Animal Reproduction: Asexual and Sexual Processes
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
Asexual Reproduction
Efficient reproduction without mating, limits genetic diversity.
Genetic Variability
Diversity in genetic makeup, crucial for adaptation.
Budding
New individuals grow from parent bodies via mitosis.
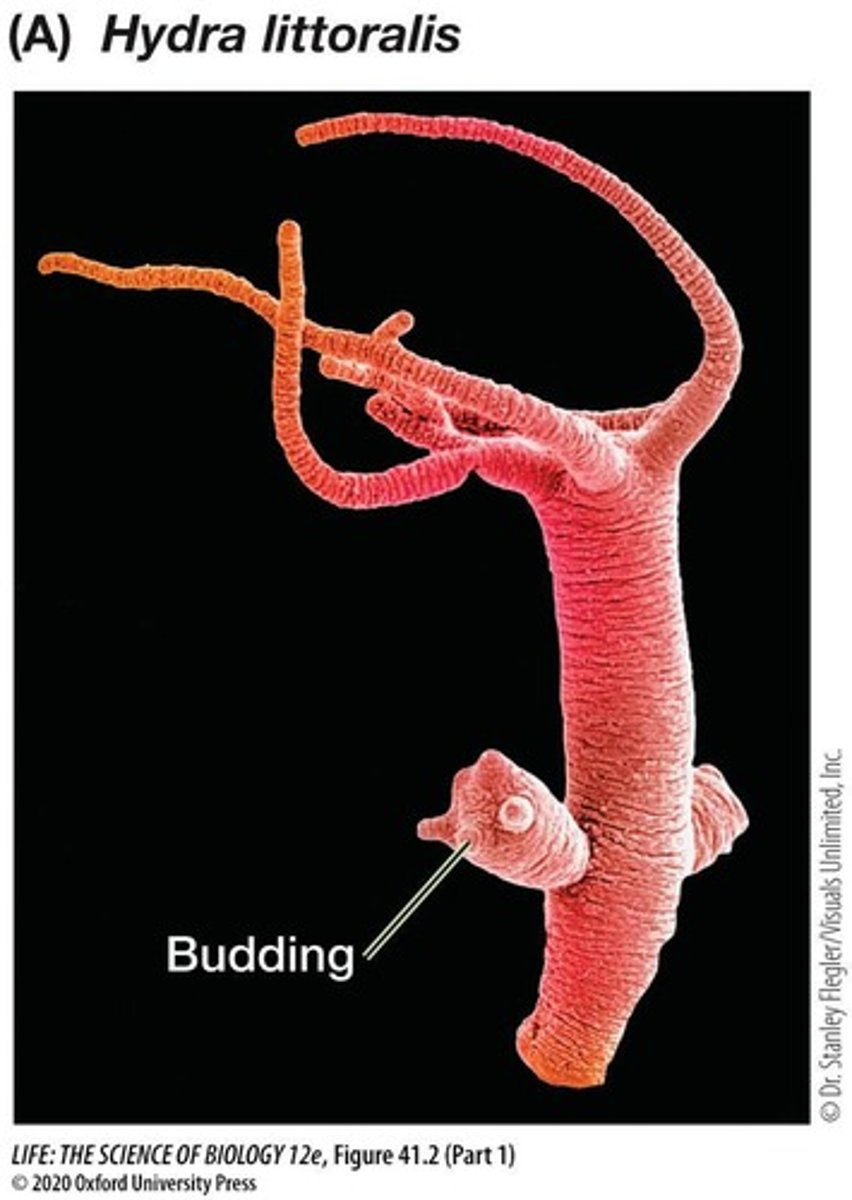
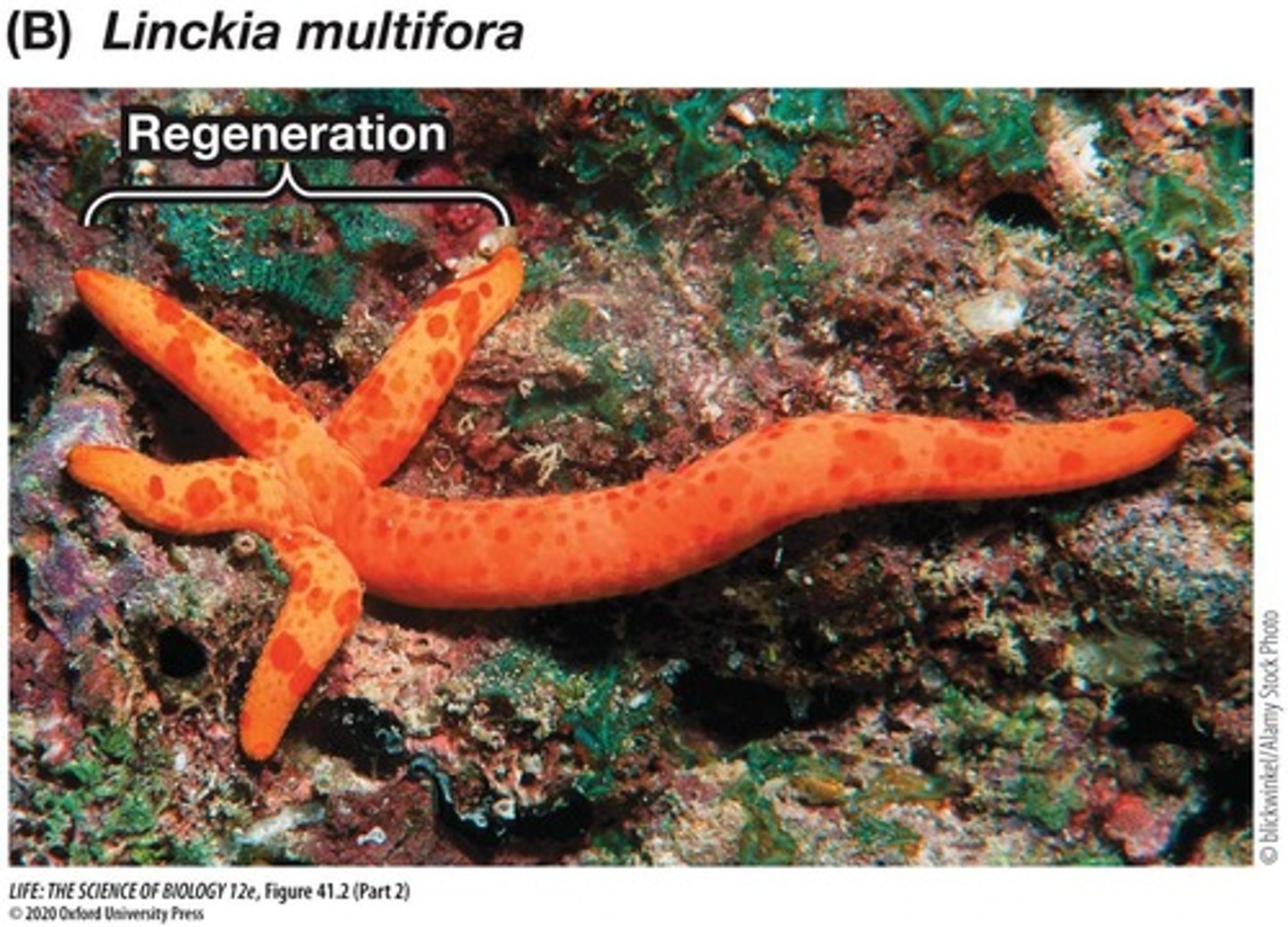
Regeneration
Replacement of lost tissues or limbs in organisms.

Fission
Splitting of an organism into two new individuals.
Parthenogenesis
Development of offspring from unfertilized eggs.
Gametes
Haploid cells formed during gametogenesis for reproduction.
Gametogenesis
Process of forming gametes in gonads.
Haploid
Cell with one set of chromosomes, e.g., gametes.
Diploid
Cell with two sets of chromosomes, e.g., zygote.
Meiosis
Cell division producing gametes with genetic diversity.
