MRI Physics Chapter 3 Spin-echo pulse sequences
1/338
Earn XP
Description and Tags
After reading this chapter, you will be able to: Explain the purpose of pulse sequences. Describe how spin-echoes are created. Understand the mechanisms of common spin-echo pulse sequences. Apply what you have learned to understand how images of different weighting are created using spin-echo pulse sequences.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
339 Terms
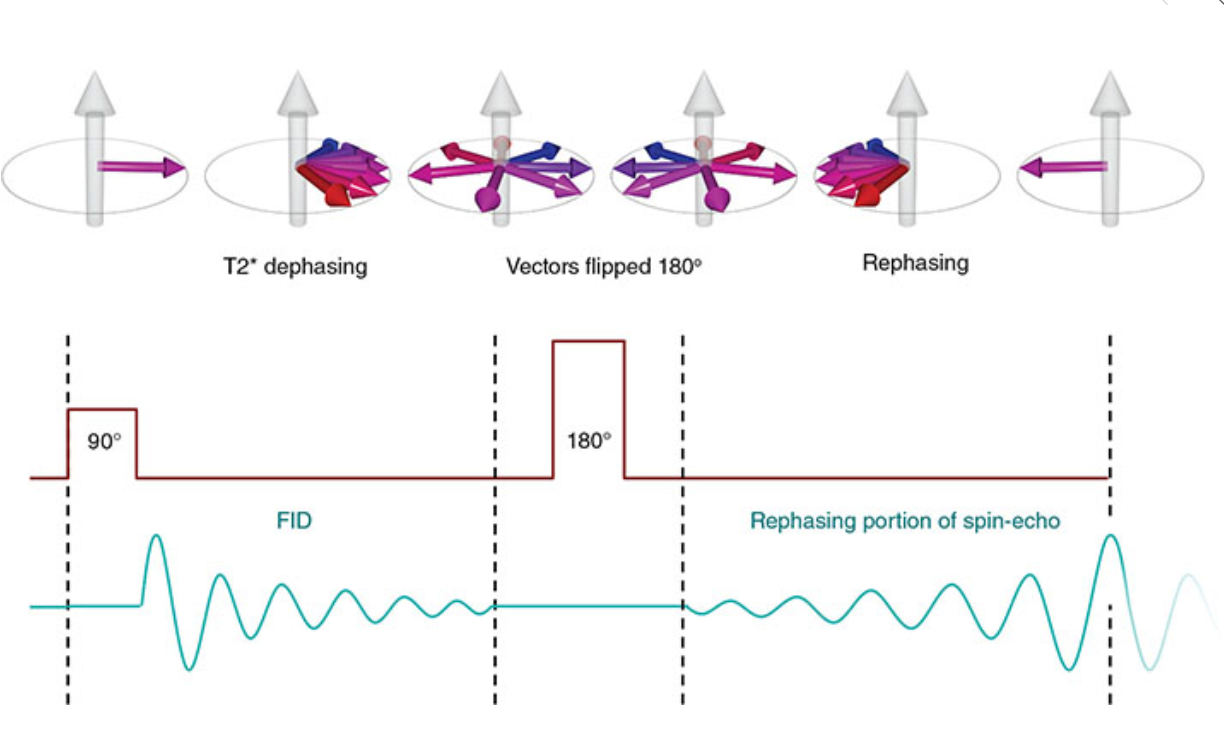
_______, caused by magnetic field inhomogeneities, produces a rapid loss of coherent transverse _______(and therefore signal) so that it reaches zero before most tissues have had time to attain their T1 or T2 _______ times.
dephasing, magnetization, relaxation
A pulse sequence is a carefully coordinated and timed sequence of events that generates a certain type of image _________.
weighting
What is the term for this definition?
time between the RF excitation pulse and the 180° RF rephasing pulse and the time between this and the echo. Sometimes used in STIR sequences as an alternative to the TI.
Tau
The spin-echo pulse sequence commonly uses a 90° RF excitation pulse to flip the ______fully into the transverse plane.
NMV
Having described the fundamental principles of _______, it is time to explore the variety of pulse sequences in the spin-echo family.
rephasing
In spin-echo pulse sequences, T2* dephasing is eliminated by the 180° RF rephasing pulse because magnetic field ________are largely predictable.
inhomogeneities
Contrast is mainly determined by the spin-echo, but there is also a contribution from the fact that the magnetic moments of hydrogen nuclei are rephased by negative _________applications of the slice select and frequency-encoding gradients [2].
polarity
_______spin-echo uses a 90° RF excitation pulse followed by one or more 180° RF rephasing pulses to generate one or more spin-echoes.
Conventional
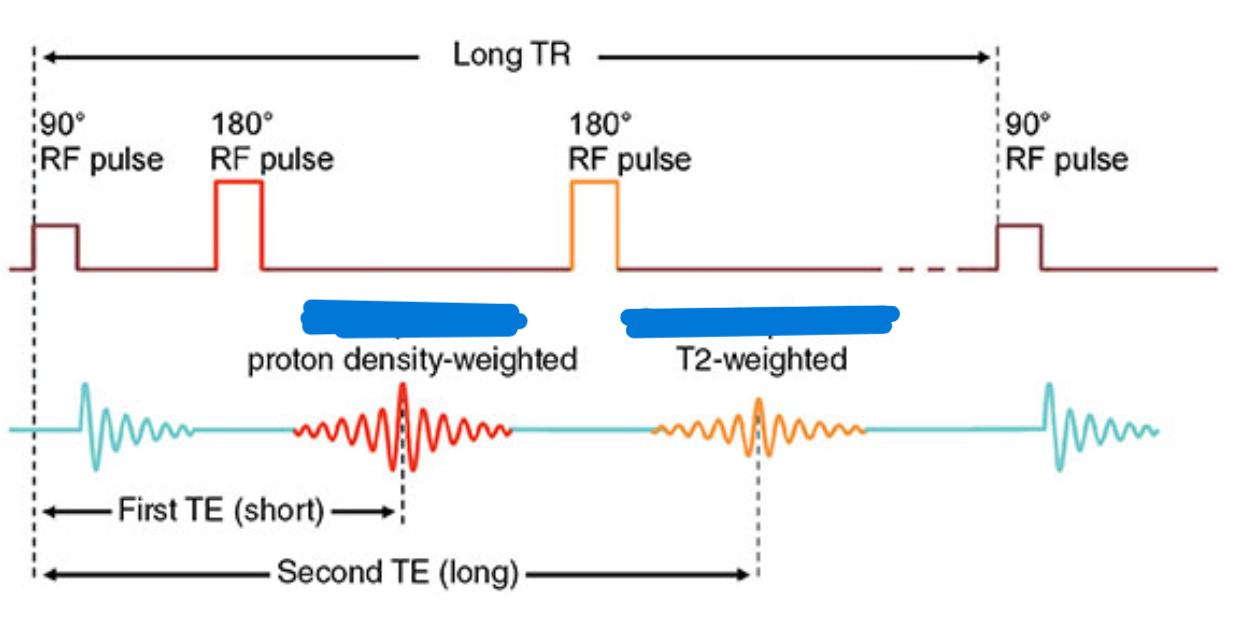
Due to relatively long scan times, PD- and T2-weighted images are often acquired using FSE/_____(see next section).
TSE
Spin-echo
echo produced as a result of a 180° RF rephasing pulse
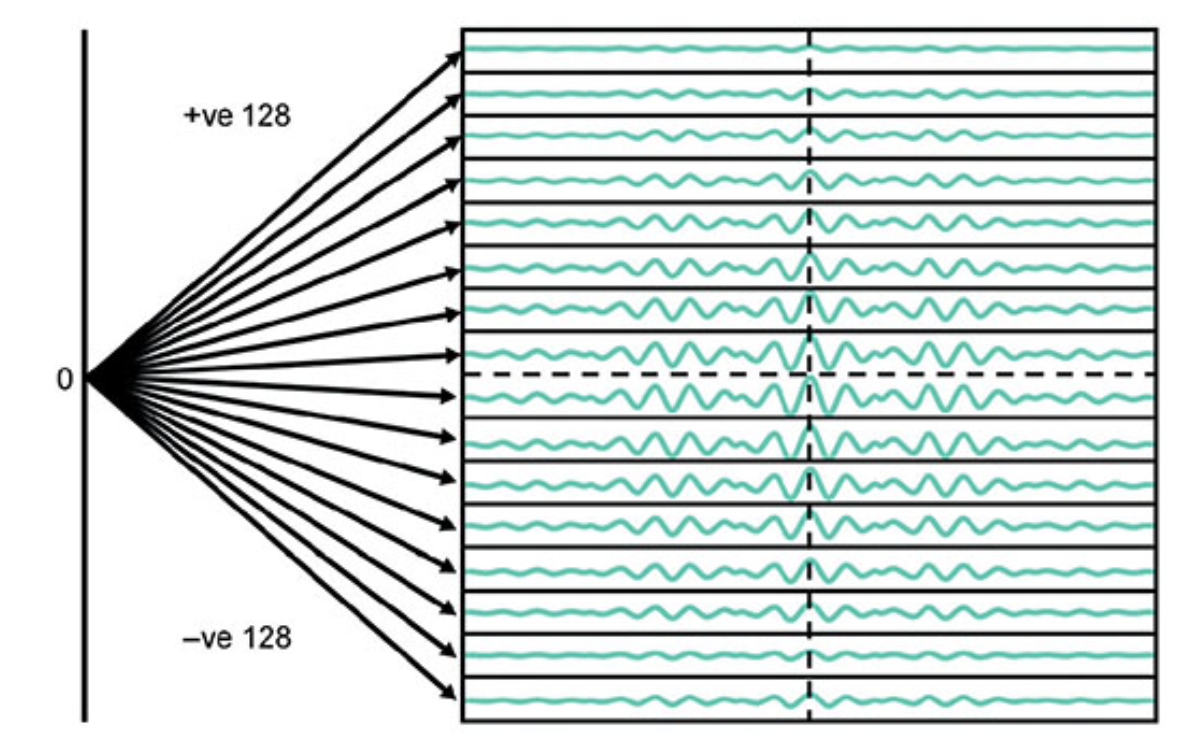
At each 180° RF pulse/phase encoding combination, a different amplitude of phase-encoding gradient ______is applied to fill a different line of k-space.
slope
In ______, the scan time is reduced by performing more than one phase-encoding step and subsequently filling more than one line of k-space per TR.
TSE
Phase encodings performed at the very beginning and end of the echo train are ______, and the signal amplitude of these echoes is therefore small.
steep
What does "NSA" stand for?
Number of signal averages
What is the term for this definition?
time between each echo in the echo train in TSE or FSE.
Echo - Spacing
Selection of a long _____factor means many of lines of k-space are filled every TR so the scan time decreases.
turbo
The longer TRs associated with _____ are relevant in T2 weighting but are far less significant than the huge scan time savings produced by a long echo train.
