Autosomal Recessive Disease
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Features of Autosomal Recessive
seen in a single generation (horizontal pattern)
parents and children of affected people are normally unaffected
males and females are equally affected and equally likely to transmit
parents of affected children must be carriers
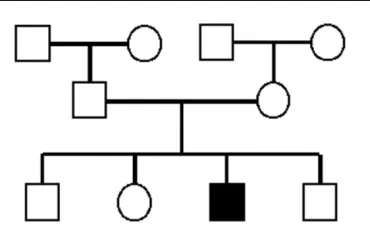
Recurrence Rate For 2 carrier parents is..
1/4
unaffected sibling of an affected sibling has?
2/3 of being a carrier
compound heterozygotes
individual with 2 different alleles, both of which are defective
severity depends upon how much residual function is retained
Heterozygote Advantage
the relatively high frequency of disease-associated alleles causing reduced fitness on homozygotes
heterozygotes (Aa) have a greater fitness than either of the homozygotes (AA or aa)
Gene Therapy
the use of DNA as a pharmaceutical agent to treat disease
Somatic Gene Therapy
replace defective genes in somatic (adult) cells so cells can produce the missing gene product to alleviate or eliminate the symptoms of the disorder
germline gene therapy
corrections are made to the germ cells such that inheritable genetic alterations are prohibited
Introduction of Genes into Somatic Cells | Liposomes
small lipid membrane microspheres containing DNA → merge with the cell membrane and deliver DNA
some nucleic acid is randomly integrated and expressed to varying degrees
Chemical Method
Introduction of Genes into Somatic Cells | Microprojectiles
gold/ platinum coated in DNA
mechanically 'shot' into cells to deliver DNA
some nucleic acid randomly integrated and expressed to varying degress
Mechanical Method
Introduction of Genes into Somatic Cells | Viral Vectors
by nature, viruses introduce DNA into cells and express their genes with high efficiency
engineer viruses to insert and express normal genes over defective genes
3 approaches to get gene to right spot | Ex Vivo
the target cells are removed from the body
cultured in the laboratory with a vector
re-inserted into the body
Suitability for Cystic Fibrosis? -→ not good (lungs cells hard to ex vivo)
3 approaches to get gene to right spot | In Vivo
the vector is introduced into the body, typically via the blood stream
the vector homes in on the cells for which it was specifically designed to alter
Suitability For Cystic Fibrosis? → best
3 approaches to get gene to right spot | In Situ
the affected tissue is directly exposed to gene therapy vector
transfected cells are not removed from the body
Suitability for Cystic Fibrosis → good but not great cause CF is a multisystem disorder
how can an autosomal recessive child be produced by a couple with 1 carrier?
germline mosaicism
de novo during embryogenesis
PKU → Gene and Mutation
PAH gene
p.Arg408Trp
PKU → Effect on phenotype
loss of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) enzyme
without PAH, phenylalanine accumulates in tissues
the amount of enzyme is the same as for normal individuals, however, activity is reduced
Most people affect with PKU are?
compound heterozygotes
Maternal effect of PKU
homozygous women with PKU have difficulties producing healthy children
significant risk of intellectual disability
Clinical Features (phenotype) Of PKU
vomiting
irritability
eczema-like rash
mousy odour to the urine
increased muscle tone | Nervous System
more active muscle tendon reflexes | Nervous System
microcephaly
prominent cheek and upper jaw bones
widely spaced teeth
poor development of tooth enamel
decreased body growth
cognitive impairment
seizures
no obvious phenotype in [zygotes] despite a [change in PAH]?
