Chapter 3 Bio
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
1
New cards
The four major classes of macromolecules are…
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
2
New cards
All organic molecules contain ________.
carbon
3
New cards
Monomers are…
individual subunits of macromolecules
4
New cards
Monomers are linked via ____ bonds to form _______.
covalent; polymers
5
New cards
Dehydration synthesis
combining molecules via loss of water
6
New cards
Hydrolysis (Dehydration reaction)
breaking down polymers into individual monomers via the addition of water
7
New cards
Biological molecules that catalyze or speed up reactions are called _______.
enzymes
8
New cards
Carbohydrates provide __ to the body in the form of ______.
energy; glucose
9
New cards
\
Monosaccharides end with the suffix ______
Monosaccharides end with the suffix ______
\-ose
10
New cards
Monosaccharides contain the carbonyl group _____
C=O
11
New cards
Greek numeral prefix before the -ose in a monosaccharide indicates the number of ______.
carbons
12
New cards
Glucose is an important source of _______.
energy
13
New cards
Galactose is part of _______.
lactose (milk sugar)
14
New cards
Fructose is part of ______.
sucrose (fruit sugar)
15
New cards
Plants store ____ in fruit to use as __________ for animals, in order to get them to disperse their seeds
fructose; bait
16
New cards
Monosaccharides assume _____ structure in aqueous solution.
ring
17
New cards
Disaccharides form when…
two monosaccharides are linked in a dehydration reaction
18
New cards
When two sugars are linked together (to become a disaccharide), they form a _____ bond.
glycosidic
19
New cards
Polysaccharides are…
long chain of monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages
20
New cards
The more complex the molecule, the _____ it is to break down.
harder
21
New cards
Starch is…
energy storage in plants
22
New cards
Cellulose is…
cell walls of plants
23
New cards
Chitin is…
cell walls of fungi and exoskeletons of arthropods
24
New cards
Glycogen is…
energy storage in animals
25
New cards
Amylose is ____ glucoseand monomers are joined by ________ glycosidic bonds
unbranched; a 1-4
26
New cards
Amylopectin is ___ glucose, and monomers are joined by ________ and ___________ glycosidic bonds.
branched; a 1-4; a 1-6
27
New cards
Cellulose is _____ glucose, and monomers are joined by ________ glycosidic linkages.
unbranched; B 1-4
28
New cards
In cellulose, every glucose monomer is _______ relative to the next one, which results in a _______,__ fibrous structure.
flipped; linear
29
New cards
Lipids ______ water.
repel
30
New cards
Lipids are a diverse group of _________.
non-polar hydrocarbons
31
New cards
Lipids are _______ energy stores.
long-term
32
New cards
Lipids provide _____ from environment for plants and animals.
insulation
33
New cards
Fats contain 2 main parts, ___ and ______, that form chains with each other.
glycerol and fatty acids
34
New cards
Triglyceride is formed by joining ___ fatty acids to a ____ backbone.
three; glycerol
35
New cards
Ester linkages have a ___________ bond.
double covalent
36
New cards
Glycerol molecules are attached to the fatty acids via ______ linkage.
ester
37
New cards
Double covalent bond gives a ______ structure that holds it in place and keeps it straight.
stronger
38
New cards
Saturated fatty acids contain ______ carbon-carbon double bonds in the carbon backbone.
no
39
New cards
Saturated fatty acids are _____ at room temperature
solids
40
New cards
Unsaturated fatty acids contain ________ carbon-carbon double bond in the carbon chain backbone.
at least one
41
New cards
Most unsaturated fats are ______ at room temperature.
liquids
42
New cards
Cis configuration in fats
hydrogens on the same side of chain
43
New cards
Trans configuration in fats
hydrogens on opposite side of chain
44
New cards
Essential fatty acids are….
required but not synthesized by the body (must be part of diet)
45
New cards
Waxes are…
long fatty acid chains esterified to long chain alcohols
46
New cards
Waxes are ______, which means they prevent water from sticking to surface
hydrophobic
47
New cards
Phospholipids are…
molecule with two fatty acids and a modified phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone
48
New cards
Phospholipids are _____, they have a hydrophobic portion and a hydrophilic portion
amphipathic
49
New cards
Steroids have a ______ structure, meaning four linked carbon rings and a short tail.
closed-ring
50
New cards
Steroids have a different form than that of other lipids because…
they move around in the bloodstream to get to other parts of the body and send signals
51
New cards
Steroids are ___, meaning they are insoluble in water
hydrophobic
52
New cards
_____ is the most common steroid, and is synthesized in the liver
Cholesterol
53
New cards
Functions of life are maintained solely by ______.
proteins
54
New cards
The most abundant organic molecule is ______.
proteins
55
New cards
Proteins are _____ molecules, meaning that they all have a function.
action
56
New cards
What macromolecule are most enzymes classified as?