TSE
In ___________ spin-echo, the time the system spends waiting to collect data is the TE.
conventional
Instead of T1-weighted images, fast IR is usually used to suppress signal from certain tissues in conjunction with T2 _______ so that water and pathology return a high signal.
weighting
In a(n) _______of TSE called driven equilibrium (DRIVE), a reverse __________excitation RF pulse is applied at the end of the echo train.
modification, flip angle
Tissues begin their ______from full inversion as opposed to from the transverse plane as in conventional spin-echo.
recovery
Unsubtracted image combination of flow sensitized data.
Magnitude image
________is an IR pulse sequence that uses a TI that corresponds to the time it takes the fat vector to recover from full _______to the transverse plane so that there is no longitudinal __________ corresponding to fat.
STIR, inversion, magnetization
Phase images include _______data but, in addition, incorporate the contribution made by the inverting pulse.
magnitude
The TI required to _____ signal from a tissue is always 0.69 times its T1 relaxation time (Equation (3.3)).
null
Double IR prep
sequence in which two 180° pulses are used to saturate blood in black-blood imaging.
Driven equilibrium (DRIVE)
pulse sequence that achieves a very high signal intensity from water even when using short TRs.
Echo
signal detected in the receiver coil at time TE. It is made up of rephased magnetic moments in the transverse plane.
Echo-spacing
time between each echo in the echo train in TSE or FSE.
Echo train
series of 180° RF rephasing pulses and echoes in a fast or turbo spin-echo pulse sequence.
Echo train length
number of 180° RF rephasing pulses/echoes/phase encodings per TR in fast or turbo spin-echo.
Effective TE
TE selected in TSE. Used to weight the image as accurately as possible given that echoes with different TEs are used to determine image weighting.
Fast spin-echo (FSE)
pulse sequence that uses multiple applications of the phase-encoding gradient to encode multilines of k-space in a TR. Also called RARE and fast spin-echo.
FLAIR
fluid-attenuated inversion recovery. A pulse sequence that suppresses signal from CSF.
Gradient-echo pulse sequence
sequence that uses a gradient to regenerate an echo.
Inversion recovery (IR)
pulse sequence that begins with a 180° inversion pulse to suppress the signal from certain tissues.
J coupling
causes an increase in the T2 decay time of fat when multiple RF pulses are applied in TSE or FSE.
k-space
an area in the array processor where data on spatial frequencies are stored.
Number of signal averages (NSA)
number of signal averages. Number of times a line of k-space is filled with data.
Null point
the point at which there is no longitudinal magnetization in a tissue in an inversion recovery sequence.
Pathology weighting
achieved in IR pulse sequence with a long TE – pathology appears bright even though the image is T1 weighted.
Phase reordering
process by which the amplitude and polarity of the phase-encoding steps are varied rather than applied linearly.
RARE
rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement. Another term for fast or turbo spin-echo.
RF rephasing pulse
additional RF pulse (usually with a magnitude of 180°) that rephases magnetic moments in the transverse plane to produce a spin-echo.
Spatial encoding
encoding or locating signal in spatial three dimensions of the imaging volume
Spin-echo
echo produced as a result of a 180° RF rephasing pulse.
Spin-echo pulse sequence
sequence that uses a 180° rephasing pulse to generate an echo
STIR
short tau inversion recovery. A pulse sequence that suppresses signal from fat.
Tau
time between the RF excitation pulse and the 180° RF rephasing pulse and the time between this and the echo. Sometimes used in STIR sequences as an alternative to the TI.
Time from inversion (TI)
time from 180° RF inverting pulse to 90° RF excitation pulse in inversion recovery pulse sequences.
Triple IR prep
adds a further inverting pulse to a double IR prep sequence to null fat and blood together.
Turbo factor
number of 180° RF rephasing pulses/echoes/phase encodings per TR in fast or turbo spin-echo.
Turbo spin-echo (TSE)
pulse sequence that uses multiple applications of the phase-encoding gradient to encode multilines of k-space in a TR. Also called RARE and fast spin-echo.
What is the conventional spin-echo sequence in MRI?
A 90° RF excitation pulse followed by one or more 180° RF rephasing pulses
What is the definition of a full echo train?
A method where the entire echo train is used for PD-weighted imaging, and the full scan is repeated for T2-weighted imaging
What is the definition of a split echo train?
A method where the echo train is divided — first half for PD-weighted imaging, second half for T2-weighted imaging
What is the definition of a shared echo train?
A method where early echoes are used for PD-weighted imaging, late echoes for T2-weighted imaging, and intermediate echoes are shared
What is the definition of periventricular leukomalacia (PVL)?
A softening and injury of white matter around the brain’s ventricles due to lack of oxygen or blood flow
What is the clinical use of an MRI sequence with a TI of approximately 300 ms?
Detecting white matter lesions and congenital gray/white matter abnormalities
What is the definition of a positive polarity gradient in MRI diagrams?
A gradient shape drawn above the horizontal line
What is the definition of a negative polarity gradient in MRI diagrams?
A gradient shape drawn below the horizontal line
What does this image show?
180° RF rephasing
What does this image show?
A basic spin-echo pulse sequence.
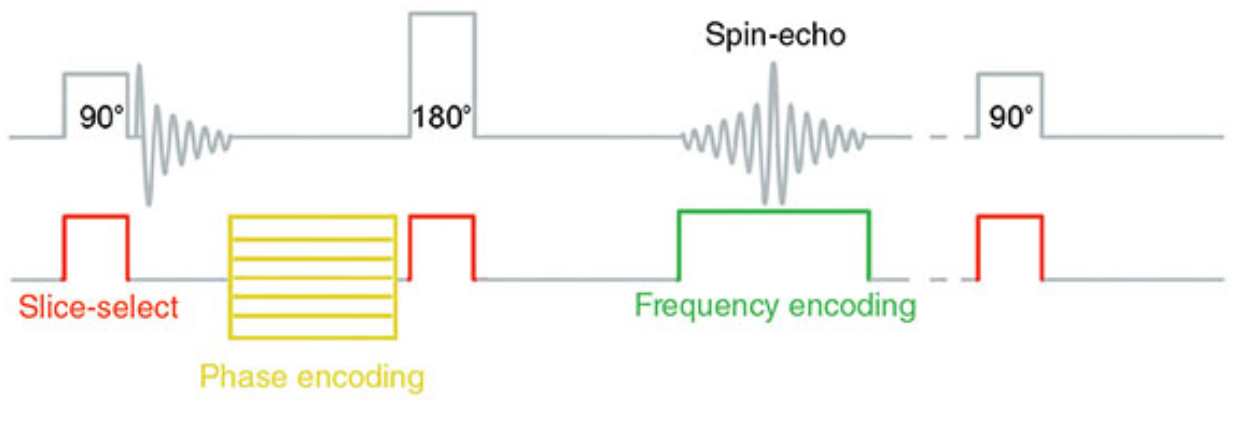
What does this image show?
Spatial encoding in conventional spin-echo
What does this image show?
Phase-encoding gradient slopes.
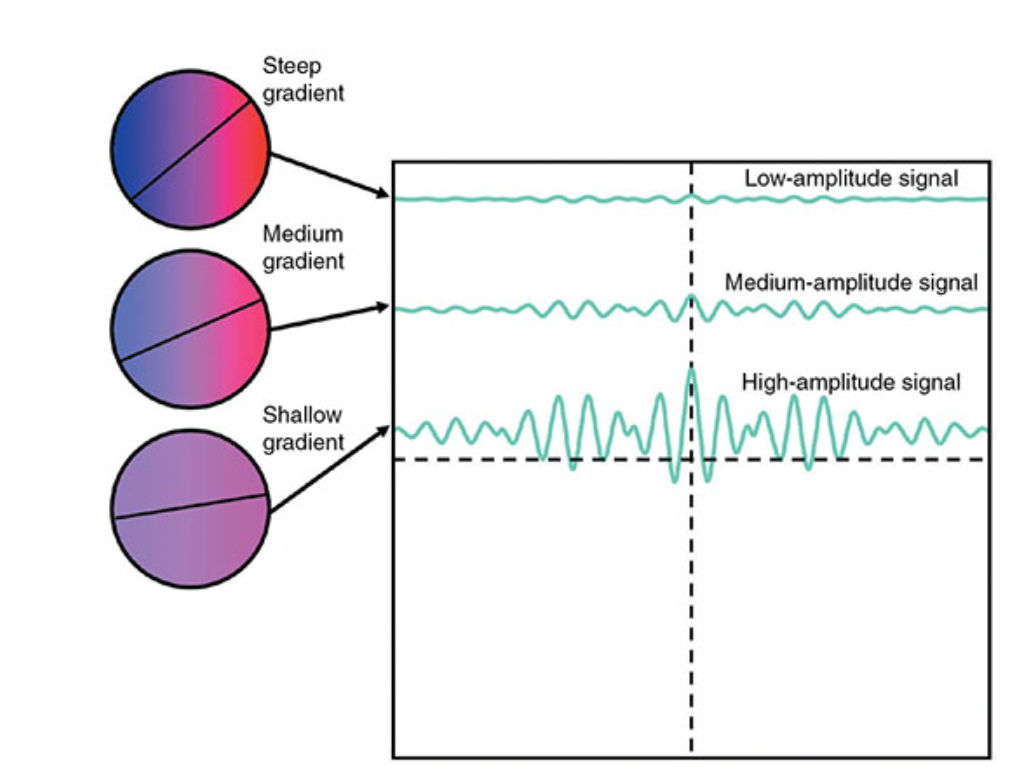
What does this image show?
Phase encoding vs signal amplitude.
