Exam 1 Material (water, biomolecules, nucleic acids, lipids)
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
How many covalent bonds can Carbon have?
4
How many covalent bonds can Hydrogen have?
1
How many covalent bonds can Oxygen have?
2
How many covalent bonds can Nitrogen have?
3
How many covalent bonds can Phosphorus have?
5
How many covalent bonds can Sulfur have?
2
Name the 5 categories of biomolecules
1. Nucleic acids
2. Lipids
3. Carbohydrates
4. Amino acids and proteins
5. Vitamins, hormones, and co-factors
What are the 2 types of nucleic acids?
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Whats are the 4 different types of lipids?
fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesterol
What are 3 properties of hydrogen bonding
1. intermolecular
2. non-covalent
3. electrostatic
What can water H-bond with?
other molecules containing oxygen, nitrogen, and other electronegative atoms
What are the 4 parts of a phospholipid
fatty acid, glycerol backbone, phosphate, and alcohol
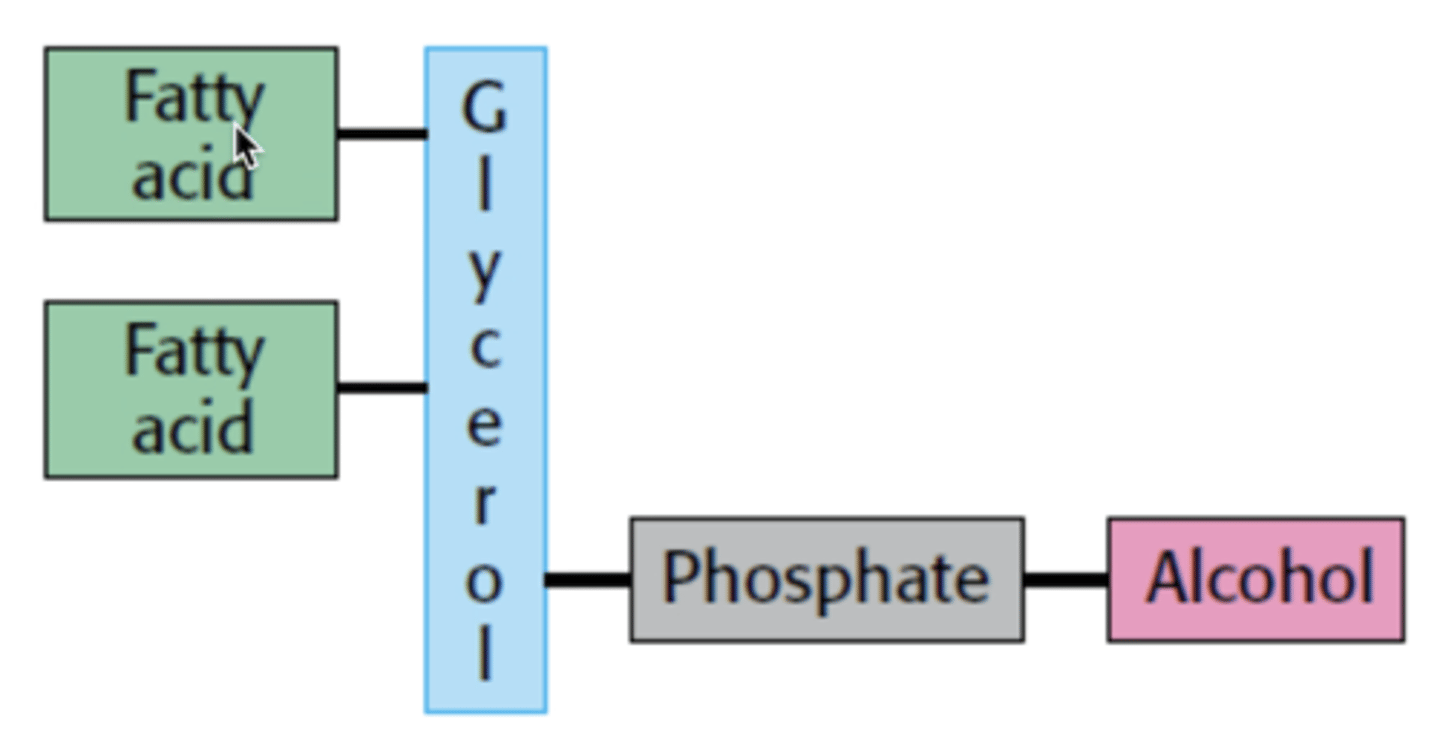
What is this molecule
phospholipid
What do amphipathic molecules form in aqueous solution?
micelles and bilayer membranes
Why are liposomes useful for transfection?
liposomes protect genetic material from degradation and their positive charge allows for promotion of uptake with the negatively charged cell membrane via pinocytosis
What is the pH equation
pH = -log[H+]
What does a cell employ to resist pH change?
buffering
What is the definition of pKa
the pH at which an ionizable molecule is 50% deprotonated
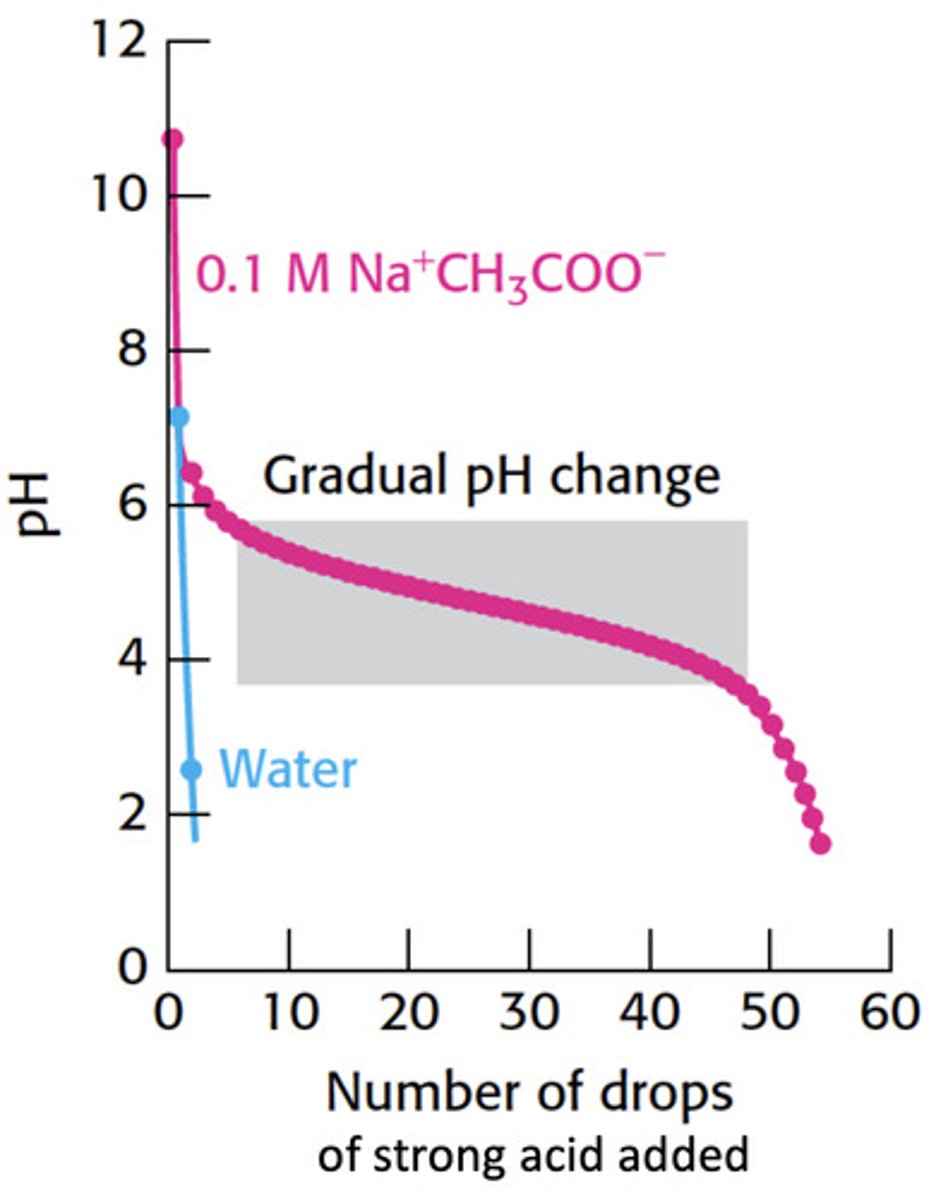
How does acetate act as a buffer
Since the conjugate base of a strong acid will NOT take the proton back, acetate (the conjugate base of a weak acid) serves as a place holder taking the protons lost by the strong acid which prevents large changes in pH.
