Data Representation (P1)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Types of Primary Storage - Virtual Memory (Definition, How it works)
An extension of RAM that enables data that is not currently being used to be transferred to the hard disk to free up space in the RAM.
RAM is full
New data needed to be stored in RAM, so data not currently in use is moved to hard drive
Space created; new data transferred into RAM
When original data is required again, it is moved back from virtual memory into RAM.
Virtual Memory Advantages
Allows more programs to be run at the same time.
More efficient utilisation of memory
Prevent requirements of more RAM
Virtual Memory Disadvantages
Slower access times compared to RAM
Thrashing - more time is spent swapping and transferring than actually working: performance decrease
Binary
Binary is a base 2 number system that only has 2 possible values - 0 or 1.
Data storage hierarchy
Bit - (A 0 or 1)
Nibble - (4 bits, like 0101)
Byte - (Single character, like A)
Kilobyte - (Short email)
Megabyte - (Minute of music)
Gigabyte - (500 photos)
Terabyte - (500 hours of films)
Petabyte - (1.5M CDs)
Denary
Denary (decimal) is the number system that has 10 possible values - 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9.
Why do computers use binary?
Computer systems consist of switches that only have two values - on (1) or off (0).
Storage Characteristics - CRAD PC
Capacity
Reliability
Access Speed
Durability
Portability
Cost
Access Speed
How quickly data on the device can be read or edited.
Capacity
The maximum amount of data that can be stored on the device.
Cost
The price to purchase a storage device.
Durability
The strength of the device to last without breaking.
Portability
How easy it is to carry/move the device.
Reliability
The likelihood of the device continuing to perform well over time.
Hexidecimal
A base 16 number system: a shorthand for binary.
Has 16 possible values: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F
Hexadecimal Advantages
Less prone to errors when reading/writing
Simpler - uses fewer characters to write the the same value in binary
Binary Addition - Overflow error
An overflow error occurs when a binary value is too large to be stored in the bits available.
With a byte, (8 bits), largest number that can be held is 255. A sum of two binary numbers that equal > 255 will result in an overflow error as its too large to be held in 8 bits.
Binary Shift (Definition, Shift types)
A method used to multiply and divide binary numbers.
Shift to left = multiply
Shift to right = divide
Shift by 1 → Effect of 2
Shift by 2 → Effect of 4
Shift by 3 → Effect of 8
Character Set: Why it’s needed and Two Main Types
A table that matches a character to a binary value. Necessary for computers to exchange data and humans to input characters.
Two types: ASCII and Unicode
ASCII + Possible characters
A 7-bit code able to represent the English alphabet, numbers, some symbols and control characters.
→ 128 possible characters
Extended ASCII + Bits + Possible characters
Uses 8 bits instead of 7, to include extra symbols, mathematical symbols and some non-English characters.
Uses 1 byte (8 bits)
→ 256 possible characters
Unicode + Bits + Possible characters
Character set used for symbols outside the English language, requiring more storage than ASCII.
Uses 2 bytes (16 bits)
→ 65,536 possible characters
Allows different languages, punctuation, symbols and emojis.
File Size of Text File Equation
bits per character * number of characters
e.g. A small text file uses ASCII, (8 bits per character) there are 300 characters in the file.
→ 300 × 8 = 2,400 bits
→ 300 bytes / 0.3 kilobytes
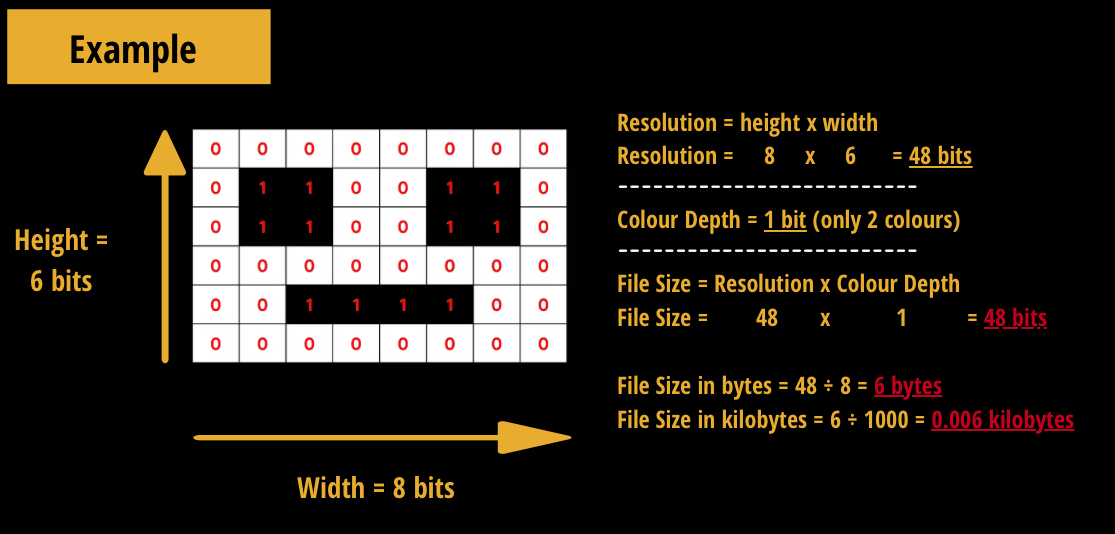
Pixel
Individual dots of colour stored as binary codes.