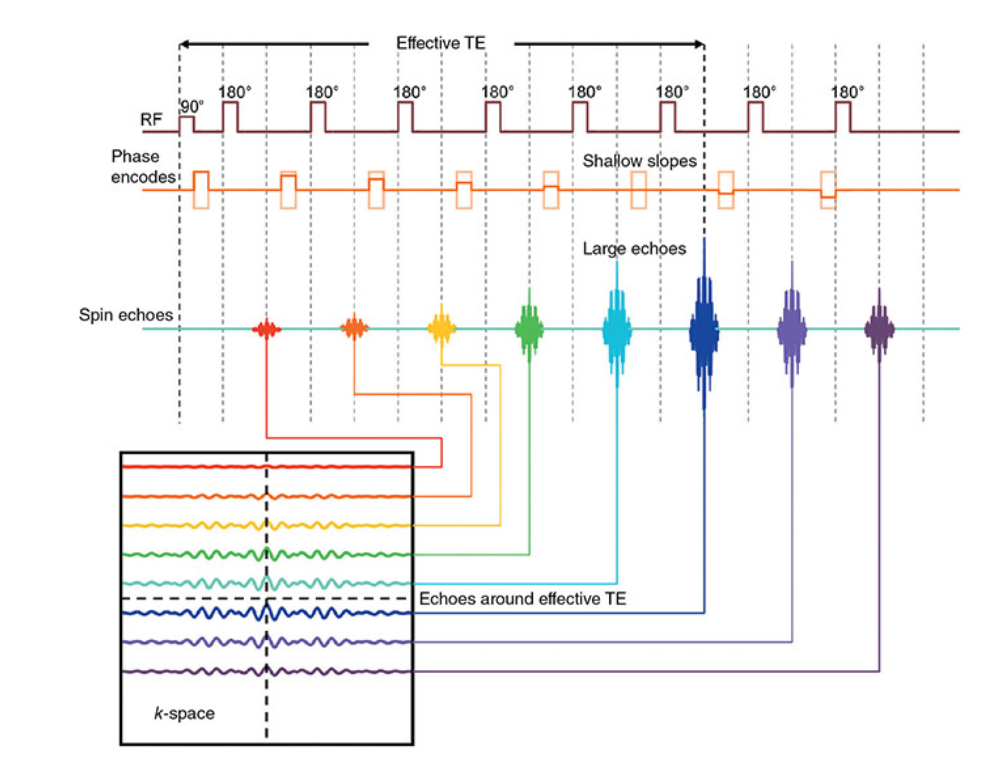
What does this image show?
k-Space filling and phase reordering.
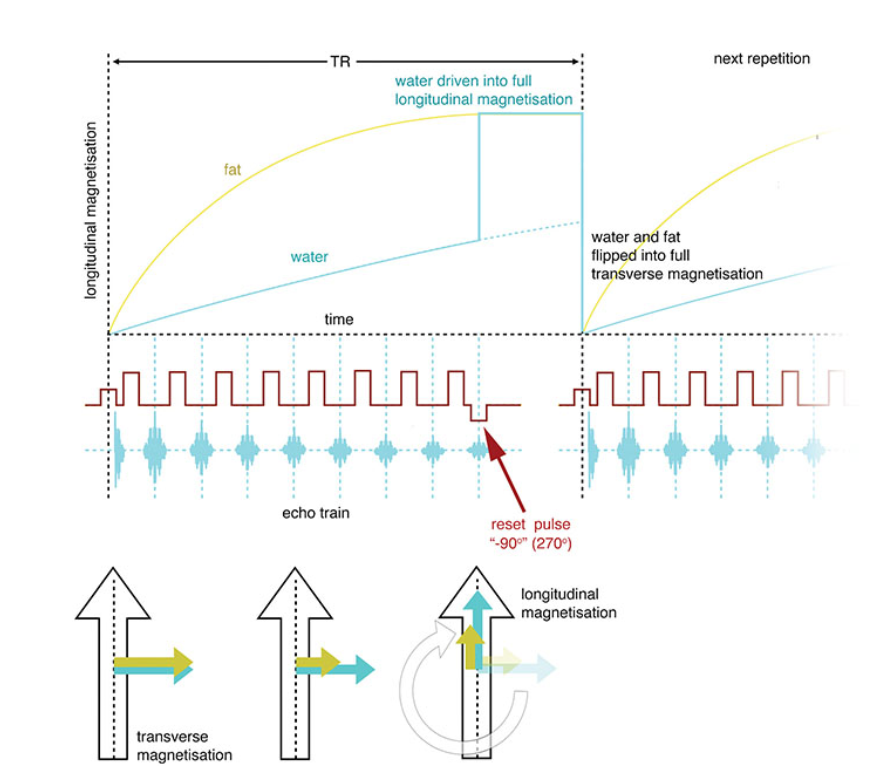
What does this image show?
DRIVE pulse sequence
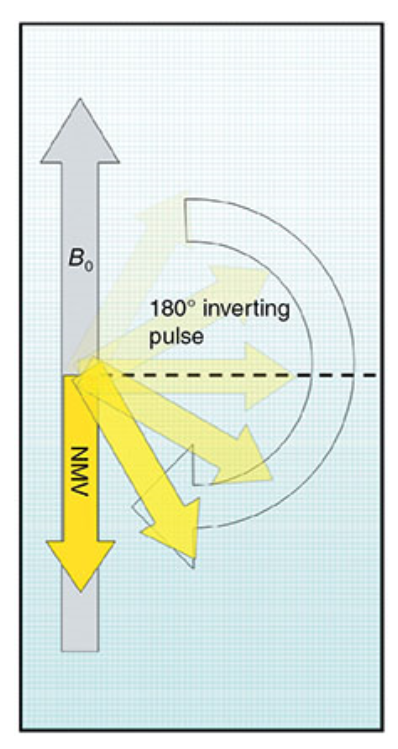
What does this image show?
The 180° inverting pulse in an IR pulse sequence.
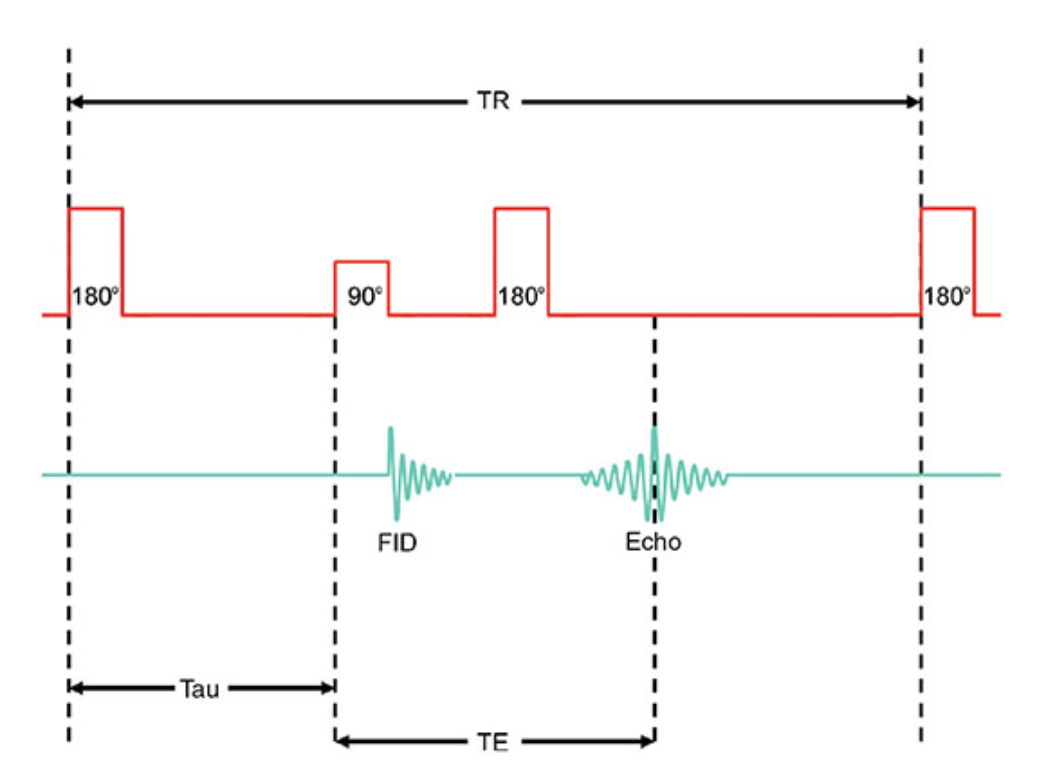
What does this image show?
The inversion recovery sequence
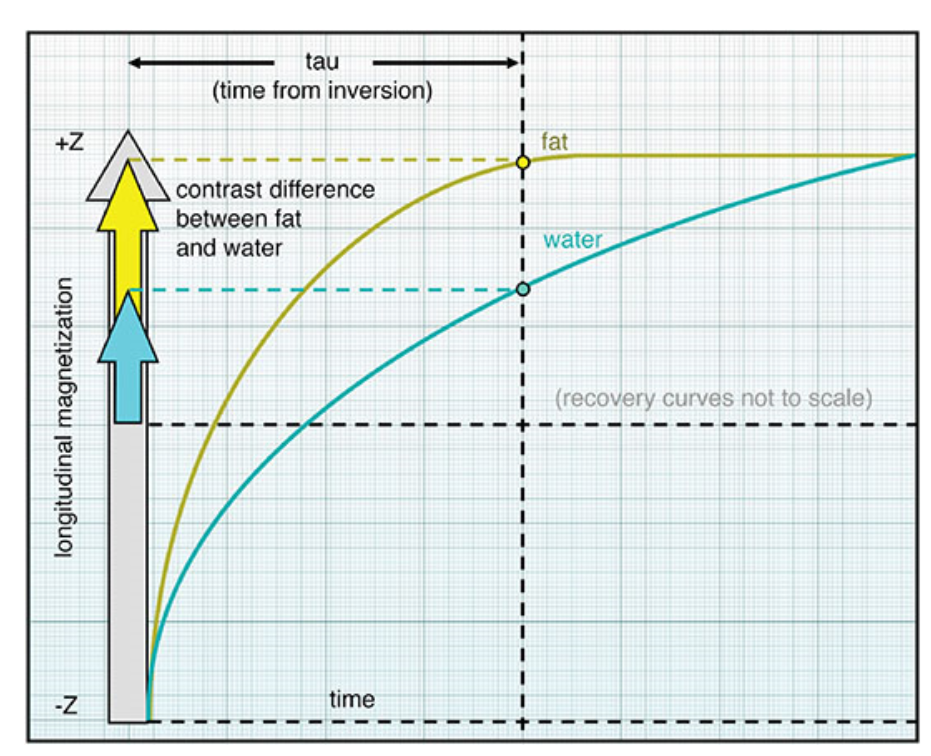
What does this image show?
T1 weighting in inversion recovery.
