Chapter 15 and 16 key terms
1/43
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Solubility
The maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specified temperature to form a saturated solution.
Solution Composition
The relative quantities of solute and solvent in a solution, expressed through various concentration units (e.g., mass percent, molarity).
Mass Percent
The concentration of a solution expressed as the mass of solute divided by the total mass of the solution, multiplied by 100%.
Mass percent
What is this formula for?
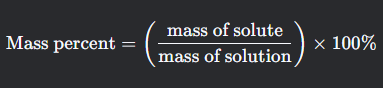
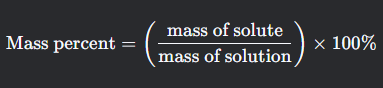
What is mass percent formula?
Molarity
The number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
Molarity
What is this formula?
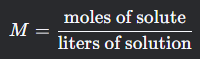
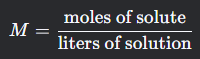
What is the molarity formula?
Dilution
The process of reducing the concentration of a solution by adding more solvent.
Dilution Equation
What is this formula?
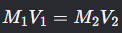
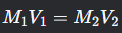
M1V1=M2V2
where M1M1 and V1V1 are the initial molarity and volume, and M2M2 and V2V2 are the final molarity and volume.
What is Dilution formula?
Stoichiometry of Solution Reactions
Calculations involving the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in solution-phase reactions, using molarity and volume.
Neutralization Reaction
A reaction between an acid and a base that produces water and a salt.
Normality
The number of equivalents of solute per liter of solution.
Normality
What is this formula?
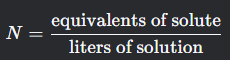
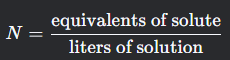
N= equivalents of solute over liters of solution
What is the normality formula?
Acids
Substances that increase the concentration of H⁺ ions in aqueous solution or proton (H⁺) donors.
Bases
Substances that increase the concentration of OH⁻ ions in aqueous solution or proton (H⁺) acceptors.
Acid Strength
The degree to which an acid dissociates in water.
Completely dissociate (e.g., HCl, HNO₃).
What’s a strong acid?
Partially dissociate (e.g., CH₃COOH).
What’s a weak acid?
Amphiprotic
A substance that can act as either an acid or a base (e.g., water, H₂O).
pH Scale
A logarithmic scale used to quantify the acidity or basicity of a solution.
pH < 7: Acidic
pH = 7: Neutral
pH > 7: Basic
What’s the pH scale range?
Buffered Solution
A solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added, typically containing a weak acid and its conjugate base.