverse effects of CBS.
Safe
Blackening of stools
Darkening of tongue
Prolonged use may lead to bismuth toxicity
Describe Helicobacter pylori and its role in peptic ulcers.
Gram negative bacillus
Can survive in acidic gastric environment
90% of duodenal ulcers
50-60% of gastric ulcers
Disturbs normal feedback mechanism of acid release
Produce other proteolytic enzymes that decrease defense
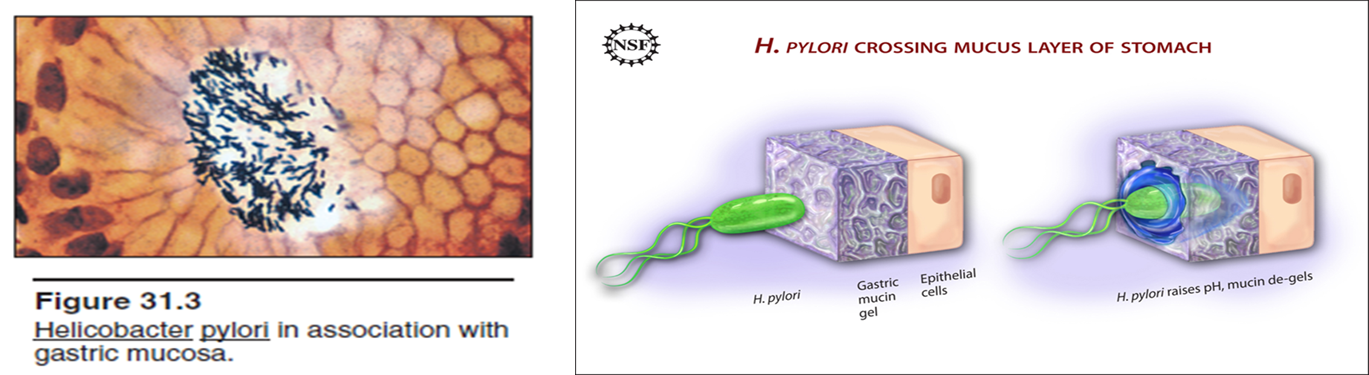
Why is single therapy relatively ineffective to treat H. pylori?
Resistance develops rapidly
How is H. pylori eradicated? Why is it beneficial?
Concurrently with PPI/H2 blocker therapy
Faster ulcer healing
Low relapse rate
Anti H. pylori Drugs
List the drugs used for triple therapy. How many days is it administered for?
Omeprazole + Clarithromycin + Amoxicillin/Metronidazole
14 days
Anti H. pylori Drugs
List the drugs used in quadruple therapy. How long is it administered for?
Omeprazole + Bismuth subsalicylate + Tetracycline + Metronidazole
14 days
Anti H. pylori Drugs
List the drugs used in sequential therapy. How long is it administered for?
Omeprazole + Amoxicillin (1-5 days)
Omeprazole + Clarithromycin + Tinidazole (next 6-10 days)
After completion of any therapy, what is done to promote ulcer healing?
Treatment with PPIs (once daily) for another 4-6 weeks