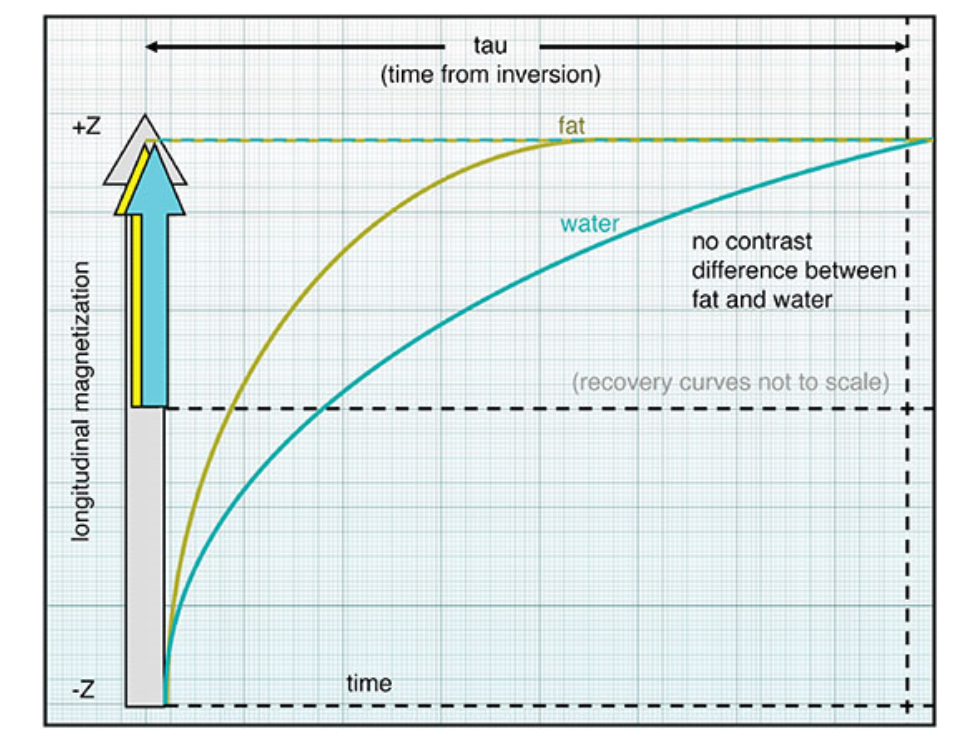
What does this image show?
PD weighting in inversion recovery
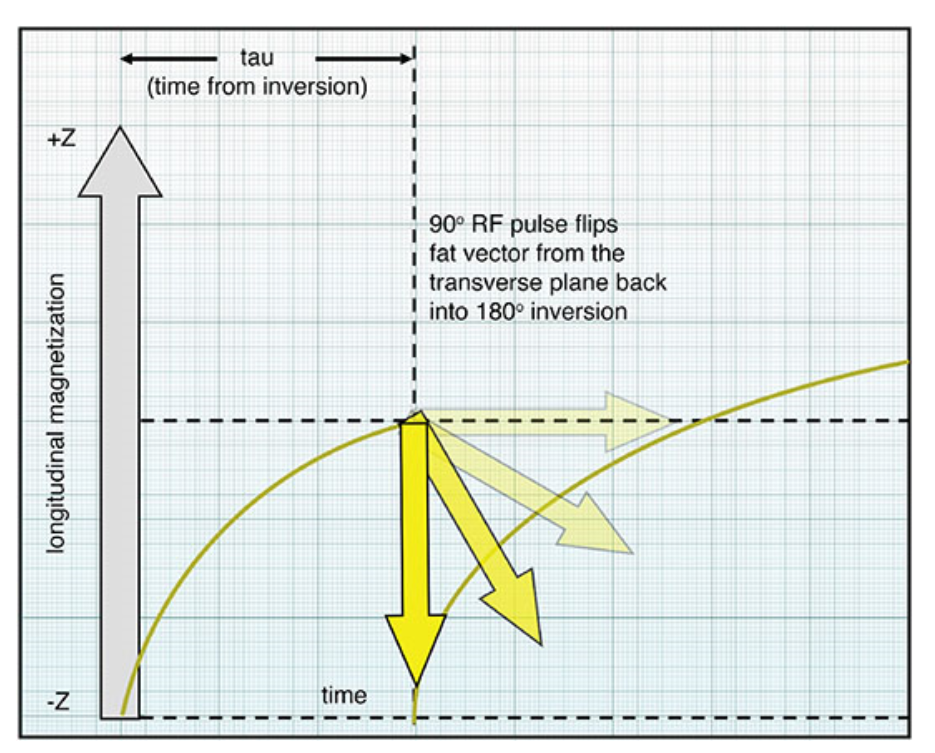
What does this image show?
The STIR sequence.
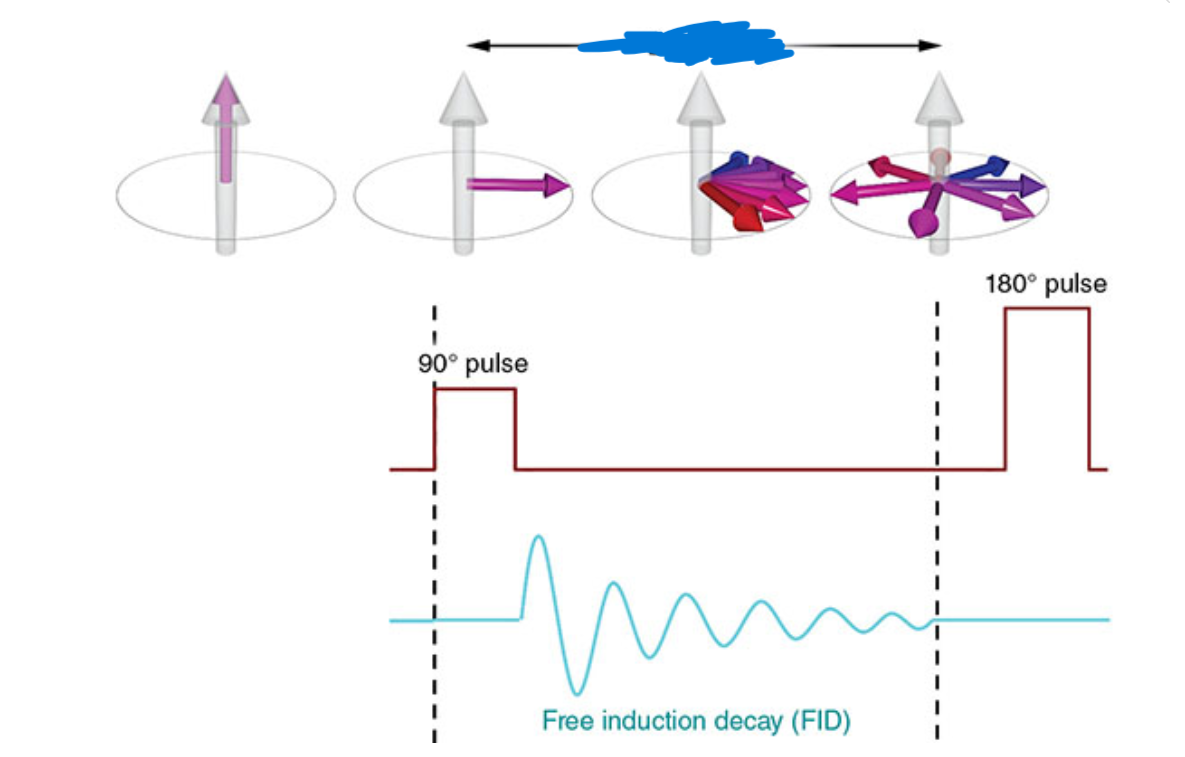
What does this image show?
T2* dephasing
What does this image show?
Tau
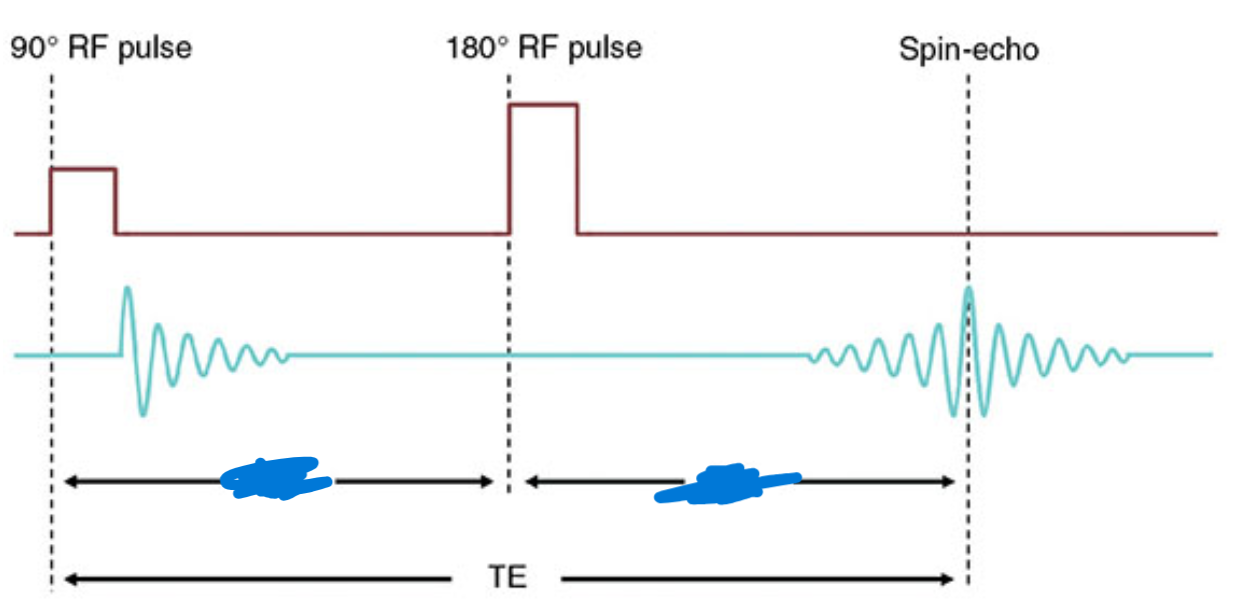
What does this image show?
Spin-echo with one echo
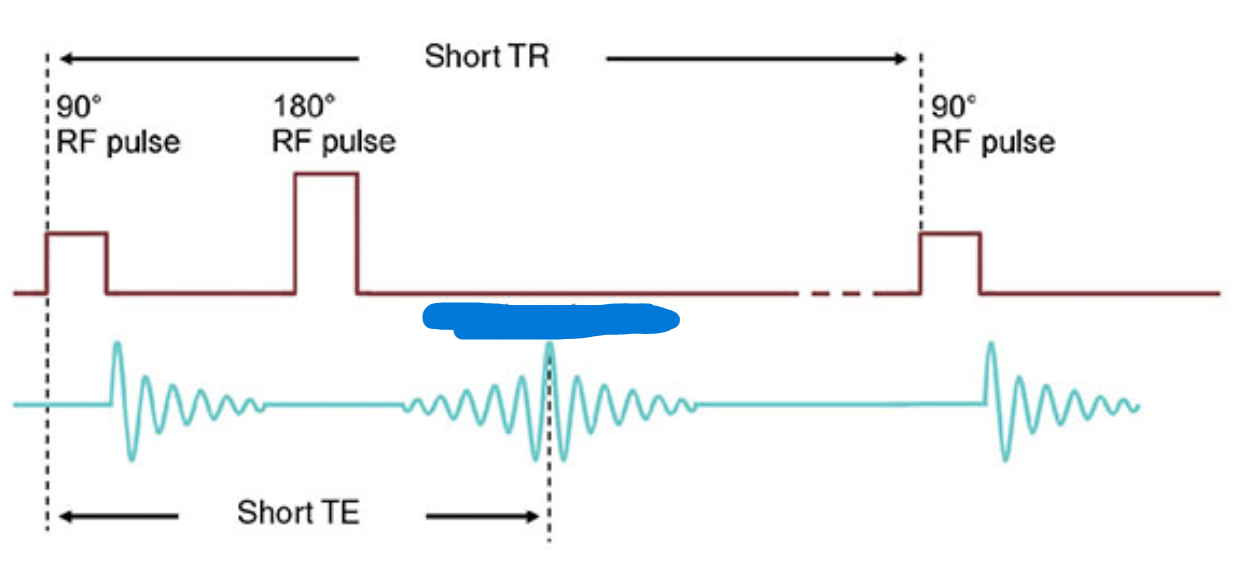
What does this image show?
