Period 2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Cecil Calvert, Second Lord Baltimore
In 1634, Cecil Calvert (Second Lord Baltimore) was the son of George Calvert (First Lord Baltimore). Cecil Calvert set about making his father's dream of a Maryland colony that would be a haven for Catholics in America.

Act of Toleration
The first colonial statue granting religious freedom to all Christians, but it called for death of all non-Christians. It was created to provide a safe haven for Catholics.
Roger Williams
A respected Puritan minister who believed that the individual's conscience was beyond the control of any civil or church authority. He was banished from the Bay colony for his beliefs. In 1636, he founded the settlement of Providence.

Providence
This settlement was founded in 1636 by Roger Williams.

Anne Hutchinson
This Puritan believed in antinomianism and was banished from the Bay colony because of her beliefs. In 1638, she founded the colony of Portsmouth.

antinomianism
The idea that faith alone, not deeds, is necessary for salvation.

Rhode Island
In 1644, Parliament granted Roger Williams a charter, joining Providence and Portsmouth into a single colony, Rhode Island.
Halfway covenant
In the 1660s, people could now take part in church services and activities without making a formal commitment to Christ. It was created because the next generation of colonists were less committed to religious faith, but churches still needed members.

Quakers
Members of the Religious Society of Friends who believed in the equality of men and women, nonviolence, and resistance to military service.

William Penn
In 1861, the royal family paid a large debt by granting his family a large parcel of American land. This Quaker, formed a colony that he named Pennsylvania.

Holy Experiment
William Penn put his Quaker beliefs to the test in his colony, Pennsylvania. He wanted the colony to provide a religious refuge for Quakers and other persecuted people, enact liberal ideas in government, and generate income and profits for himself.

Charter of Liberties
In 1701, the Pennsylvania colony created this written constitution which guaranteed freedom of worship for all and unrestricted immigration.

rice plantations
These plantations required a large land area and many slaves.
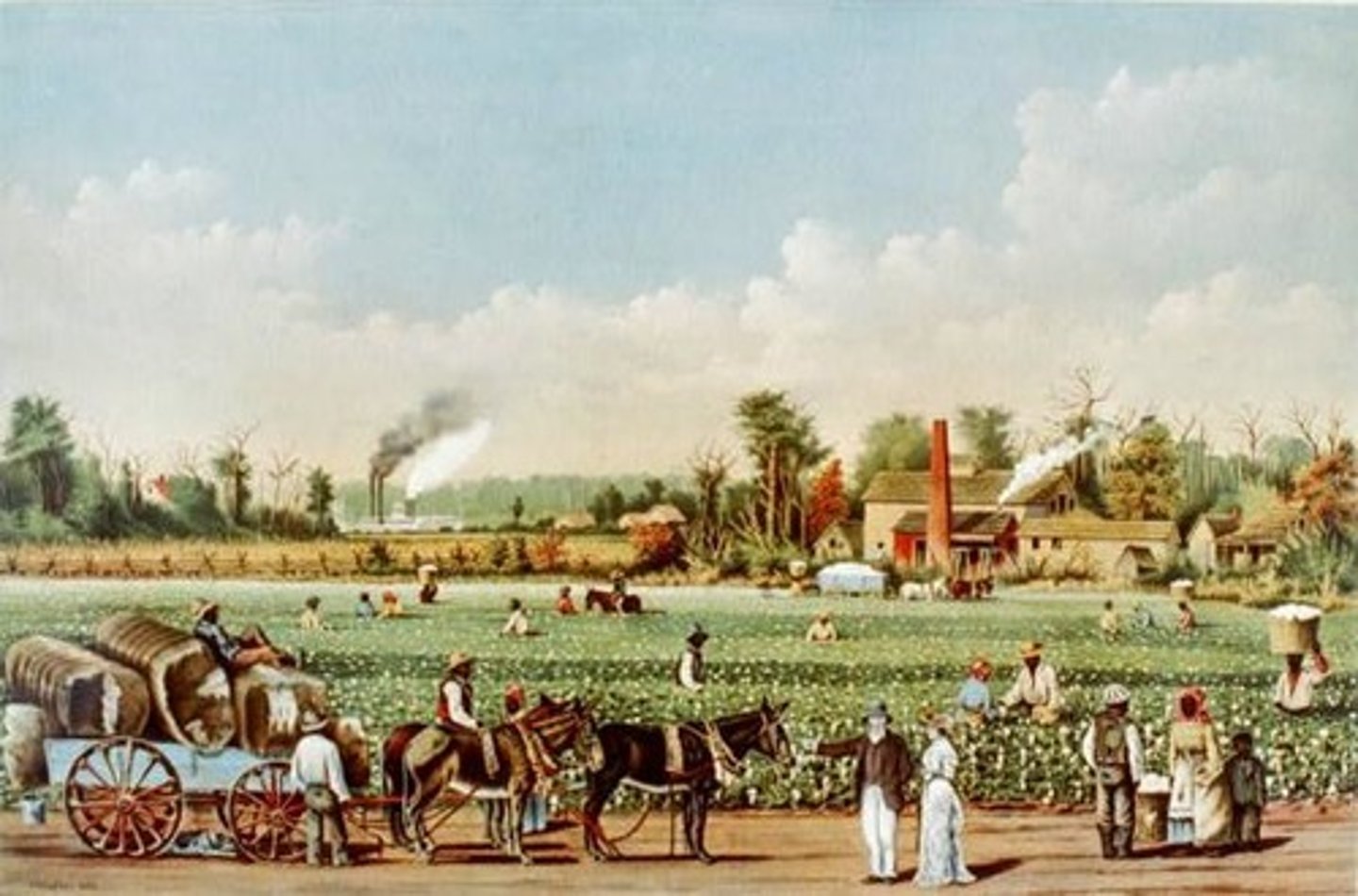
tobacco farms
As Tobacco prices fell, rice and indigo became the most profitable crops.

John Cabot
First Englishman to explore lands in North America which England would later settle in the early 1600's.

