2. Factorial ANOVA
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
How many independent variables are there in a Factorial Independent ANOVA?
Multiple
two-way = 2 IVs
three-way = 3 IVs
How many dependent variables?
One
Do participants differ between conditions in factorial ANOVAs
Different ppts in all conditions
How does this factorial design differ from One-way ANOVA
One- way ANOVAs look at the main effect of IV
Factorial designs look at how variable interact. The effect of one IV may depend on the level of another IV.
e.g. a drug to treat OCD will only affect people with OCD and have no effect for controls
two variables:
drug
clinical status
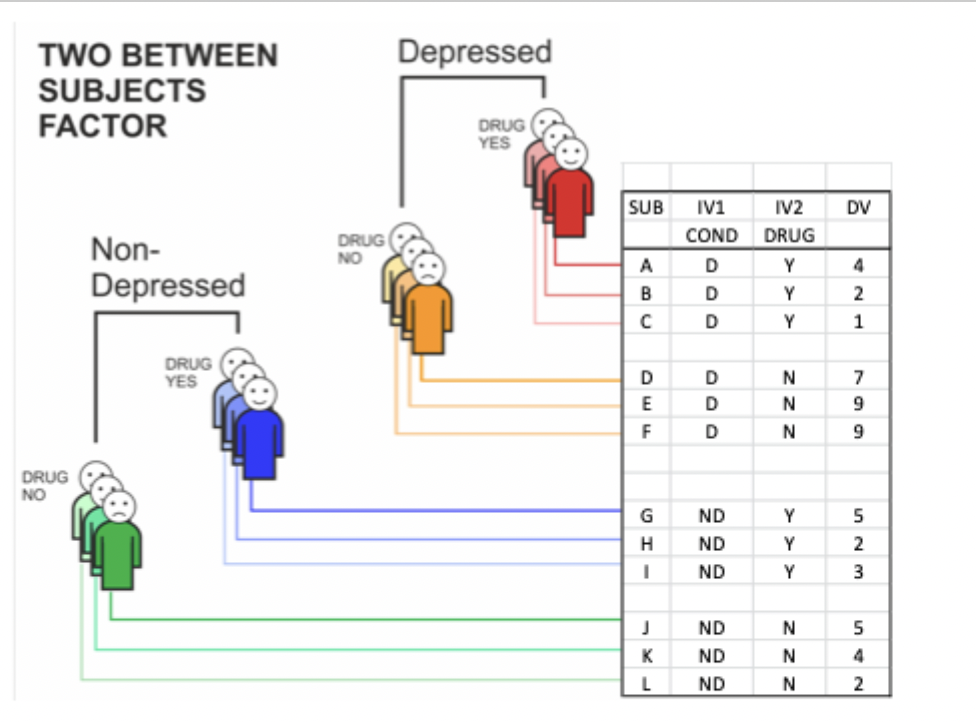
What are the assumptions of factorial ANOVA?
Independence
Normality (K-S or Shapiro Wilk/ observe graphs)
Homogeneity of Variance (Levene’s test/ observe graphs)
If assumptions are violated - non-parametric alternatives
What kind of graph do we use to inspect the data for a factorial ANOVA?
line graph with multiple lines
In the SPSS output for a factorial ANOVA what is the name of the table that highlights the main effects of our IVs?
Tests of Between-subjects effects
What is an interaction?
Effect of IV1 changes depending on IV2.
Whether there’s a difference depends on which group you’re in.
If gradient of the lines in the same - no interaction.
Important to discuss interactions in discussion section
What can we use as a follow up test if ANOVA is significant?
Planned contrasts
What are planned contrasts?
more systematic and used for testing specific prior hypotheses about differences between group means
make smaller number of comparisons, but can include multiple conditions in each comparison
What does using planned contrasts aim to achieve regarding variance?