Spin-echo with two echos
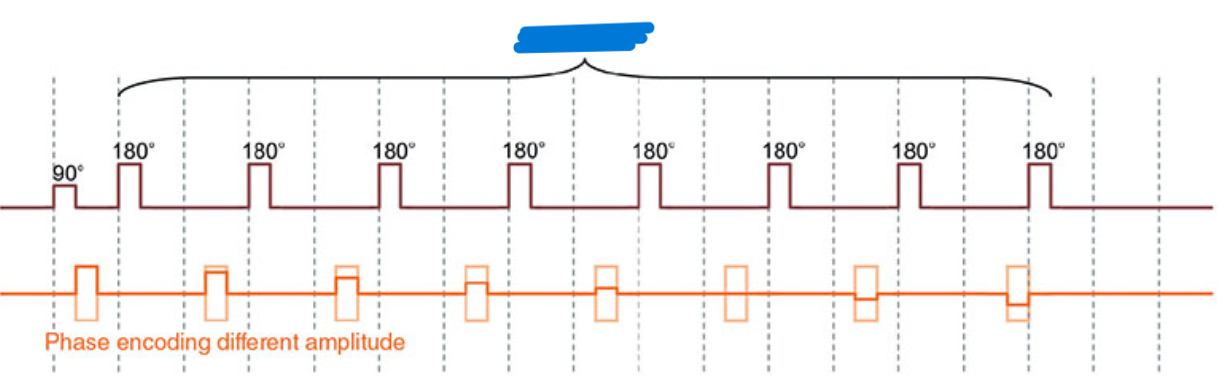
What does this image show?
The echo train
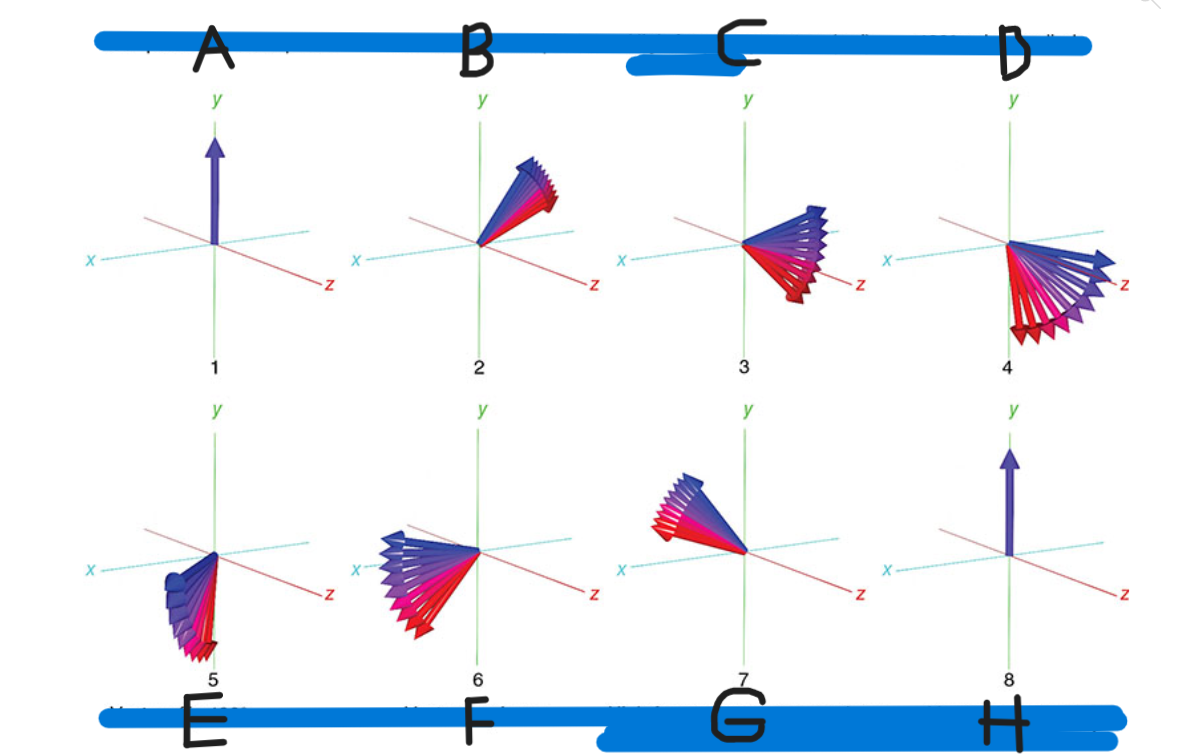
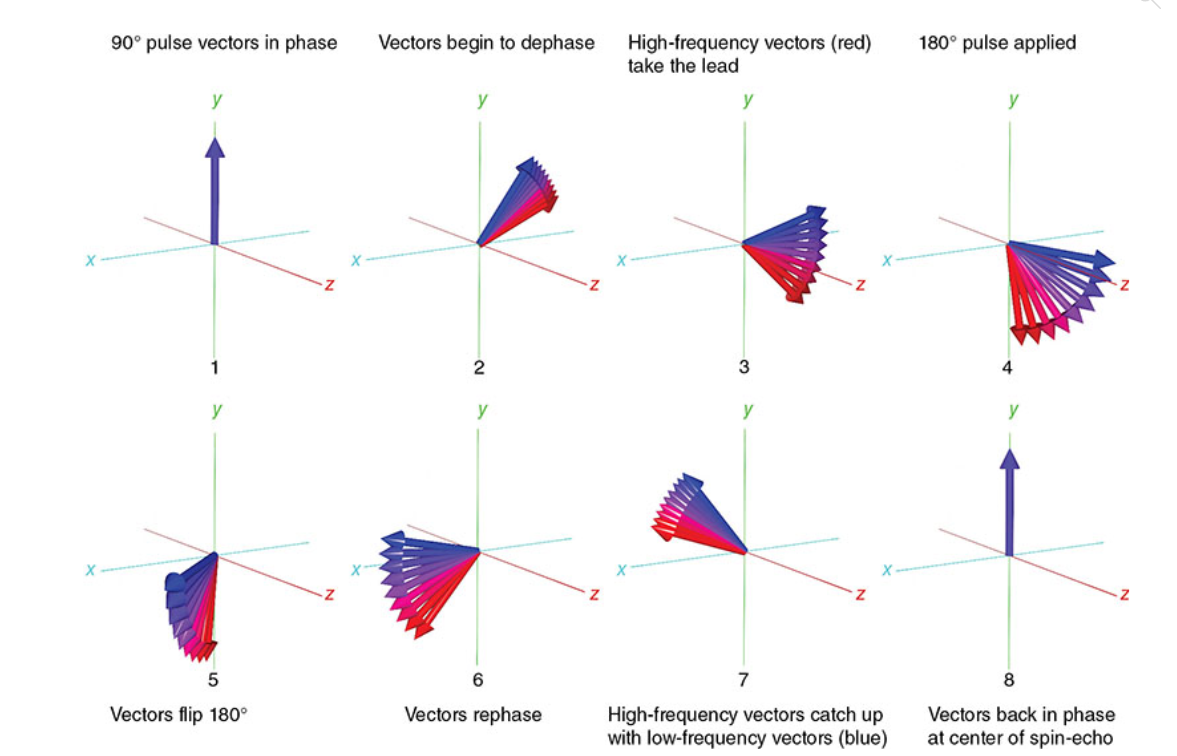
What is A
90 pulse vectors in phase
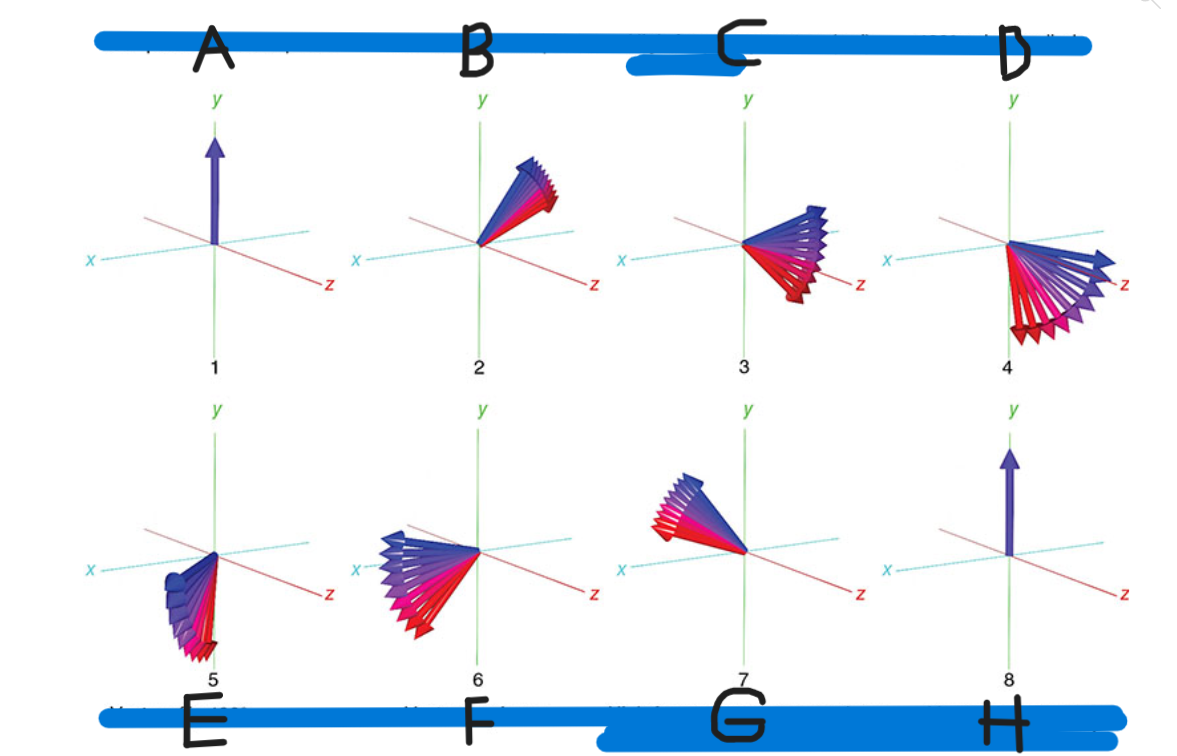
What is B
Vectors begin to dephase
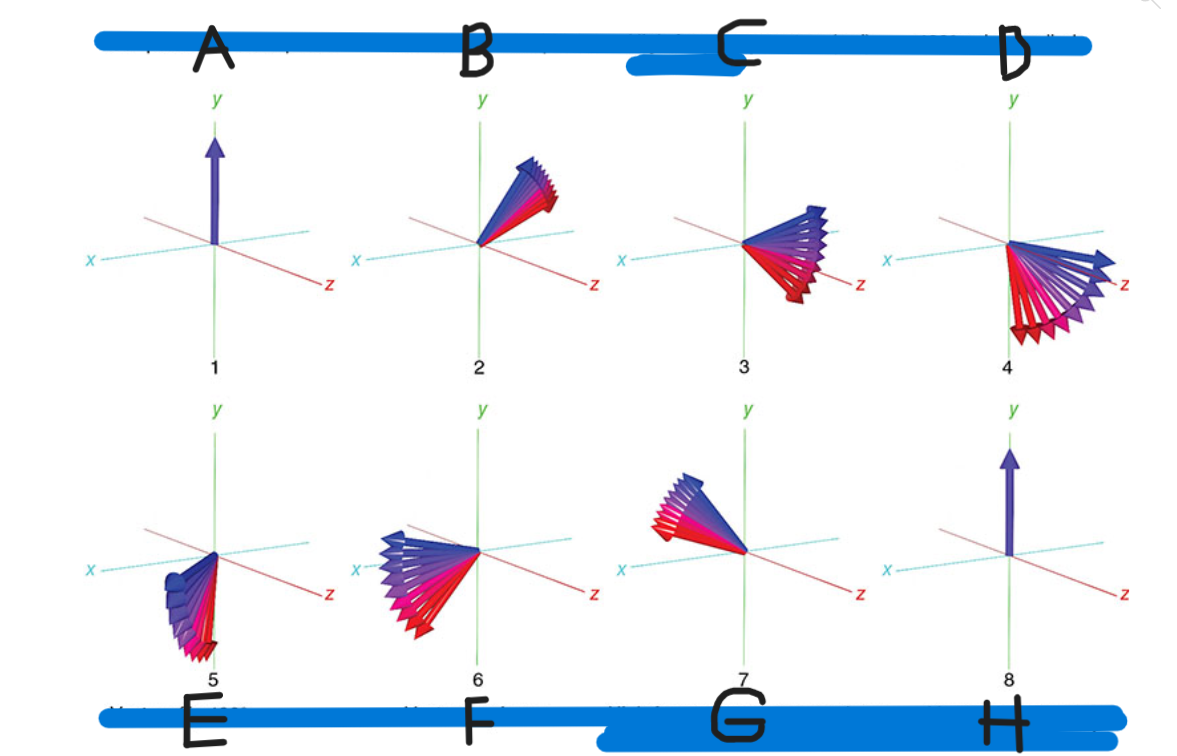