heterozygotes
~50% reduction in PAH enzyme activit
PKU → Screening Test
newborn heel prick test (assess phenylalanine levels)
PKU → Treatment
maintain blood phenylalanine within normal levels (2-10 mg/dL)
Strict Diet
PKU → Litestyle Changes
avoid high protein food
PKU → Quality Of Life
normal quality of life and life span if vigilant
Thalassemia → Gene and Mutation
HBA1/2 gene → α-thalassemia
HBB gene → β-thalassemia
Thalamessia → Affect of Phenotype
incorrect or no synthesis of hemoglobin globin chains
α-thalassemia if α globin chain
β-thalassemia if β globin chain
Thalassemia → Gene Location
4 α globin genes → 2 on each copy of chromosome 16
2 β globin genes → 1 on each copy of chromosome 11
Note**remember that evens are with evens (2, 16) and odds are with odds (1, 11)
Thalassemia → normal structure of haemoglobin
hemoglobin is a tetramer of 2 α-like and 2 β-like globin subunits
subunits change to suit the gas-carrying needs of the embryo, fetus, and adult
alpha - thalassemia | Different Types | Silent Carrier
1 of 4 α-globin genes mutated
typically asymptomatic
alpha - thalassemia | Different Types | Minor
2 of 4 α-globin genes mutated
mild anaemia
alpha - thalassemia | Different Types | HBH/ Hemoglobin H
3 of 4 α-globin genes mutated
mild to moderate anaemia, enlarged spleen, jaundice
Treatment → transfusions may be needed during hemolytic or aplastic crises
alpha - thalassemia | Different Types | Hb Barts
4 of 4 α-globin genes mutated
severe form where excess fluid builds up in the developing baby due to severe anaemia
baby usually does not survive long after birth
Treatment → no effective treatment
beta - thalassemia | Different Types | minor
1 of 2 β-globin genes mutated
may have lifelong mild anaemia
beta - thalassemia | Different Types | intermediate
2 of 2 β-globin genes mutated
mild to moderate anaemia
slow growth and bone changes
symptoms may appear in early childhood or later in life
Treatment →
splenectomy
sporadic blood transfusions
folic acid supplementation and iron chelation
beta - thalassemia | Different Types | Major
2 of 2 β-globin genes mutated
children develop life-threatening anaemia within the first year of life
failure to thrive, jaundice, enlarged spleen, bone changes and developmental delay
Treatment →
bone marrow transplantation
cord blood transplantation
regular transfusions correct the anemia, suppress erythropoiesis, and inhibit $\uparrow$ iron absorption
Thalamessia | More Info
Group of heterogeneous blood disorders where one of the globin
chains of hemoglobin has not been synthesized correctly.
B+= reduced β chain synthesis
B0 = NO β chain synthesis
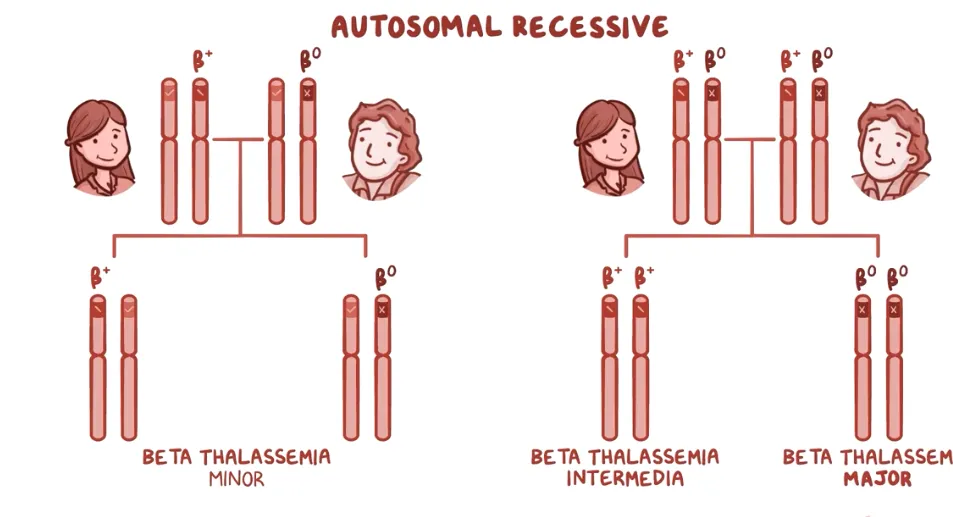
Thalassemia → Screening Test
hematologic testing of RBC indices
peripheral blood smear
supravital stain to detect RBC inclusion bodies
electrophoresis
Thalassemia → Diagnostic Test
molecular genetic testing of HBA1/2 and HBB
Thalassemia → Hard to diagnose heterozygote
most have mild symptoms and undiagnosed due to incomplete dominance
Thalassemia → Gene therapy
haemoglobin switching - partner γ globin partners with α globin in place of defective β globin
Thalassemia → Effect on life expectancy
mild forms of thalassemia do not shorten life span
thalassemia major babies are normal at birth but become anemic between 3-6 months, why is death delayed?
switch from γ to β globin subunits
Sickle Cell Anemia → gene and mutation
HBB (HbA → HbS)
p.Glu6Val (non-conservative)
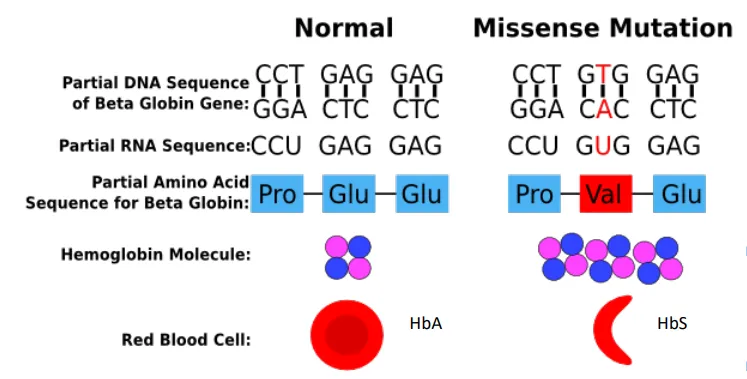
Sickle Cell Anemia → Base changes of RNA
GAG → GUG
Sickle Cell Anemia → Base changes of DNA
CTC → CAC
Sickle Cell Anemia → Phenotype
fibre formation within RBCs → distorted RBC shape
Sickle Cell Anemia → Screening Test
blood screening for deformed erythrocytes using a microscope
electrophoresis
newborn heel prick test
Sickle Cell Anemia → Management
based on crisis prevention
Drink plenty of fluids (pain)-
Pain medications -
Blood transfusions
Outlook is good if routinely
checked.