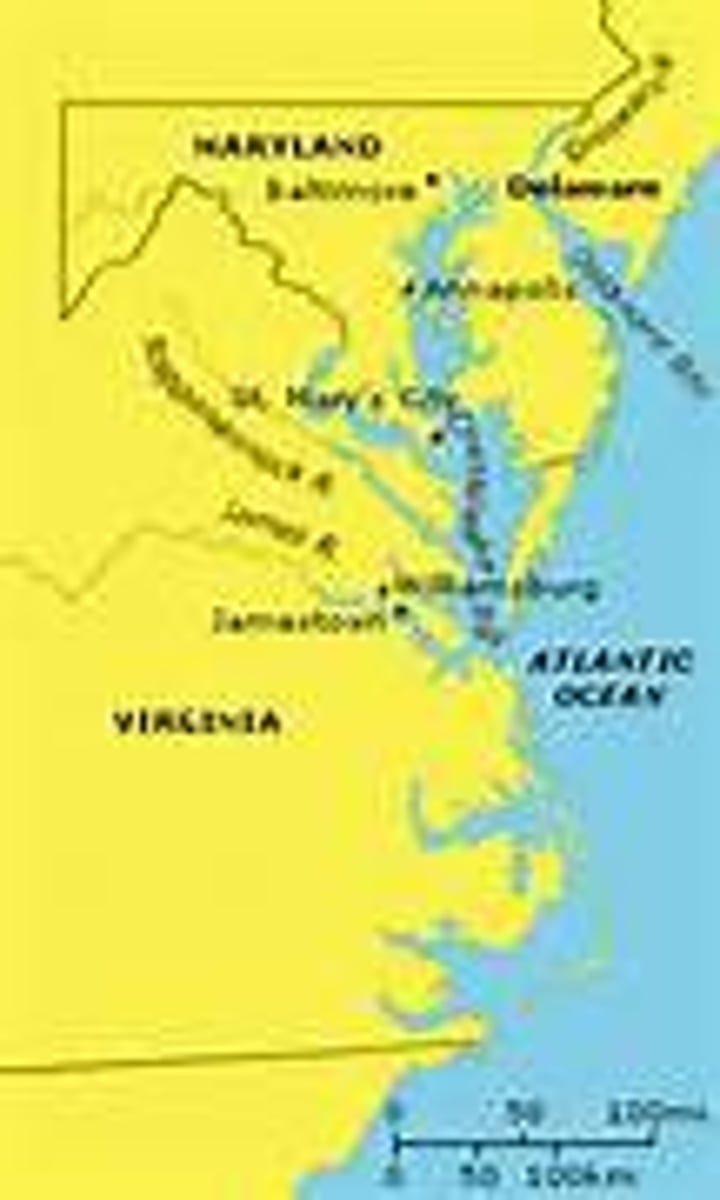
Jamestown
In 1607, the first permanent English colony in America was founded at this location. The Virginia Company, was a a joint-stock company chartered by England's King James I.

Captain John Smith
Because of his forceful leadership, Jamestown barely survived its first five years.

John Rolfe
He helped Jamestown develop a new variety of tobacco which became popular in Europe and became a profitable crop.

Pocahontas
She was the American Indian wife of John Rolfe in early settlement days in Jamestown.

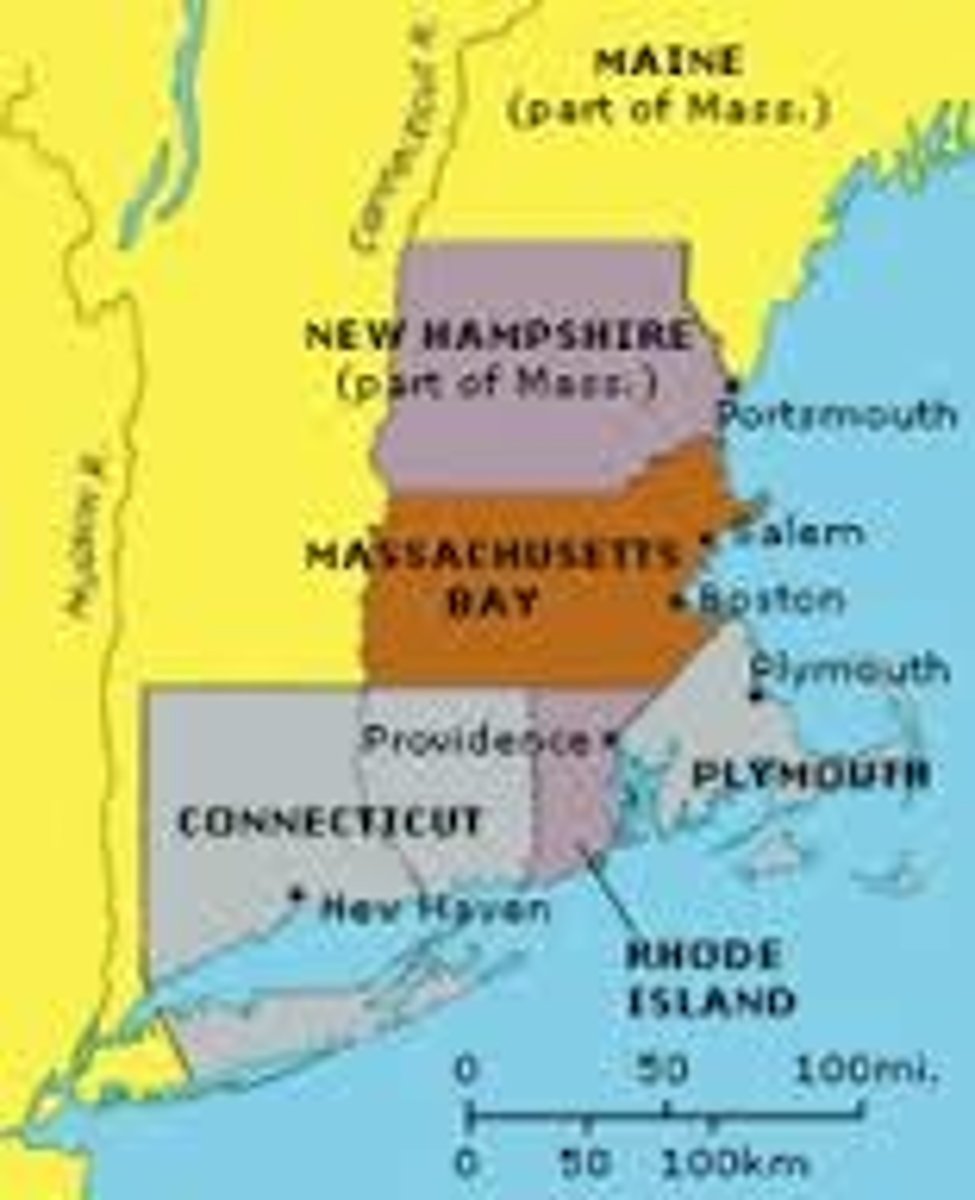
Puritans
Group of dissenters that wanted to purify the Church of England. In 1630 they founded the Massachusetts Bay Colony at Boston.

Separatists
Radical dissenters to the Church of England, they were known by this name because they wanted to organized a completely separate church that was independent of royal control. They became known as Pilgrims, because of the travels.

Pilgrims
They were radical dissenters to the Church of England. They moved to Holland, then in 1620, they sailed to America on the Mayflower in search of religious freedom. They established a new colony at Plymouth on the Massachusetts coast.

Mayflower
In 1620, the boat that the Pilgrims sailed to Plymouth.

Plymouth Colony
This colony was started by the Pilgrims at Plymouth (Massachusetts). In the first winter nearly half of them perished. They were helped by friendly American Indians and celebrated the first Thanksgiving in 1621.
John Winthrop
In 1630, he led about a thousand Puritans to America and and founded Boston and several other towns.

Great Migration
This movement started because of a civil war in England. Nearly 15,000 settlers came to the Massachusetts Bay Colony.
Virginia
Sir William Berkeley, the royal governor of Virginia use dictatorial powers to govern on behalf of the large planters.
Thomas Hooker
In 1636, he led a large group of Boston Puritans dissatisfied with the Massachusetts Bay colony to found Hartford, which is now Connecticut. In 1639 they drew up the first written constitution in American history.

John Davenport
In 1637, he founded a settlement south of Hartford, by the name of New Haven.

