🖨️ Lecture 4: Eukaryotic Transcription Initiation
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Transcription Initiation at Eukaryotic Promoters
Some Things to Keep in Mind
At most TATA and or Initiator Inr containing promoters
Transcription initiates and proceeds in one direction
At CpG island promoters
Transcription initiates in both directions
Polymerase stalls and falls off in one direction
Transcription proceeds in the other direction only
Textbook Note
Current textbook has no good CpG island initiation figure
Figure shown is from the 8th edition
RNA Polymerase II
Loaded onto promoters by GTFs
Pauses downstream of the initiation site
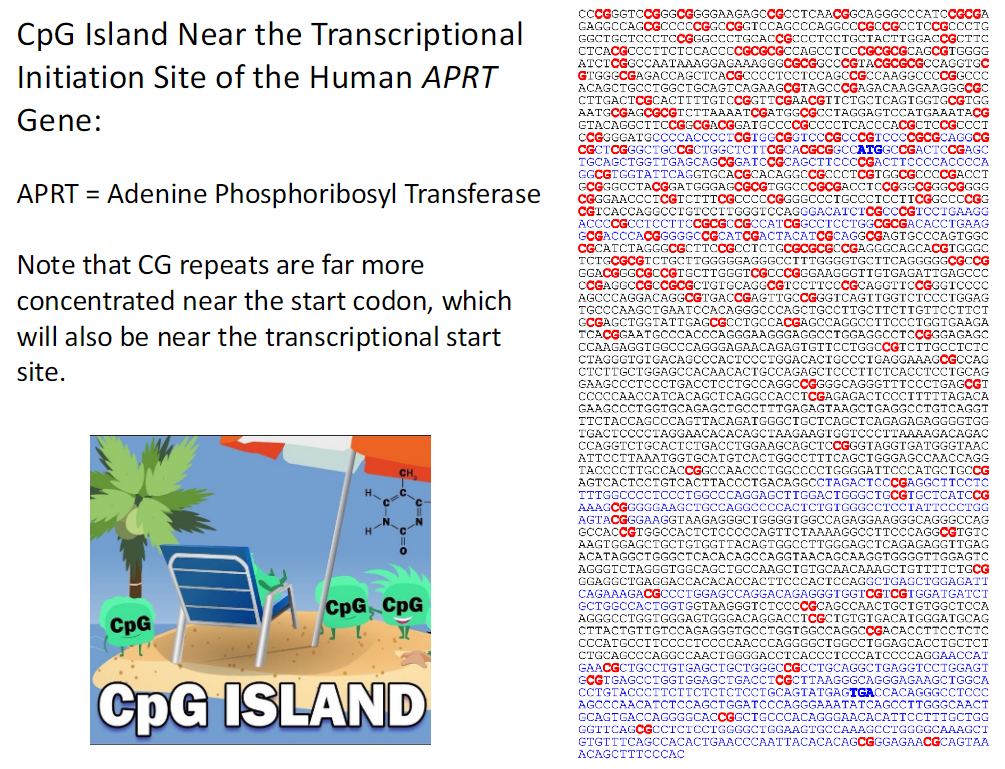
CpG Island Near the Transcriptional Initiation Site of the Human APRT Gene
APRT Gene
APRT stands for Adenine Phosphoribosyl Transferase
CpG Island Location
CpG islands are located near the transcriptional initiation site
CG repeats are highly concentrated near the start codon
Relationship to Transcription
The start codon is located close to the transcription start site
High CG density is associated with transcription initiation
CpG Islands and Gene Transcription
CpG Island Promoters
CpG islands occupy the promoters of about 70 percent of vertebrate genes
