Chapter 3 - Nucleotides, Nucleic Acids and Genetic Information
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Nucleotides
Composed of a nitrogenous base linked to a pentose sugar to which at least one phosphate group
Nucleoside
Composed of a nitrogenous base linked to a sugar without the phosphate group
Purine (NH group)
Adenine and Guanine. Binds to sugar at N9. Two ring structures
Pyrimidine (N group)
Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil. Binds to sugar at N1. One ring structure
Adenine
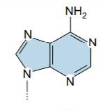
Guanine
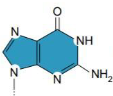
Cytosine
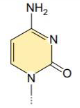
Thymine
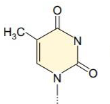
Ribose
Pentose sugar with oxygen on the 2 carbon
Deoxyribose
Pentose sugar with no oxygen on the 2 carbon
Phosphate bridges
the 3’ and 5’ positions of neighboring ribose units
phosphodiester bond
the linkage between individual nucleotides
phosphodiester bond formation
condensation reaction catalyzed by DNA
Sequence of nucleotide residues
written from 5’ to 3’ with a free phosphate group at 5’ end
Observations lead to double helix model
(1) Nucleotide bases are mainly present in their keto form
(2) X-ray diffraction photograph of a DNA fiber predicting its a helical molecule
(3) Chargaff’s rule C=G and A=T
Watson and Crick model of DNA
(1) two polynucleotide chains wind around a common axis to form a double helix.
(2) the two strands of DNA are antiparallel and form a right-handed helix.
(3) the bases occupy the core of the helix and sugar-phosphate chains run along the periphery
(4) The suface of the double helix contains two grooves: major and minor
(5) Each base to hydrogen bonded to a base in the opposite strand to form a planar base pair
bases per turn
10.4
Histones
small, positively charged proteins that are crucial for DNA packaging. They bind tightly to the negatively charged DNA, helping condense and organize it within the cell’s nucleus
Nucleosomes
The fundamental unit of chromatin. It consists of a segment of DNA wrapped around a core of eight histone proteins
Chromatin
The complex of DNA and proteins (primarily histones) that makes up chromosomesC
Chromosomes
Highly condensed structures of chromatin
Human DNA
23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total)
5’GAGA3’
3’CTCT5’
RNA
Single-stranded DNA, which usually forms compact structures rather than loose extended chains
When a cell divides
each DNA strand acts as a template to form its complementary strand
Each DNA molecule consists of
one parental strand and one daughter strand
Replication
Daughter strands are synthesized by the stepwise polymerization of nucleotides using parental strand as template
DNA replication catalysis
DNA polymerase
DNA helicase
Catalyzes unwinding of DNA helix
DNA ligase
Seals gaps between fragments
Topoisomerase
Relieves strain ahead of replication, prevents tangling
DNA polymerase
Adds nucleotides dNTPs to growing DNA strand
Polymerase Chain Reaction
An exponential amplification of a piece of DNA without a live cell
the four ingredients of PCR
DNA template, primers, nucleotides, Taq polyermase
Primers
Short stretches of DNA fragments complementary to sequences of flanking the target gene. Primer binds to unwound single stranded DNA template.
Taq polymerase role
incorporates nucleotides and extends the chain
strand separation temp
94 celsius
primer annealing temp
55
primer extension temp
70
after pcr cycles
2n copies after each cycle
Central dogma of molecular biology
DNA replicates, DNA is transcribed into RNA, RNA is translated into amino acids for protein formation
RNA strands synthesis
From free ribonucleoside triphosphates using DNA strand of a gene as a template
messenger RNA (mRNA)
the RNA corresponding to a protein coding gene
transfer RNA (tRNA)
mRNA is transported to ribosomes, where each set of three nucleotides in the mRNA pairs (codon) with three complementary nucleotides
Mutations
Alterations to the genetic material of an organism may result in proteins with altered structures and functions
single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
DNA sequence differs among individuals at one nucleotide
Genome
Genetic material of an organism
Genomics
The study of the genome’s side, organization, and gene content
Transcriptomics
the study of gene expression
Proteomics
The study of the proteins (proteome)
Although an organism’s genome remains unchanged through its lifetime,
, it’s transcriptome and proteome vary significantly among different types of tissues, developmental stages, and environmental conditions