Resolution - Impact on image quality and file size
Total number of pixels in an image.
A higher resolution means more pixels are used to represent the image, increasing image quality.
→ Also increases file size as more data is needing to be stored.
Bit (colour) depth - Impact on image quality and file size
Number of bits used to represent the colour of each pixel, determining the number of colours displayed.
Higher bit depth means more colours can be represented, increasing image quality.
→ Also increases file size as more data is needing to be stored.
Metadata and examples
Additional data about a file.
Height and width in pixels
Colour depth
Resolution
Date created
File type
Author details
Bitmap Images and Characteristics
Image made of pixels where each pixel is assigned a binary value and represents a single dot of colour.
Increased number of pixels = Increased resolution = Increased quality
Larger file size - storing information of every pixel
Suitable for photos, images capturing real-world objects.
Re-sizing issues - stretching or shrinking pixels leads to quality loss.
Vector Images and Characteristics
Images created using mathematical equations and points, rather than individual pixels.
Usually smaller in file size - only store mathematical information
Ideal for illustrations, Logos and Web design - can be rescaled without quality loss
Resize-ability - can be resized without quality loss, not pixel based
File size of Bitmap Equation
file size = resolution * colour depth
→ resolution = width of pixels * height in pixels
→ colour depth == bit depth
Converting Analogue Sound to Binary
Analogue sound waves must be digitally recorded and stored as binary.
To record the sound, the amplitude (height) of the analogue sound waves is measured and recorded in binary at specific intervals.
Sampling an Analogue Sound Wave
Digital sampling is discrete (separate) and not continuous like analogue waves.
To get the highest quality sound, sample rates must increase (samples per given time) to recreate the analogue wave as closely as possible.
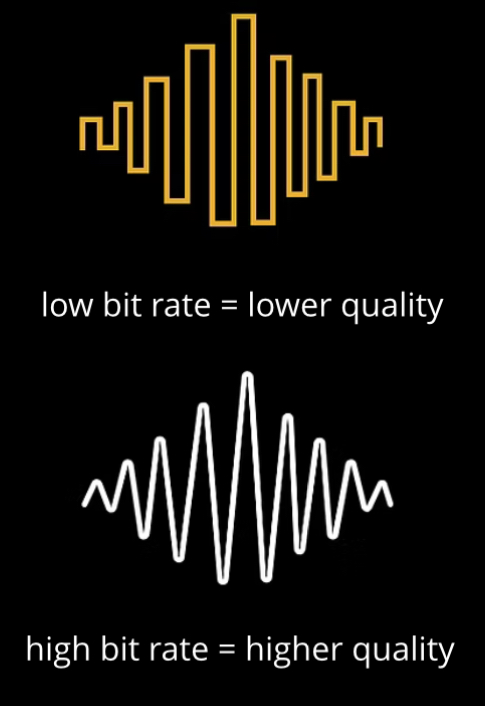
Sample Rate
Number of samples taken per second, measured in Hertz.
Higher sample rate means better audio quality - digital wave resembles the analogue wave more closely.
→ Larger files sizes - more data is stored for each individual sample.
Bit Depth - Impact on sound quality and file size
Number of bits available to represent each sample.
→ Common bit depth is 16 bits.
Higher bit depth means more bits available to be used for each sample - quality increase as digital wave more closely resembles the analogue wave.
Increase file size - each sample stores additional bits.
Sound File Size Equation
sound file size = sample rate * bit depth * duration
E.g. A short audio sample has a bit depth of 4 and a sample rate of 10 samples per second. The clip is 15 seconds long.
→ 4 × 10 × 15 = 600 bits
→ 600 / 8 =75
→ 75 bytes
Compression and benefits
Process of making a file’s size smaller.
Files take up less storage space.
Files can be transferred quicker.
Files can be read from or written to quicker.
Lossy Compression
Method of data compression that reduces file size by permanently removing some data.
Algorithms remove data that is least likely to be noticed
Original file cannot be restored from compressed version
Suitable for images and videos
Lossless Compression
Method of data compression where file size is reduced without permanently removing any data, meaning no quality is lost.
Algorithms looks for patterns in the data - repeated data is only stored once, including information about restoration
Original file can be restored
Suitable for text files and audio