These genes are often essential
They are transcribed at a low but constant rate
Chromatin Features
CpG rich DNA contains fewer nucleosomes
Fewer nucleosomes make DNA easier to transcribe
Transcription Initiation
At CpG islands transcription initiates at any position within the island
Initiation site is not precisely defined
Transcription initiates in both directions
Transcription proceeds only toward the Open Reading Frame ORF
ORF is the DNA region that codes for protein
Textbook Note
Deamination and stability of methylated C in CpG islands in mammals is not important for this class

Bi Directional Transcription at CpG Islands
Experimental Approach
RNA is labeled with Br UTP
Br UTP is a UTP analogue
Labeling is done after ChIP using an RNA Pol II antibody
RNA is then sequenced
Results
Plot shows intensity of transcription across the analyzed locus
RNA synthesis initiates in both directions
Key Term
TSS means Transcription Start Site
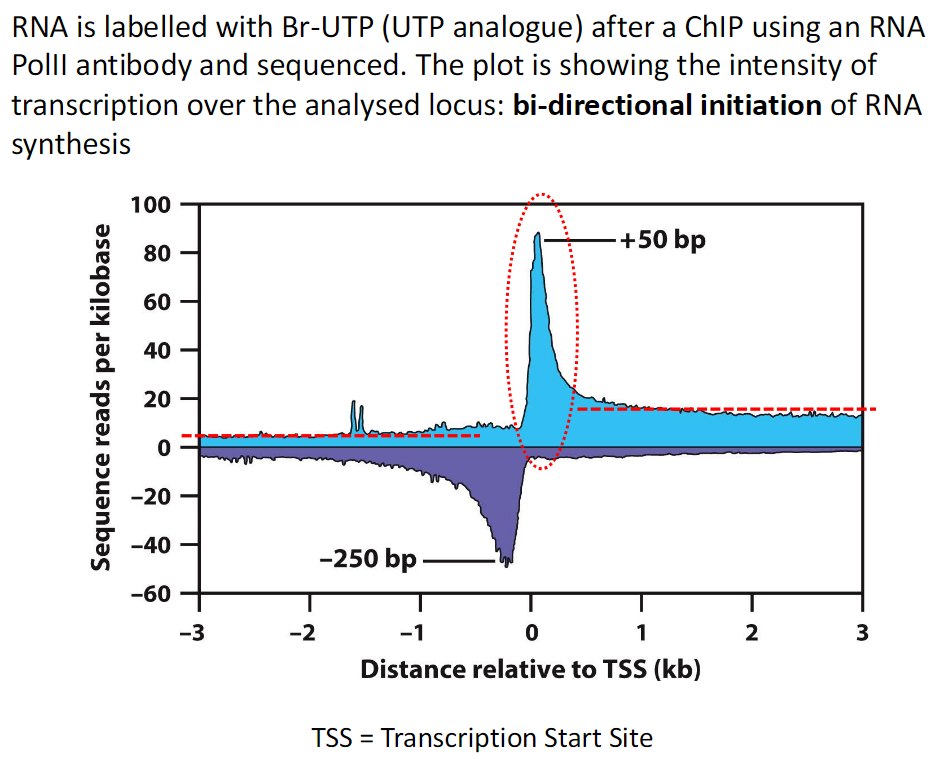
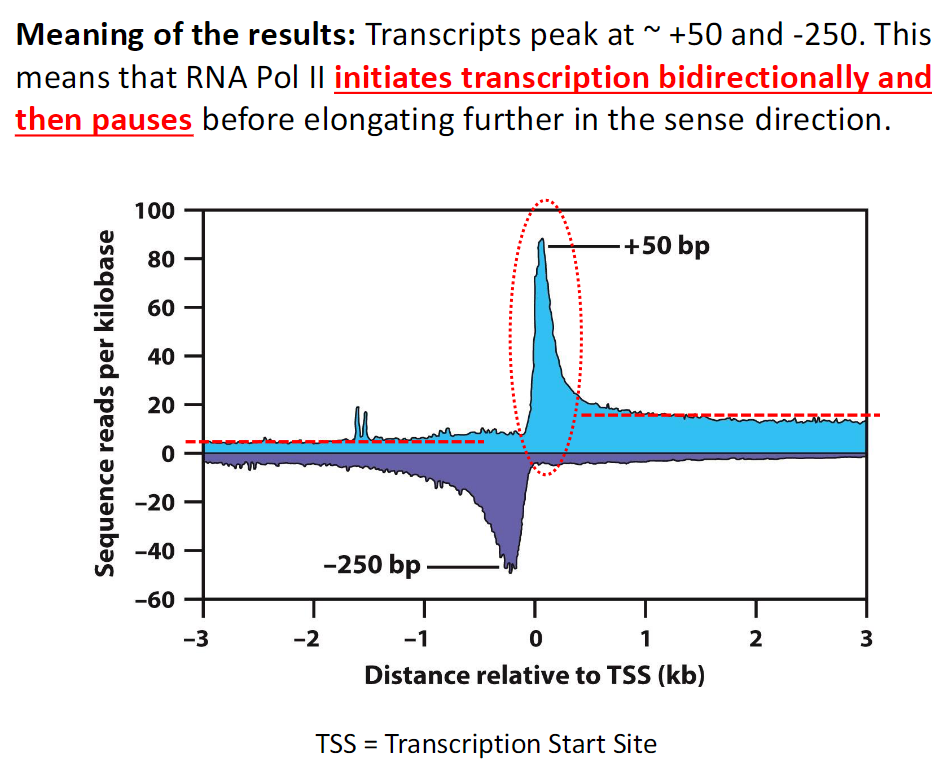
Meaning of the Results
Transcript Peaks
Transcripts peak at approximately +50 and −250
Interpretation
RNA Pol II initiates transcription in both directions