At what pH do buffers function best?
Their pKa
What is an equivalence point
the point where the moles of added base equals the initial moles of acid
What is the Henderson-Hasselbach equation?
pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]) or [A-]/[HA] = 10^pH-pKa
What in the human body requires buffering and why?
Blood since hyperventilation can cause respiratory alkalosis and hypoventilation can cause respiratory acidosis
What acts as a buffer to blood?
carbonic acid
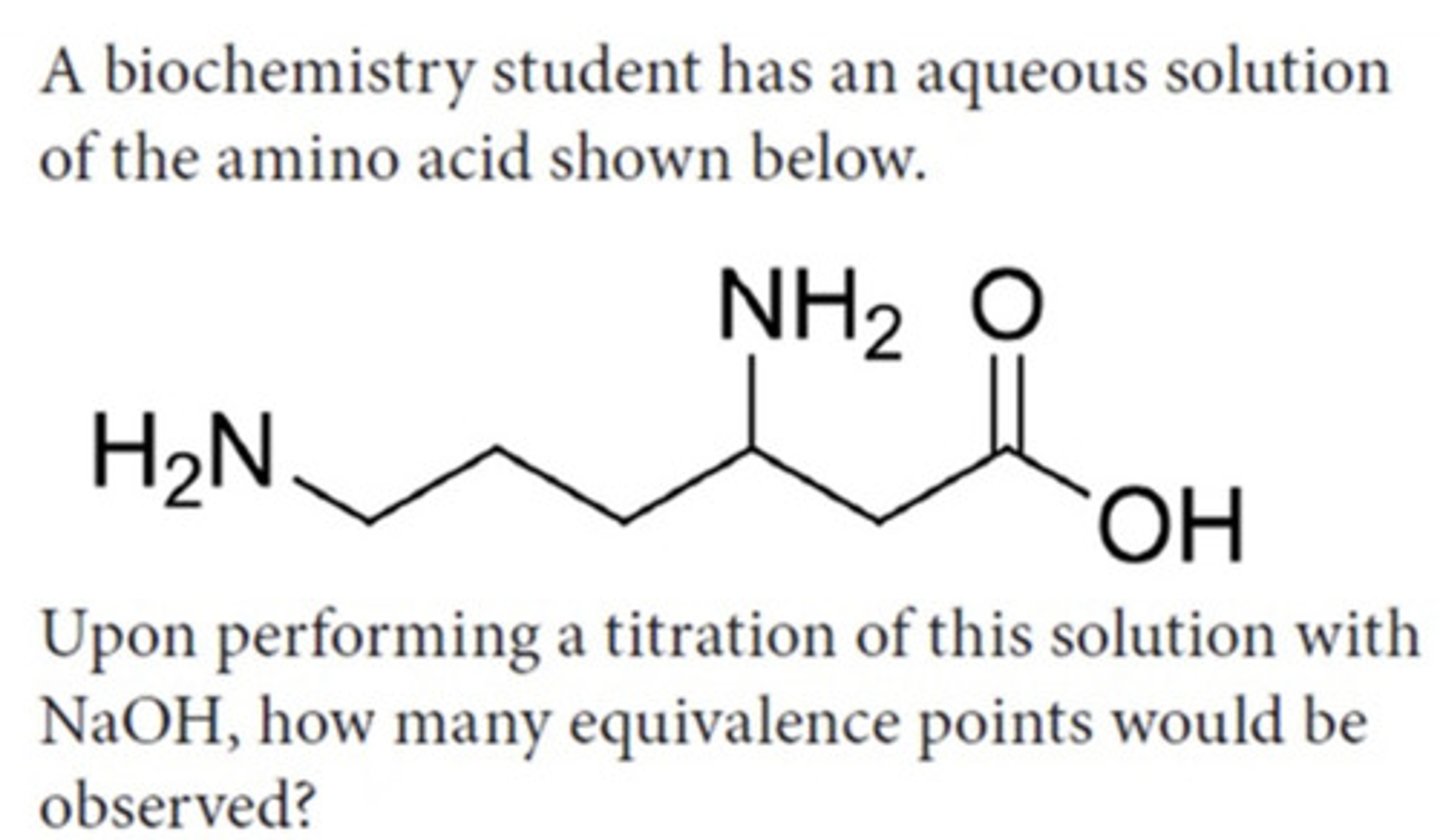
Answer the following question
3
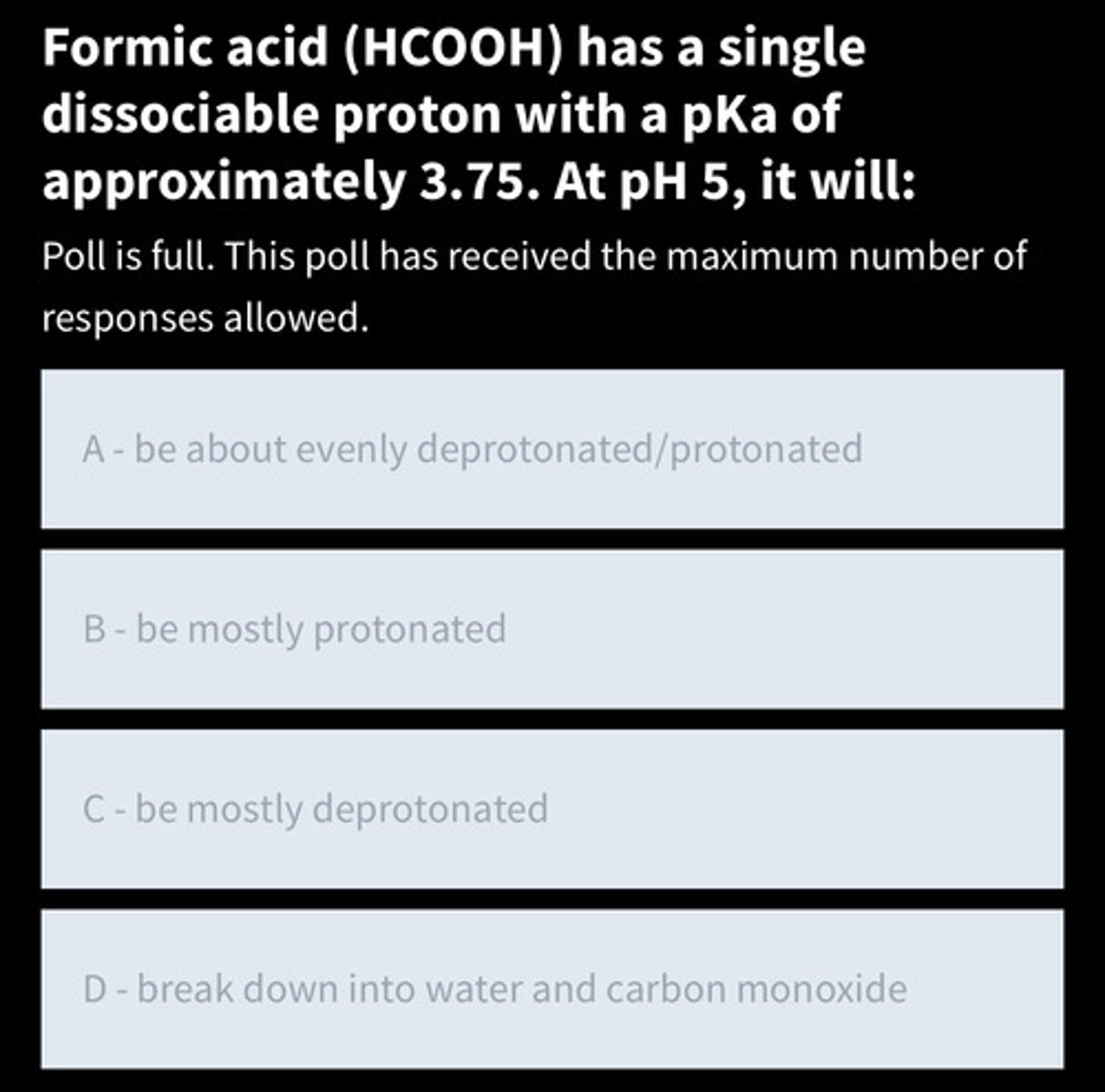
Answer the following question
C - be mostly deprotonated
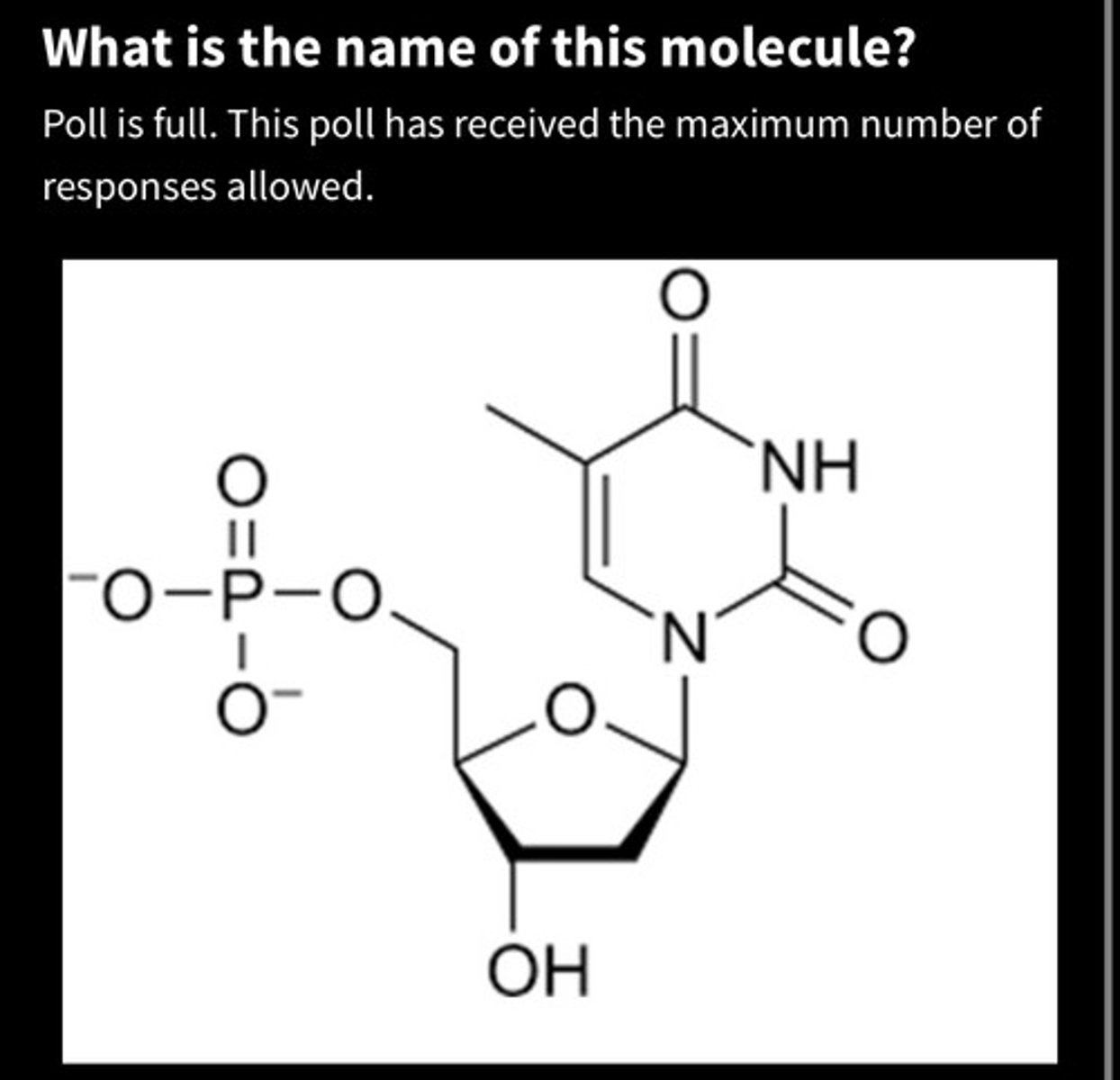
A. Deoxyadenosine triphosphate
B. Guanosine monophosphate
C.Uracil diphosphate
D. Uracil monophosphate
E. Deoxythymidine monophosphate
F. Deoxyguanosine monophosphate
E. Deoxythymidine monophosphate
What is negentropy
the decrease of entropy, increased order
How do living things combat their thermodynamic breakdown (increase of entropy)?
extracting energy from high order states in their environment (must do this due to the second law of thermodynamics)
Why is DNA an aperiodic crystal?
their genetic information is conveyed through an irregular pattern
Is the rough strain of pneumococcus virulent or nonvirulent?
nonvirulent
Is the smooth strain of pneumococcus virulent or nonvirulent?
virulent
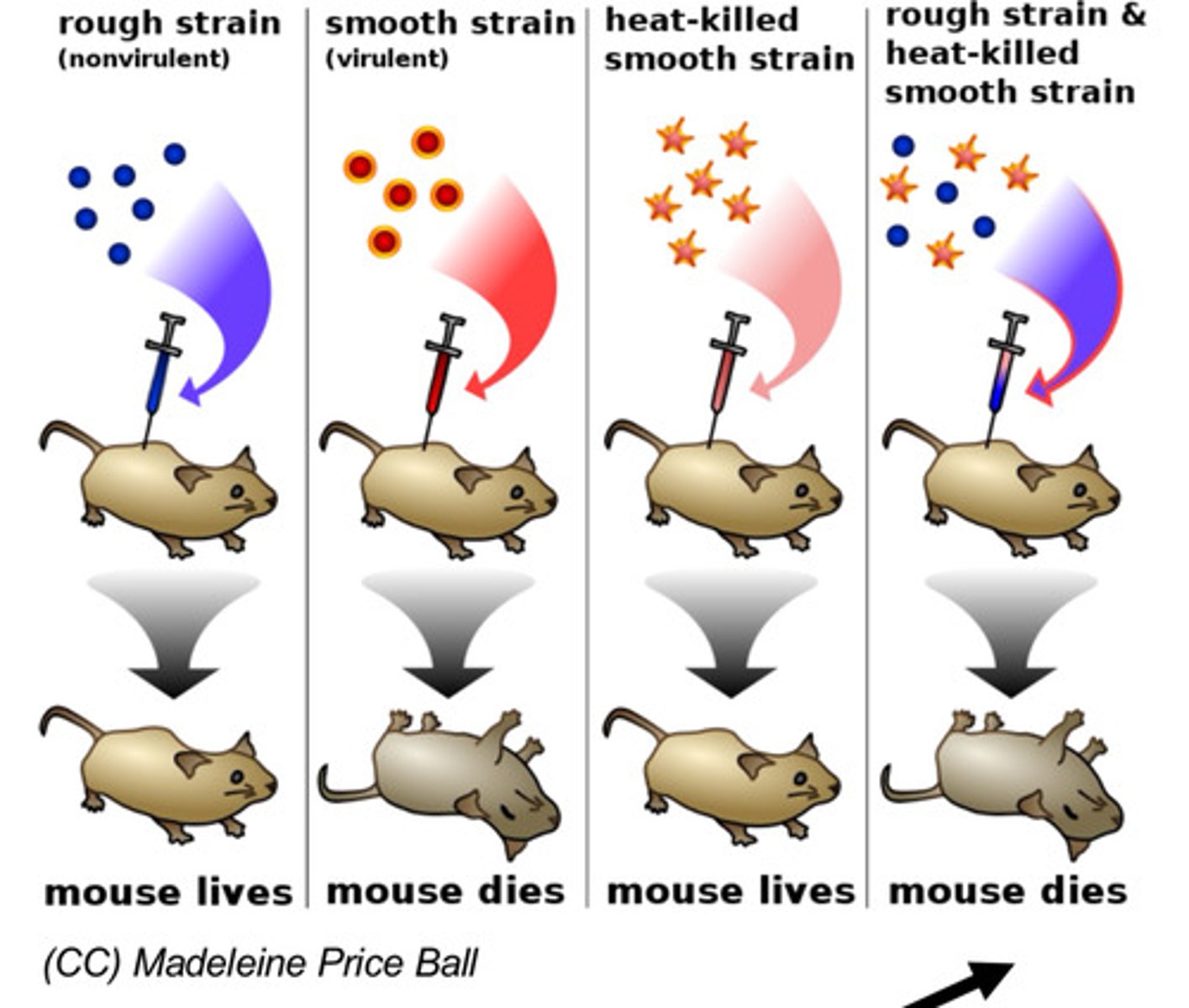
Why does a mouse with a mixture of the rough strain and heat-killed smooth strain die?
The DNA which contains the genetic information of the virus was not killed by the heat and was able to replicate with the rough strain
How would one be able to abolish the virulent effect in a virus?
