Lecture 2 - Vectors and Projectile Motion
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is mechanics
A branch of physics dealing with motion of objects and the forces that cause the motion to change
Kinematics vs Dynamics
Kinematics = how objects move (Galileo)
Dynamics = why objects move (Newton)
Distance vs Displacement
Distance = scalar quantity = total length travelled
Displacement = vector quantity = change in position of the object from starting point
average speed and average velocity
average speed = distance/time taken
average velocity = displacement/time taken
acceleration
change in velocity/time taken
motion under gravity
at any given location on the earth and in the absence of air resistance, all objects fall with the same constant acceleration
addition of vectors in two dimensions
graphical method = ruler and protractor
analytical methods = trigonometry
What is a projectile
an object moving in two dimensions under the influence of Earth’s gravity, it’s path is a parabola
Why does vertical velocity vary during the time of flight of a soccer ball and horizontal velocity remain constant?
No force acts in the horizontal direction, force of gravity acts in the vertical direction
angle for maximum range
45 degrees
if you throw a ball vertically upwards and continue walking at a constant velocity, where will the ball land
in your hand
A plane is travelling with a package strapped underneath it, if the speed of the plane was doubled, how would it affect the drop time of the package and where will the package land in comparison to before
drop time will be the same since height package being dropped is the same BUT the package will land at twice the distance
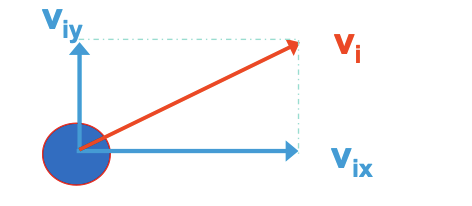
how to find the initial velocity in the x and y directions
v ix = v(i) cos theta
v iy = v(i) sin theta
time taken to reach maximum height in projectile motion equation
t = (v(i) sin theta)/g
maximum height reached in a projectile motion equation
y = v(iy) t + 0.5gt²
horizontal distance/range of a projectile equation
x = v(ix) t
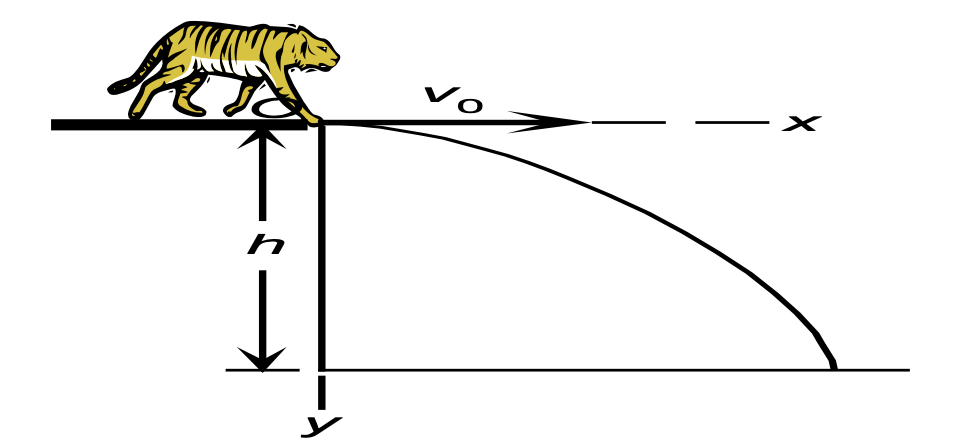
EG) A tiger leaps horizontally from a 6.5 m high rock with a speed of 3.5 m/s. How far from the base of the rock will she land?
1) find the time required to fall to the ground
y = y(i) + v(iy) t + 0.5gt²
-6.5 = 0 + 0 * t + 0.5(-9.8)t² = 1.15s
2) find the horizontal distance from the base of the rock
x = v(ix) t
= 3.5 × 1.15 = 4 m
EG) the pilot of an airplane travelling 160 km/h wants to drop a package 160m below to flood victims, the package should be dropped how many seconds before the plane is directly overhead
1) choose origin at the release point and set
x(i) =0
y(i) = 0
upward + y
2) find the time of the fall of the package
y = y(i) = v(iy)t + 0.5gt²
-160 = 0 + 0 x t + 0.5(-9.8)t²
t = 5.7