What is C
High-frequency vectors (red) take the lead
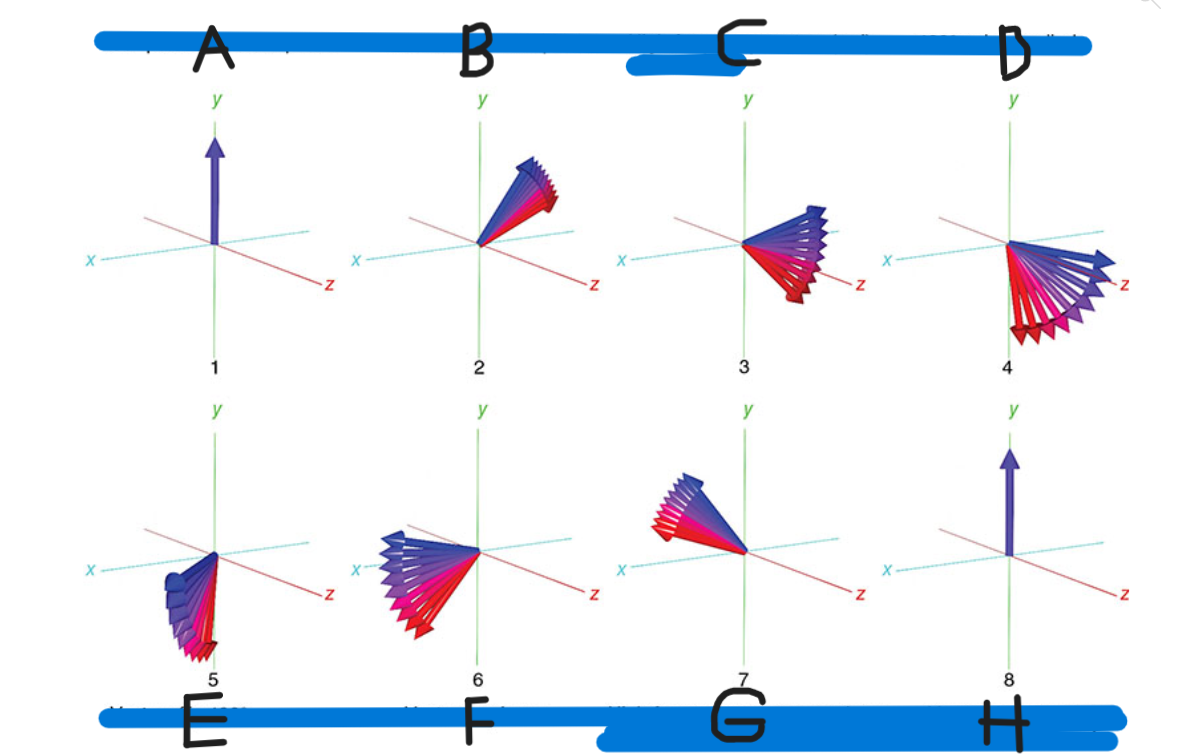
What is D
180 pulse applied
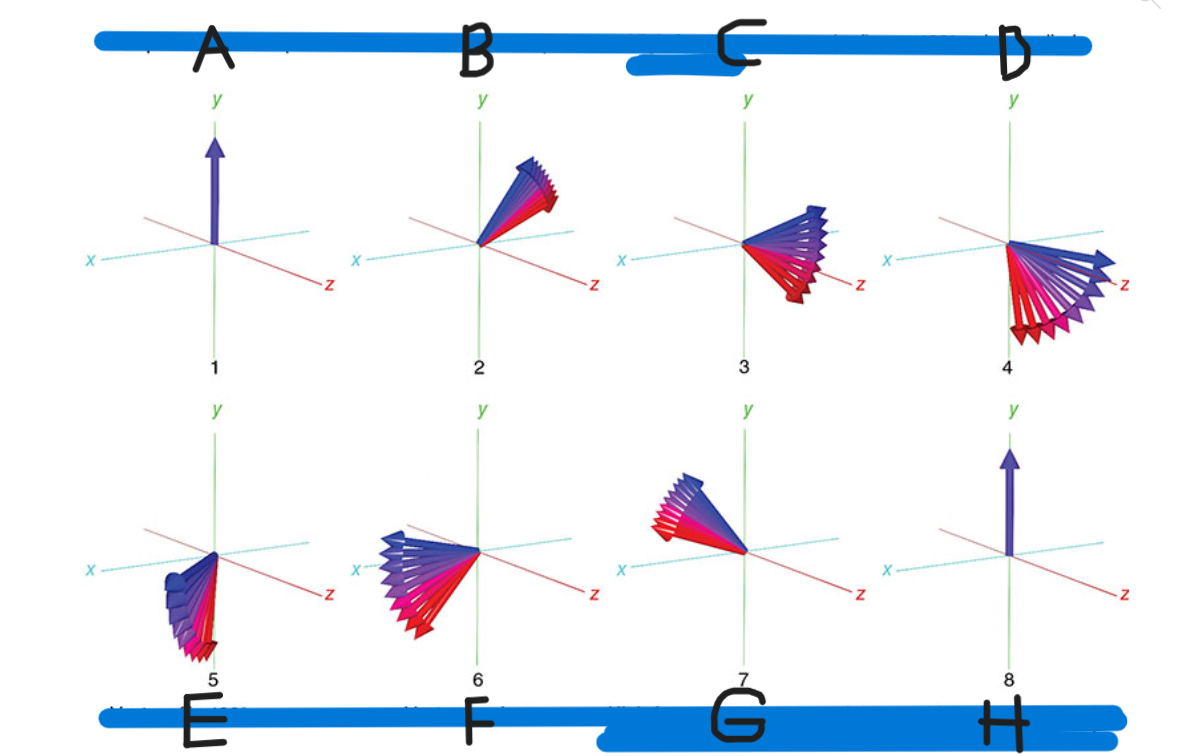
What is E
Vectors flip 180
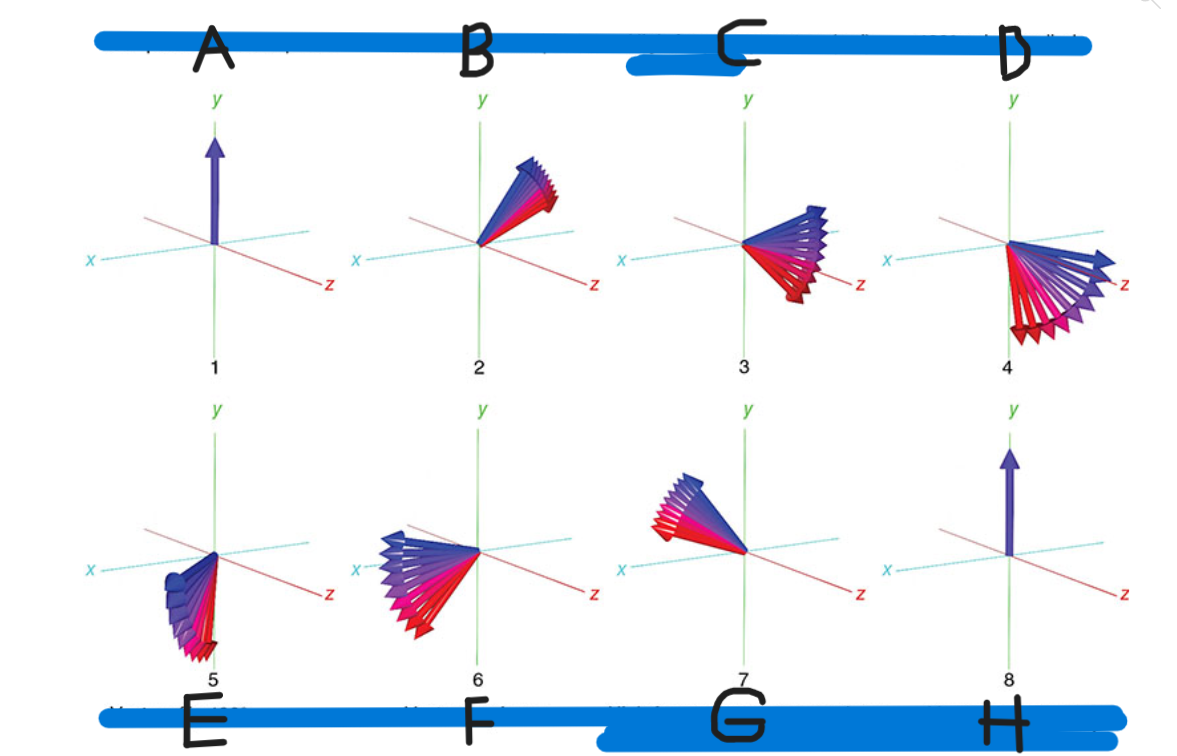
What is F
Vectors rephase
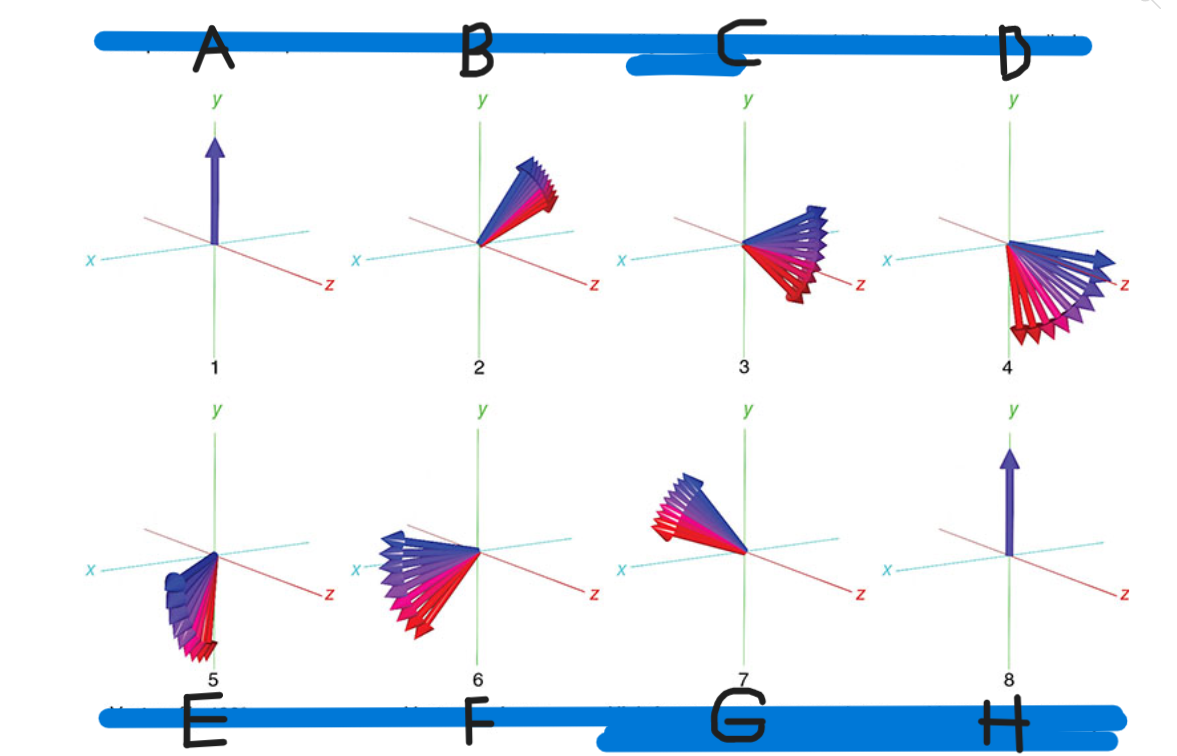
What is G