Treat the virulent strain with a DNA specific endonuclease
What is the process of DNA being copied into RNA called?
transcription
What is the process of RNA being read by ribosomes in order to make a protein called?
translation
What is all the genetic information in a cell called?
genome
What are all the RNA molecules in a cell called?
transcriptome
What is the entire set of proteins that is, or can be, expressed by a genome, cell, tissue, or organism at a certain time called?
proteome
What is the name of the genome, transcriptome, and proteome all working together called?
metabolome
What are the 4 biochemical functions of nucleotides
1. building blocks of DNA and RNA
2. energy unit (ATP or GTP)
3. involved in biosynthesis (UDP glucose in glycogenesis)
4. signal transduction
cAMP to activate proteins, ATP provides phosphate in phosphorylation, and adenosine binds to sleep promoting adenosine receptor
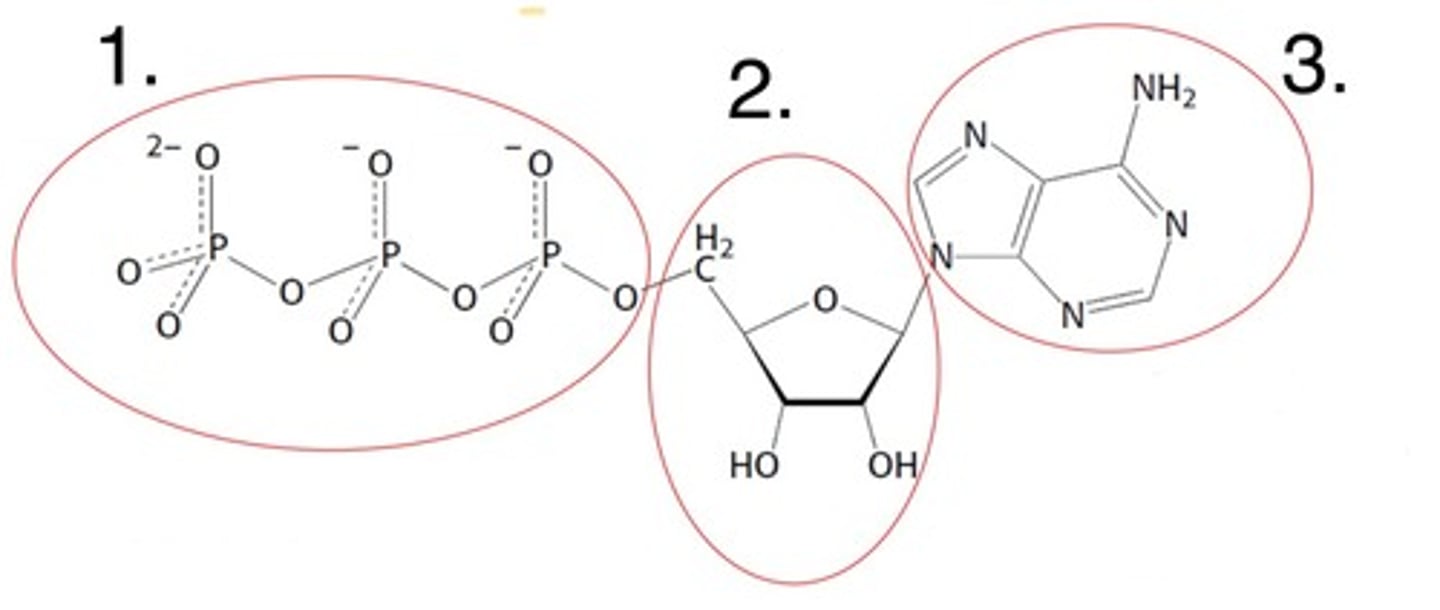
What part of the nucleotide is labelled 1
the 5' carbon bonded phosphates
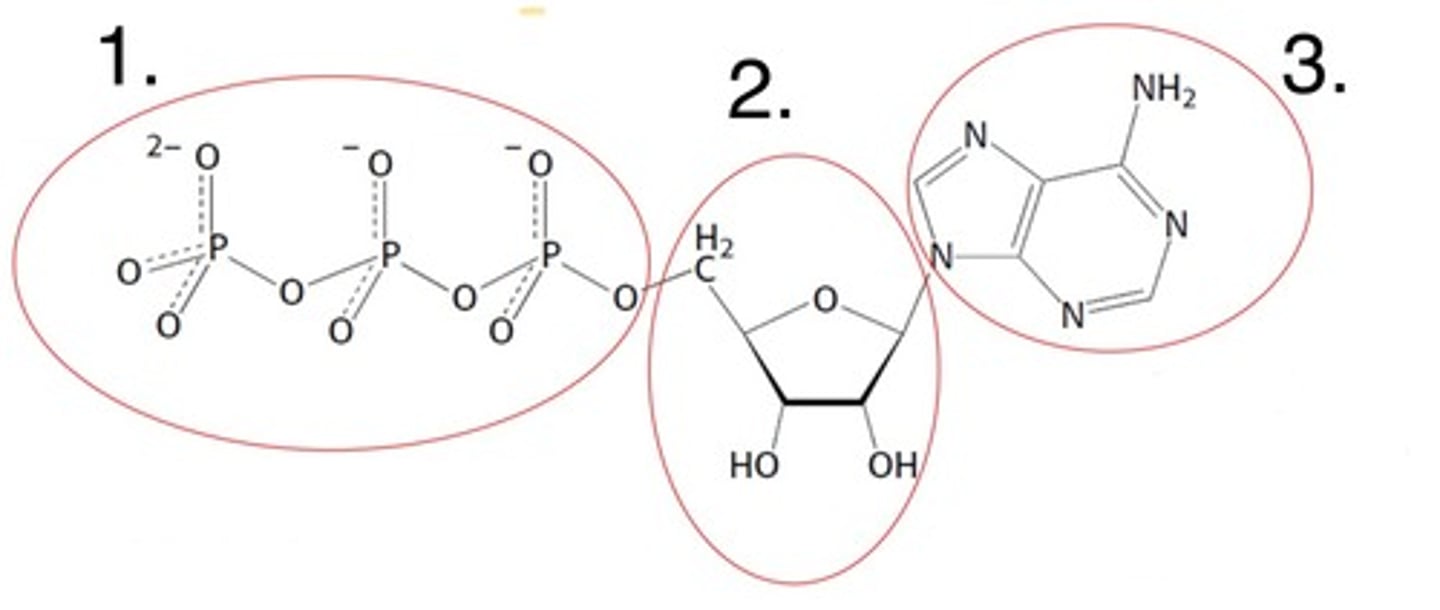
What part of the nucleotide is labelled 2
the 5-carbon sugar (ribose here)
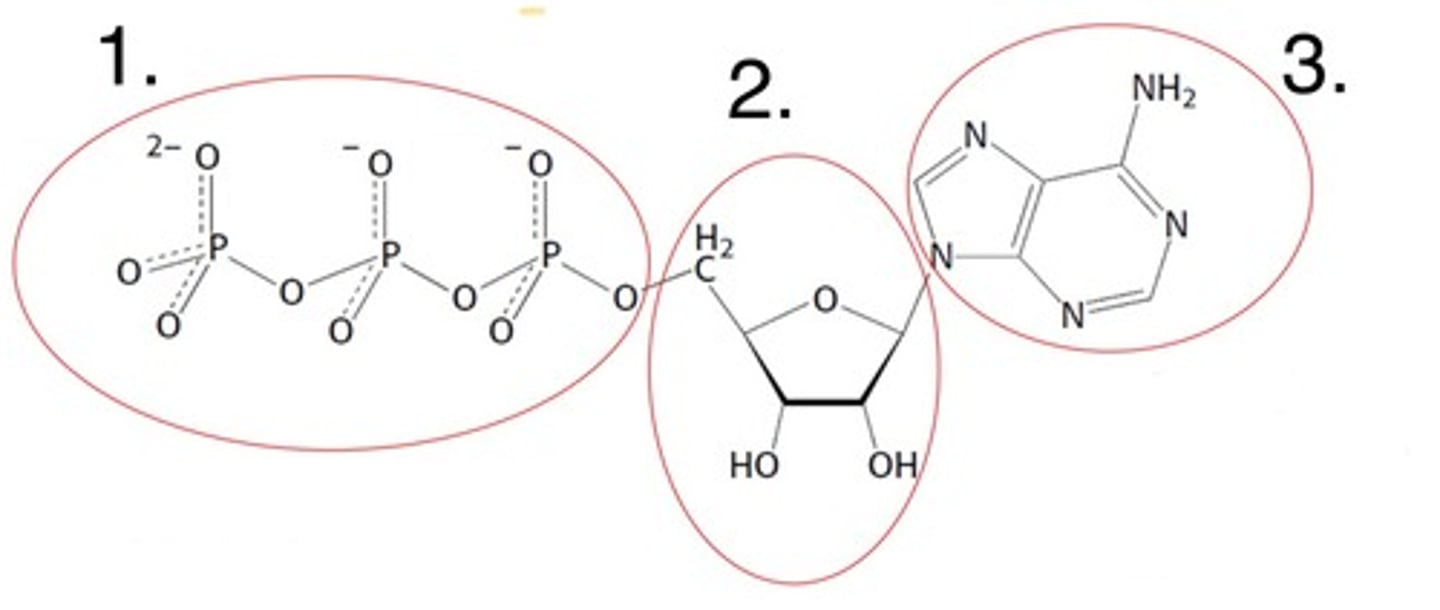
What part of the nucleotide is labelled 3
the nitrogenous base (adenine here)
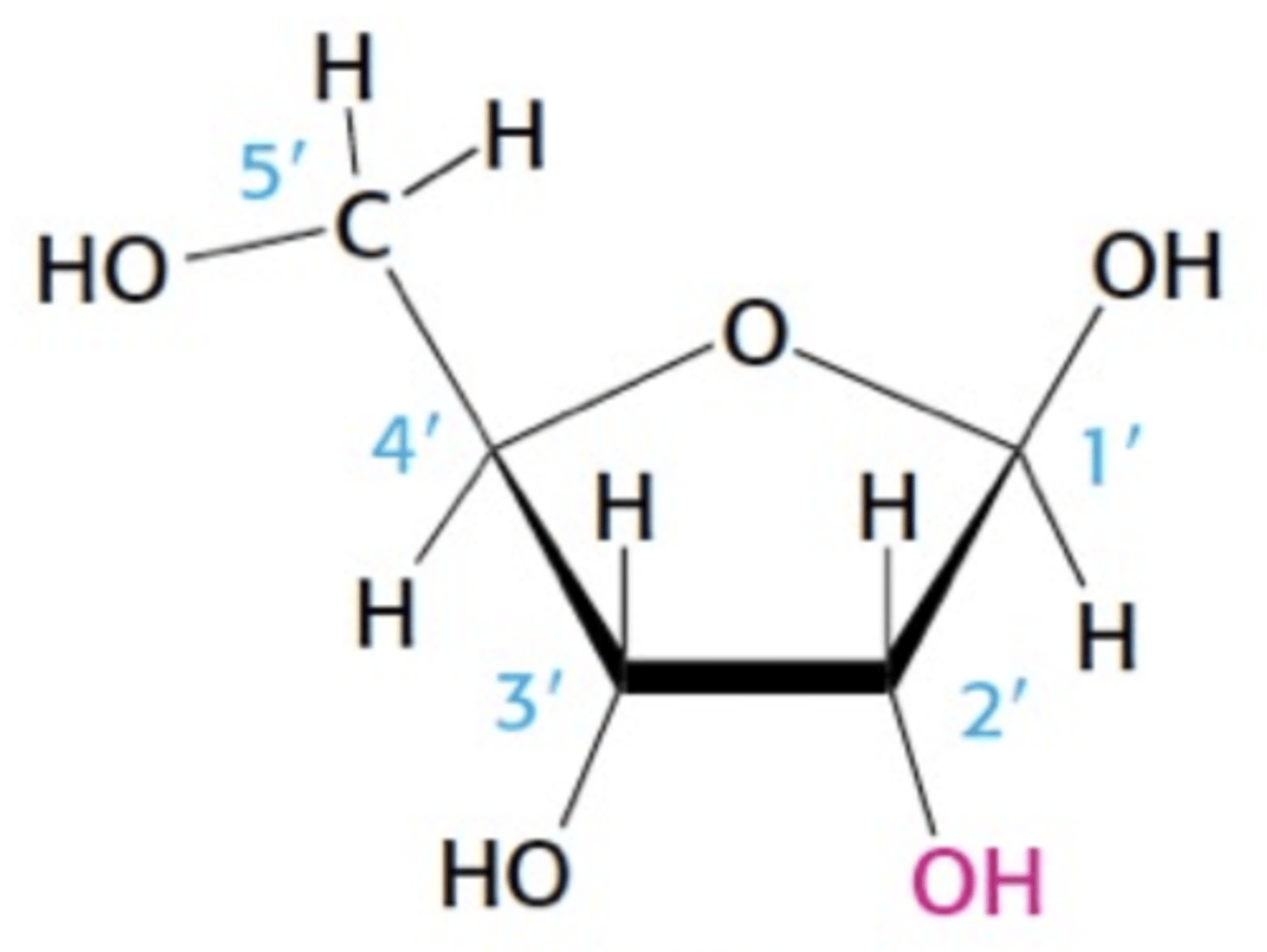
Name this structure
Ribose
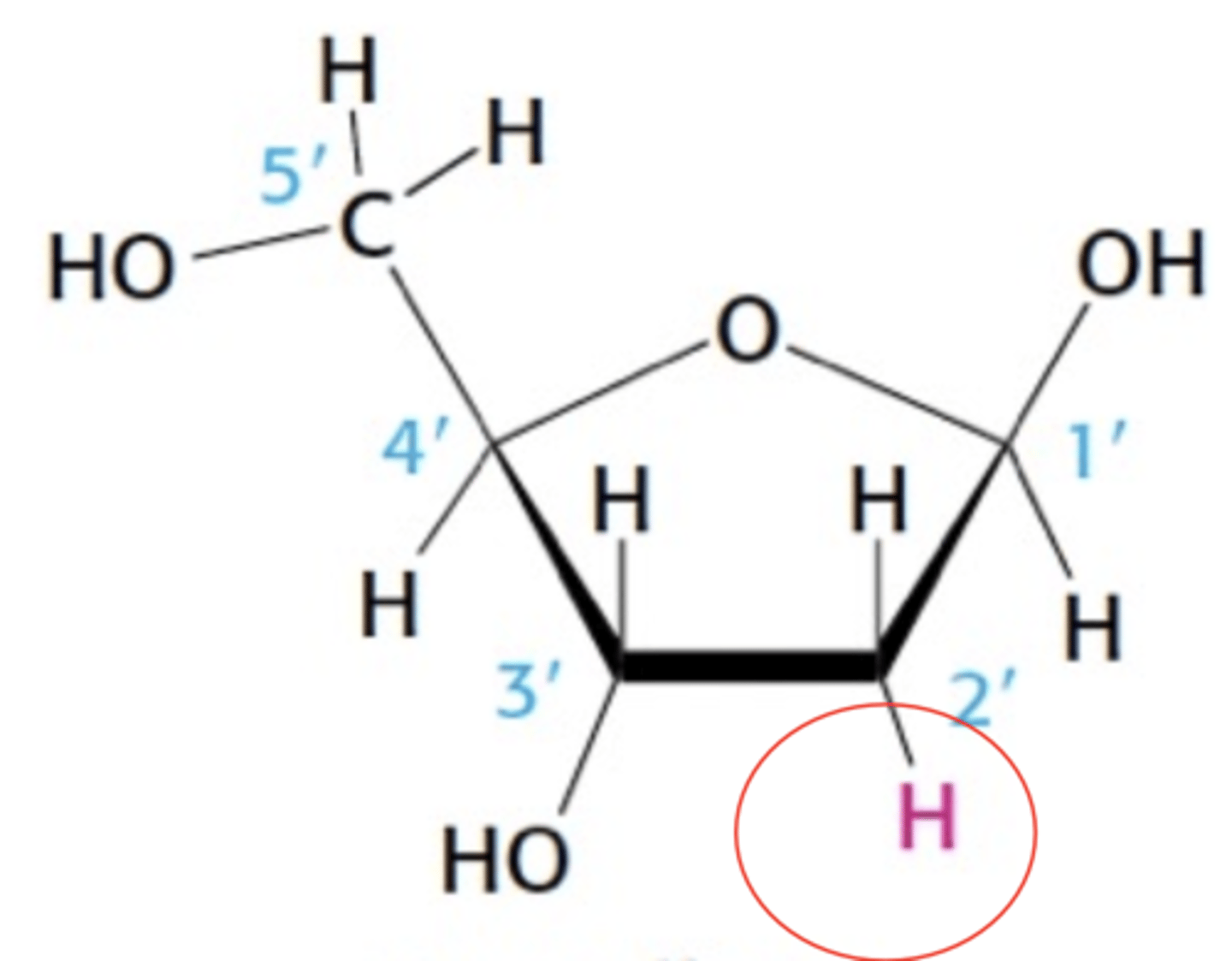
Name this structure