Connecticut
In 1665, New Haven and Hartford joined to form the colony of Connecticut under a royal charter.
New Hampshire
Hoping to increase royal control in the colonies, King Charles II separated New Hampshire from Massachusetts in 1679 and made it a royal colony.
The Carolinas
In 1663, King Charles II granted eight nobles the Carolinas. In 1729, the Carolinas were split into two royal colonies. In South Carolina, the economy was based on the fur trade and growing food for the West Indies, which led to many plantations. In North Carolina, there were many small tobacco farms and fewer plantations.
New York
In 1664, King Charles II granted his brother, the Duke of York (future King James II) the land now known as New York. James took control of the Dutch colony that was located there, but the Dutch were treated fairly. James was unpopular because of his taxes and refusal to institute a representative government. Finally in 1683, he agreed to grant broad civil and political rights to the colony.
New Jersey
The territory of New York was split. In 1674, land was granted to Lord John Berkeley and Sir George Carteret. Eventually they sold to the Quakers. In 1702, the two Jerseys were combined into a single royal colony, New Jersey.
Pennsylvania
In 1861, the royal family paid a large debt by granting William Penn's father a large parcel of American land. He then formed a colony from the land.
Delaware
In 1702, William Penn granted the lower three colonies of Pennsylvania their own assembly. In effect, Delaware became a separate colony, even though its governor was the same as Pennsylvaniaá until the American revolution.
Georgia
In 1732, Georgia was formed to provide a buffer between wealthy Georgia and Spanish controlled Florida, and to provide a place for the many debtors of England to begin again.
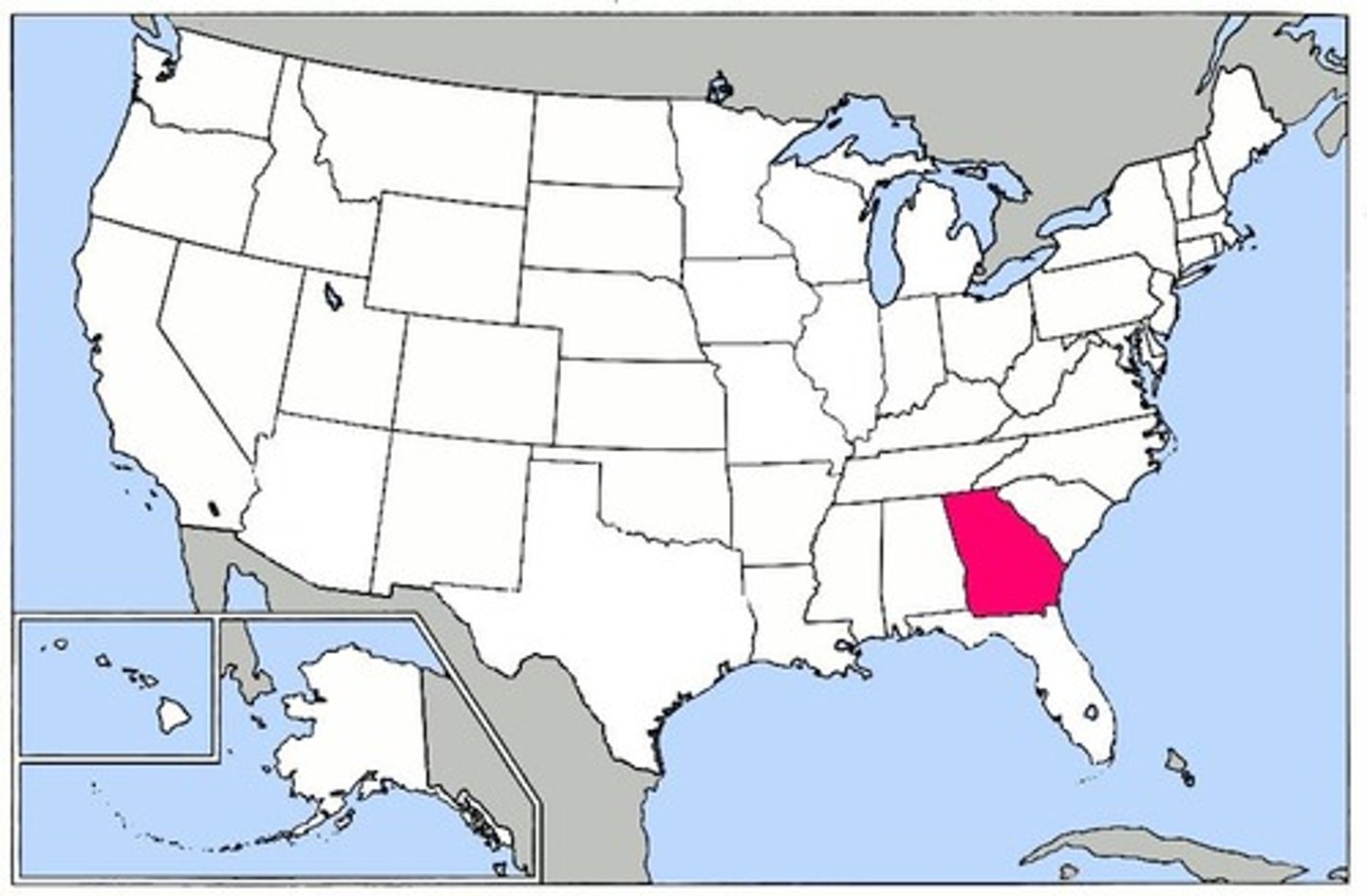
James Oglethorpe
Founder of Georgia's first settlement, Savannah, in 1733. He acted as governor of Georgia and had strict laws which included a ban on rum and slavery.

Wampanoags
An American Indian tribe led by Metacom.

Metacom
This American Indian chief was known to the colonists as King Philip. He joined together the Native American tribes to fight the colonists in King Philip's War, a war that lasted from 1675 to 1676.

King Philip's War
From 1675 to 1676, the American Indian chief Metacom (King Philip), waged a vicious war against the English settlers in southern New England.

Mayflower Compact
In 1620, while they were sailing to America on the Mayflower, the Pilgrims created this document that pledged them to make decisions by the will of the majority. It was a rudimentary written constitution.

Virginia House of Burgesses
In 1619, just 12 years after the founding of Jamestown, Virginia's colonists organized the first representative assembly in America, the Virginia House of Burgesses.

Sir William Berkeley
Royal Governor of Virginia who favored large plantation owners and did not support or protect smaller farms from Indian raids. He put down Bacon's rebellion in 1676.

