Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI) often referred to as? And it is characterized by what 3 things?
it is an inherited disorder of what tissue, or novel ___?
what type of collagen is missing and how does this affect the bones?
what is the incidence?
what has been identified for OI?
- aka brittle bones disease, characterized by lax joints, weak muscles, diffuse osteoporosis
- inherited disorder of connective tissue, or novel mutation
type I collagen missing —> bones are weak and fragile
- incidence 1:10,000
- several causative factors have been identified
1978 Sillence and Danks classified how many genetic types of OI?
it has expanded to how many?
Which types affects COL1A1 and COL1A2?
encode for what collagen?
Which types do not have type I collagen defect?
classified 4 genetic types
expanded to over 20 types
I-IV affect COL1A1 and COL1A2
type I collagen
V-XXI do not have type I collagen defect
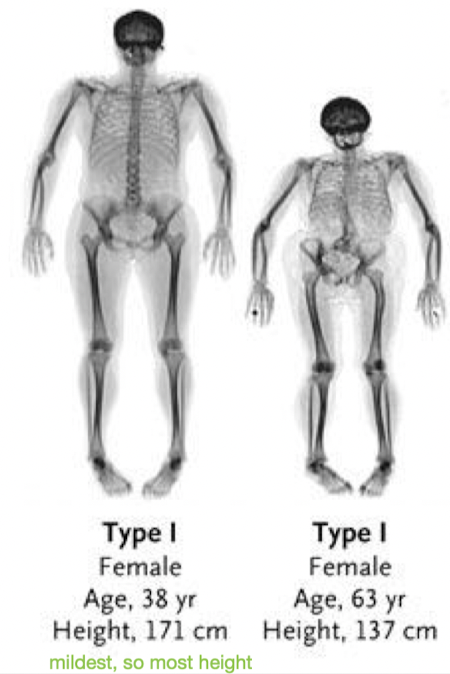
In type I OI, how much bone fragility is there? how many fractures?
how much bone malformation?
when do most fractures occur?
what is the birth height/weight?
are the muscles strong/weak?
joint laxity or hypomobility?
what feet position?
dislocations and what?
what is life expectancy?
associated w/ what color sclera, shape of face, and type of hearing loss?
○ Mild to moderate bone fragility with few to several fractures
○ Little or no bone malformation
○ Most fractures occur before puberty
○ Normal birth height/weight
○ Muscle weakness
○ Joint laxity
○ Flat feet
○ Dislocations and sprains
○ Average life expectancy
○ Associated with blue sclera, triangle face, and conductive hearing loss
How severe is Type II OI? How much bone fragility?
Not compatible with what?
How much do not survive and when?
- most severe form
extreme bone fragility
- not compatible with life
- 80% do not survive past 1 week
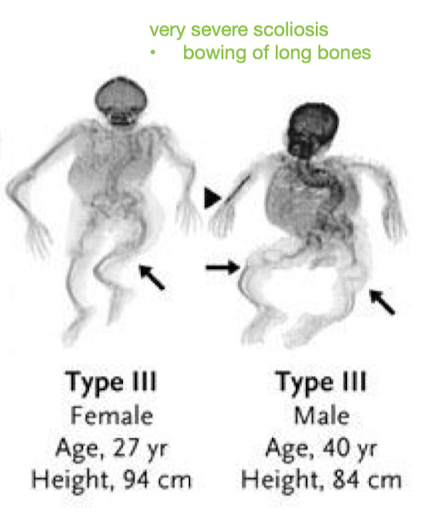
Is OI Type III often autosomal dominant or recessive inheritance?
___ presentation?
Progressive deformity of long ___, skull, and ___ = short stature
How does type III affect teeth?
Hearing loss?
How is the kyphoscoliosis?
what may it result in?