RNA Pol II then pauses before elongating further in the sense direction
Key Term
TSS means Transcription Start Site
Meaning of the Experiment
CpG Island Transcription
At CpG islands equal numbers of RNA polymerase initiate in both sense and antisense directions
Sense Direction
Sense transcripts pause before elongating further
Antisense Direction
Antisense transcripts pause at the opposite end of the CpG island
They do not continue transcription
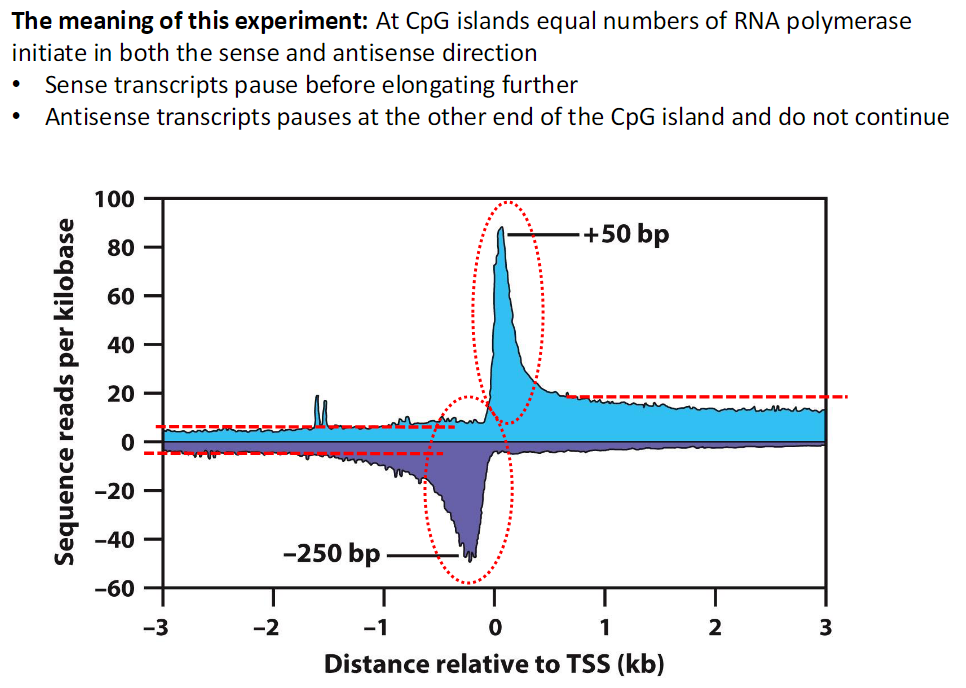
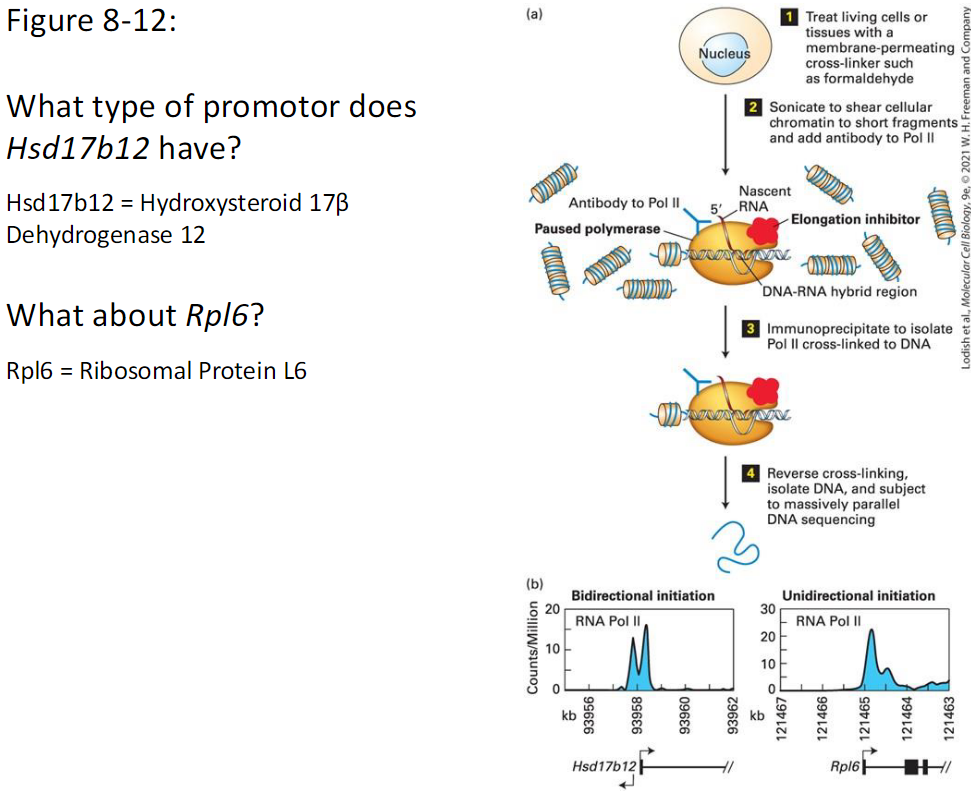
Figure 8-12 Promoter Type Analysis
Genes Shown
Hsd17b12: Hydroxysteroid 17β Dehydrogenase 12
Rpl6: Ribosomal Protein L6
Question
What type of promoter does Hsd17b12 have
What type of promoter does Rpl6 have
Experimental Overview
Cells treated with formaldehyde to cross-link DNA and proteins
Chromatin sheared by sonication
Antibody to RNA Pol II added
Paused polymerase and nascent RNA captured
Pol II–DNA complexes immunoprecipitated
Cross-links reversed
DNA sequenced
What the Figure Shows
RNA Pol II signal across each gene
Direction of transcription initiation is visible
Interpretation
Bidirectional initiation → CpG island promoter
Unidirectional initiation → TATA or Inr promoter
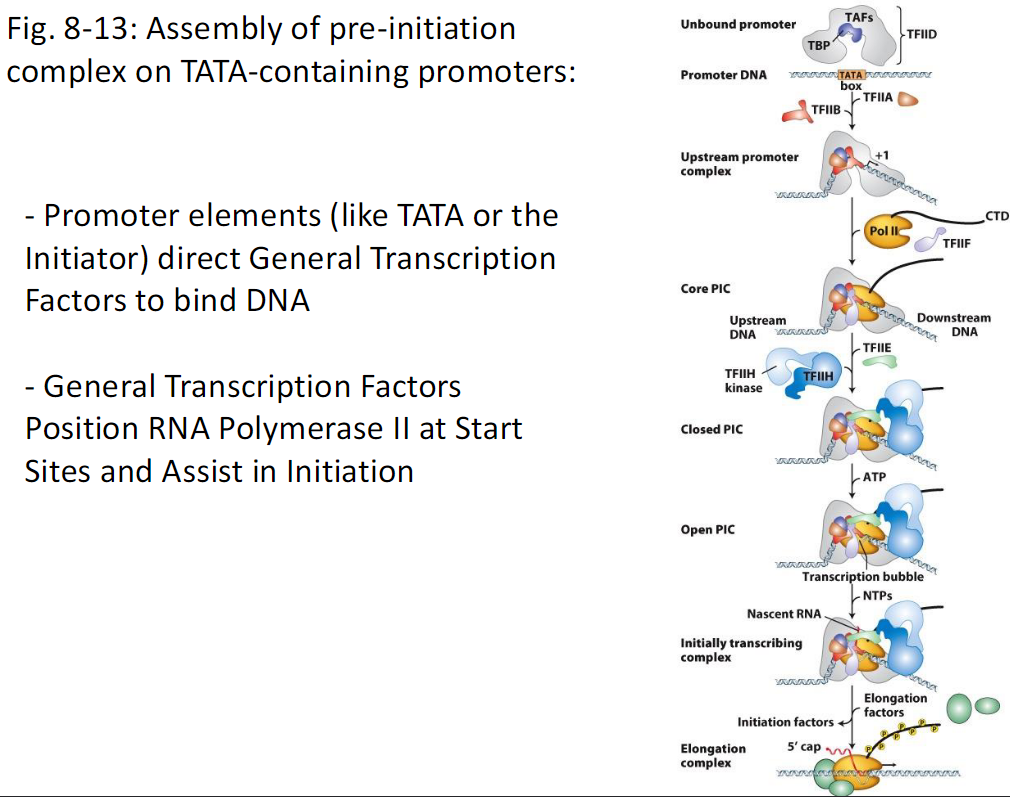