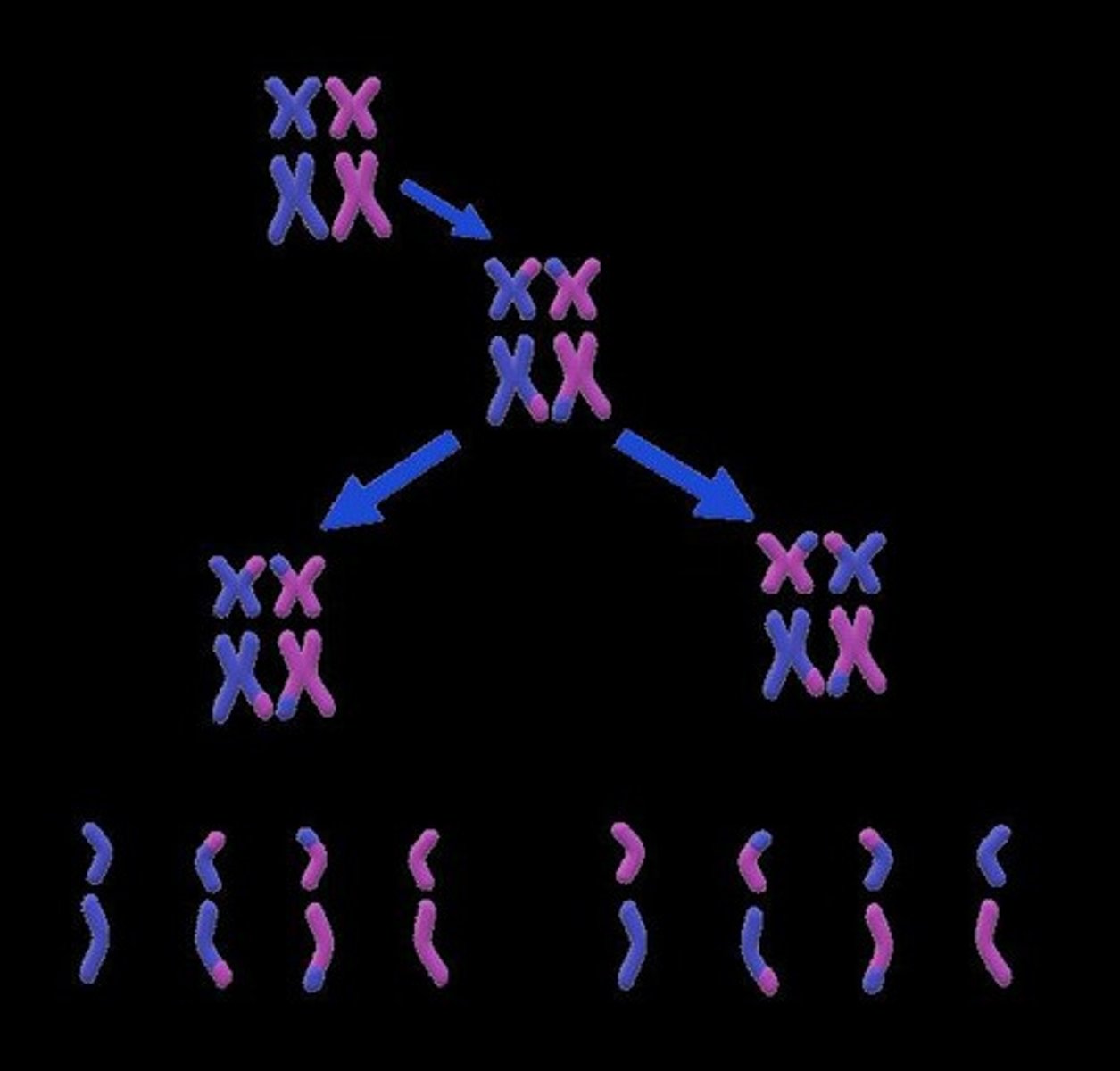
Crossing Over
Exchange of genetic material during meiosis.
Independent Assortment
Random distribution of chromosomes during gamete formation.
Testes
Male gonads producing motile sperm.
Ovaries
Female gonads producing nonmotile ova (eggs).