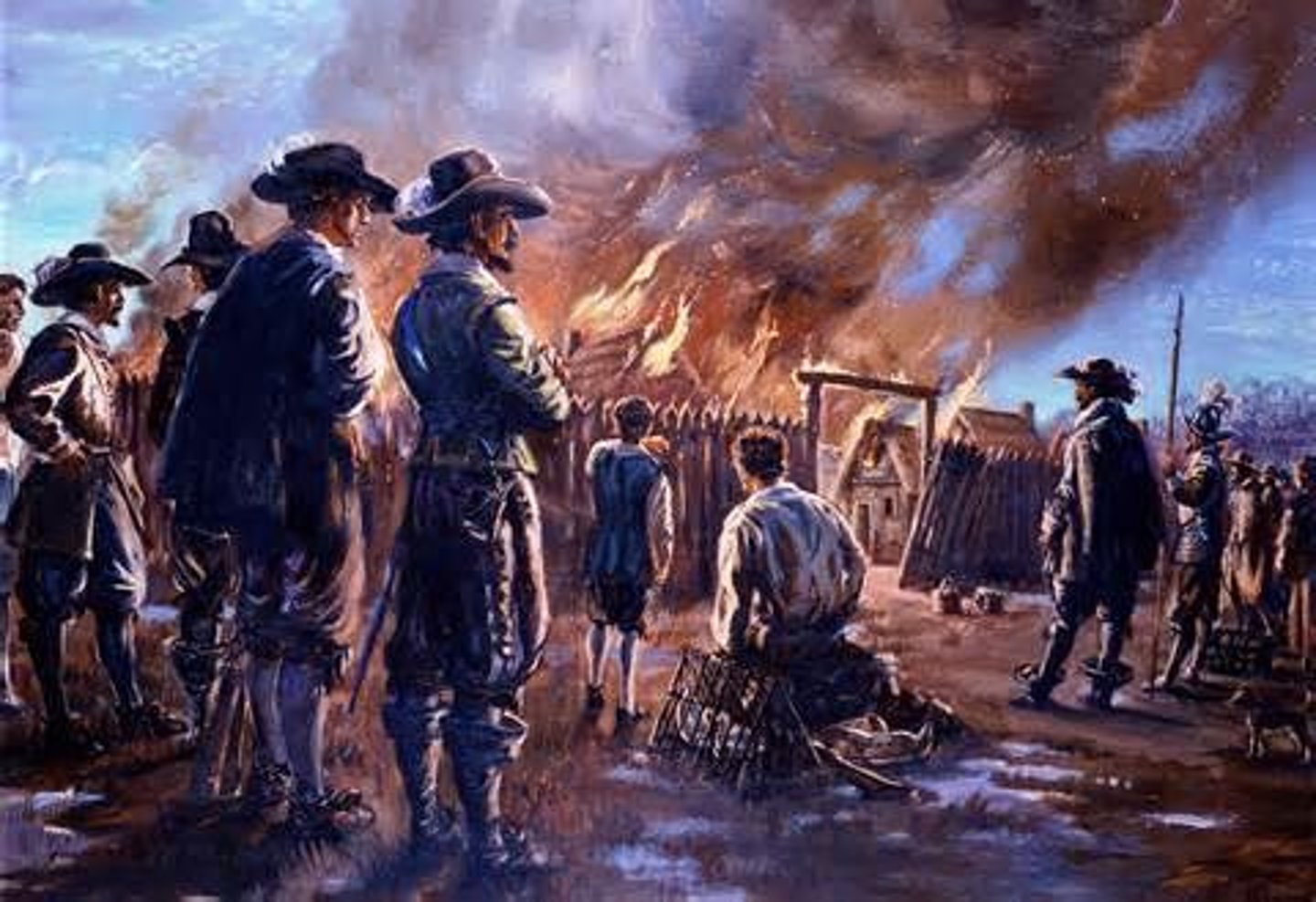
Bacon's Rebellion
In 1676, Nathaniel Bacon led a group of army volunteers that raided Native American villages, fought the governor's forces, and set fire to Jamestown. The rebellion lost momentum when Bacon died of dysentery. The rebellion was caused by the Governor's unfair favoritism of large plantation owners and refusal to protect small farms from Native American raids.

Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
In 1639, the Hartford settlers drew up the first written constitution in America. It established a representative government made up of a legislature elected by the people and a governor chosen by the legislature.

New England Confederation
In 1643, Plymouth, Massachusetts Bay, Connecticut, and New Haven colonies formed a military alliance to deal with the threat from the Native Americans. It lasted until 1684.

Frame of Government (1682)
In 1682-1683, William Penn provided the Pennsylvania colony with a Frame of Government which guaranteed a representative assembly elected by landowners and a written constitution.

corporate colonies
Colonies operated by joint-stock companies during the early years of the colonies, such as Jamestown.
royal colonies
Colonies under the direct authority and rule of the king's government, such as Virginia after 1624.

proprietary colonies
Colonies under the authority of individuals granted charters of ownership by the king, such as Maryland and Massachusetts.

Chesapeake Colonies
In 1632, the area once known as the Virginia colony, has divided into the Virginia and Maryland colony. Maryland became the first proprietary colony.
joint-stock company
Corporate colonies, such as Jamestown, were operated by joint-stock companies, at least during the colony's early years.

Virginia Company
England's King James I chartered the Virginia Company, a joint-stock company that founded the first permanent English colony in America at Jamestown in 1607.
mercantilism
An economic policy in which the colonies were to provide raw materials to the parent country of growth and profit of the parent country.

