turbine 1
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
PT6 is divided into # separate rotating sections
gas section, power section
gas section
supplies hot high velocity gas to power section
powered by starter
gas generation drives the accessories
power section
uses high velocity gases to drive the prop through a reduction gearbox
PT6 is a ____ flow engine
reverse flow engine
inlet is at rear
exhaust is at front
jet propulsion is based on what
newtons 3rd law
types of reaction engine
rocket jet, ram jet, pulse jet
types of gas turbine engine
Turbo jet
Turbo fan
Prop fan
Turbo prop
Turbo shaft
rocket jet
operate outside Earth’s atmosphere because it carries its own source of oxygen and fuel
combustion starts and finishes until all fuel is burned
fuel is solid or liquid
ram jet
requires forward velocity to compress the air to support combustion
changes velocity to static pressure for combustion
pulse jet
similar to ram jet but has air inlet check valves
check valves open for intake and close for combustion
turbojet
1 airflow path through the engine
5 fundamental sections - inlet, compressor, combustion, turbine, exhaust

air inlet
divergent duct - air velocity decrease and static pressure increase
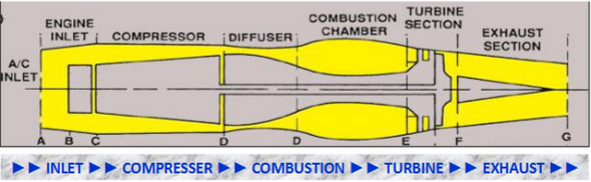
compressor
compresses air
increase static pressure and decrease air velocity
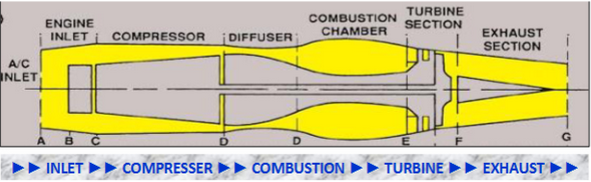
diffuser
divergent duct - increase static pressure and decrease air velocity
maximum potential energy
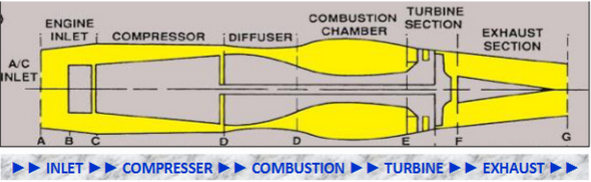
combustion
potential energy converts to kinetic energy
fuel mixed with high pressure air and ignited > BOOM
high energy and velocity air exiting combustion chamber flows rearward to power turbines
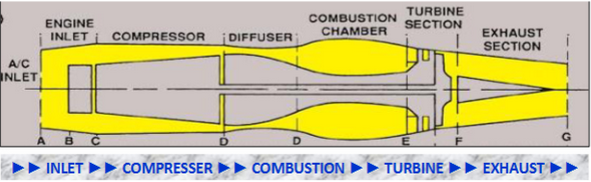
turbine
kinetic energy converts to mechanical energy
high energy and velocity air rotates compressor
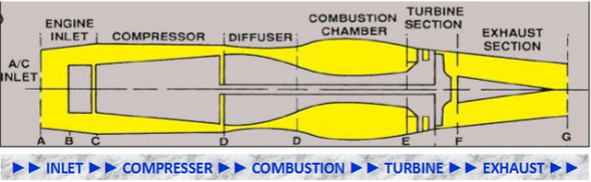
exhaust
convergent duct - static pressure decrease and velocity increase for thrust
high velocity and temperature for thrust
spool
single shaft with a compressor at the front and turbine at the back
compressor, shaft and turbine rotate at same rpm
turbofan
uses large fan assembly that increases mass airflow to create thrust
cruise at subsonic speeds with short field takeoff capabilities
turbofan inlet air is divided into
2 airflow - primary (core) and secondary (bypass)
what generates thrust in turbofan
secondary (bypass) airflow
thrust ratio
thrust of the fan vs thrust of the core
bypass ratio (BPR)
ratio of bypass airflow vs core airflow
fan pressure ratio
ratio of air pressure entering vs exiting the fan
aspect ratio
ratio of blades length vs width
turboprop
basic gas turbine engine to power a propeller through a reduction gearbox by fixed or free turbine
fixed turbine engine
prop is connected directly to the compressor section through the reduction gearbox
free turbine engine
engine is divided into gas generation section and power section
gas generator section powers an independent free-wheeling turbine that drives the propeller through the reduction gearbox
advantages of free power engine
Reduced noise levels
Improved fuel consumption
Environmentally cleaner
disadvantages of free power engine
Rapidly loses power due to increased drag at high speeds
Slower airspeed
free power vs fixed
Reduced noise and blade erosion > propeller is low rpm
Engine is easier to start, especially in cold weather
Lower vibration due to independent operation from gas generator section
Can apply brake to prop during aircraft loading without shutting down engine
turboshaft
uses gas turbine engine to turn drive shaft output
same as free turbine turboprop
helicopter, APU
propfan
consists of 2 contra-rotating unducted fans mounted aft of engine