Deoxyribose
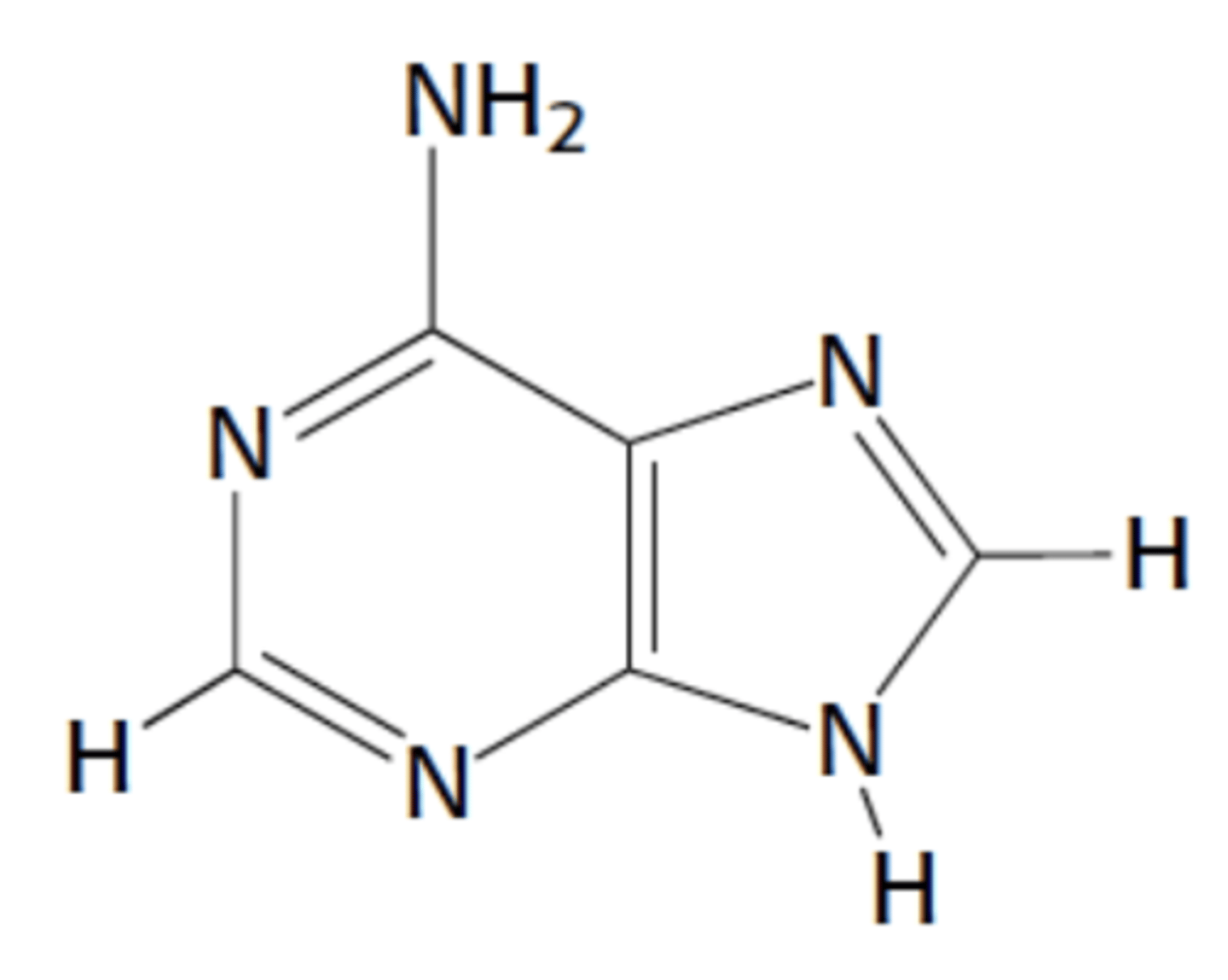
Name this structure
Adenine, purine
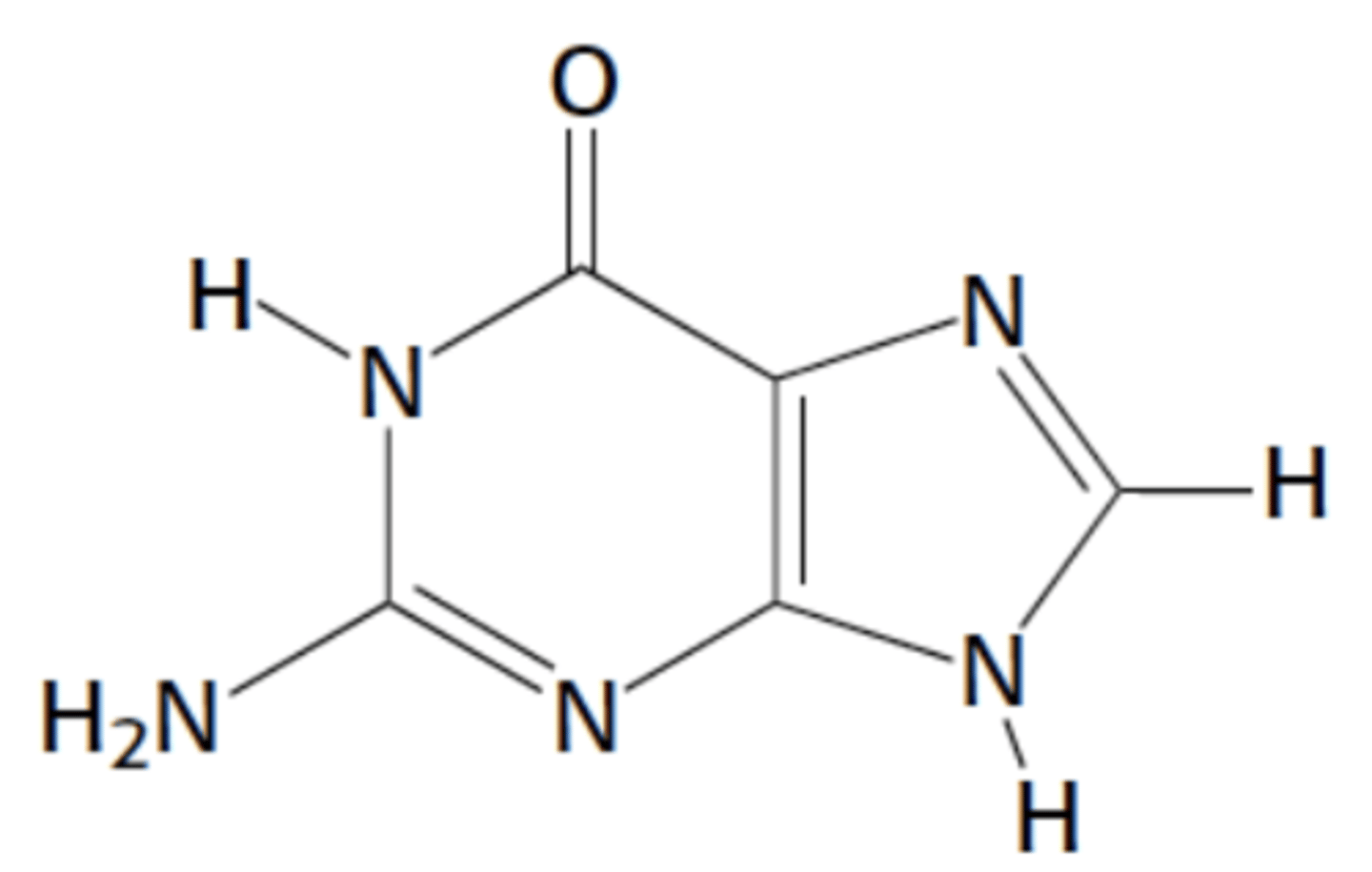
Name this structure
Guanine, purine
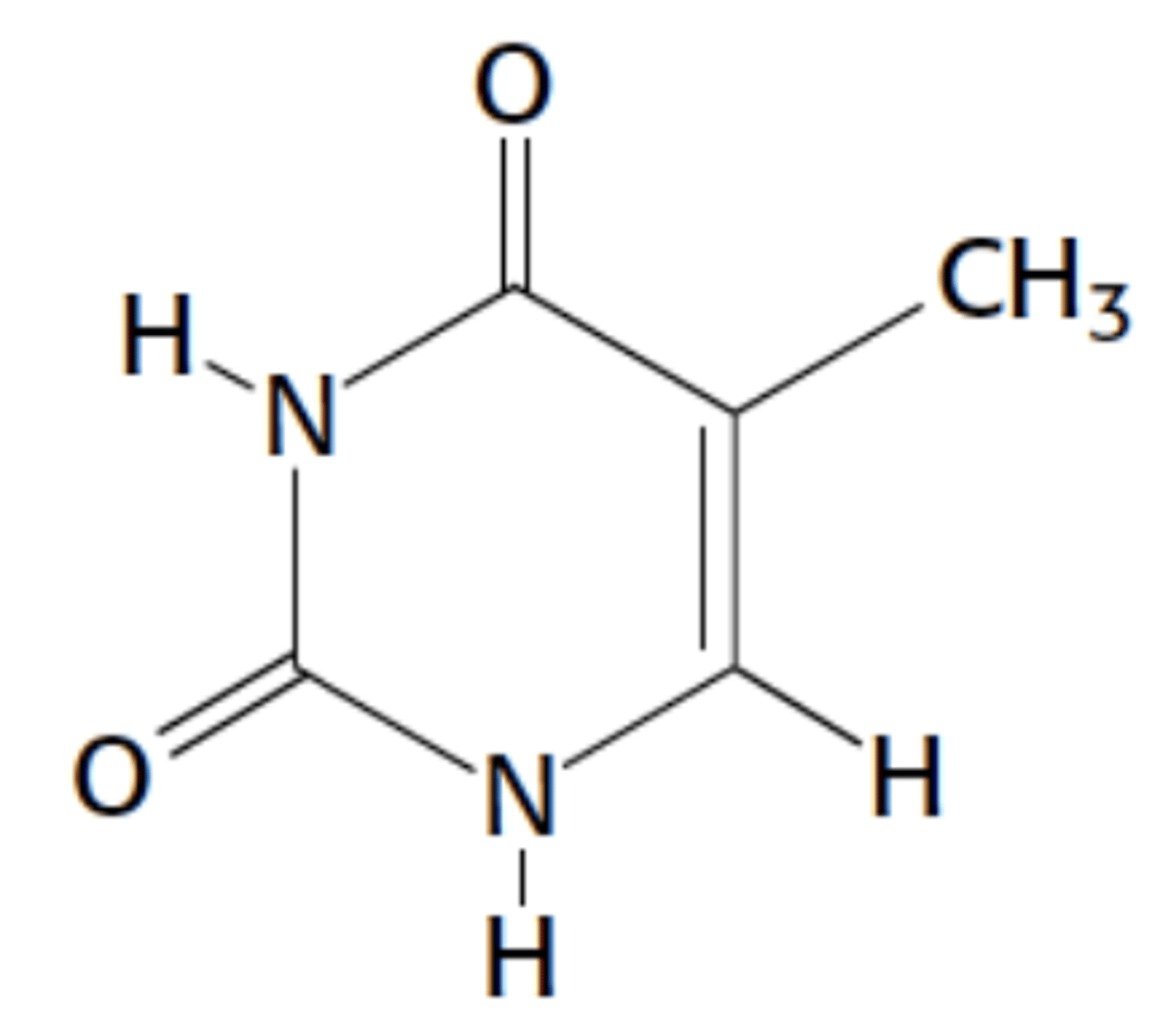
Name this structure
Thymine, pyrimidine
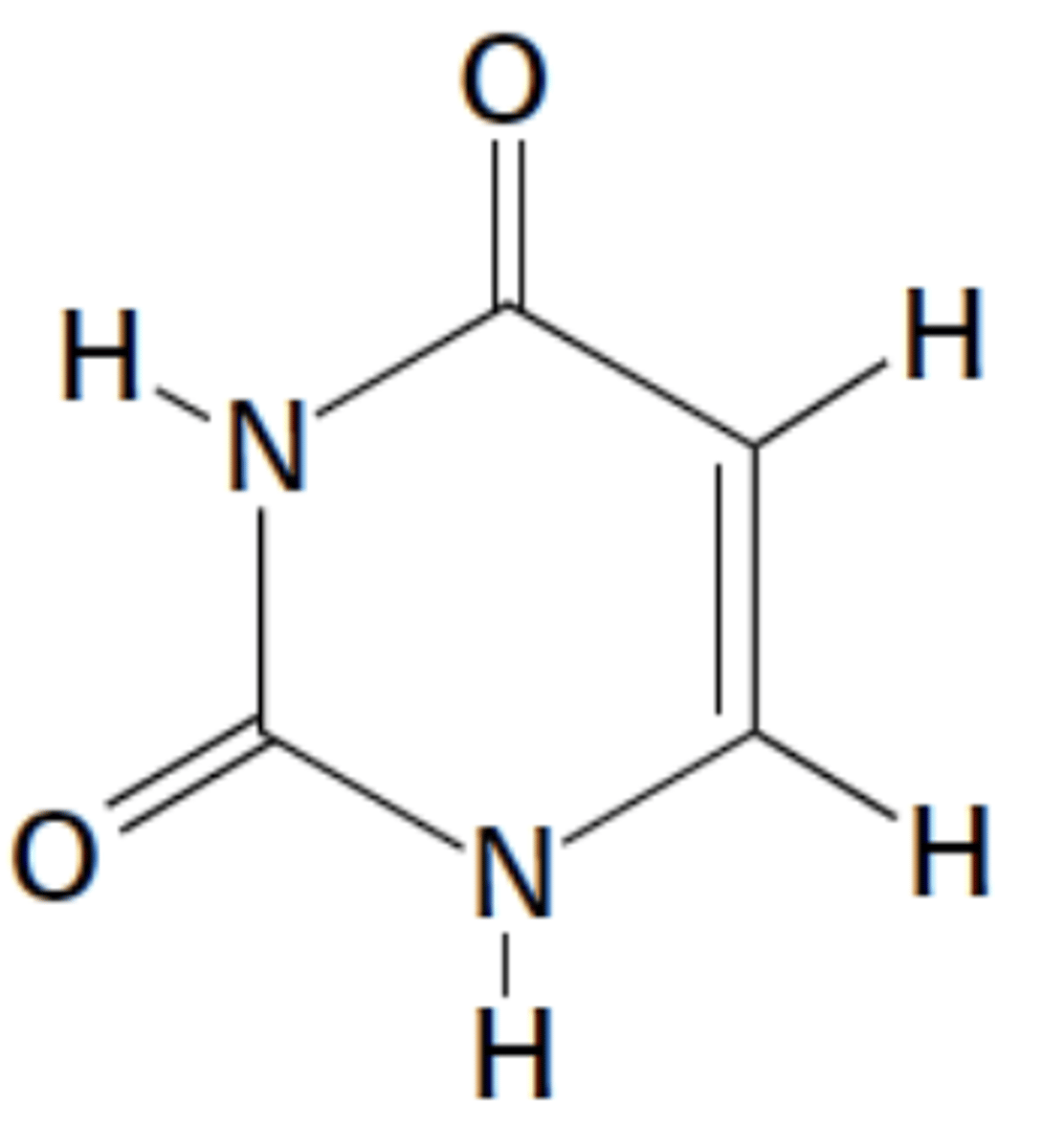
Name this structure
Uracil, pyrimidine (mostly in RNA)
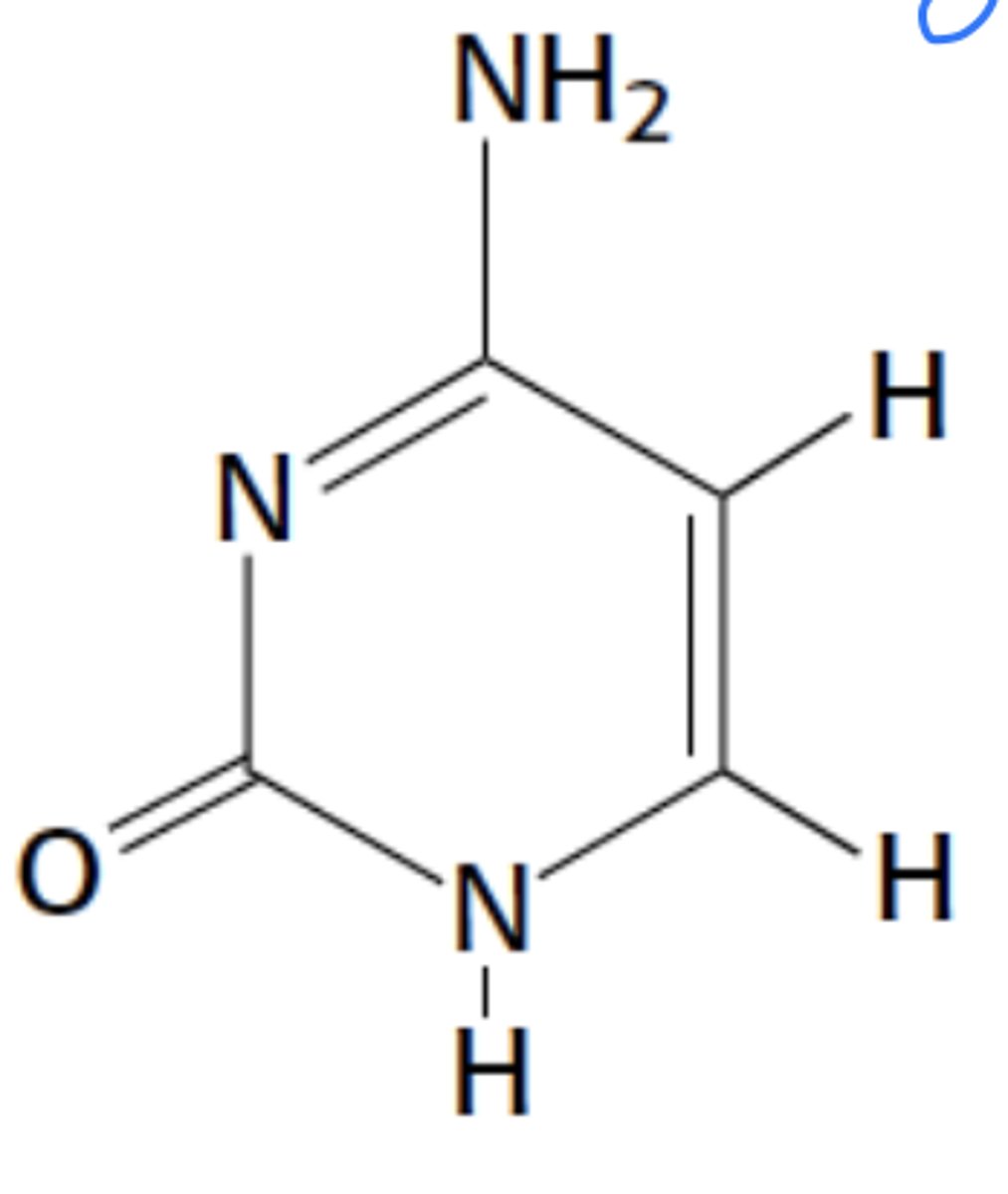
Name this structure
Cytosine, primidine
Whats the difference between adenine and adenosine?
adenine is just the base and adenosine has the base and the sugar (nucleoside)
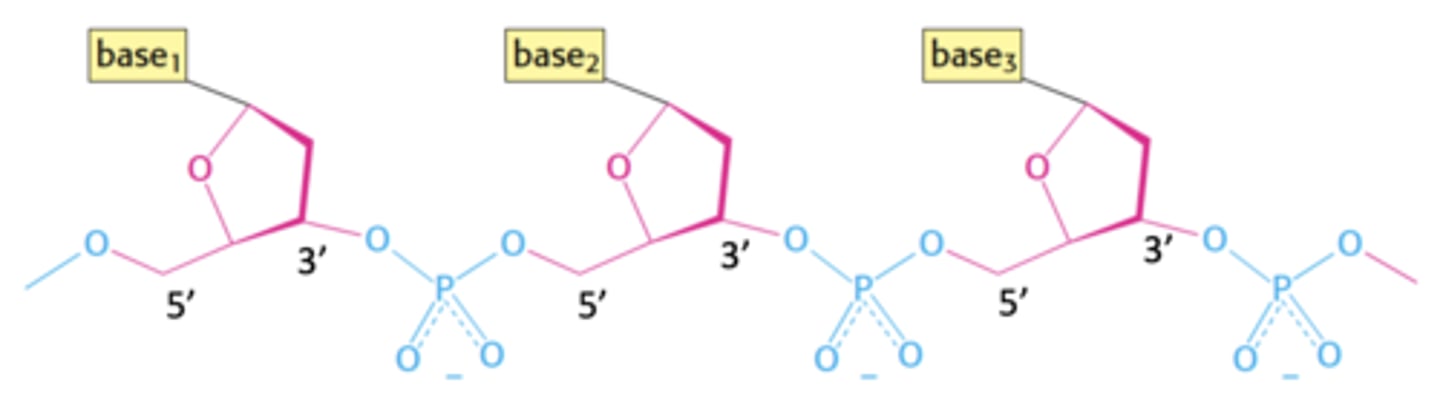
What kind of bond is shown in this polymer?
phosphodiester bond
What direction are DNA bases written in?