Assembly of Pre-Initiation Complex on TATA-Containing Promoters
Promoter Elements
Promoter elements such as the TATA box or Initiator direct General Transcription Factors to bind DNA
Unbound Promoter
Promoter DNA contains a TATA box
TFIID binds first
TFIID contains TBP and TAFs
TBP binds the TATA box
Upstream Promoter Complex
TFIIA and TFIIB bind to stabilize TBP on DNA
This forms the upstream promoter complex
Core Pre-Initiation Complex Core PIC
RNA Polymerase II binds with TFIIF
Pol II contains a CTD tail
TFIIE and TFIIH bind
Upstream and downstream DNA are positioned
This forms the closed PIC
Open Pre-Initiation Complex Open PIC
TFIIH uses ATP
DNA is unwound forming a transcription bubble
Initially Transcribing Complex
NTPs are added
Nascent RNA is synthesized
Initiation factors are present
Elongation Complex
RNA Polymerase II escapes the promoter
Elongation factors associate
5′ cap is added to the RNA
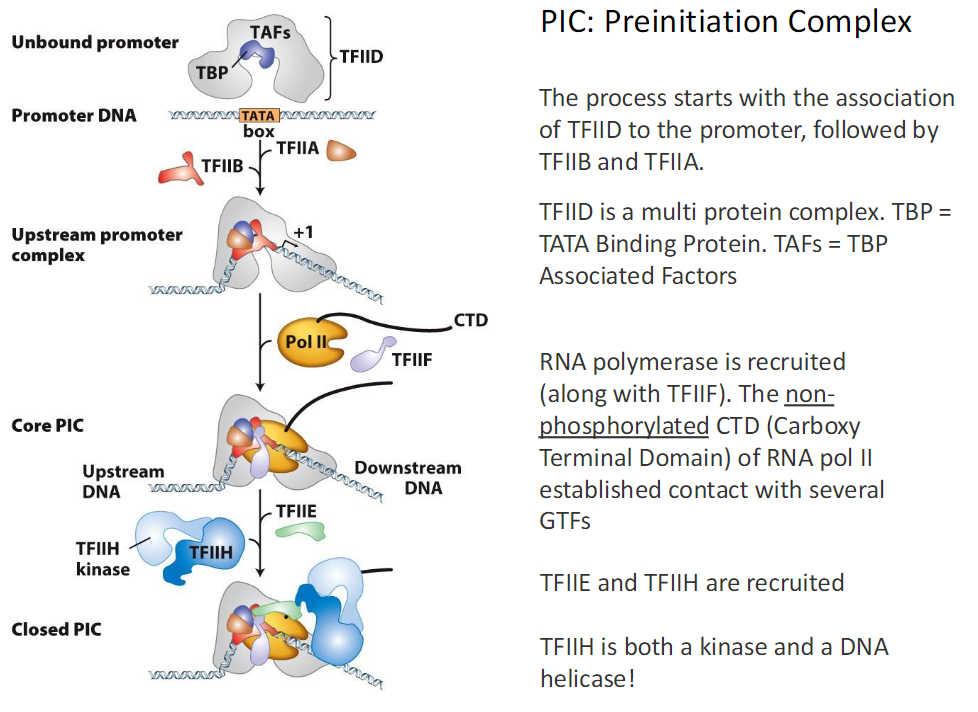
Unbound Promoter and Closed Pre-Initiation Complex
Unbound Promoter
Promoter DNA contains a TATA box
Consensus shown as ΥΥΥΛΛΑ TATA ΥΥΥ
TFIID binds first
TFIID is a multi protein complex
TBP means TATA Binding Protein
TAFs are TBP Associated Factors
Early Factor Binding
TFIIB binds after TFIID
