KIN 216 - Linear Kinematics
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
what is biomechanics?
the effect of forces on living systems
OR
the study of forces and their effects on living systems
what did borelli do?
contributed to scientific investigation by testing hypothesis against observation.
studied the mechanics of animal locomotion
what did etienne-jules marey do?
interested in capturing animal movements; animal mechanism
developed cameras that could record several phases of movement (flying pelican 1882)
allowed movement to be studied
who coined the term “biomechanics”?
Nikolai Bernstein
the first ergonomist: study of the workplace
wanted to make the workplace safer
examined movement during manual labour to optimise productivity (1922)
what did nikolai bernsteins research show?
that most movements are composed of smaller movements
these little movements effect eachother
what types of equipment did they have in the 20th century to measure and record forces and motions?
cameras and pressure-sensitive equipment
what was one of the first texts, released in 1955, to emphasise mechanics/technique?
the Scientific Principals of Coaching
biomechanics is…
the study of structure and function of biological systems
define sport and exercise biomechanics:
the study of forces and their effects on humans in exercise and sport
focus: goal-directed tasks
what is quantitative reasoning?
using numbers to try and solve a problem
what is biomechanics about
reason, model, solve problems
why biomechanics is helpful?
PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT: to improve performance by improving technique, changing the equipment used, and making modifications in training
REDUCTION AND REHABILITATION OF INJURY: to prevent or recover from injury by finding techniques to reduce injury, and designing equipment to reduce injury
what is kinematics?