5' -> 3'
What direction is the complimentary DNA strand in?
antiparallel
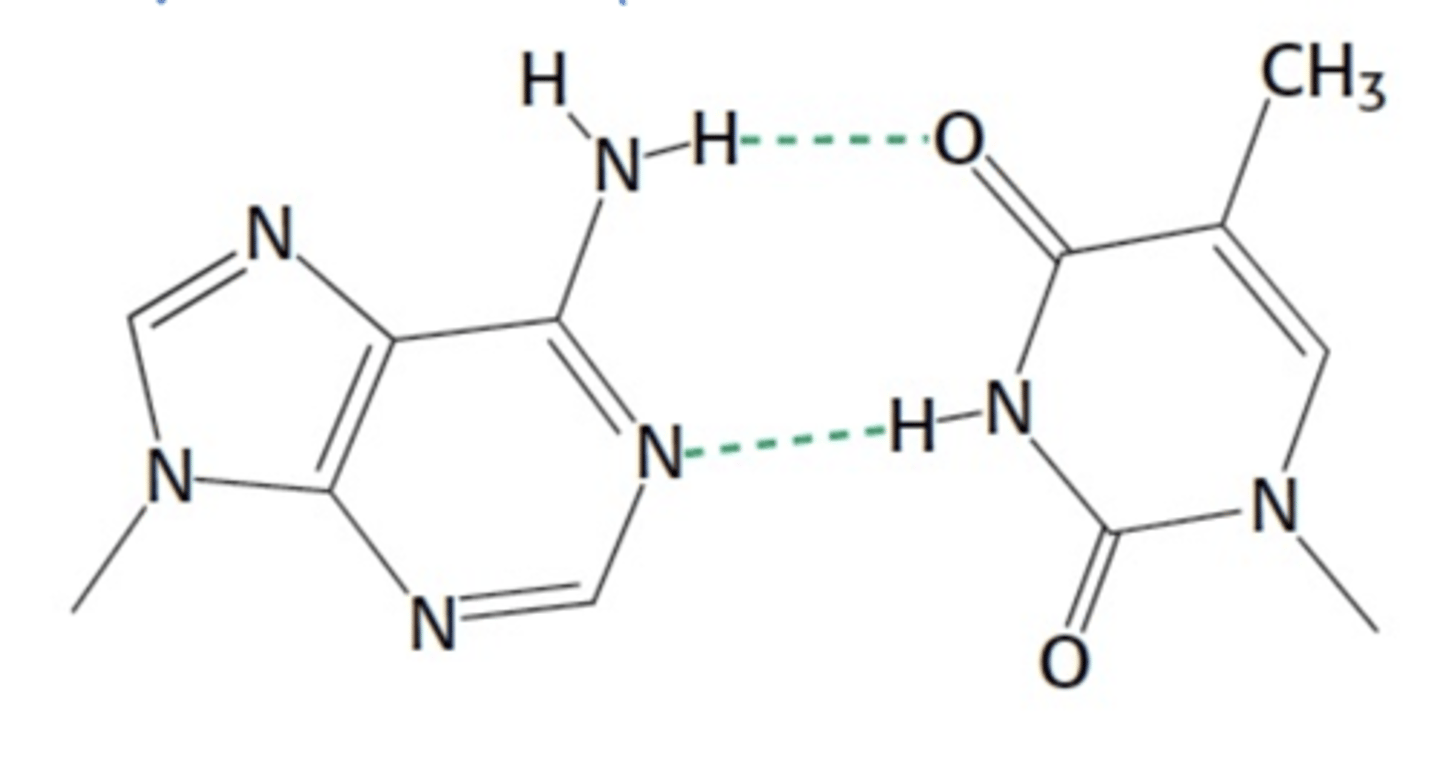
What is shown below
Adenine and thymine base pair
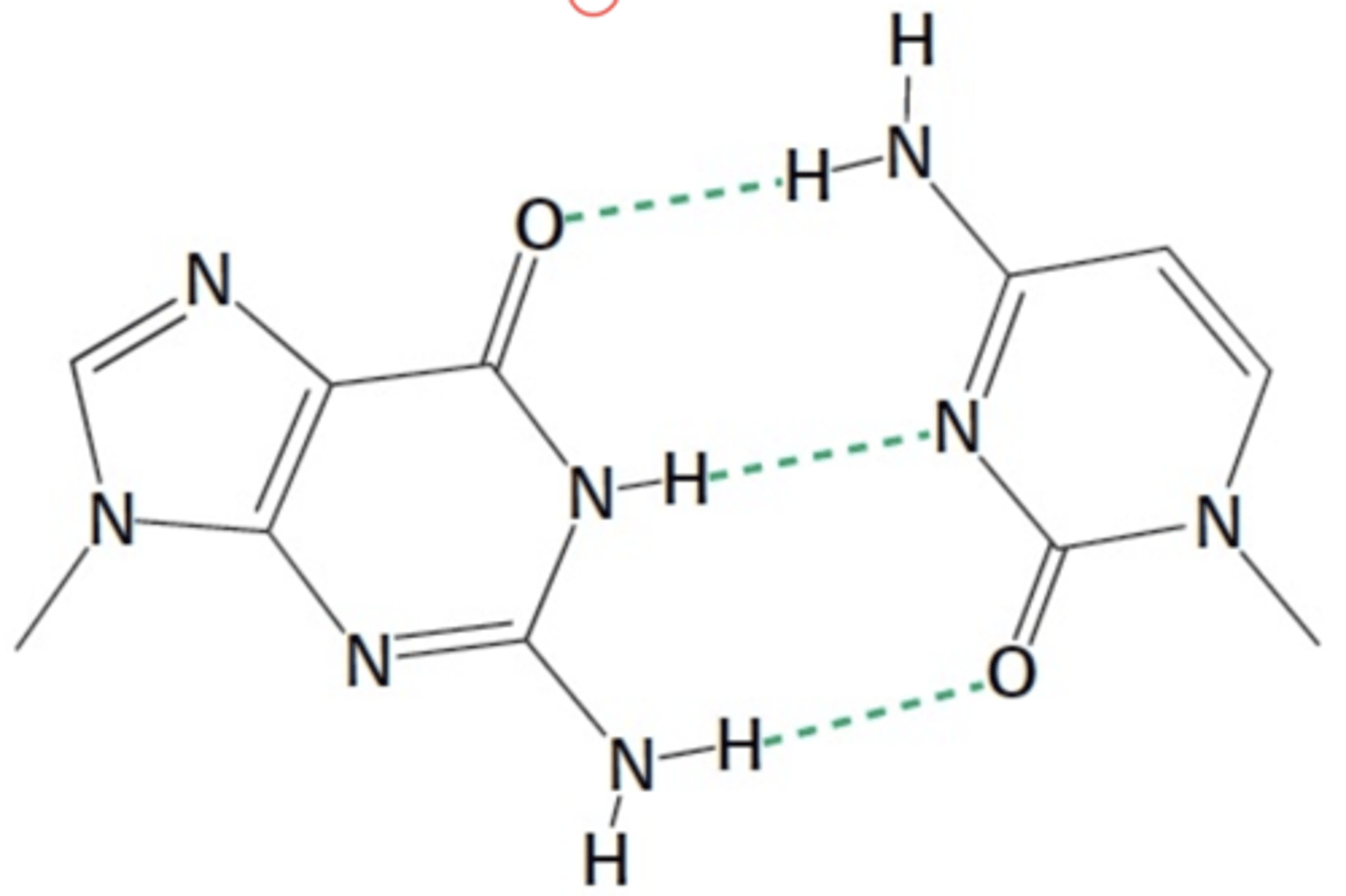
What is shown below
Guanine and cytosine base pair
What is a stronger pair?
adenine and thymine or cytosine and guanine
cytosine and guanine (3 H-bonds)
What shape is DNA
a chiral, right handed helix
What are the 3 forms of DNA?
Alpha: dehydrated
Beta: hydrated
Z: complexed with proteins
How could one reversibly melt DNA strands?
Adding base to an aqueous solution to disrupt the H-bonds
What did the Meselson-Stahl Experiment show?
That DNA replication is semi conservative
How did the Meselson-Stahl Experiment work?
Using E. coli bacteria and heavy (¹⁵N) and light (¹⁴N) nitrogen isotopes, the experiment demonstrated that after one generation, DNA molecules were a hybrid of heavy and light isotopes, confirming the semiconservative mechanism
How do eukaryotes pack so much DNA in their nucleus?
DNA is wrapped around histones which organize into nucleosomes. These form condensed chromatin which forms chromatids then chromosomes
What kind of chromatin is quiet, closed, and condensed?
heterochromatin
What kind of chromatin is loud and ready to replicate?
euchromatin
What are the ingredients for PCR?
1. DNA template
2. Primers
3. dNTPs
4. Buffer
5. Magnesium ions
What does CRISPR do?
knocks out a gene when and where you want
How many parts does CRISPR have?
2 parts:
1. cas9 nuclease
2. single guide RNA
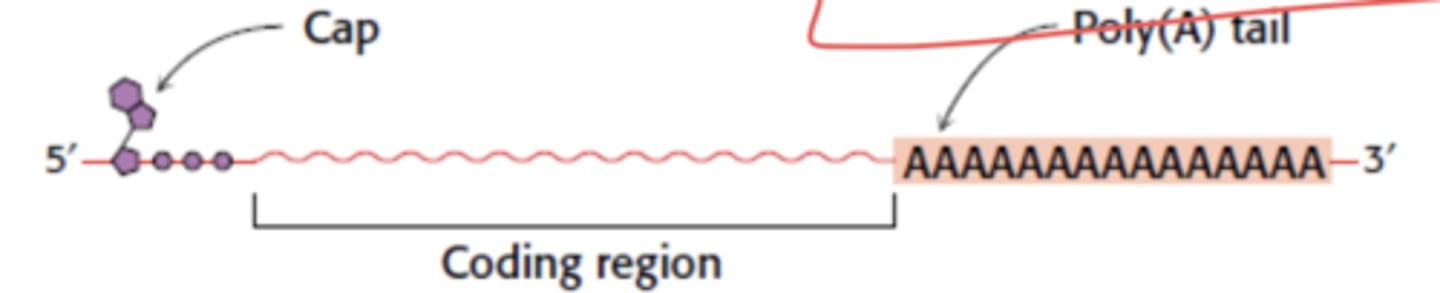
What kind of nucleotide has a 5' cap and poly(A) tail?
mRNA (messenger)
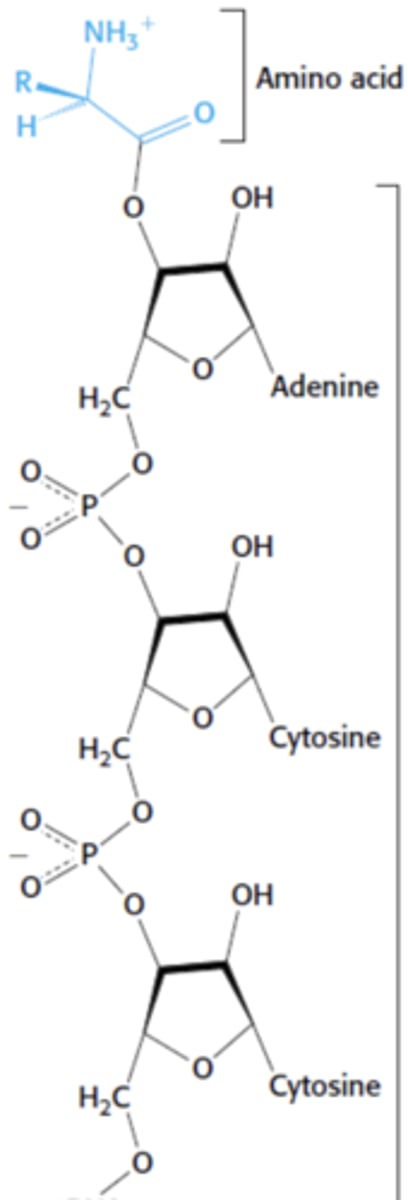
What is this?
the amino acid attached to tRNA
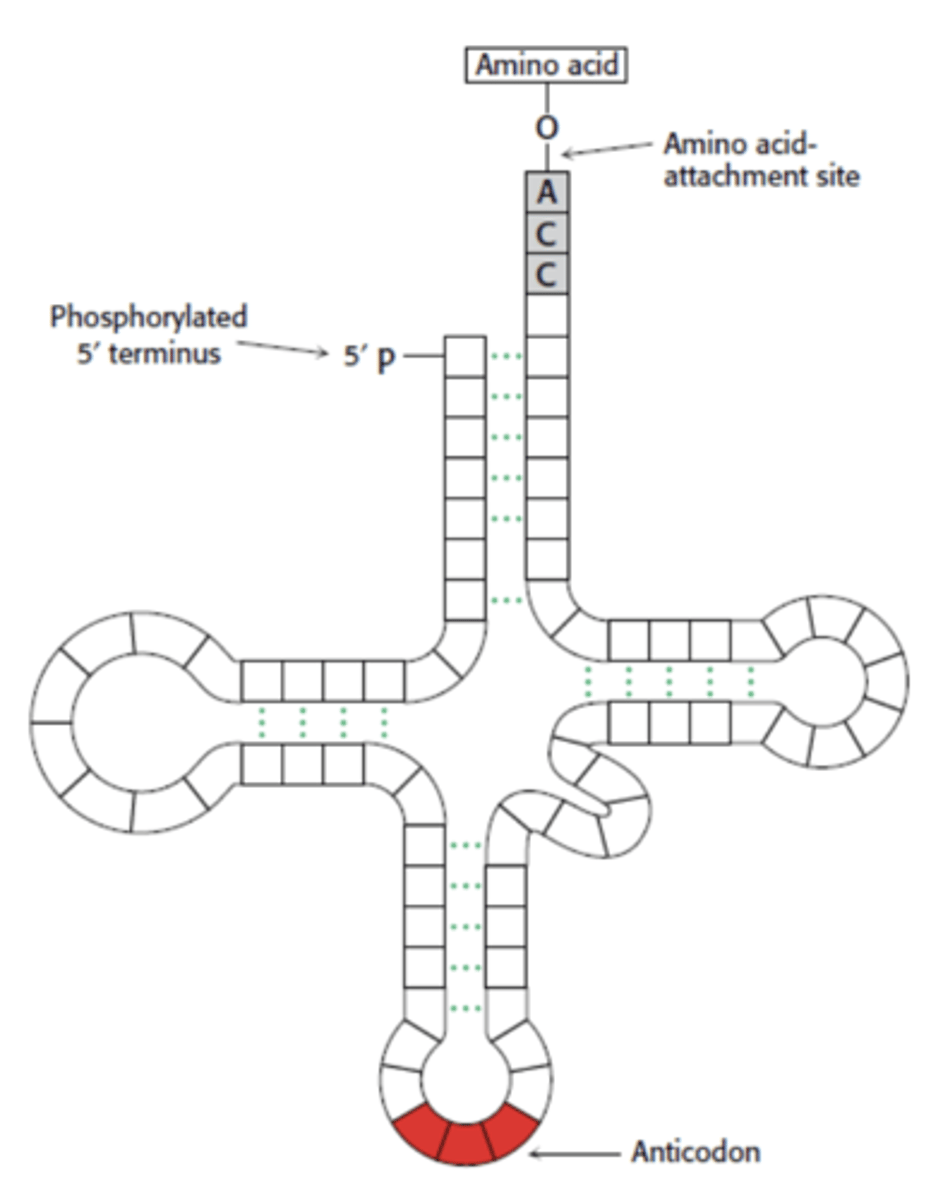
What is this?
tRNA (transfer)
List the following elements from most electronegative to least: C, H, O, N, P, S
O, N, S, C, H, P
Only, Nancy, Sees, Charlie, Huff, Paint
What percent of the atmosphere is oxygen?