TFIIA binds to stabilize the complex
This forms the upstream promoter complex
RNA Polymerase II Recruitment
RNA Polymerase II is recruited with TFIIF
Pol II contains a CTD
CTD means Carboxy Terminal Domain
CTD is non phosphorylated at this stage
Non phosphorylated CTD contacts several GTFs
Core Pre-Initiation Complex Core PIC
TFIIE and TFIIH are recruited
TFIIH functions as a kinase and a DNA helicase
Upstream and downstream DNA are positioned
This state is called the Closed PIC
Key Term
PIC means Pre-Initiation Complex
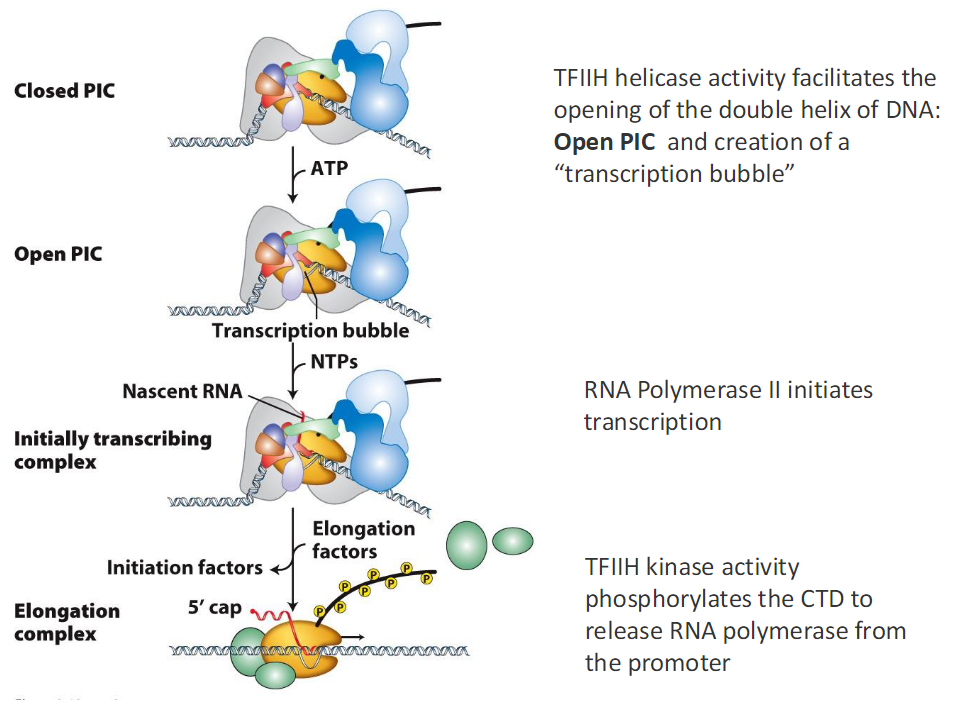
Closed PIC to Elongation
Closed PIC
TFIIH uses ATP
TFIIH helicase activity opens the DNA double helix
Open PIC
DNA opening creates a transcription bubble
Initially Transcribing Complex
NTPs are added
Nascent RNA is synthesized
RNA Polymerase II initiates transcription
Initiation factors are present
CTD Phosphorylation
TFIIH kinase activity phosphorylates the CTD
Phosphorylation releases RNA Polymerase II from the promoter
Elongation Complex
Elongation factors associate
RNA synthesis continues
5′ cap is added to the RNA
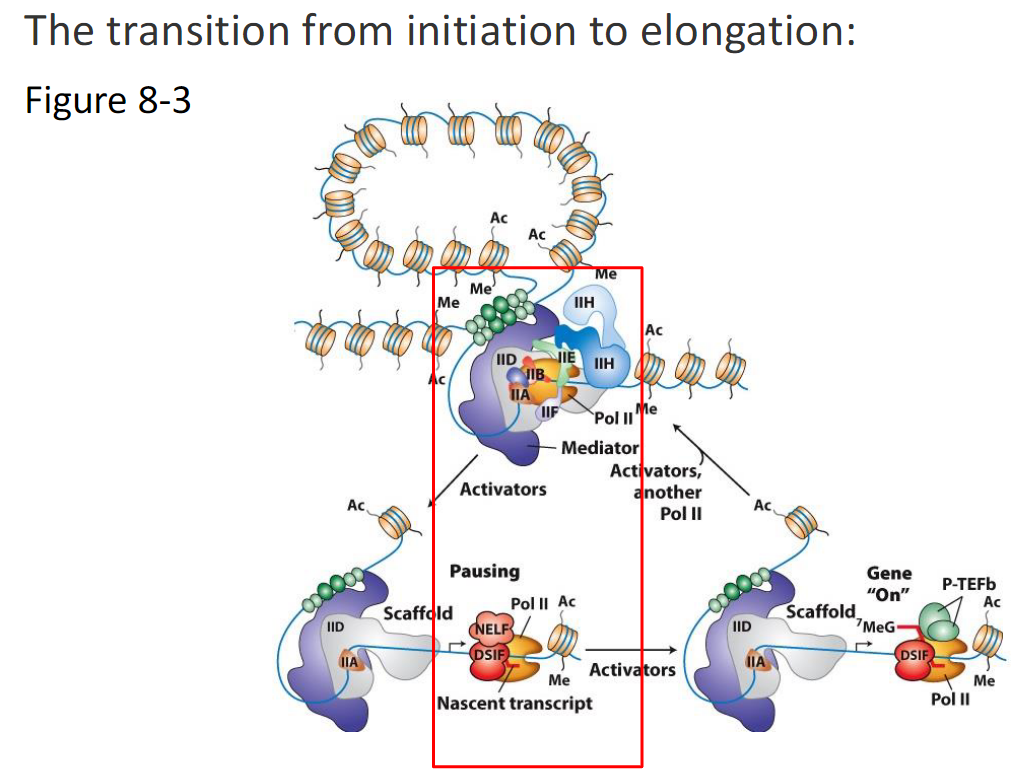
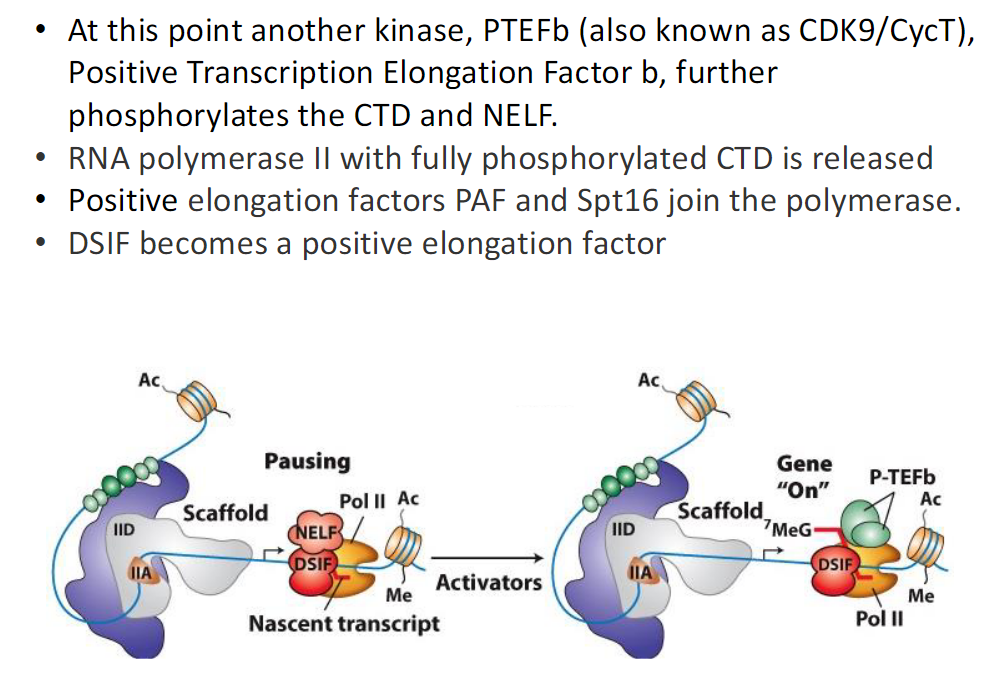
Transition from Initiation to Elongation (Figure 8-3)