high density air
low temperature, low altitude, low humidity
greater thrust and improved engine performance
low density air
high temperature, high altitude, high humidity
degrades engine performance
force
tendency to produce work
force = pressure x area
work
force acting on a body causing it to move
work = force x distance
power
rate of doing work
power = work/time
velocity
how far an object moves and how long and direction
velocity = distance/time
acceleration
change in velocity with respect to time
acceleration = change in velocity/time
mass
amount of matter in an object
momentum
product of mass and velocity
potential energy
stored energy
kinetic energy
release of stored energy
brayton cycle
constant-pressure thermodynamic cycle where fuel energy transformation occurs in gas turbine engine
intake pressure vs exhaust pressure > constant
pressure is inversely proportional to volume
temperature is proportional to pressure
brayton cycle concept in engine
fuel (chemical energy) > heat energy > gas pressure increase > kinetic energy in the form of high velocity airflow > mechanical energy as gas rotates turbines
gross thrust
total thrust produced without deduction of drag caused by the momentum of incoming air (ram drag)
net thrust
gross thrust - intake ram drag
how is thrust increased
increase mass airflow through the engine
increase jet velocity
ram drag
loss of thrust caused by increasing the velocity of air entering the engine (negative thrust)
ram effect (ram recovery)
ram drag is recovered by using a divergent inlet duct and high aircraft speed to increase mass airflow and jet velocity
Factors that affect thrust
Propulsive efficiency - through design
Thermal efficiency - through design
Inlet density - through atmospheric conditions
Selected compressor rpm - through operating conditions
propulsive efficiency
measure of effectiveness when engine converts kinetic energy into useful work
engine exhaust velocity vs aircraft speed
thermal efficiency
Ratio of the total work produced by the engine to the fuel (chemical) energy input
factors affecting thermal efficiency
Turbine inlet temperature
Compression ratio
Compressor & turbine efficiencies
Compressor inlet temperature
Burner efficiencies
inlet density
thrust is proportional to inlet air density
high density = high mass airflow = high thrust
factors that influence inlet density
Altitude
Temperature
Airspeed
propeller mount
prop reduction gearbox
exhaust
2 stage free power turbine
1 stage gas generator turbine surrounded by the combustion chamber
1 centrifugal and 4 axial compressor stage
air intake
accessories
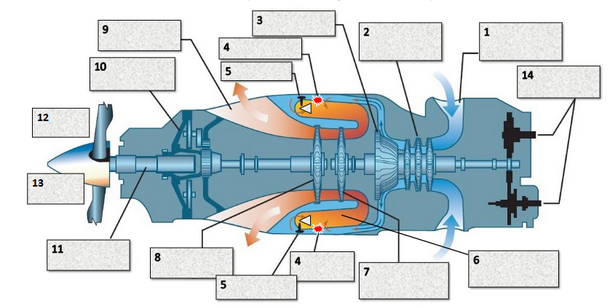
Air inlet
3 stage axial flow compressor
1 stage centrifugal compressor
Igniter
Fuel nozzle
Combustion chamber
Compressor turbine (gas producer)
Free power turbine
Exhaust outlet
Reduction gearbox
Propeller drive shaft
Propeller
Prop spinner
Accessory gearbox
hero’s aeolipile
converted steam pressure into mechanical power
sphere filled with water > heated > steam escapes through nozzle > sphere spins > reaction principle
chinese rocket
Solid fuel rocket using black powder, charcoal, sulfur and saltpeter (potassium nitrate)
first chemical reaction rocket
da vinci’s chimney jack
Used heat to drive a reaction type turbine to power a rotating skewer (rotisserie)
branca’s turbine device
Used steam-driven turbine (impulse wheel) to operate reduction gears
newton’s horseless carriage
Used reaction principle to propel a carriage
Frank Whittle
patented first turbojet aircraft engine
patented first turbofan aircraft engine
Hans Von Ohain
developed first axial flow engine
ultra low bypass
< 1:1 BPR
low bypass
<2:1 BPR
medium bypass
2:1 - 4:1 BPR
high bypass
4:1 - 9:1 BPR
ultra high bypass
> 10:1 BPR