20.9%
What kind of hydrocarbons are fatty acids?
highly reduced aliphatic hydrocarbons
What makes an acid saturated?
When the carbon chain has no double bonds
What is a monosaturated fatty acid?
A fatty acid with one double bond
What is a polysaturated fatty acid?
A fatty acid with more than one double bond
The conjugate base of acetic acid is called....
acetate
At a physiological pH are more acids ionized or deionized
deionized
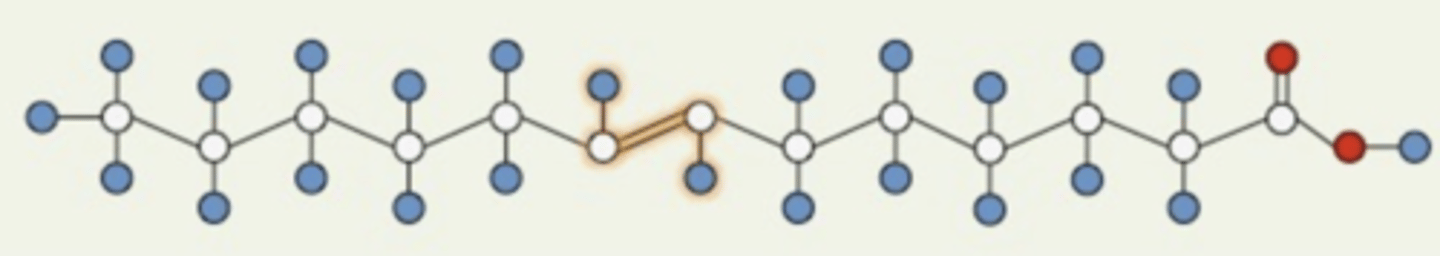
What configuration is this double bond in?
trans
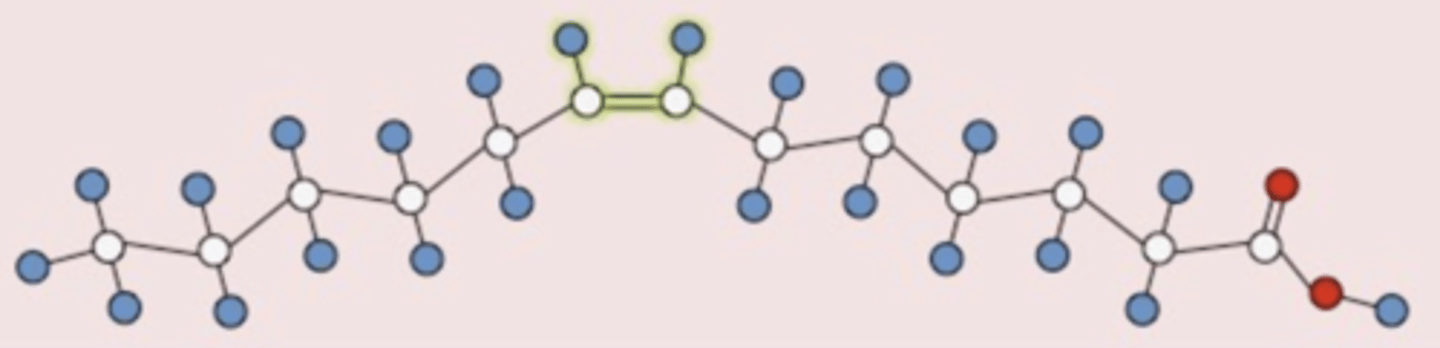
What configuration is this double bond in?
cis
Which carbon do you start counting from when using the delta notation?
the ACID carbon
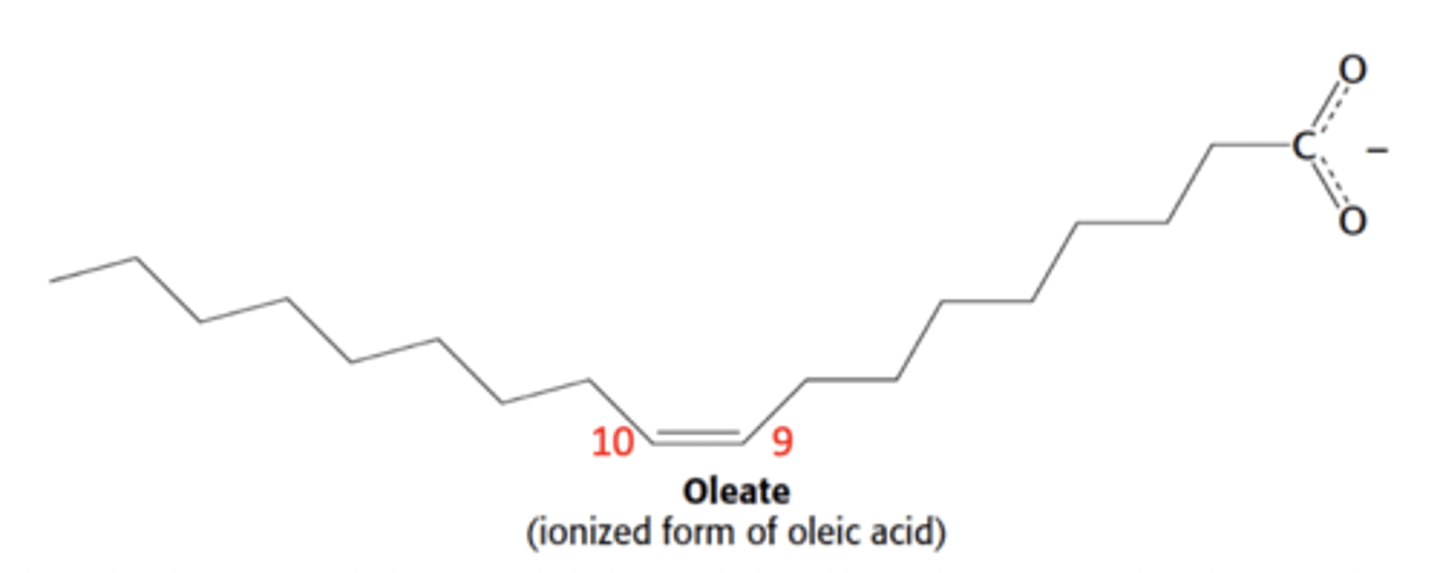
What is the delta notation name of this fatty acid
cis-Δ^9-octadecanoate
Which carbon do you start counting from when using the omega notation?
the END carbon
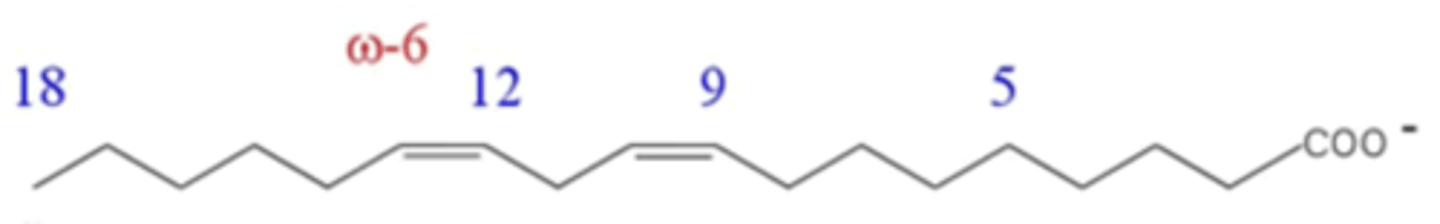
What is the common name of this fatty acid?
linoleate
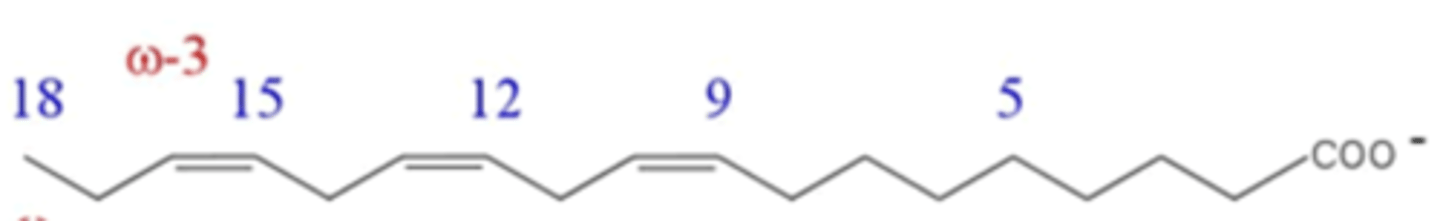
What is the common name of this fatty acid?
linolenate
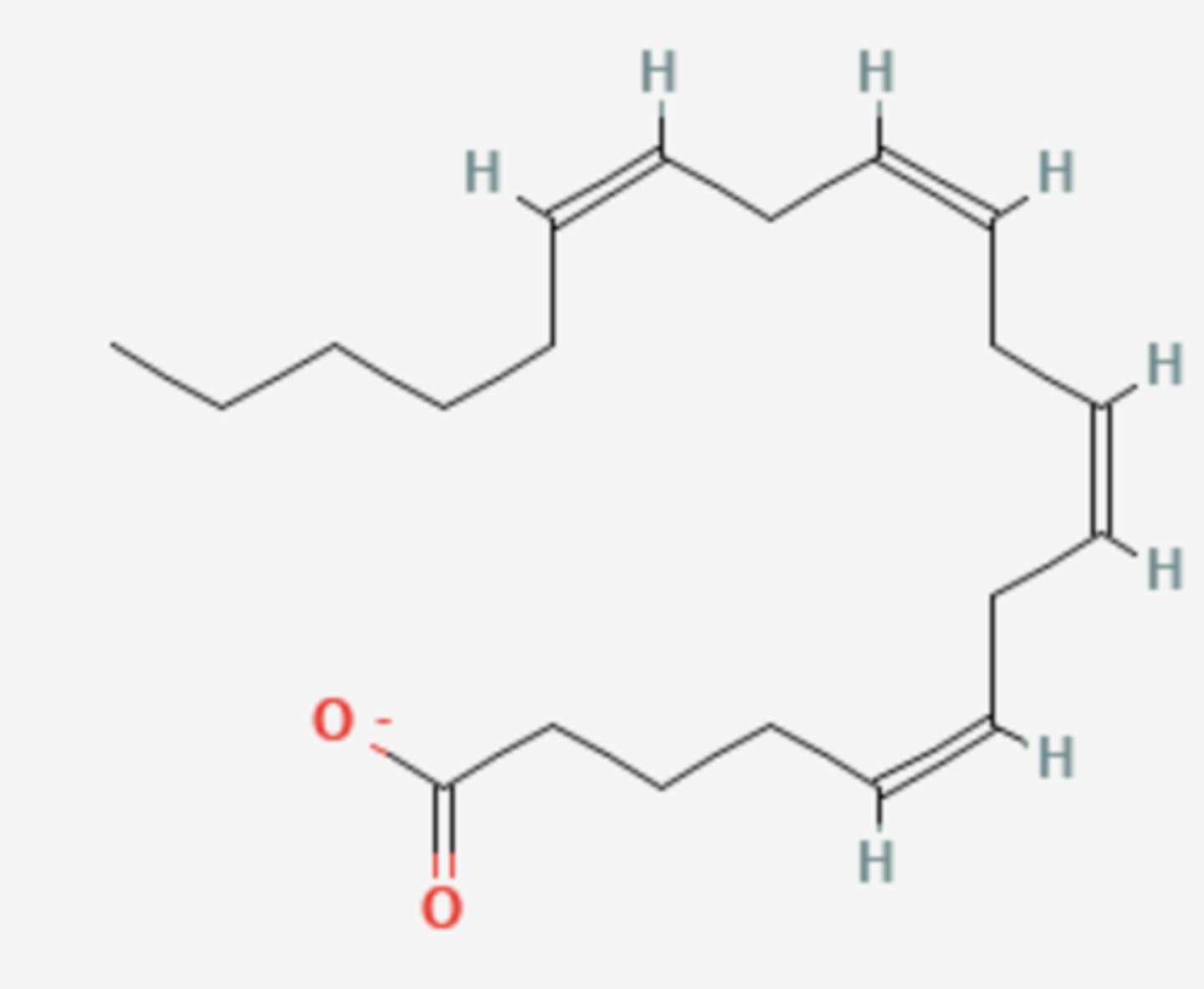
What is the common name of this fatty acid?
