L4 - Formation and composition of the planets
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
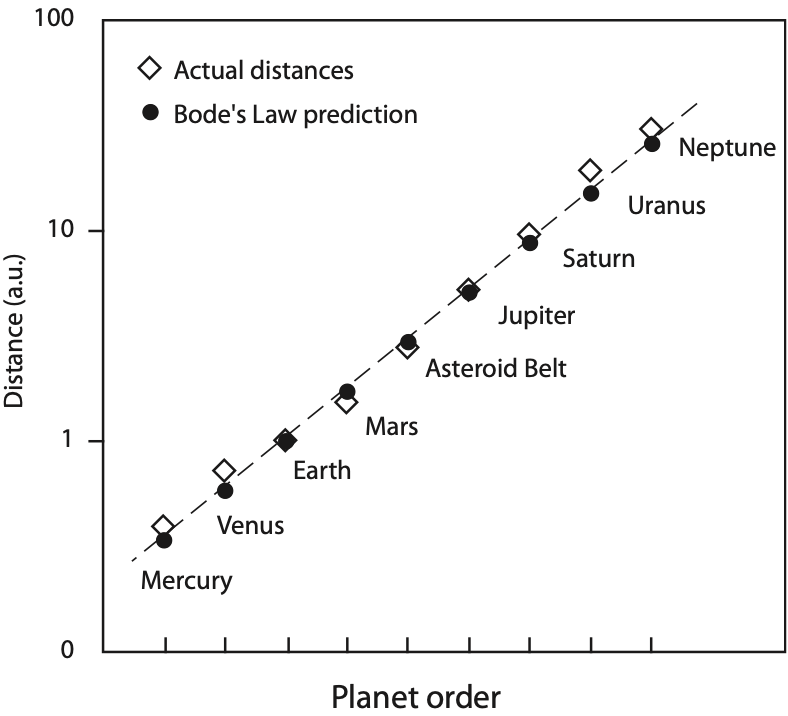
What is Bodé’s law?
There seems to be regular spacing between the planets
Position of the asteroid belt suggests it was once a planet that has since been broken up
Unsure whether this regular spacing is significant or not
Planets spin in time with the sun: this gave way to the idea that the planets and the sun are all connected.
What are the properties of the terrestrial planets?
Lighter, smaller, denser
The planets closer to the sun must be made of more denser elements and non-volatile oxides and silicate minerals
Hydrogen, helium, silica, etc.
No coincidence that the inner planets closer to the sun are likely made of less volatile compounds
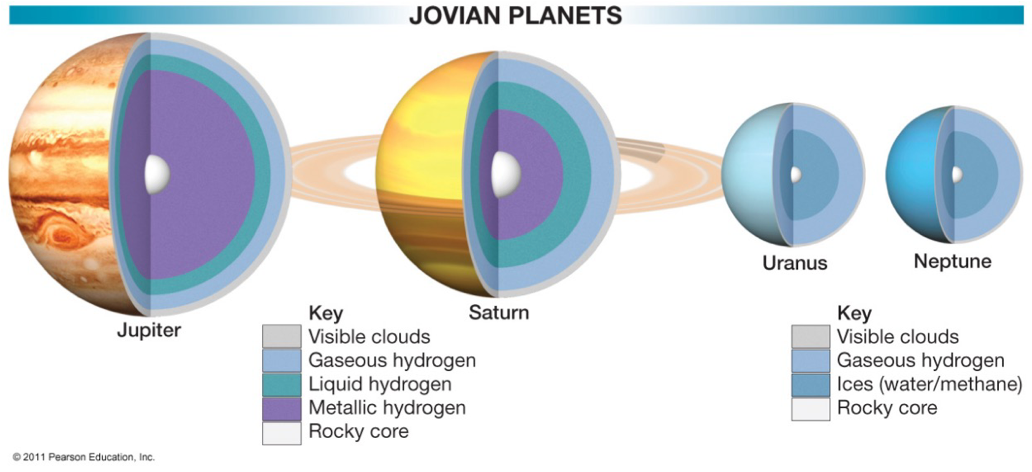
What are the properties of jovian planets?
Heavier, larger, and less dense
Further planets, which are colder, are made of more volatile compounds
Sufficiently cold for the volatile compounds to solidify.
What are chondrules?
Thought to represent spherical droplets of gas, formed during the composition of our solar system, which was then condensed to form liquid droplets which froze.
Between the chondrules are fairly carbon-rich compounds
What do carbonaceous chondrites tell us?