Initiation State
RNA Polymerase II assembles with General Transcription Factors
Mediator and activators are present
Pol II begins transcription
Nascent transcript is produced
Pausing
RNA Polymerase II pauses shortly after initiation
Pausing is stabilized by NELF and DSIF
Polymerase remains near the promoter
Release from Pausing
P-TEFb is recruited
P-TEFb phosphorylates factors associated with Pol II
NELF dissociates
DSIF becomes a positive elongation factor
Elongation
RNA Polymerase II transitions into productive elongation
Elongation factors associate
Additional Pol II molecules can initiate
Gene is transcriptionally on
Scaffold
Some General Transcription Factors remain at the promoter
This scaffold allows repeated rounds of transcription
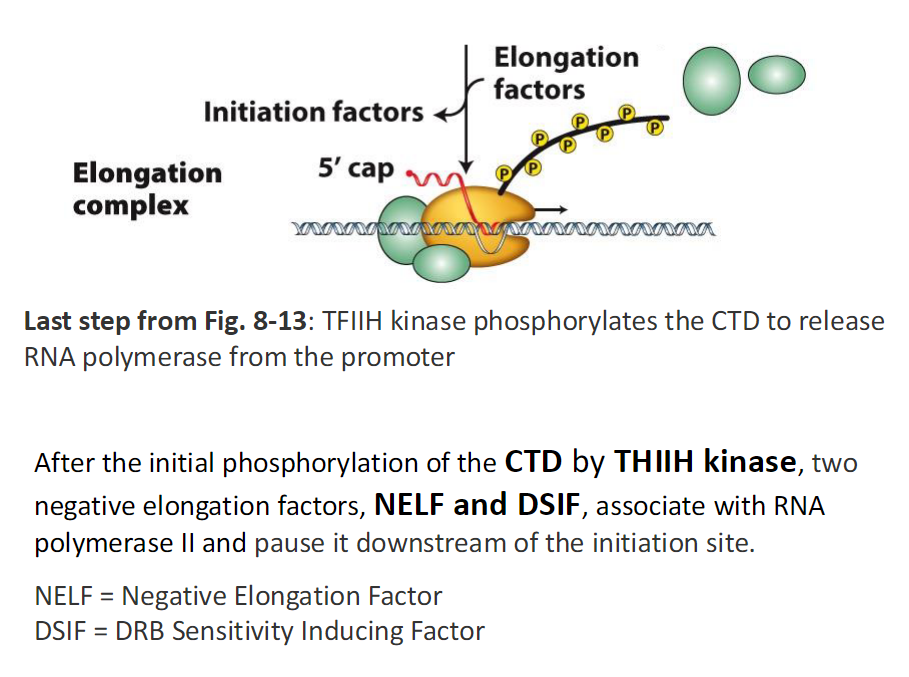
Elongation Factors and Polymerase Pausing
Last Step of Initiation (Fig 8-13)
TFIIH kinase phosphorylates the CTD
Phosphorylation releases RNA Polymerase II from the promoter
CTD Phosphorylation
Initial phosphorylation of the CTD occurs by TFIIH kinase
This marks the transition away from the promoter
Early Elongation and Pausing
After CTD phosphorylation RNA Polymerase II moves downstream of the initiation site
Two negative elongation factors bind