Navigation Acts
Between 1650 and 1673 England passed a series of acts which establish rules for colonial trade.
* Trade to and from the colonies could be carried only by English or colonial-built ships, which could be operated only by English or colonial crews.
* All goods imported in the colonies, except some perishables, had to pass through the ports in England.
* Specified goods from the colonies could be exported only to England.
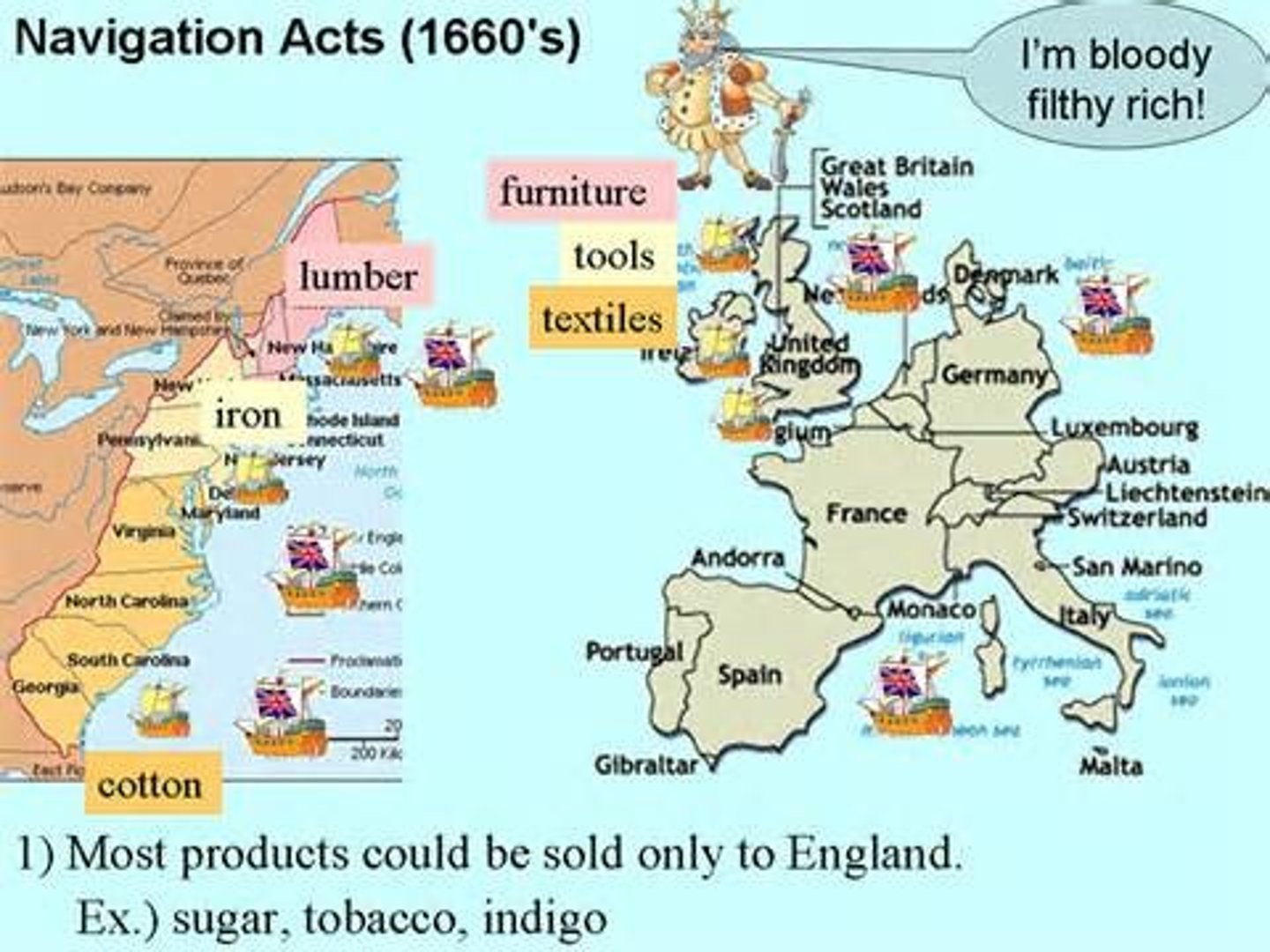
Dominion of New England
James II wanted to increase royal control in the colonies, so he combined them into larger units and abolished their representative assemblies. The Dominion of New England was combined New York, New Jersey, and the other New England colonies into a single unit.
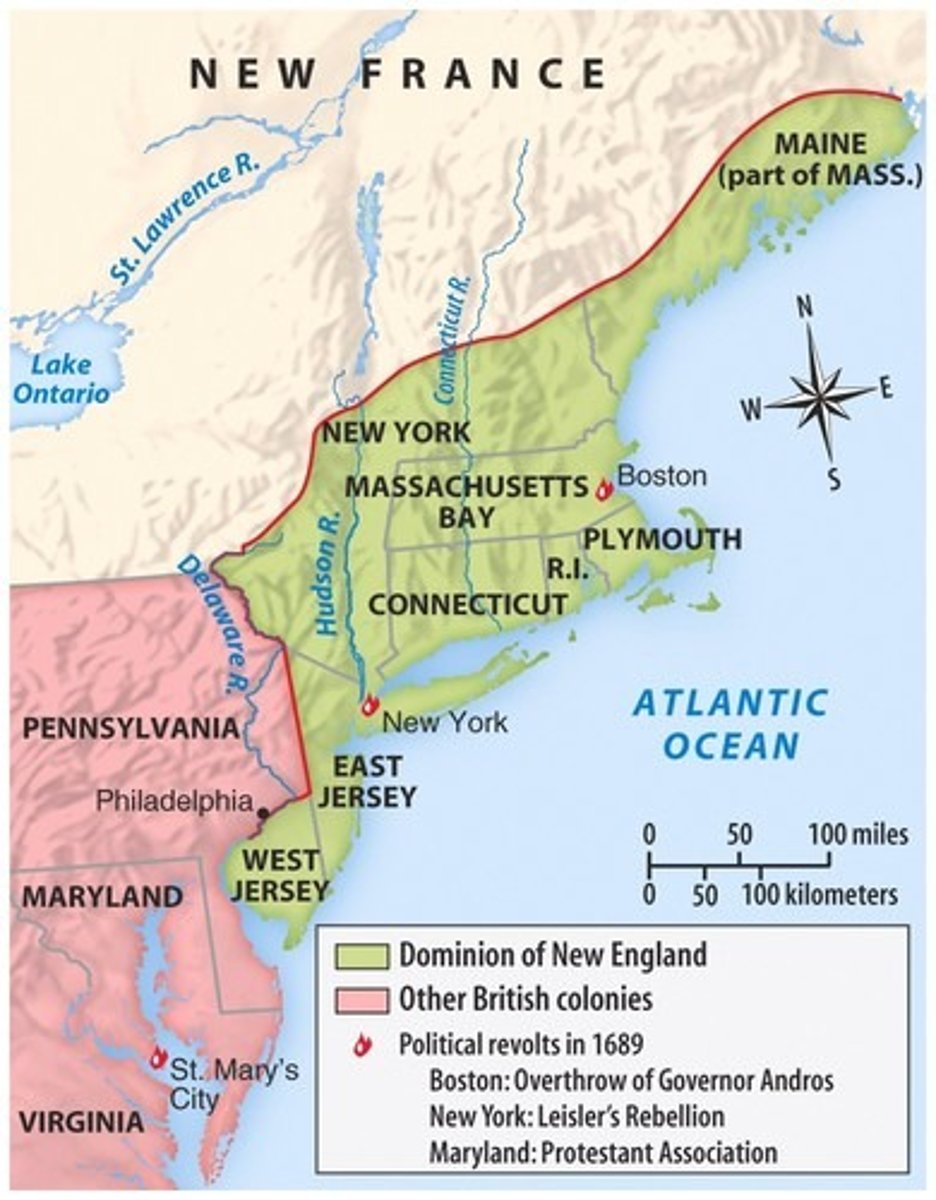
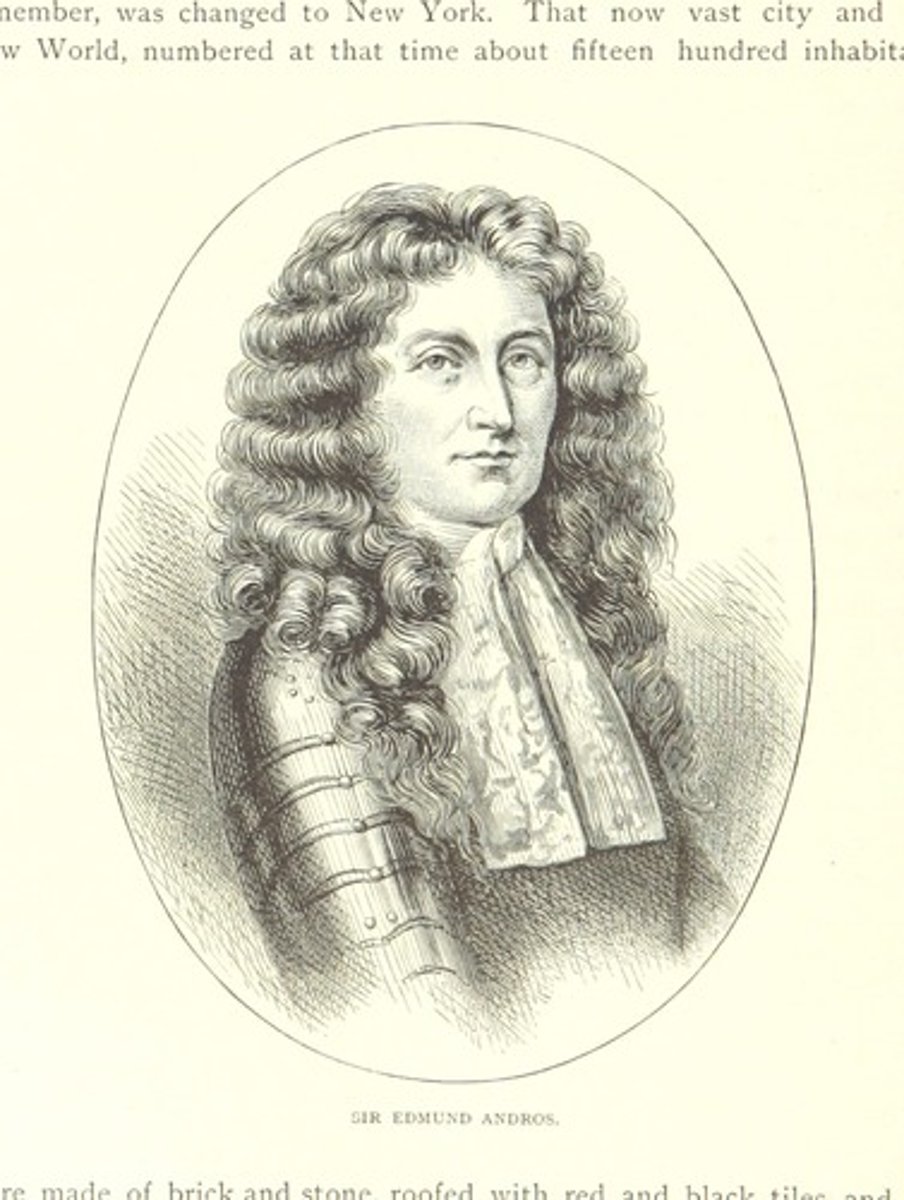
Sir Edmund Andros
In 1686, King James II combined New York, New Jersey, and additional New England colonies into a single unit called the Dominion of New England. He was sent England to govern the dominion. he was very unpopular by levying new taxes, limiting town meetings, and revoking land titles.