Arachidonate
What is human's main source of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids?
Sufficient amounts of fatty acids must be consumed through diet.
What are eicosanoids?
20+ carbon FAs
What are omega-6 and omega-3 FAs needed to synthesize?
eicosanoids and endocannabinoids
What kind of FA is essential for lipid raft formation?
omega-6 and omega-3 FAs
What kind of FA is essential for activation of transcription factors in the nucleus?
omega-6 and omega-3 FAs
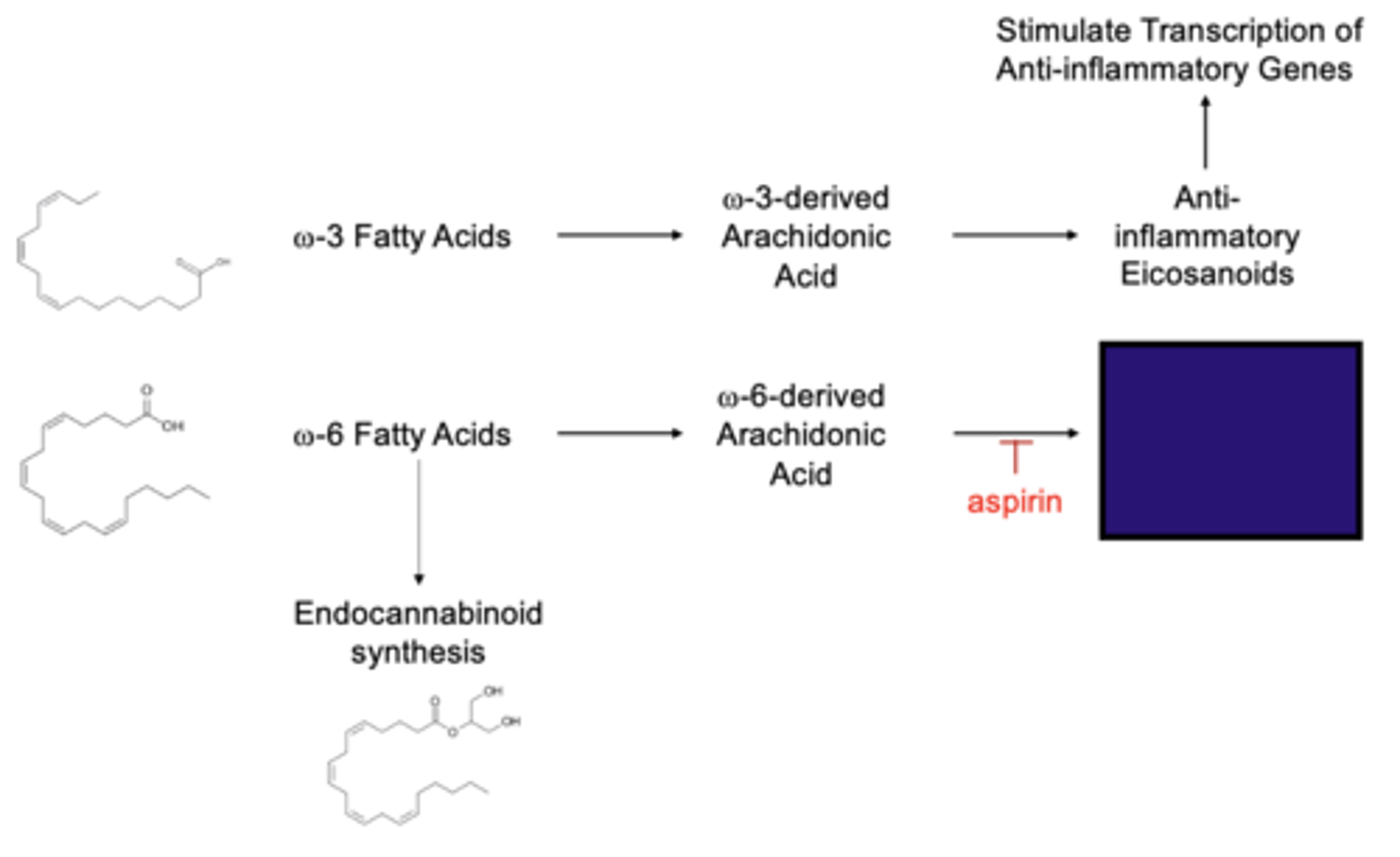
What is after the last arrow?
pro-inflammatory eicosanoids
What is the COX-1 enzyme responsible for?
Converting arachidonic acid into pro-inflammatory prostaglandin D2
What does aspirin block
the action of the COX-1 enzyme
What happens if someone has too many trans-fats in their diets?
It significantly increases the risk of coronary heart disease
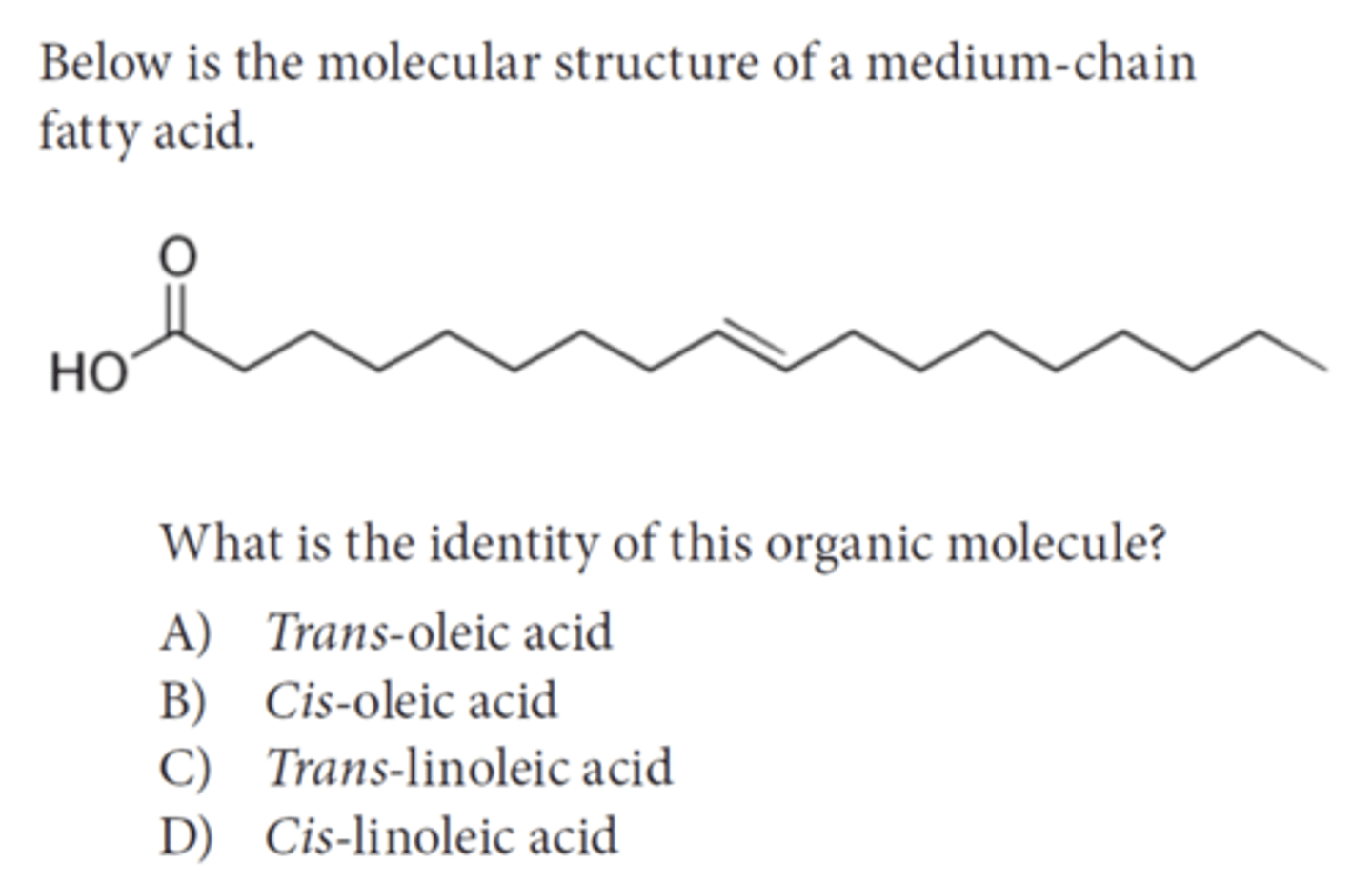
Answer this question
A trans-oleic acid
what does linoleic mean?
multiple double bonds
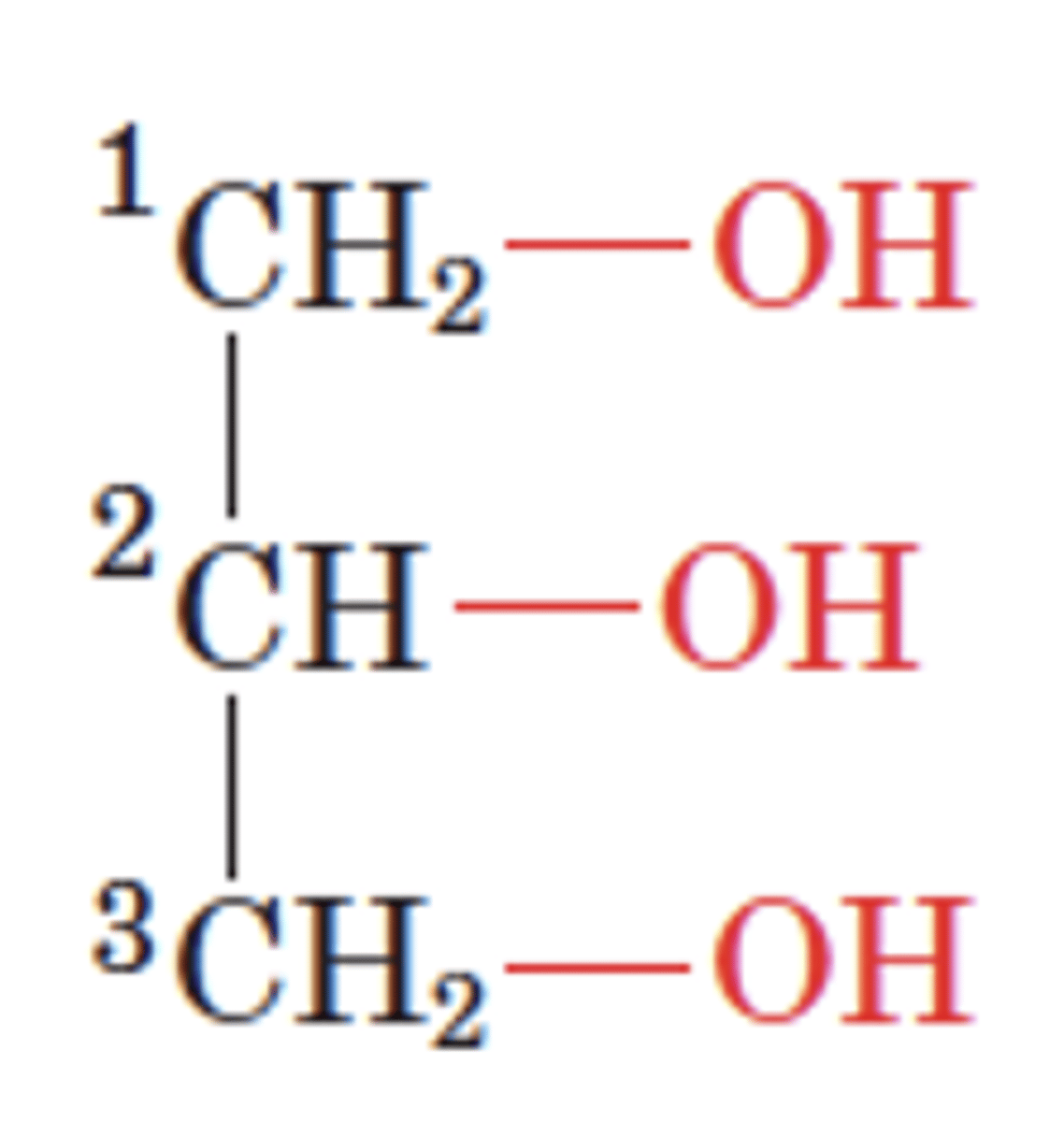
What is this?
glycerol