cardiac output and blood
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
phys lecture 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
functions of the cardiovascular system
delivery of O2, glucose and other nutrients to active tissues
removal of CO2, lactate and other waste products from active tissues
transport of metabolites and other substances to and from storage sites
transport of hormones, antibodies and other substances to site of action
moves blood to transport stuff in the blood
total body water (tbw) of males and females
60% in males
~50% in females
distribution of body water between inside and outside of cells
two thirds found in the ICF
one third found in the ECF
extracellular fluid found in solid organs/ tissue is known as
interstitial fluid
plasma, lymph, and interstitial fluid are all components of:
the extracellular fluid
a person weighing 70kg holds about how many liters of blood?
5L
blood makes up what percentage of our body mass?
6-8%
percentage composition of plasma and cells in the blood:
55% plasma
45% cells
cells in the blood:
erythrocytes (rbc)
leukocytes (wbc)
platelets
role of erythrocytes
deliver oxygen and nutrients to the cells
remove carbon dioxide and waste from the cells
role of leukocytes
immune response
role of platelets
blood clotting
arterioles
small arteries
venules
small veins
which blood vessels accept blood from the ventricles of the heart?
arteries
which blood vessels deliver blood to the atria of the heart?
ventricles
blood capillaries
where exchange of materials occur between the blood and body cells
systemic arteries have:
oxygenated blood
pulmonary veins have:
oxygenated blood
blood flow through the vascular system is produced by the (?) blood pressure
arterial to venous
high blood pressure in (1) vs low blood pressure in (2)
arteries
veins
diastole
relaxation of the heart
heart fills with blood
systole
contraction of the heart
heart empties out blood
diastolic pressure
lowest systemic arterial pressure during diastole (80mmHg avg)
systolic pressure
highest systemic arterial pressure during systole (120mmHg avg)
how to write blood pressure
systemic arterial pressure as systolic/ diastolic e.g. 120/80mmHg
pulse pressure
the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure (40mmHg)
mean arterial pressure
the arterial pressure averaged over the cardiac cycle (90-95 mmHg)
cardiac output
the amount of blood pumped by the heart each minute
flow rate out of one side of the heart by volume pumped per unit time
cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate
5-5.5L/min
stroke volume
volume of blood pumped by a ventricle in one contraction
70-80ml avg
heart rate
number of contractions per unit time
generally beats per minute
70 beats/min avg
venous return
flow rate into the heart
5-5.5L/min
end diastolic volume
volume of blood present in the heart before it contracts
the end volume of diastole
~130 ml
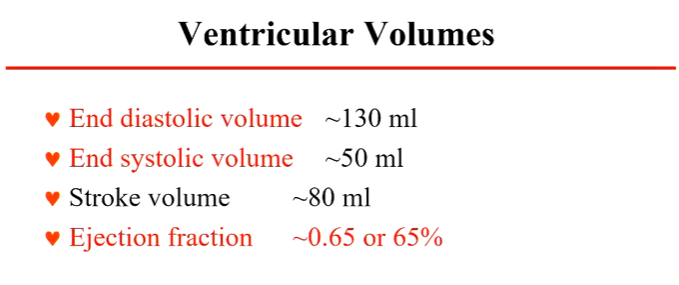
end systolic volume
volume of blood present in the heart before it relaxes
the end volume of systole
~50 ml
ejection fraction
~0.65 or 65%