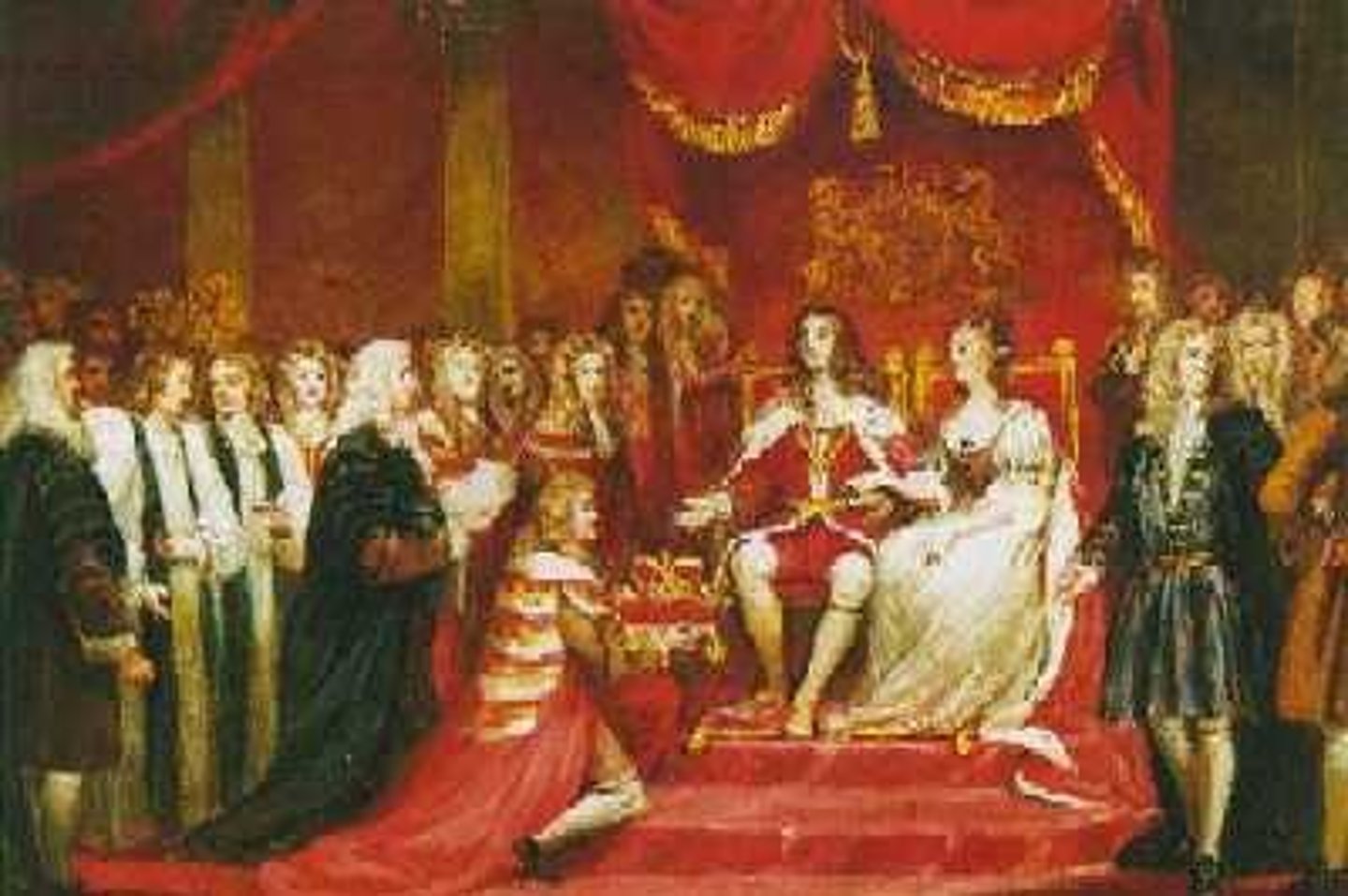
Glorious Revolution
In 1688, King James II was deposed and replaced with William and Mary. This brought the end to the Dominion of New England, and the colonies operated under their previous structure.