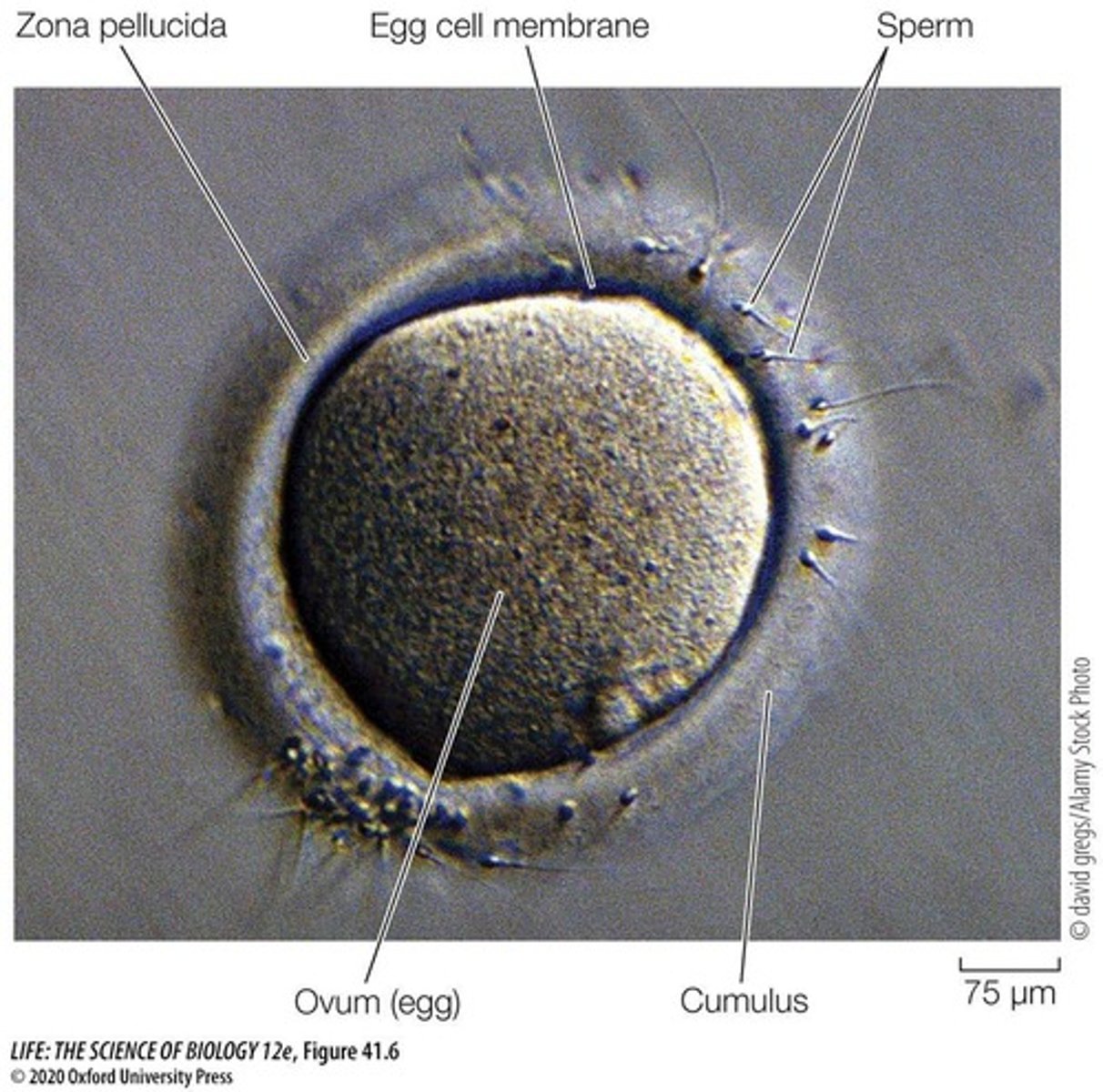
Fertilization
Union of sperm and egg forming a diploid zygote.
Sperm Recognition
Specific interaction ensuring correct fertilization.
Egg Activation
Metabolic activation of the egg post-fertilization.
Somatic Cells
Body cells distinct from germ cells.
Germ Cells
Cells that develop into gametes during reproduction.
Mating Behavior
Actions involving courtship and pairing for reproduction.
Environmental Change
Alterations in surroundings impacting species adaptation.
Sexual Reproduction
Involves union of haploid gametes, enhancing genetic diversity.
Aquatic Fertilization
Sperm and eggs released into water for reproduction.

Haploid
Cell with a single set of chromosomes.
Internal Fertilization
Sperm deposited directly into female reproductive tract.
Cumulus
Cells in a gelatinous matrix surrounding the egg.