Proteins
57
New cards
Nearly all enzymes end in the suffix -____.
\-ase
58
New cards
Catabolic enzymes…
breakdown substrates
59
New cards
Anabolic enzymes…
build substrates, or more complex molecules
60
New cards
Catalytic enzymes…
speed up or slow down a reaction
61
New cards
The function of digestive enzymes (such as amylase, lipase, pepsin, and trypsin) is to…
help digestion of food by catabolizing nutrients into momeric units
62
New cards
The function of transport proteins (such as hemoglobin and albumin) is to…
carry substances in the blood or lymph throughout the body
63
New cards
The function of structural proteins (such as actin, tubulin, and keratin) is to…
construct different structures, like the cytoskeleton
64
New cards
The function of hormones (such as insulin and thyroxine) is to…
coordinate the activity of different body systems
65
New cards
The function of defense proteins (such as immunoglobulins) is to…
protect the body from foreign pathogens
66
New cards
The function of contractile proteins (such as actin and myosin) is…
muscle contraction
67
New cards
The function of storage proteins (such as legume storage proteins and egg white, or albumin) is to…
provide nourishment in early development of the embryo and the seeling
68
New cards
Amino acids are the monomers that make up _____.
proteins
69
New cards
The structure of amino acids contains…
* Central carbon atom (a-carbon)
* Amino group (-NH₂)
* Carboxyl group (-COOH)
* Hydrogen
* Side chain (R-group)
* Amino group (-NH₂)
* Carboxyl group (-COOH)
* Hydrogen
* Side chain (R-group)
70
New cards
Each amino acid has a different _____-group.
R
71
New cards
The purpose of R-groups is to determine the ______ of each amino acid.
chemical nature
72
New cards
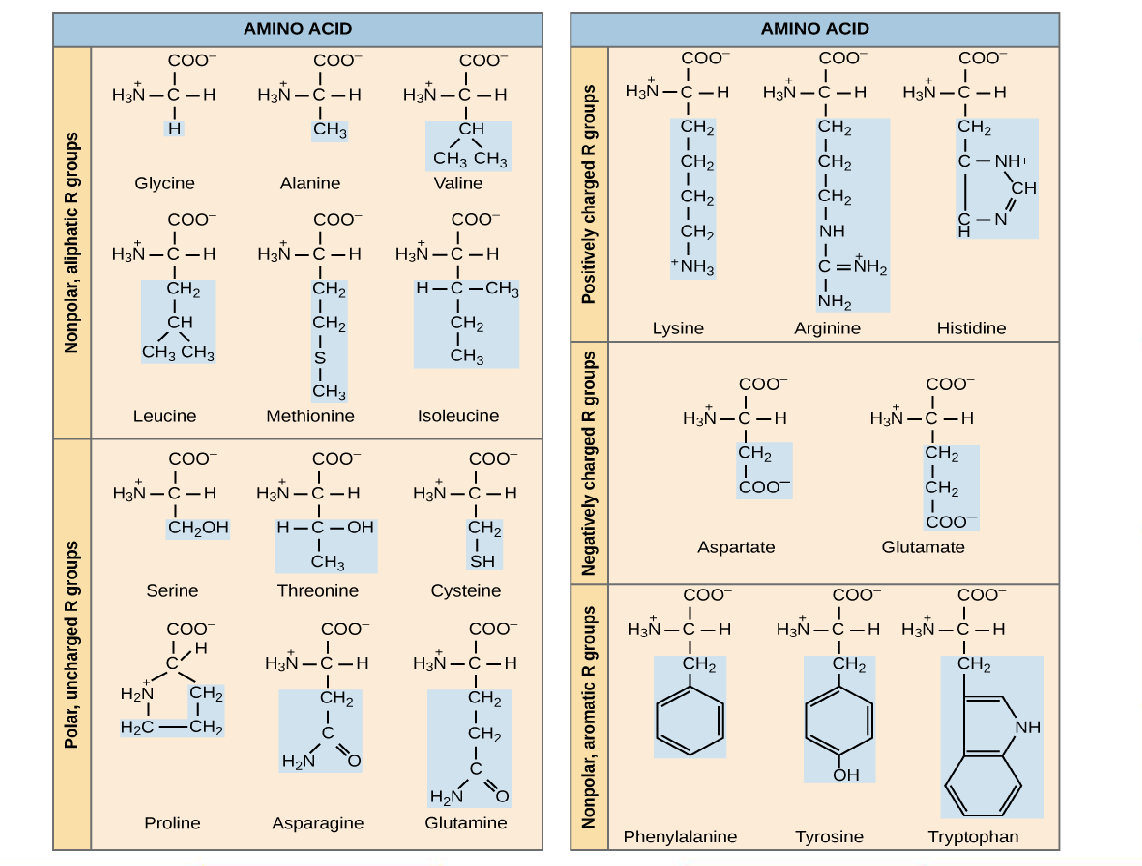
Be familiar with some of these and what makes their R-groups unique (not completely memorized but just know some of them)
Okay!