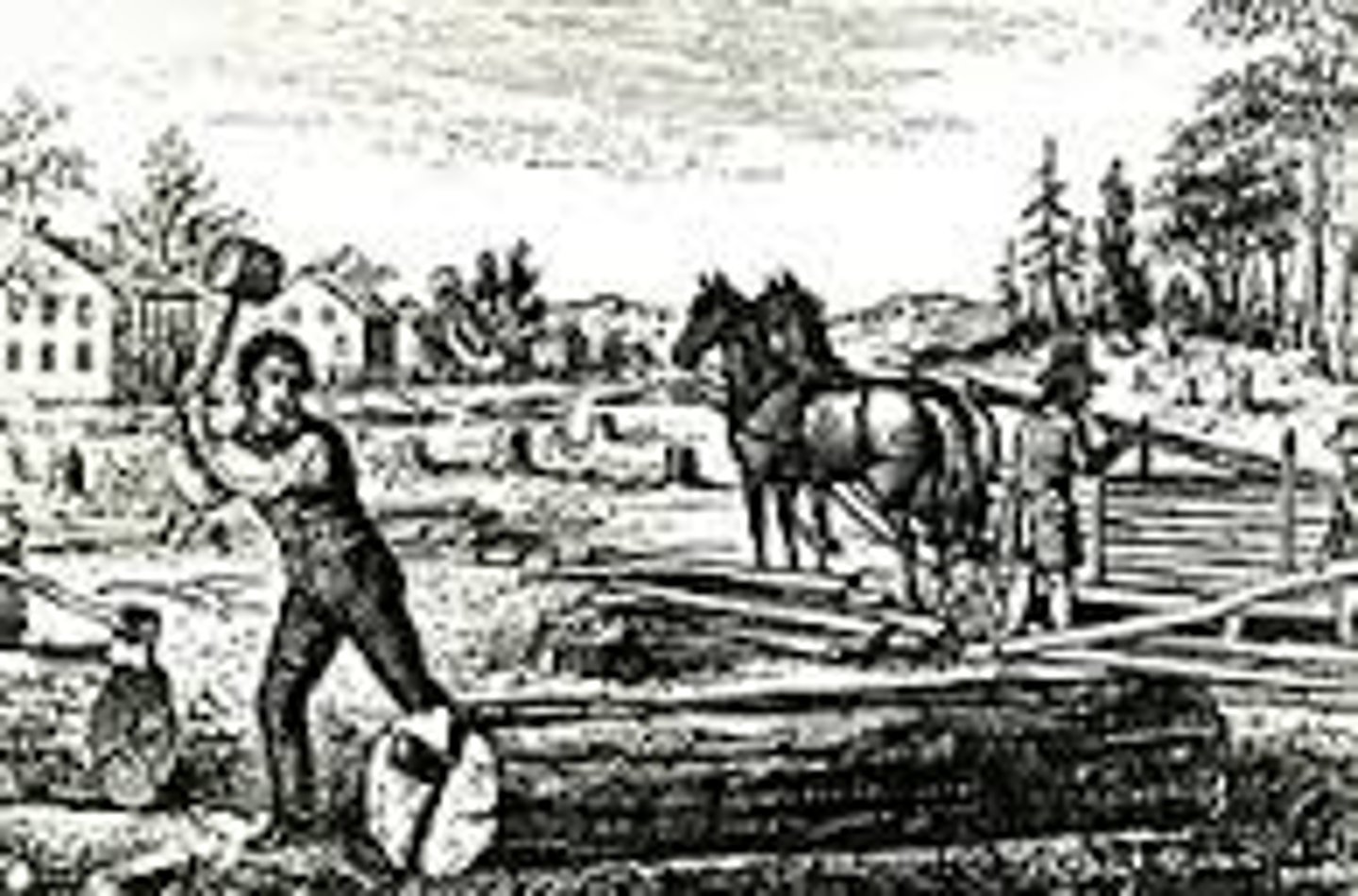
indentured servants
Young people from England under contract with a master who paid for their passage. Worked for a specified period for room and board, then they were free.

headright system
A method for attracting immigrants, Virginia offered 50 acres of land to each immigrant who paid for passage to America and to any plantation owner who paid for an immigrants passage.

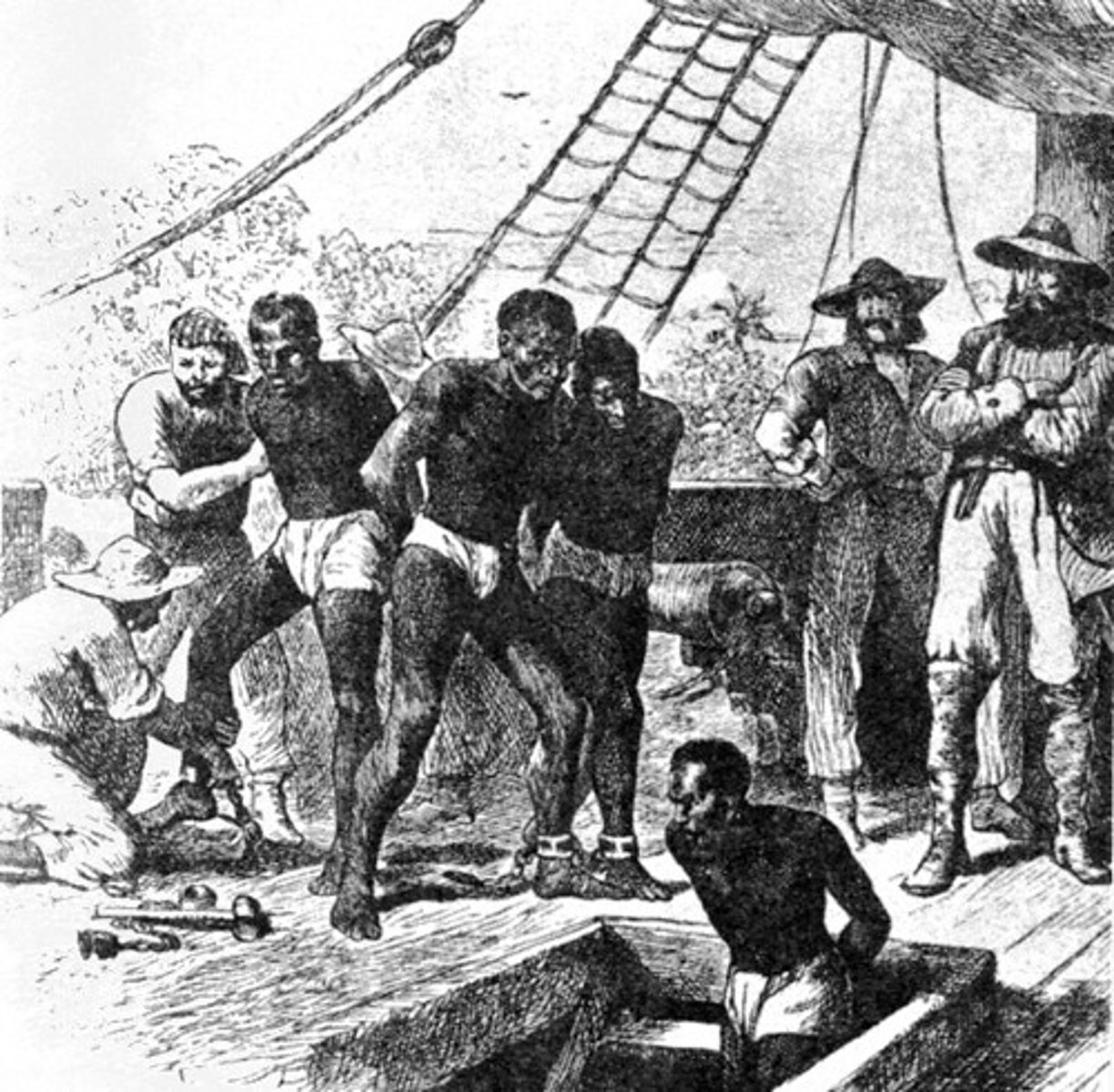
slavery
The first slaves arrived in the colonies in 1619, they were not slaves for life, but worked for a period of time, like an indentured servant. Then discriminatory laws were passed, slaves and their offspring were kept in permanent bondage.