- often autosomal dominant, rarely recessive
- severe presentation
- long bones, skull, and spine
- dentinogenesis imperfecta 45%
- hearing loss common
- kyphoscoliosis - severe
may result in respiratory compromise
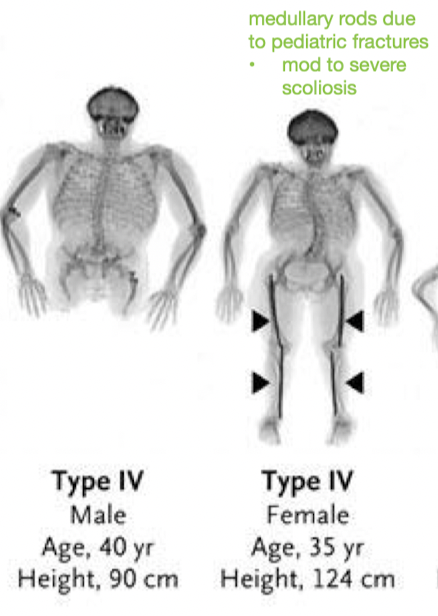
How much bone fragility in OI Type IV?
which deformity?
Is there dentinogenesis imperfecta?
Hearing loss?
Prognosis for ambulation?
- Mild to moderate bone fragility
Long bone deformity
- Dentinogenesis imperfecta - common
- Variable hearing loss
- Prognosis for ambulation is excellent
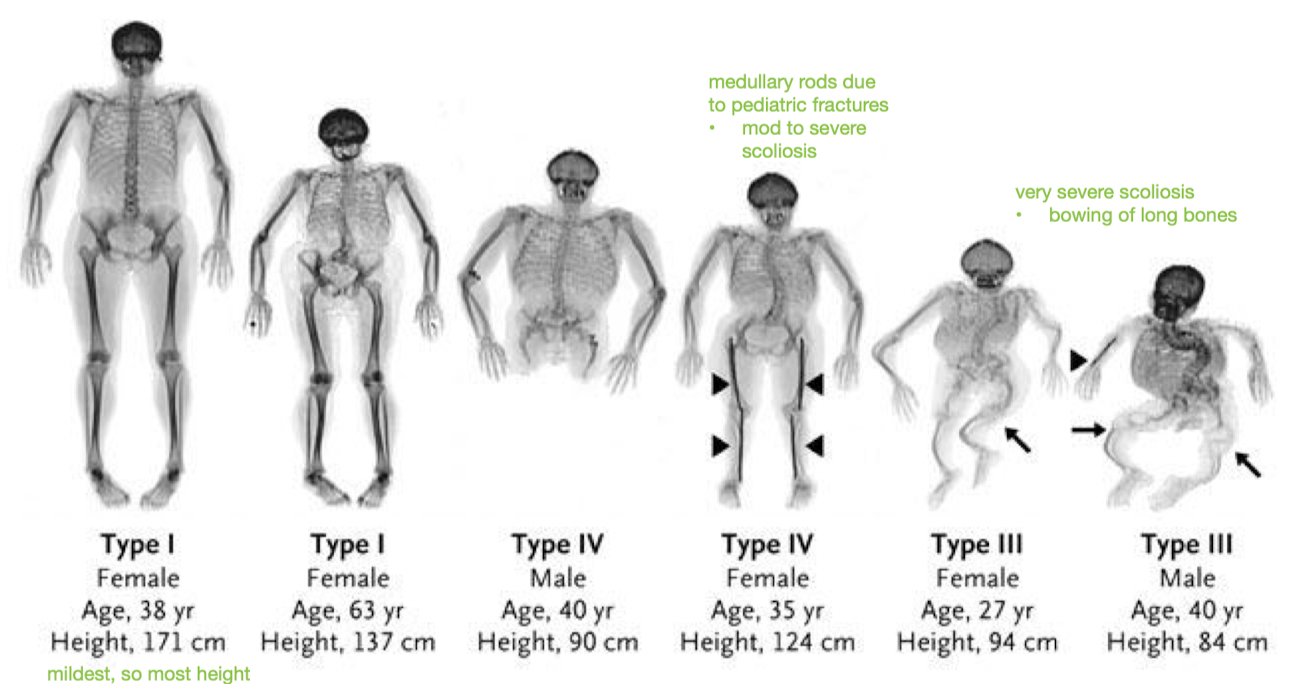
What is the order from mild to severe of the 4 types of OI?