High-frequency vectors catch up with low-frequency vectors (blue)
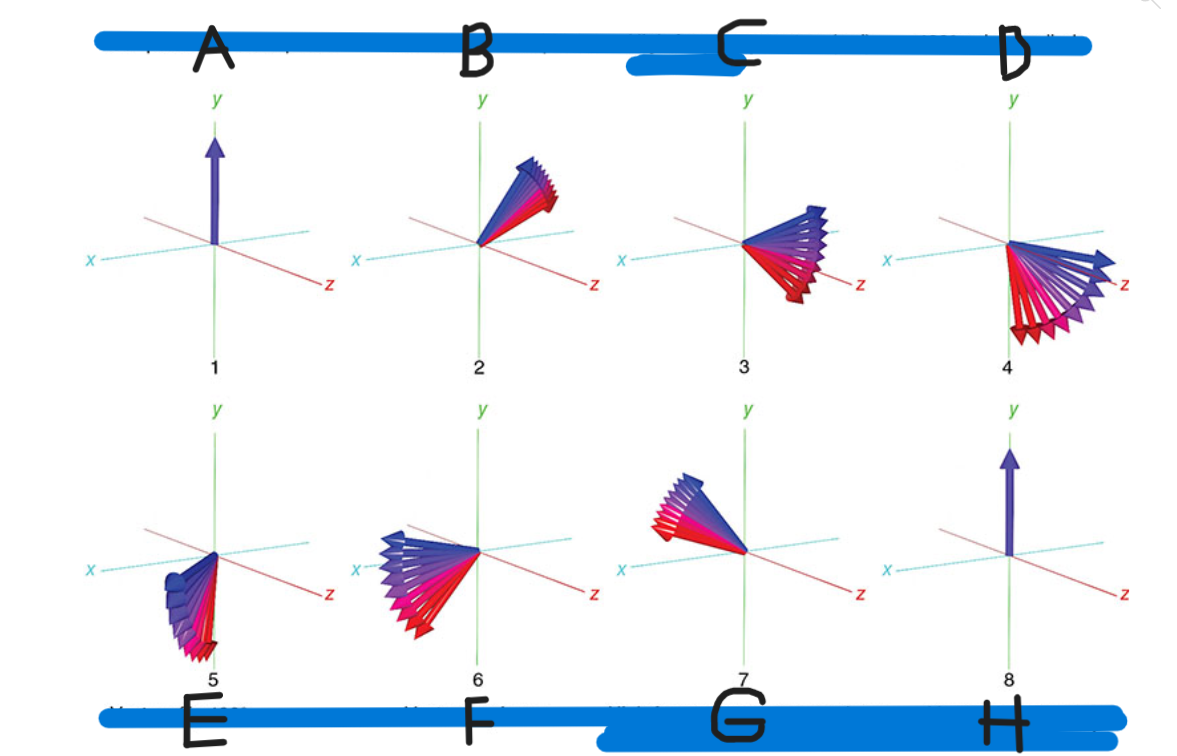
What is H
Vectors back in phase at center of spin-echo
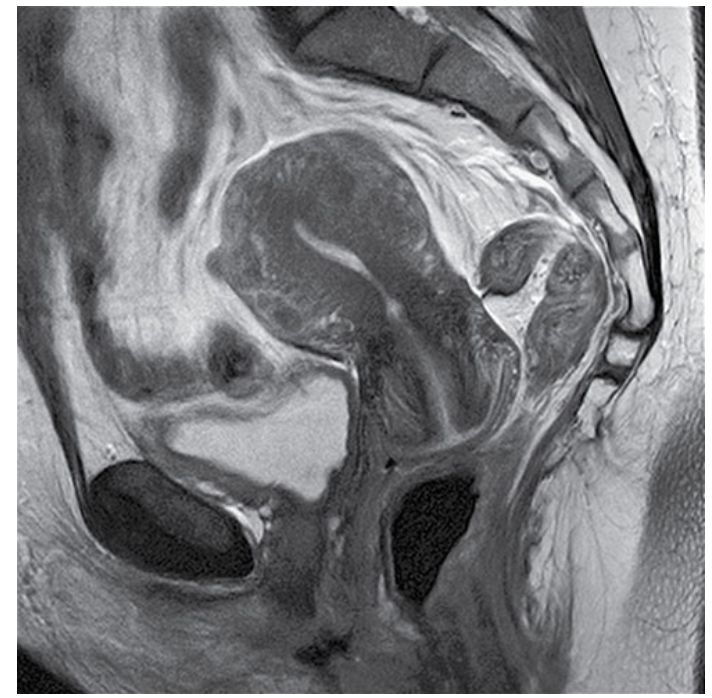
What does this image show?
Sagittal TSE T2-weighted image of a female pelvis
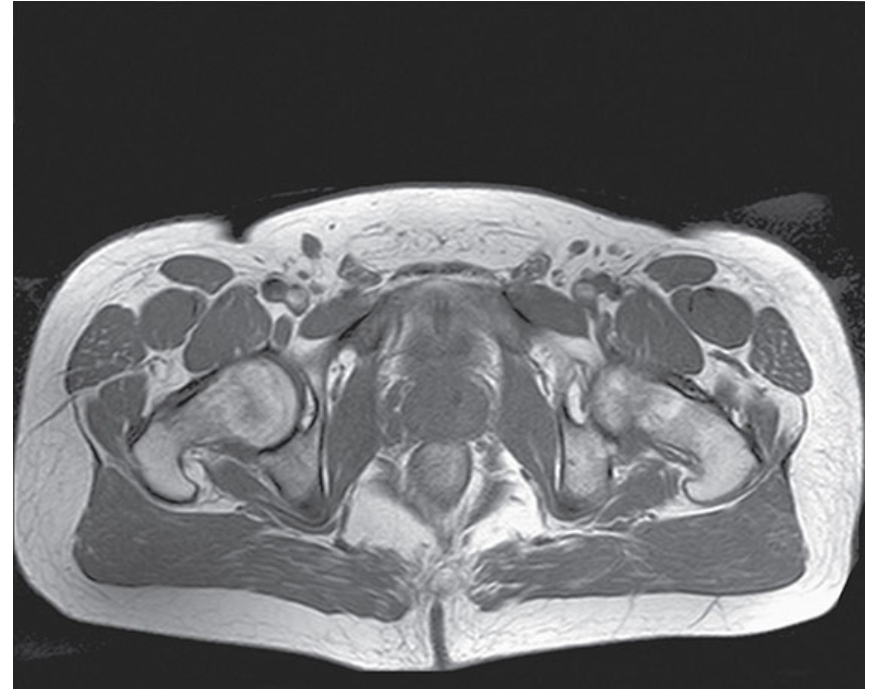
What does this image show?