Dividing the variance explained by the model
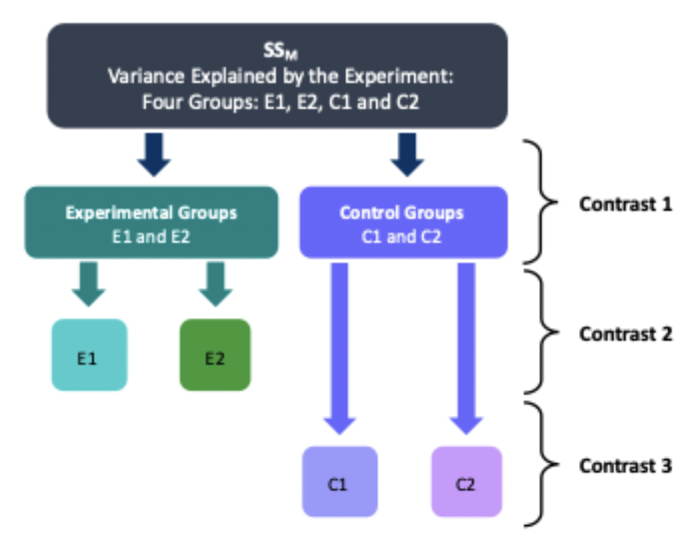
What is a deviation planned contrast?
Compares the mean of each condition to the overall mean
What is a simple planned contrast?
Compares the mean of each condition to either the first or last condition (e.g. compare with a control group)
What is a Helmert planned contrast?
Compares the mean of one condition to the average of all other conditions
What is a difference planned contrast?
The reverse of Helmert contrasts - compares the mean of a condition to the average of all previous conditions
What is a repeated planned contrast?
Compares sequential pairs of conditions
What is a polynomial planned contrast
looks for trends in the data
Within the rules of custom contrasts, how must contrasts be independent?
Each contrast must test a unique hypothesis
no double dipping
In a custom contrast, how many chunks can be compared at once
only 2
In a custom contrast, how many contrasts should you end up with?
K-1
you should always end up with one less contrasts than the number of groups
e.g. 4 conditions with simple contrast: 1v2, 1v3, 1v4
How should groups be weighted within custom contrasts?
each group gets assigned a weight/coefficient
positive weights compared with negative weights
sum of weights for a comparison = 0
To remove a group from a contrast, give it a weight of 0
If a group is singled out in a comparison, it should not be used in any subsequent contrasts
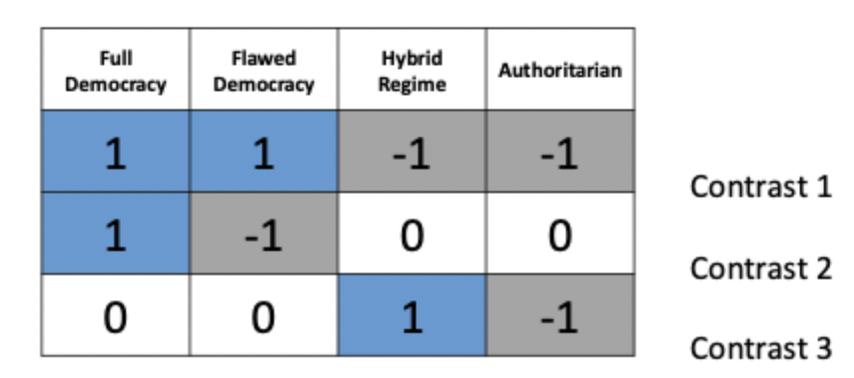
What are the two main types of effect size?
effect sizes based on the difference in means - scaled by variance
effect sizes that tell you what proportion of the variance has been explained by the test
What is eta squared?
Effect size used for a one way ANOVA
same as R-squared
What is partial eta squared?
effect size for use with factorial ANOVAs
SPSS will give this in ANOVA table
tells you the proportion of variance that is uniquely explained by the IV
What are eta squared values scaled between?
scaled between 0 and 1