describing motion over space and time
static
in a constant state of motion
can be motionless or constant speed
a = 0
dynamic
a change in velocity
acceleration is present
basic units of measurement
MSK
meters: length
seconds: time
kgs: mass
linear kinematics is the movement between
points
biotribology examines;
how living systems interact with objects during motion
orthodics help to:
even out the contact forces between the foot and the ground to reduce pain and discomfort
shoes with firm midsoles…
reduce the degree of lateral movement
What does it mean to move?
a change in position
how do we quantify movement?
where we are in space (our position)
how long the movement took (time)
linear motion
translation
change in position
body moves unified, in the same direction, at the same distance
what are the two different types of linear motion?
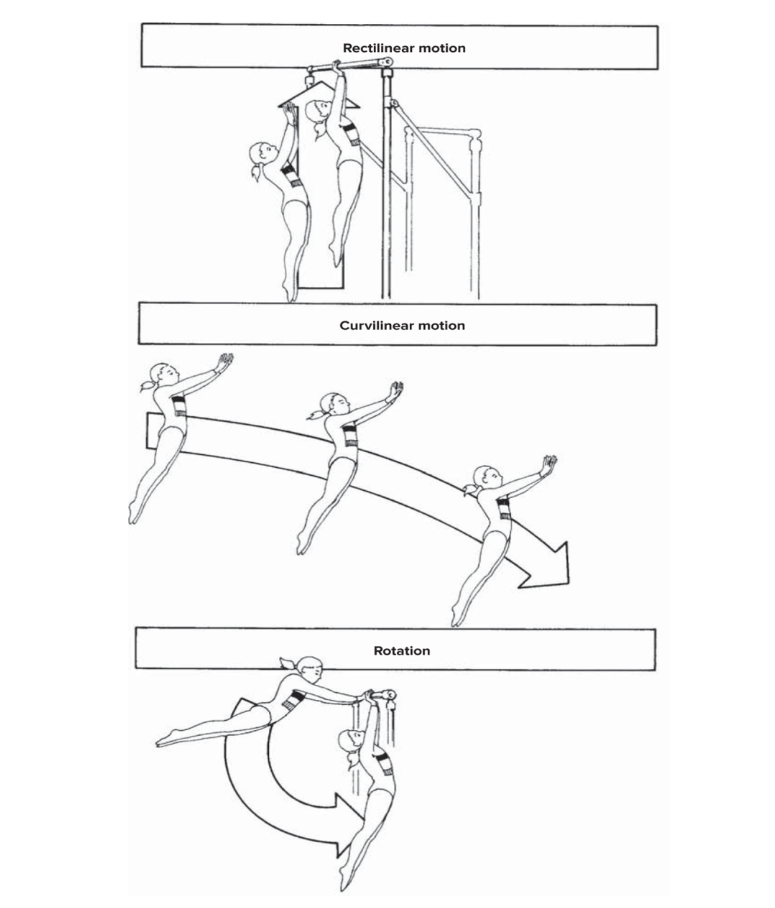
rectilinear motion
curvilinear motion
rectilinear motion
movement along a straight line: jumping from low to high bar (pretend no swing), elevator, 50m dash
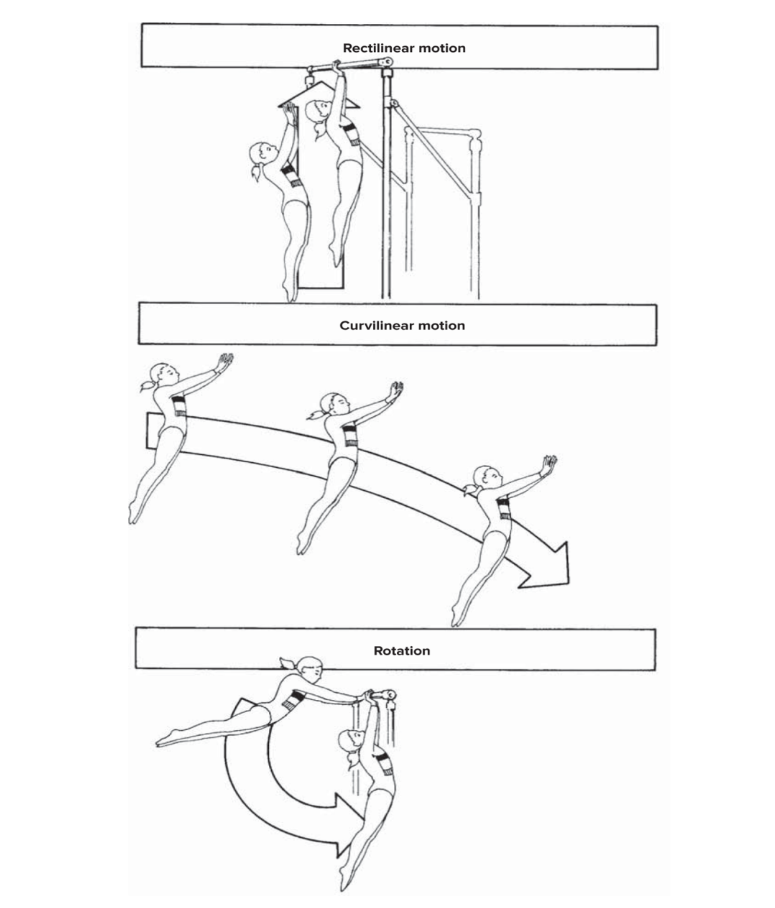
curvilinear motion
movement along a curved line: motion of a snake
linear kinematics is concerned with the description of:
linear motion
describing where you are in space (where u began, where you finish)
how fast it takes you to get from point a to point b
were u in a static (constant velocity) or dynamic state
position is defined as
location in space
could be described in 3 different dimensions
up/down
left/right
forward/back
to identify position, we need to identify:
a starting point for movement
what is the most common spatial system of refrence?
the Cartesian coordinate system
measured in x and y (horizontal and vertical)
the upper right box is which quadrant?
quadrant I
the upper left box is which quadrant?
quadrant II
scalars are concerned with?
size only.