73
New cards
Amino acids are represented by a ___ upper-case letter or _____ letters. (ex: Valine = V or Val)
single; three
74
New cards
Essential amino acids ______ produced naturally in humans, so they must be supplied in diet.
are not
75
New cards
Some essential amino acids include…
\
* Isoleucine
* Leucine
* Cysteine
* Isoleucine
* Leucine
* Cysteine
76
New cards
Shape, size and function of amino acids is determined by…
the sequence and number of amino acids
77
New cards
The length of amino acid chains determines…
how the proteins function
78
New cards
Amino acid monomers are linked via…
peptide bond formation
79
New cards
Polypeptide chain
a chain of amino acids joined together in peptide linkages
80
New cards
Protein
a polypeptide or multiple polypeptides with a biological function
81
New cards
The difference between a polypeptide and a protein is that…
proteins have specific unique structures and functions
82
New cards
Many proteins are modified following _______.
translations.
83
New cards
Primary structure
the unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (order of proteins matters)
84
New cards
What could happen if there was a change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA?
it could change the amino acid and lead to change in structure and function
85
New cards
Sickle cell anemia is an example of how…
change in amino acids can impact human health
86
New cards
Sickle cells are __ shaped, normal cells are ___ shaped.
crescent; disc
87
New cards
Secondary structure
local folding of the polypeptide
88
New cards
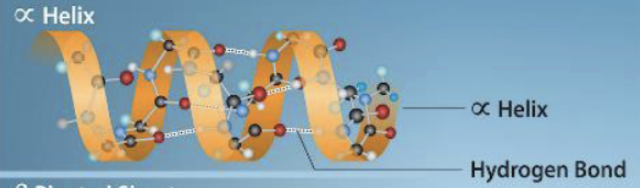
a-helix
formed by hydrogen bond between oxygen in carbonyl group and an amino acid 4 positions down the chain
89
New cards
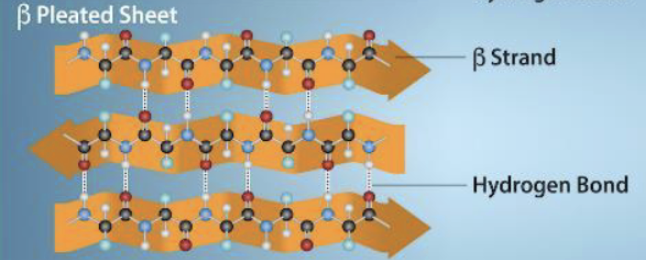
B-pleated sheet
hydrogen bonding between atoms on the backbone of the polypeptide chain
90
New cards
a-helix and B-pleated sheets are ____ structures of proteins.
secondary
91
New cards
_____ structure, or ORDER, effects if the chain comes out as a helix or pleated sheet.
Primary
92
New cards
Tertiary structure
the unique three dimensional structure of a polypeptide
93
New cards
Tertiary structures are formed due to…
chemical interactions between R-group on amino acids
94
New cards
R-groups with like charges are ____ from one another
repelled
95
New cards
R-groups that are _____ will cluster in interior of protein
hydrophobic
96
New cards
_____ side chains form ____ bridges in tertiary structure.
Crysteine; disulfide
97
New cards
In tertiary structure, hydrophobic interactions…
create space
98
New cards
In tertiary structure, ionic bonding is…
weak and water can get in
99
New cards
In tertiary structure, hydrogen bonding is…
easy to break apart
100
New cards
In tertiary structure, disulfide linkages are _____.
stronger