NELF associates with RNA Polymerase II
DSIF associates with RNA Polymerase II
These factors pause the polymerase
Elongation Complex
Elongation factors are present
Initiation factors dissociate
5′ cap is added to the nascent RNA
Key Terms
NELF means Negative Elongation Factor
DSIF means DRB Sensitivity Inducing Factor
Release into Productive Elongation
P-TEFb Kinase
Another kinase P-TEFb also called CDK9 Cyclin T
P-TEFb means Positive Transcription Elongation Factor b
Further Phosphorylation
P-TEFb further phosphorylates the CTD of RNA Polymerase II
P-TEFb also phosphorylates NELF
RNA Polymerase II with fully phosphorylated CTD is released
Elongation Factor Switch
NELF dissociates from the polymerase
DSIF switches from negative to positive elongation factor
Positive Elongation Factors
PAF joins the polymerase
Spt16 joins the polymerase
Gene Activation
RNA Polymerase II moves into productive elongation
Nascent transcript continues to grow
Gene is transcriptionally on
Promoter Scaffold
Some General Transcription Factors remain at the promoter
This scaffold allows additional Pol II to initiate
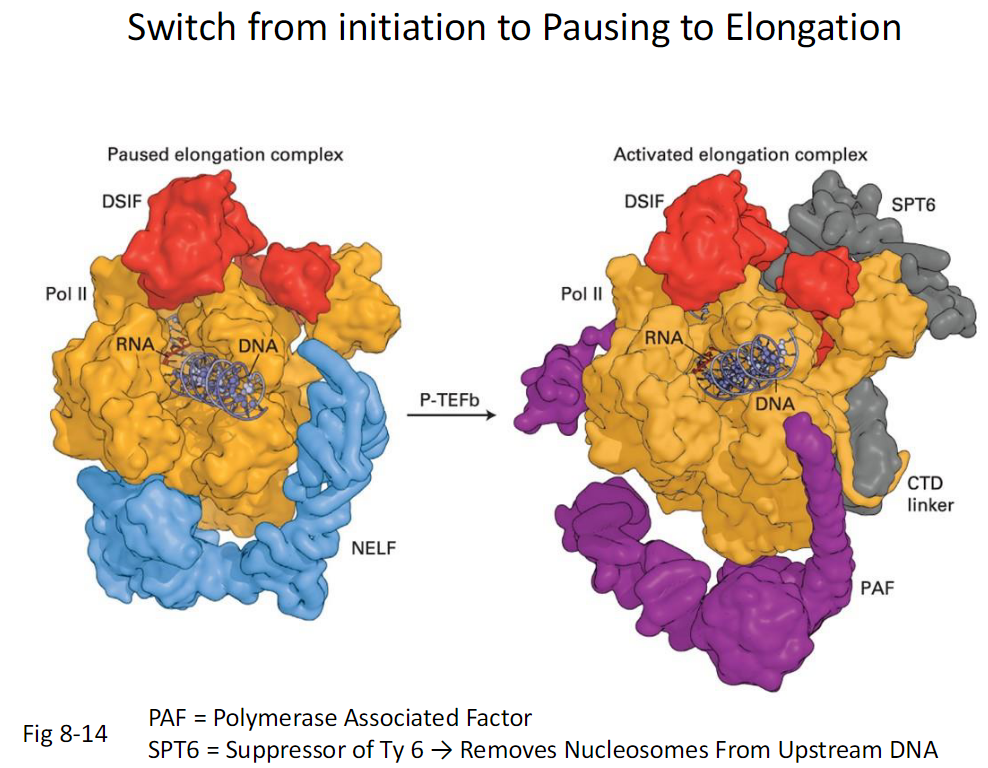
Switch from Initiation to Pausing to Elongation (Fig 8-14)
Paused Elongation Complex