(magnitude)
ex. distance, speed, pace
vectors are concerned with what?
magnitude and direction
ex. displacement, velocity and acceleration
the length of the arrow indicates what of the vector
the size/magnitude
the total length of travel =
distance
the change in position =
displacement
speed and velocity both measure how fast or slow a system moved BUT speed measures __________ and velocity measures ___________
speed measures change in distance (this is a scalar quantity)
velocity measures change in displacement (vector quant
pace is:
how many minutes it takes someone to run a km
it is the inverse of speed
gives runners something to brag about, everyone can run 5k but everyone does it at a different time
change in time / change in distance
for aceleration to be present, what must also be present?
a force must be present; forces are what produce a change in velocity
dynamic motion is characterised by a change in…
velocity
acceleration is
the change in velocity / change in time
if the final velocity is greater than the initial velocity, then a is
positive
if the final velocity is smaller than the initial velocity, then a is
negative
if the final velocity is equal to the initial velocity, then a is _________ and the system is in a ________ state
0
static
velocity is constant
pediatricians use linear kinematics for
assessments
coaches use linear kinematics for
teaching movements
therapists use linear kinematics for
therapy
movement is described over
a period of time
(t2 - t1)
characteristics of average time period
occuring over a designated interval of time?
typically a longer time period
simplified, overall behaviour
characteristics of instantaneous time period?
occuring during a finite interval of time
typically during a smaller time period
describing motion at critical time intervals
differentiation
obtaining information using another value
the process of going from displacement to velocity to acceleration
how much a quantity is changing at a given point. allows you to calculate the slope of the proceeding quantity
CALCULATING THE SLOPE
the slope =
rise / run
y2 - y1 / x2 - x1
the slope of a displacement vs. time graph at any given point is equal to… ?
the velocity at that given point
the slope of a velocity vs. time graph at any given point is equal to… ?
the acceleration at that given point
integration
obtaining information using another value
the process of going from acceleration to velocity to displacement
to bring together / incorporate parts into a whole
CALCULATING THE AREA UNDER THE SLOPE
the area under the slope of a velocity vs. time graph is equal to… ?
the displacement
the area under the acceleration vs time graph is equal to… ?
the change in velocity
would a bullet fired horizontally from a gun, or another bullet dropped from the same height, hit the ground first?
they would hit the ground at the same time because horizontal and vertical components are independent of each other therefor analyzed separately
what is a projectile?
a body projected into the air or dropped from a height
the moment it is in the air, there are no other forces acting upon it other than gravity or air resistance
projectiles are ONLY under the influence of… ?
air resistance and gravity
if air resistance is too small to measure, the only force acting upon it is gravity
what is the acceleration due to gravity?
-9.81 m/s2
or
9.81 m/s2 downward
if the force of gravity is constant, this means that… ?
the acceleration of the system will not change (uniform acceleration)
vertical and horizontal components are analysed seperately because?
the two components are independant of each other
gravity only influences vertical motion (up/down)
air resistance only influences horizontal motion
once a body is projected into the air, velocity is constantly
trajectory
the path travelled when describing projectile motion
initial velocity on projectile motion:
IS NOT equal to 0, in a projectile motion there will always be that initial velocity because it was being launched into air
apex
the highest point in the travelled path of a projectile motion
in a projectile motion, acceleration is… ?
constant
range
the maximum horizontal displacement travelled
if the take off and landing heights are the same, what does that mean for the total (horizontal) time in terms of the vertical time up?
the verticle time up is equal to the verticle time down, therefore the verticle time up is half the total (horizontal) time.
if you have the time it takes to get to horizontal you can times that by 2 to get total time
what three factors effect projectile motion
projection speed (vi)
projection angle (theta)
relative projection height
what is terminal velocity
as an object is free falling the force of gravity is always acting upon it, meaning that projectiles continue to accelerate while in free fall
as the speed of the system increases, an upward air resistance is created,
the drag force, acts opposing to gravity as a type of friction,
eventually, the drag force will equal the gravitational pull on the system
AT THE POINT the object ceases to accelerate and continues to fall but at a constant speed.
this is called terminal velocity
what effects terminal velocity?
the projected area
what are the laws of constant acceleration
the force of gravity os constant so the acceleration of the system will not change (uniform acceleration)
horizontal and vertical components of a projectile are independent of each other
v2 = v1 + at
v2² = v1² + 2ad
d = v1t + (1/2)at²
in a projectile, what determined the motion?
the initial conditions