pheromones quick flashcards
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what are arthropods
have jointed limbs
have cuticles mainly made of chitin
have to molt to replace the cuticle as it is rigid and would inhibit growth
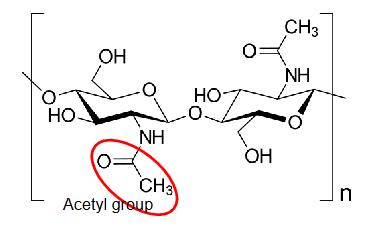
what is chitin
long chain polymer of N-acetylglucosamine
can be used as fertilizer
used in industry to thicken and stabilize foods
used for protein purification after protein expression in host cells
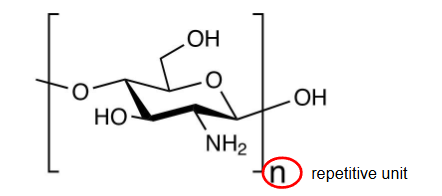
what is chitosan
partially deacetylated glucosamine
more soluble in aqueous media than chitin
can be used as biopesticide
can be useful to reduce bleeding, antibacterial agent, help deliver drugs through skin
what are beenfits of insects to humans
pollination
production of honey, wax, silk, lacquer
food
decomposers
disadvantages of insects to humans
diseases
eg malaria, yellow fever, filariasis
what is the role of insects in biotechnology
higher eukaryotic system than yeast - able to carry out more complex post translational modifications than other systems
best machinery for the folding of mammalian proteins
what are insect antimicrobial peptides used for
overcoming acquired bacterial drug resistance
what is bombyx mori
attractant pheromone emitted by silkworm moth females
advertises female availability and location
how can we identify new pheromones
fractional distillation and behavioral assay
what pheromones are commonly found in dipteran species (flies, mosquitos)
long chain dienes and monoene hydrocarbons found on the cuticular surface can influence mate choice and induce courtship
cuticular hydrocarbons can act as anti-aphrodisiacs and play role in preventing interspecies attraction
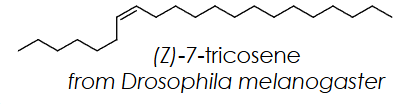
what does (Z)-7-tricosene do
prevent interspecies courtship and establishes species barrier between drosphila melanogaster and other drosophilids
what is kin recognition
mediated by cuticular hydrocarbons
the signals are qualitatively identical between colonies but quantitatively distinc
can cuticular lipid profiles be altered
yes
by diet, temperature and physiological state
what maintains social hierarchy in bees
pheromones exuded by the queen advertises the fecundity of the queen and suppresses reproduction in workers
what are alarm pheromones
flight or fight responses
often confused with attraction or recruitment
can cause dispersal of conspecifics and predators or increase recruitment and aggression towards antagonist
tend to be less specialized than other pheromones
can give communication cues recieved by other species
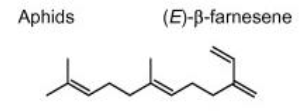
what is (E)-β-farnesene
released by many aphid species upon predation and signals conspecifics to stop feeding and diperse

what is isopentyl acetate
released by stressed honey bees
smoke inhibits receptors involved in the detection of isopentyl acetate and is used to calm hives
what are food trail pheromones
laid down by ant works as they walk by touching the gaster (large posterior section of their body) to the floor
induces other workers to follow it and allows trunk trails to be laid to new food sources
why is mass recruitment favoured by natural selection
workers can rapidly go to new food sources, prevent competitors from getting it
it is autocatalytic (self reinforcing) governed by pos feedback mechanisms
what is the general size of pheromones
about 5 to 20 carbons
what are some classes pheromones are from
hydrocarbons
fatty acetate esters
alcohols
acid epoxides
ketones
isoprenoids
triacylglycerides
what is mass trapping
trap with sticky surface and synthetic pheromone catches insects
what is lure and kill
insect pest is attracted by a semiochemical (pheromone) lure and subjected to a killing agent
what is mating disruption
synthetic pheromone is released from multiple sources
the males are unable to locate the females and number of matings and offspring is reduced
how can (E)--farnesene be used in insect control
could be used to rapidly disprese insects that react in a flight response
pheromone needs to be species speicif so other insects that have a fight response won’t react to it