Tell us how the meteorite formed
What chondrites are made of will give us an idea of what those protoplanets would have been made of
Thought to have been formed by relatively high temperature and lower temperature materials colliding together.
What are the characteristics of meteorites?
Very dense
Very metal-rich
Very little silica
Characterised by 'Widmanstätten pattern’
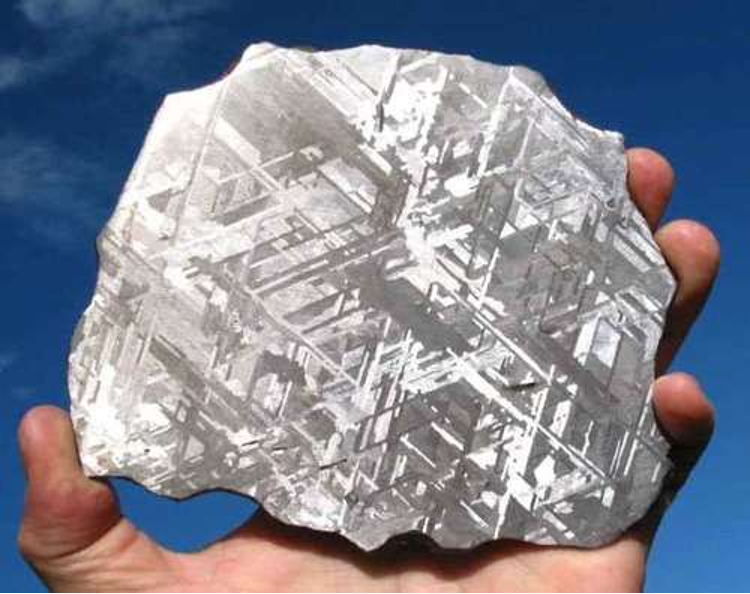

What is the significance of widmanstätten pattern?
60o angles between ‘stripes’
Formed when molten iron and nickel is cooled very slowly
Cannot replicate these kind of textures on earth
Very confident that iron-nickel meteorites did not form on earth but cooled down very slowly in space
What is the relationship between carbonaceous chondrites, the basaltic meteorites, and the iron-nickel meteorites?
If the iron and nickel are separated from a chondritic meteorite, the iron-nickel will have the same composition of this meteorite:
And the remaining material will have the same composition as the basaltic meteorite

What does this mean (Q8)?
It is thought that this material collided and combined to form larger bodies.
As they became bigger, they melted in the middle
As they melted, they formed immiscible liquids
If this molten material is spun, the iron-rich material will move to the centre of the body.
When these bodies were hit by other rocks, they were separated out.
How is a star formed?
Begins with the explosion of a supernova, creating a gas cloud of elements.
Over time, gravity will have pulled this material together. This cloud would have flattened and began to spiral
At the centre, hydrogen, helium, etc. will be accumulated
These elements will be forced together in nuclear fusion, creating a star.
How are planets formed?
This gas cloud will cool down and condense as liquids and solids. This material will be rotating in the same direction as the sun.
Particles will collide which each other and gradually combine. As they become larger, they will develop some gravity to it, and will attract more particles.
That gravity will allow them to maintain some sort of atmosphere
What will have formed between the sun and earth?
Temperatures would have cooled to around 1000K
Sufficiently cool for non-volatile compounds to start to precipitate or solidify from the ‘gas phase’
What will have formed between earth and Jupiter?
Temperatures about 100-200K.
Sufficiently cool for more volatile compounds to solidify
Somewhere between the asteroid belt and Jupiter is the cutoff temperature for volatile compounds to freeze and solidify.
Why was the T-Tauri phase hypothesised?
Following the formation of stars and planets, it was expected that there would be bits of dust, hydrogen and helium between the planets (but there weren’t)
It was also expected that the sun would be spinning faster
What is the T-Tauri phase?
A period, as the sun as evolving, where it emits a large amount of particles and solar wind.
There was a sudden burst and release of the elements that had been previously produced
This solar wind is thought to have moved and carried away this helium and dust away from the planets.
This emission phase involved the sun losing a lot of energy, explaining why the sun now rotates more slowly.
What do Potassium/Uranium ratios tell us?
Potassium = broadly non-volatile, but relatively volatile compared to uranium
If looking at compounds on a planet, the less volatile rich that planet is, the lower its K/U ratio.
Closest to the sun has relatively low K/U ratio
How do volatile compounds vary on earth?
Earth has some volatile compounds, but the isotopic ratios of neon, argon, and some other volatiles look out of place
It is thought that a lot of volatiles came from space, i.e. meteorites delivering volatiles