L6 Depth perception
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is depth perception?
The ability to perceive the world in three dimensions despite receiving a two-dimensional image on the retina.
What are the four main cues to depth perception?
Oculomotor cues, pictorial (monocular) cues, motion-produced cues, and binocular disparity.
What are oculomotor cues?
Depth cues that rely on our ability to sense the position of ours eyes and eye muscle tension
What is convergence?
When eye muscles cause the eyes to move inward to focus on a nearby object.
Convergence is greater when an object is ?
closer
What is accommodation?
The lens bulging, by ciliary muscles tightening, to focus on a near object.
The position of the eyes and the shape of the lens are correlated with what?
the distance of the object we are observing
At what distances (in feet) are oculomotor cues effective?
Up to about 5–10 feet
What are pictorial cues?
Depth cues that can be depicted in a still 2D picture
What is not required for pictorial cues to work, and means it also works better
do not require viewing with both eyes
Why do pictorial cues often work better with one eye?
They eliminate binocular disparity, making depth perception clearer in some cases.
Examples of pictorial cues
TV, photos
Name 7 pictorial cues
overlap/interposition, relative size, relative height, atmospheric perspective, familiar size, linear perspective, shadowing

What is overlap (interposition/occlusion)?
When one object partially obscures another
What is relative size?
Objects appear smaller on the retina as they move farther away.
As distance increases, retinal image size ?
decreases
What is size constancy?
The perception that an object remains the same size despite changes in retinal image size.
What is Emmert’s Law?
Objects with the same retinal size appear physically larger when perceived as farther away.
What is relative height?
Objects closer to the horizon appear farther away.

According to relative height as a pictorial cue, if objects are above eye height then the lowest object is ?
further away

According to relative height as a pictorial cue, if objects are below eye height then the lowest object is ?
closest
How does atmospheric perspective affect depth perception?
Distant objects appear less sharp
Why do distant objects appear less sharp
more air and particles to look through
What is familiar size?
Using prior knowledge of an object’s size to judge its distance, regardless of its size on the retina
What is linear perspective?
Parallel lines appear to converge as they get further away
What is shading (attached shadows)?
Depth information provided by the way light and shadows fall on an object.
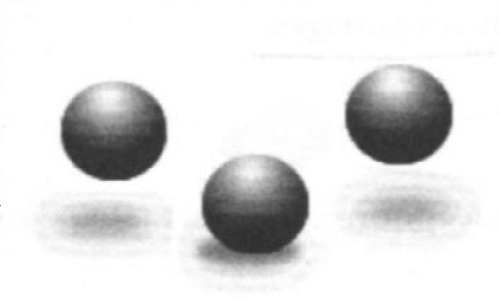
How do detached shadows contribute to depth perception?
They provide cues about an object’s position relative to a surface.
What is a texture gradient?
The gradual reduction in texture detail as a surface recedes into the distance.
What are motion-produced cues
cues that depend on movement of the observer, or movement of objects in the environment
2 motion-produced cues
motion parallax, and deletion and accretion
What is motion parallax?
Nearby objects appear to move faster than distant ones as we move.
What is deletion?
When an object moves in front of another, covering more of it.
What is accretion?
When an object moves away, revealing more of the background.
What is binocular disparity?
a cue that depends on the fact that slightly different images of a scene are formed on each eye
How does binocular disparity create depth perception?
The brain processes differences between images from each eye to judge depth.
What are corresponding retinal points?
Points that would overlap if one retina were superimposed on the other.
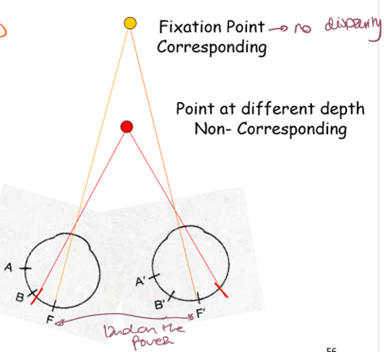
What are non-corresponding retinal points?
Points that do not align, creating disparity and depth perception.
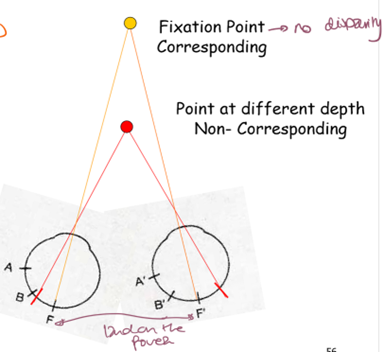
What happens when an object is fixated on?
It is imaged on corresponding retinal points, resulting in no disparity.
How does the cue of binocular disparity change with distance?
It diminishes as distance increases.
How is binocular disparity determined
by distance of the two eyes
What is hyperstereo?
An increased depth effect using exaggerated disparity, such as with a telestereoscope.
what does it mean to be stereoblind
inability to perceive depth or three-dimensional vision using binocular vision, which is the ability to combine and compare images from both eyes