RNA Polymerase II is paused
DSIF is associated
NELF is associated
CTD is not fully phosphorylated
Activated Elongation Complex
P-TEFb acts on the complex
CTD is further phosphorylated
NELF dissociates
DSIF remains and functions positively
Additional Elongation Factors
PAF associates with RNA Polymerase II
SPT6 associates with RNA Polymerase II
SPT6 removes nucleosomes from upstream DNA
Key Terms
PAF means Polymerase Associated Factor
SPT6 means Suppressor of Ty 6
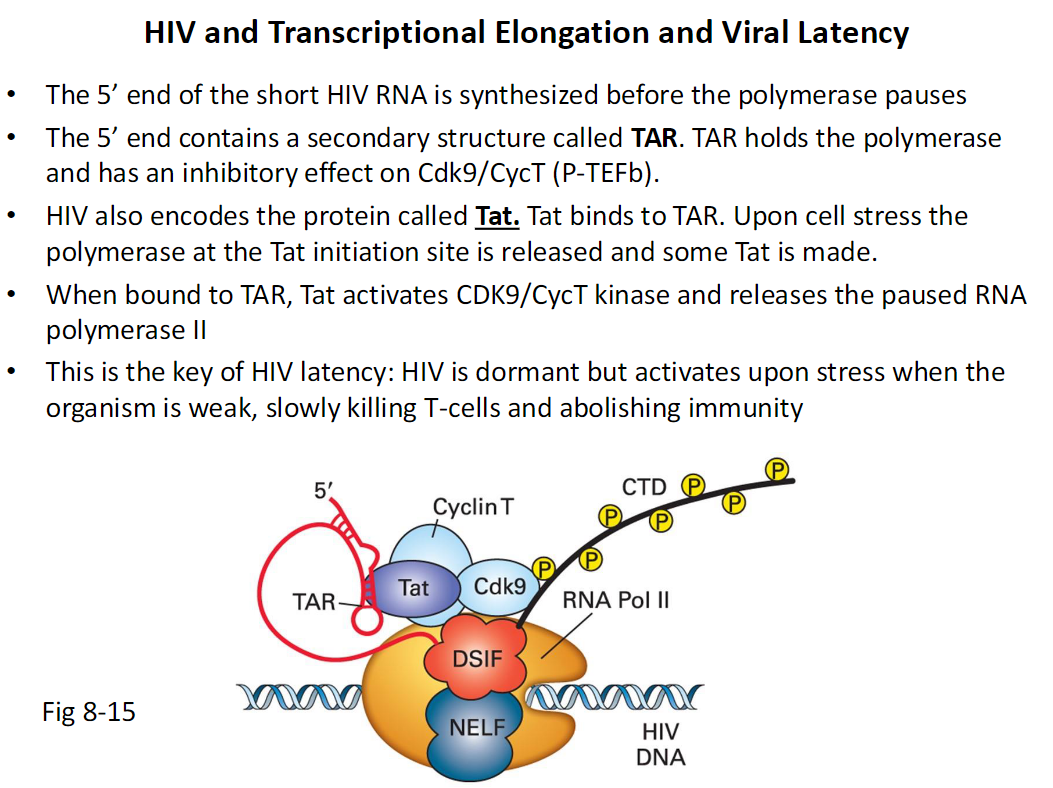
HIV Transcriptional Elongation and Viral Latency (Fig 8-15)
Early Transcription
The 5′ end of a short HIV RNA is synthesized
RNA Polymerase II pauses shortly after initiation
TAR Structure
The 5′ end contains a secondary RNA structure called TAR
TAR holds the paused polymerase
TAR inhibits Cdk9 Cyclin T also called P-TEFb
Tat Protein
HIV encodes a protein called Tat
Tat binds to TAR
Under cell stress paused polymerase is released
This allows some Tat protein to be produced
Release of Pausing
Tat bound to TAR activates CDK9 Cyclin T kinase
Activated P-TEFb releases paused RNA Polymerase II
Viral Latency
HIV remains dormant when polymerase is paused
Stress activates transcription
Activated virus kills T cells and abolishes immunity