Zona Pellucida
Protective layer beneath the cumulus of the egg.
Acrosomal Reaction
Sperm head reaction triggered by zona pellucida.
Acrosome
Membrane-enclosed structure containing enzymes on sperm.
Polyspermy
Fertilization by multiple sperm, usually lethal.
Sodium Influx
Na+ influx alters egg membrane charge.
External Fertilization
Gametes released into water for fertilization.
Spawning
Release of gametes into aquatic environments.
Gonads
Primary sex organs producing gametes.
Accessory Sex Organs
Additional genitalia components aiding reproduction.
External Genitalia
Visible reproductive structures, e.g., penis.
Copulation
Joining of male and female reproductive organs.
Spermatophores
Packets of sperm deposited in the environment.
Dioecious Species
Species with distinct male and female individuals.
Monoecious Species
Species with individuals producing both sperm and eggs.
Simultaneous Hermaphrodite
Individual producing both gametes at the same time.
Sequential Hermaphrodite
Individual changing sex during its life cycle.
Oviparous Animals
Lay eggs; embryos develop outside the body.
Viviparous Animals
Retain embryos inside the mother's body.
Embryo Development
Varies among mammals at birth stage.
Uterus
Holds embryo until birth in females.
Placenta
Facilitates nutrient and waste exchange with mother.
Ovoviviparity
Retaining fertilized eggs until hatching in some species.
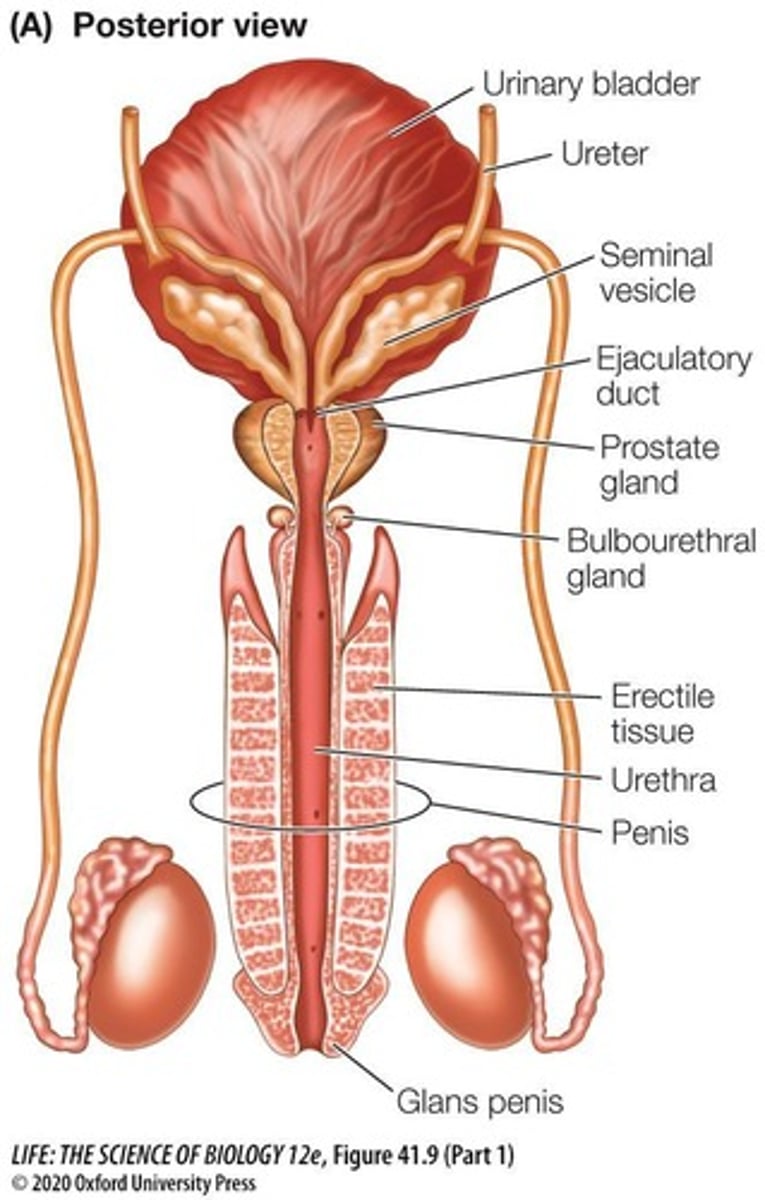
Semen
Contains sperm and fluids supporting fertilization.