triangular trade
Merchants traded colonist rum for African slaves, African slaves for West Indies sugar cane, and sugar cane was brought back to the colonies to make rum.
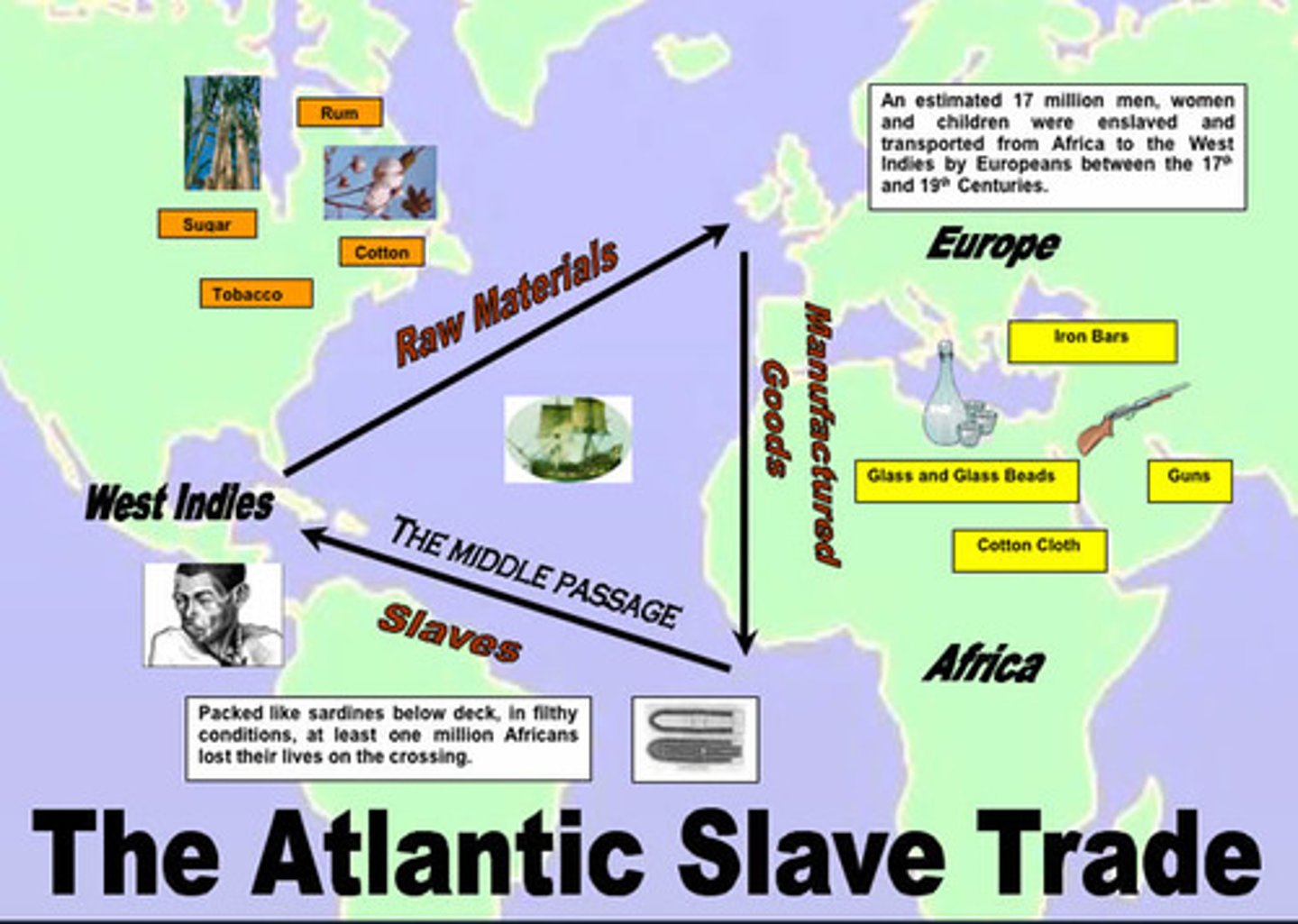
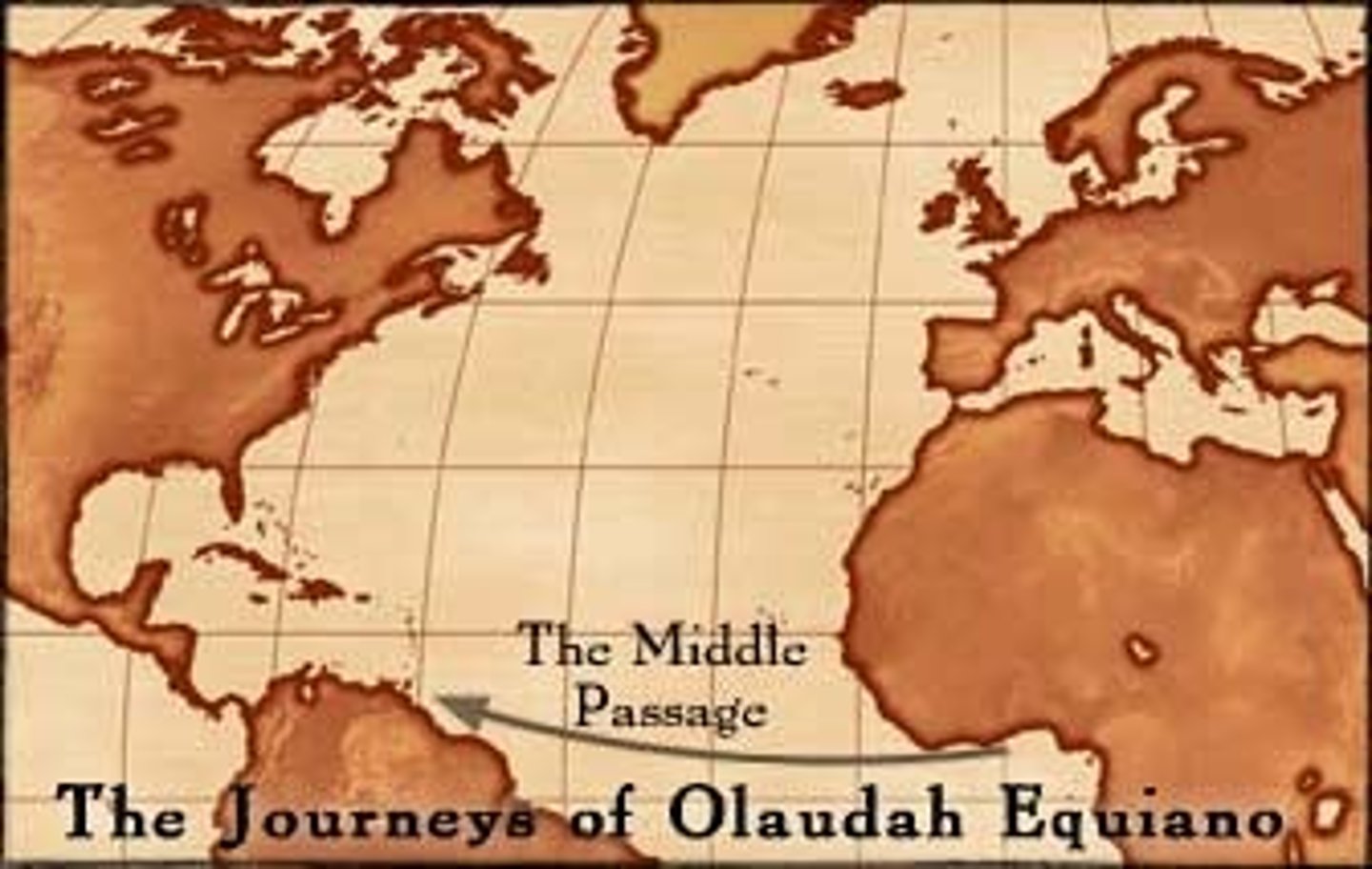
Middle Passage
Voyage from West Africa to the West Indies. It was miserable for the slaves transported and many died.