1 - 4 - 3 - 2
For diagnosis of OI, what manifestations do you look for?
___ biopsy for those w/ ___ deficits
ID ___ defect or mutation present
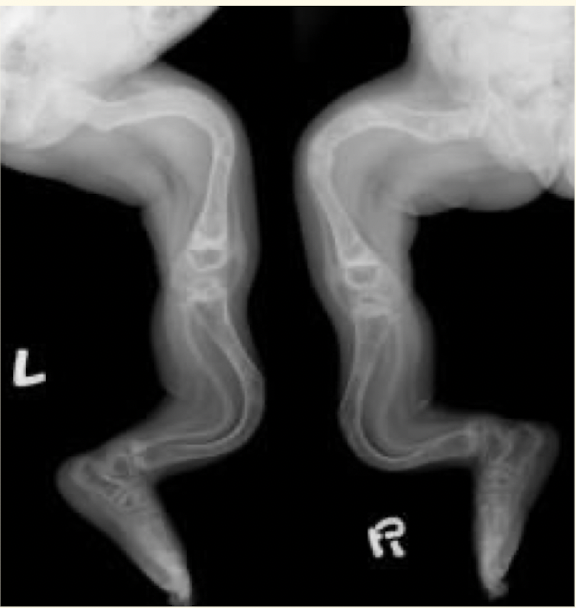
X-rays and bone scans show evidence of multiple old ___ and skeletal ___
of the bone, where are fractures usually?
clinical manifestations
skin biopsy for those w/ collagen deficits
ID collagen defect of mutation present
evidence of multiple old fractures and skeletal deformities
fractures usually in the shaft of the bone, not epiphysis
Medical Management: Is there a cure?
use of bispho____ - medicine used in what?
what is whole body vibration being researched to increase? (2)
no cure
use of bisphosphonates - meds used in osteoporosis
to increase bone density and strength
Medical Management: Internal fixation w/ intramedullary rods to the femur is best when?
____ rods can be used to ___ w/ patients
but there are complications w/ ___ and ___ of rods
Early WB w/ orthotic support when?
For spinal deformities like scoliosis/kyphosis, are braces required?
- to the femur is best done after 4-5 y/o
telescoping rods can be used to grow w/ patients
complications w/ rotation and migration of rods
Early WB w/ orthotic support ASAP after surgery
spinal deformities (scoliosis/kyphosis) = bracing not usually recommended
In infancy, rib and skull fractures may compromise what? (2)
Why might parents hold their infant less?
how much bonding occurs? so what is important?
What size head do infants have, and what skull and limbs?
Special needs regarding ___ (3)
whose role is important, to minimize what?
- Rib and skull fractures may compromise respiratory and neural status
- Fear of fracturing infant's bones leads to less holding of infant
less bonding —> need to educate parents a lot
- Infants often have large head with soft membranous skull and bowed limbs
- Special needs regarding handling, positioning and playing
Caregiver role is paramount in minimizing fractures
Examination: What assessment identifies pain?
What 3 activities to assess caregiver handling/positioning techniques?
Which range of motion do you and do you not assess, for what?
- pain: FLACC
- 1) diapering 2) dressing 3) bathing
- assess AROM, not PROM for functional ranges
Examination: How do you examine muscle strength? (2)
Gross motor developmental eval is important to determine sitting by 10 months is what?
which 2 assessments would you use?
What 3 functional tests would you use for walking or speed?
- muscle strength through observation and palpation of muscles
- sitting by 10 months = good predictor of future walking ability
PDMS-2, Bayley
- Functional tests: 1) gait speed, 2) timed walk tests, 3) TUG
Examination: What assessment for school?
What does the PEDI or PEDI-CAT assess for? (3)
Assess what needs?