Axial T1-weighted TSE image of a male pelvis
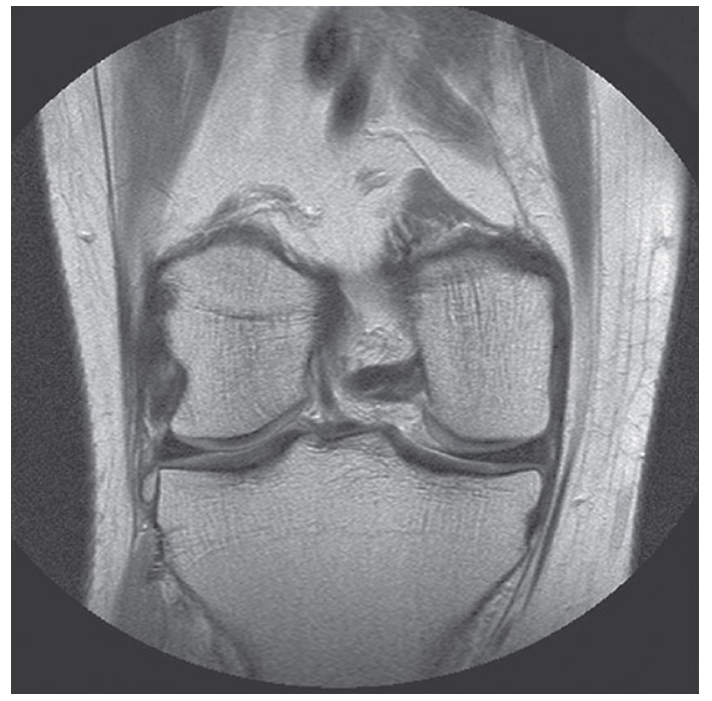
What does this image show?
Coronal TSE PD-weighted image of a knee
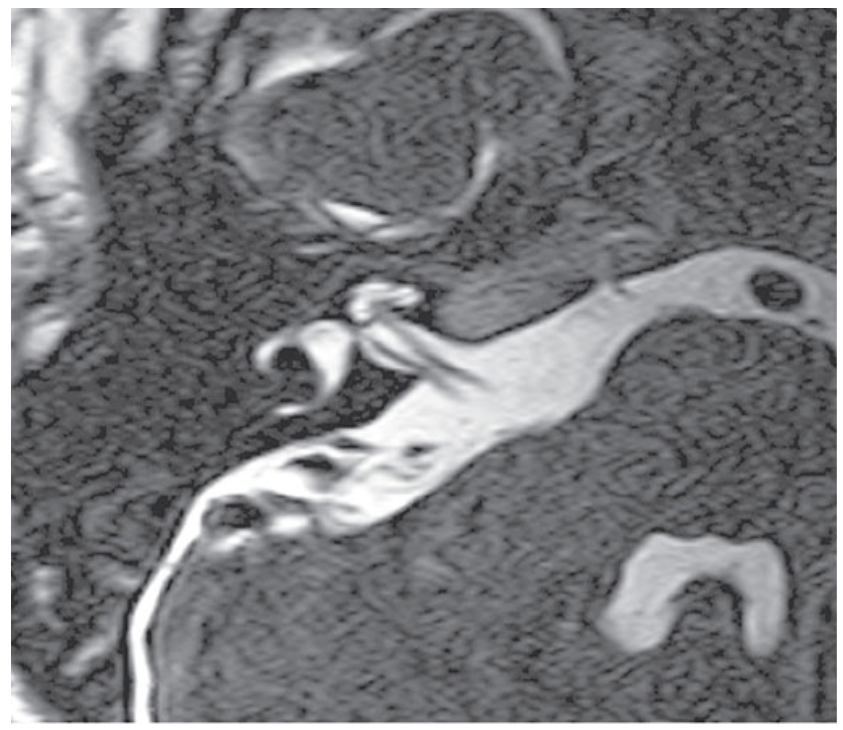
What does this image show?
Axial DRIVE image through the right internal auditory meatus
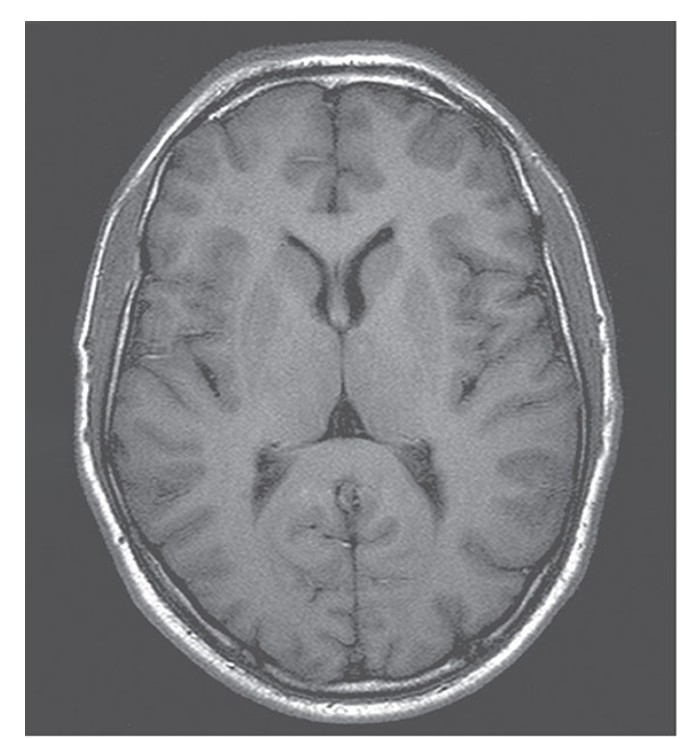
What does this image show?
Axial T1-weighted inversion recovery sequence of the brain
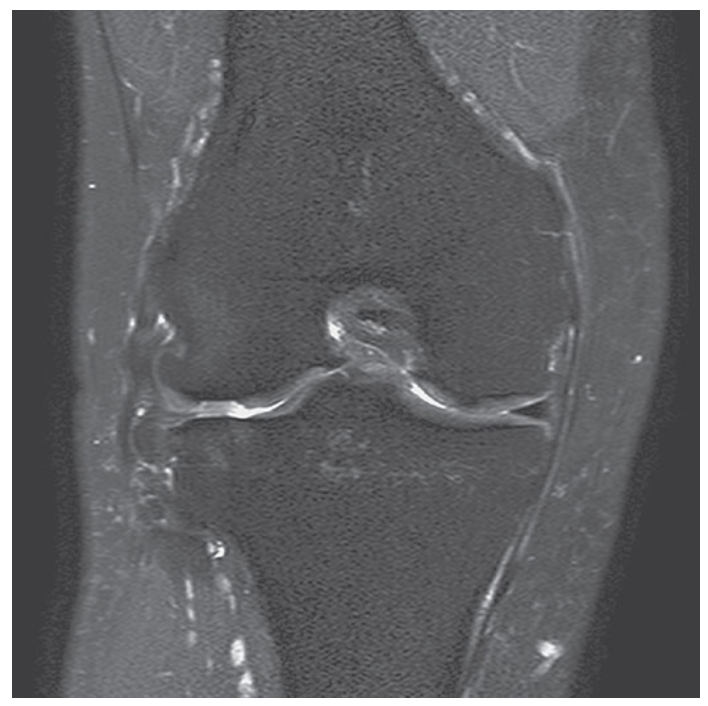
What does this image show?
Coronal STIR of the knee.
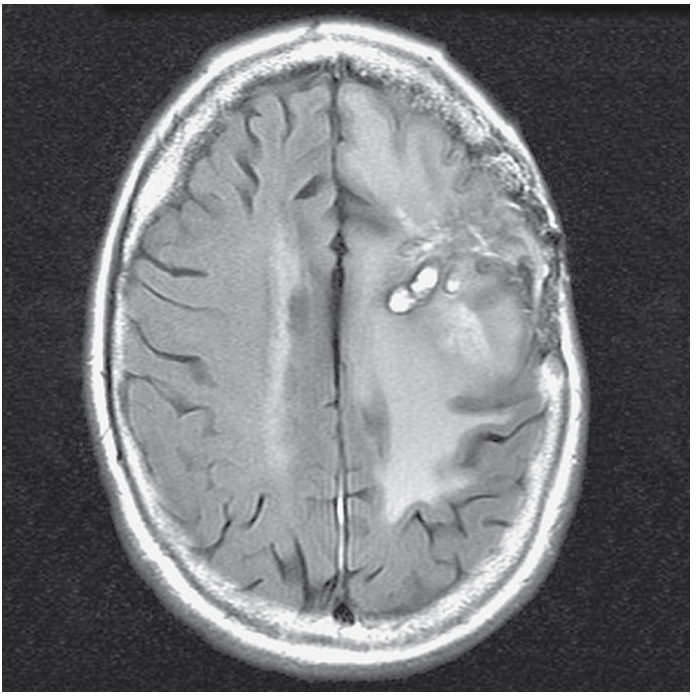
What does this image show?
Axial T2-weighted FLAIR of the brain
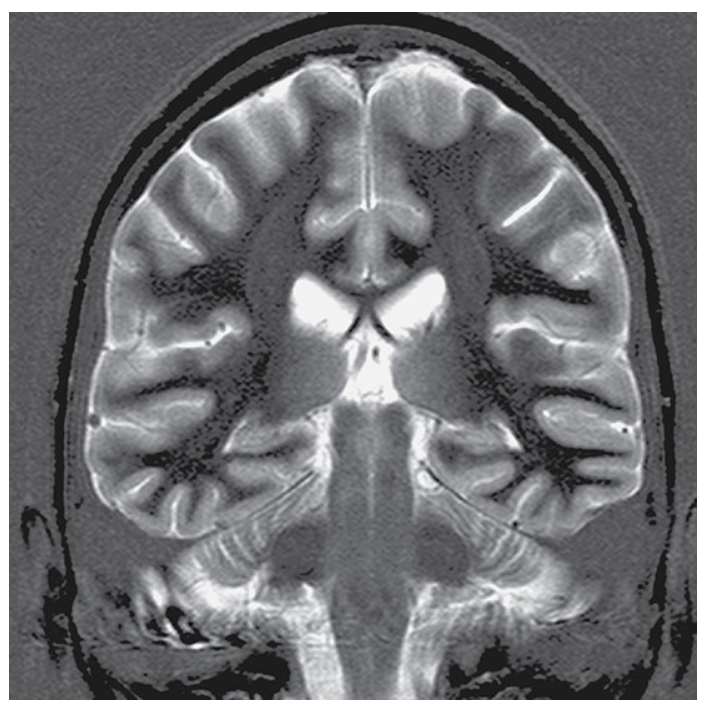
What does this image show?
Coronal IR-TSE T2-weighted image with a TI selected to null white matter.
A pulse sequence is a set of events that occur in a particular order to produce an image.
True/False
True
The purpose of a pulse sequence is to manipulate the contrast, resolution, and scan time of an MRI image.
True/False
True
In conventional spin echo sequences, the first echoes are referred to as “free” because they do not require an additional RF pulse.
True/False
False
The extrinsic contrast parameter unique to TSE/FSE is the echo train length (ETL).
True/False
True
Increasing the echo train length results in increased image blurring and decreased scan time.
True/False
True