Unit 2 : Genetics, Inheritance, and Evolution
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIOL 1003
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
DNA
-made of nucleotides, double stranded
-in nucleus
-transcribed into RNA
gene
-a section on one strand of nucleotides
-in/on DNA
-transcribed into RNA
chromosome
-two strands of nucleotides, wrapped around proteins
-in cytoplasm
-passed from parent to offspring in meosis
nucleotide
link together to form the macromolecule in DNA or RNA
gene expression
process of going from DNA to RNA to protein
coding DNA strand to RNA
A → U
T → A
G → C
C → G
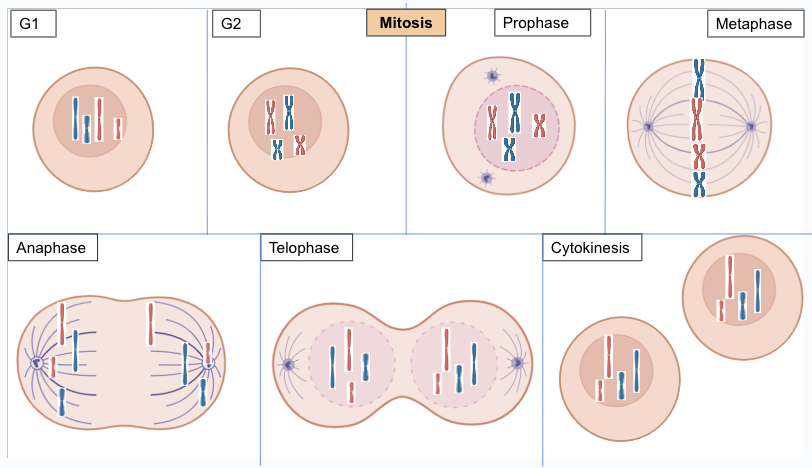
mitosis
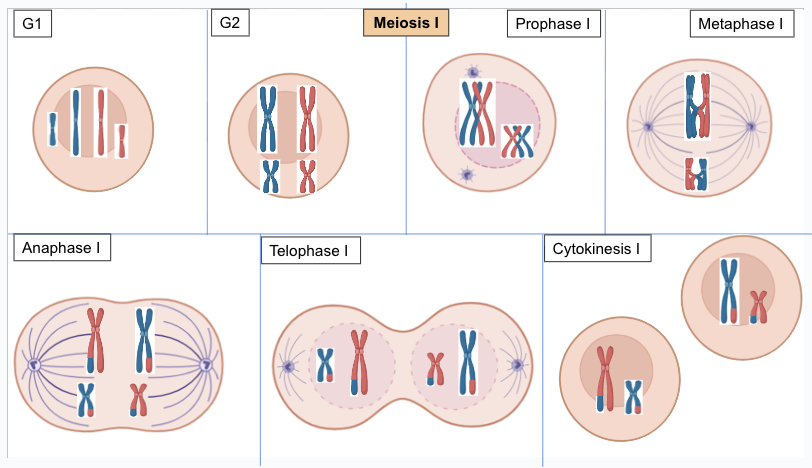
meiosis 1
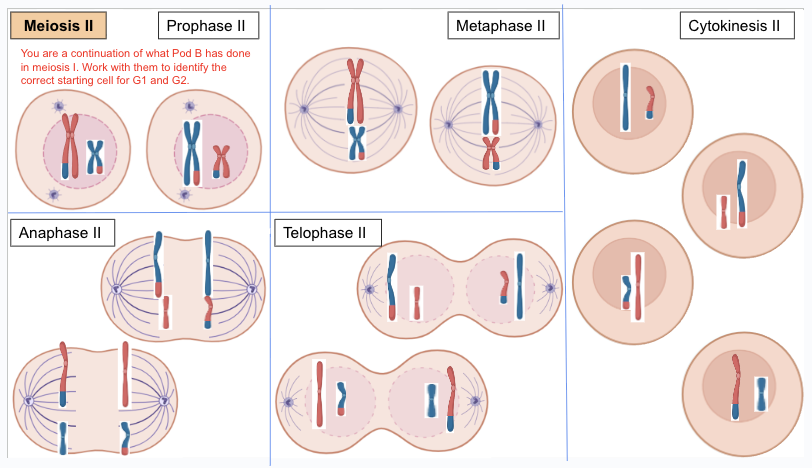
meiosis 2
sex
gamete size
anisogamy
when gametes exhibit a different size (female = large gamete / male = small gamete)
isogamy
when gametes are the same size
hermaphrodite
individual who produces both egg and sperm
cell cycle
series of events that take place in a cell as it grows and divides
sister chromatids
replicated, identical, result in a copy of DNA
must be same length and are the same alleles
homologous chromosomes
2 chromosomes that have the same GENES
must be the same length, can have different alleles
heterozygous
two different alleles for a specific gene (Aa)
homozygous
the same alleles for a specific gene (AA or aa)
ploidy
number of sets of a chromosome in a cell
haploid = 1 set / diploid = 2 sets
ways that sexual reproduction creates new alleles
crossing over
independent assortment
random fusion of gametes
independent assortment
the long chromosome pairs line up independent of how the short chromosome pairs line up (left and right)
during metaphase 1
mutation
error in replication
during interphase
crossing over
exchange genetic information between chromosome from sperm and chromosome from egg
during prophase 1
dominant
one chromosome must be present, masks recessive gene
recessive
two chromosomes must be present
co dominant
both phenotypes are fully expressed
incomplete dominant
there is no clear dominant allele, a different phenotype is expressed, “in between” phenotype
two fold cost of sex
cost of producing males → males cannot birth offspring
cost of passing on fewer genes → only 50% of genes (from each parent are passed down)
additional costs of sex
cost of finding a mate → time, energy
cost of infection → STD
muller’s ratchet
an explanation for why asexual reproduction can result in offspring that are less fit than their parent
sexual reproduction
producing offspring that are genetically different from yourself
deleterious alleles
harmful alleles that make an organism less fit
asexual reproduction
producing offspring that are genetically identical to yourself; clone
parasite or pathogen
organisms (or viruses) that harm other organisms
red queen hypothesis
an explanation for why sexual reproduction may be more adaptive than asexual reproduction; sexual reproduction speeds up evolution by creating more variation
coevolution
an arms race between pathogens and their hosts in which the host evolves to be resistant to the pathogen, and then the pathogen evolves to be able to infect the host, and so on
inbreeding
mating between closely related individuals
p value
a statistical measure used to determine the likelihood that an observed outcome is the result of chance (rather than the actual effect you are studying)
p < 0.05
reject the null (alternative hypothesis is supported)
p > 0.05
fail to reject the null (null hypothesis is supported)
disassortative
mating with mates who are different from yourself
cryptic female choice
when females control a male’s mating success by “deciding” whether or not to use the male’s sperm to fertilize her eggs, after they’ve already mated
bet hedging
spread risk across multiple options (offspring of multiple phenotypes) in order to increase the chances of survival and reproductive success of offspring