- School Function Assessment
- PEDI/PEDI-CAT - function in ADLs, mobility, social/cognitive
- assess equipment needs
Intervention - Education on proper handling and positioning:
Avoid putting forces across what bones?
how can you position the legs and arms to support head and trunk?
may carry infant w/ what?
Dress w/ tight or loose clothing?
in addition to Velcro closures, snaps along where?
avoid overdressing to reduce what?
- Avoid putting forces across the long bones
Support head and trunk with the legs and arms gently draped across the supporting arm
May carry infant supported on a pillow
- Dress with loose clothing
Snaps along the front or side, or Velcro closures
Avoid overdressing to reduce excessive sweating
Intervention - Education on proper handling and positioning:
What do you avoid in diapering?
Bathing in a ___, plastic basin
Infant carrier designed to safely support which 3 body parts?
used for what?
- avoid lifting by ankles for diapering
- padded, plastic basin
- carrier to support head, trunk, and extremities
used for household transportation
Intervention:
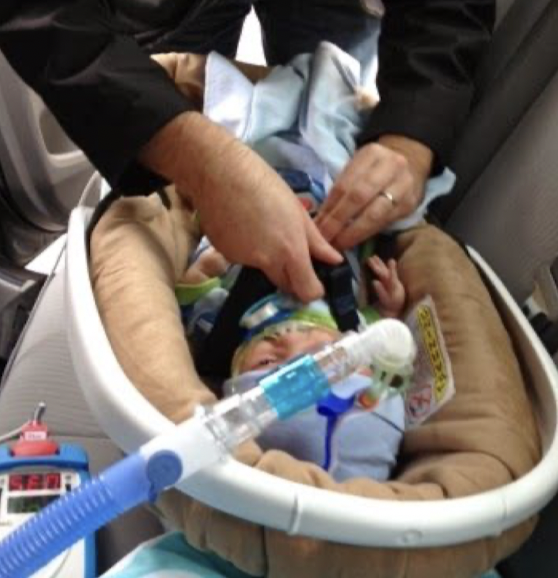
In the car seat, what can they be supported by?
What else may be indicated depending on needs?
What are they safest in? What harness distributes pressure and for how long?
what may be needed?
- can use pool noodles
- car bed padded around
- safest in rear facing car seat, for as long as possible w/ 5-point harness
may need extra padding
Intervention - Infancy - Positioning:
In side lying, supported by?
child can be what? (2)
In prone, start w/ what?
advance to positioning over what? (2)
In supine, provide what?
hip position w/ what?
how often to change positions and should not restrict what?
important for preventing ___ and minimizing what?
- Sidelying- supported by towel rolls
Child can be active and is protected
- Prone- start with child on the caregiver
Advance to positioning over towel roll or with soft wedge
- Supine- provide support for arms
Hips should be in a neutral position with knees over a roll
- Position should be changed frequently and should not restrict active spontaneous movement
- Important for preventing fractures and minimizing joint malalignment and deformity
*go to slide 64 and 65*
grrr
School age & adolescence:
Emphasis on what 3 types of fitness?
What posture is common?
of the legs?
of the feet?
Which joint often dislocates?
- emphasis on muscle strengthening, aerobic conditioning, & protected ambulation
- scoliosis and kyphosis
bowing of legs
pes valgus
- patellofemoral joint
School age & adolescence:
When does frequency of fractures decrease?
What 2 factors of health are important and are we worried about at this age?
Sweating?
Core strength and ability to sit scoot to help with what? (2)
- decrease after puberty
- weight management and physical activity
- excessive sweating
- to help w/ ADLs and transfers
Transition to Adulthood:
To keep them moving and enhance lifelong health:
regular ___?
___ management
___ rich diet
limited ___
avoidance of ___
incidence of scoliosis approaches ____% in teens and adults
most have what (2) for community mobility?
regular exercise
weight management
calcium rich diet
limited caffeine
avoidance of tobacco
incidence of scoliosis approaches 80-90% in teens and adults
most have power or manual wheelchair for community mobility