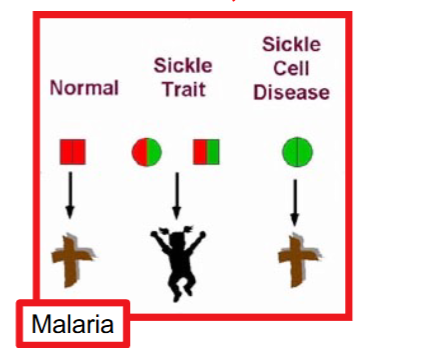
How does it protect against malaria
malarial parasites grow poorly in HbS/HbS and HbS/Hb+ RBCs so HbS alleles are maintained at high levels in populations exposed to malaria due to selective advantage
Why is Sickle Cell is a good example of compound heterozygotes
The relatively high frequency of disease-associated alleles causing reduced
“fitness” on homozygotes (eg. sickle-cell anaemia in Africans) has been
explained by assuming that the heterozygotes (Aa) have a greater fitness than
either of the homozygotes (AA or aa).
Haemochromatosis → Gene and Mutation
HFE gene
p.Cys282Tyr → most common in Caucasians (where it is homozygous) and accounts for the most cases of Hereditary Haemochromatosis
p.His63Asp
Hemochromatosis → Effect on Phenotype
mutant HFE does not bind properly to the transcriptional regulation of Hepcidin (master iron regulatory hormone)
absorb all protein-associated iron from food → stored in body tissues
Hemochromatosis → Clinical Features
joint pain (most common)
fatigue
bronze pigment
abdominal pain
increased libido
Hemochromatosis → Symptoms presenting
30-50 years (♀) and >50 (♂)
It is later women because removal of iron through menstruation
many show few symptoms before irreversible organ damage commences
Haemochromatosis → Screening Test
iron content in blood (serum transferrin saturation)
iron content in liver (serum ferritin)
Haemochromatosis → Treatment
regular phlebotomy
Cystic Fibrosis → Gene and Mutation
CFTR gene
p.Phe508del (ΔF508) (misfolded protein does not migrate to the cell membrane)
Cystic Fibrosis → Clinical Features | Pancreas
glands becomes clogged → formation of cysts and eventually becomes fibrous
decreased fat digestive enzymes → undernourishment and steatorrhea
Cystic Fibrosis → Clinical Features | Lungs
mucus is thicker and not cleared by cilia so it accumulates in the lungs
persistent cough and recurrent lung infections
Cystic Fibrosis → Clinical Features | Reproduction
infertility due to a blocked ductus deferens
Cystic Fibrosis → Clinical Features | Sweat Glands
no re-uptake of secreted salt→ salty residue on the skin and a salt deficit in the body
Carriers vs affected incidents in Australia
1/25 people unknown carriers
1/2,500 babies (1 every 4 days)
Cystic Fibrosis → Screening Test
newborn heel prick test (assess [pancreatic immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT)])
pancreatic glands produce trypsinogen → transported to the small intestine and converted into trypsin but in CF mucus blocks pancreatic ducts that lead to the small intestine
Cystic Fibrosis → Screening Test (Carriers)
12-panel mutation screen for carriers
Cystic FIbrosis → Diagonistic Testing
sweat chloride test
Medication for CF
antibiotics (treat and prevent infections)
mucus-thinning drugs (expel mucus via coughing)
bronchodilators (open airways)
oral pancreatic enzymes (improve nutrient absorption)
Gene Therapies for CF | potentiators →ivacaftor
binds to CFTR channels to help them open (enhance CFTR activity)
Gene Therapies for CF | correctors → lumacaftor
helps/ corrects processing of CFTR proteins (gets it to the membrane)
CF → Treatment/ Lifestyle Changes
organ transplant
chest physical therapy
pulmonary rehabilitation
nebulisers every morning/ night
psychological counselling
nutrition/ exercise
What disease does CF protect heterozygosity protect from?
cholera (fewer chloride channels in intestinal cells to prevent water loss)
De Novo Mutations
New mutations that arise (not seen in either of an individuals parents). These
can occur in somatic cells or in gametes and as such can be passed onto the next
generation.
Guthrie Test AKA Heel Prick
A newborn baby screening test that screens for serious genetic conditions. Blood
from a neonatal heel prick is collected onto pre-printed cards known as Guthrie
cards