Testes
Produce sperm and testosterone, located in scrotum.
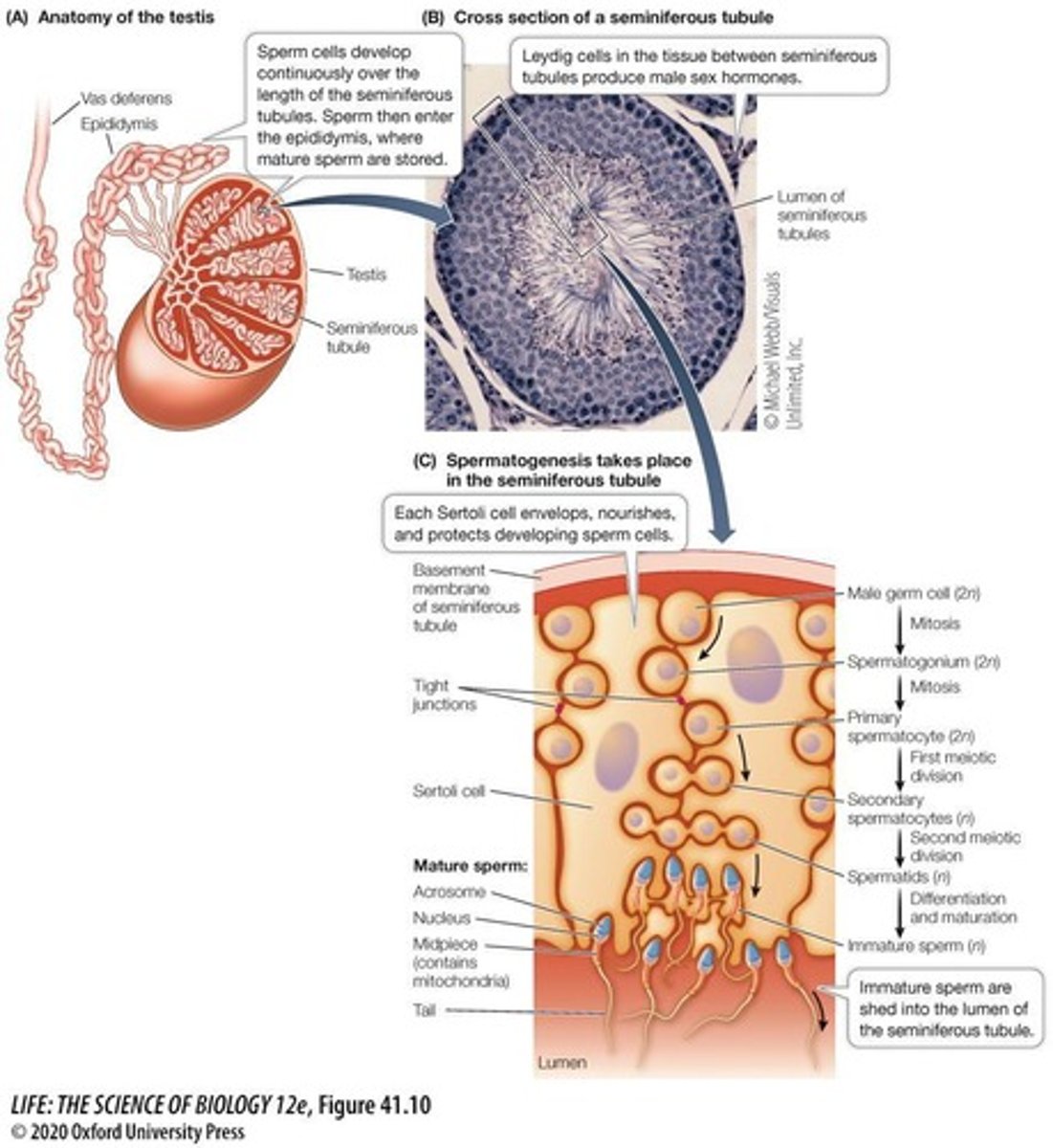
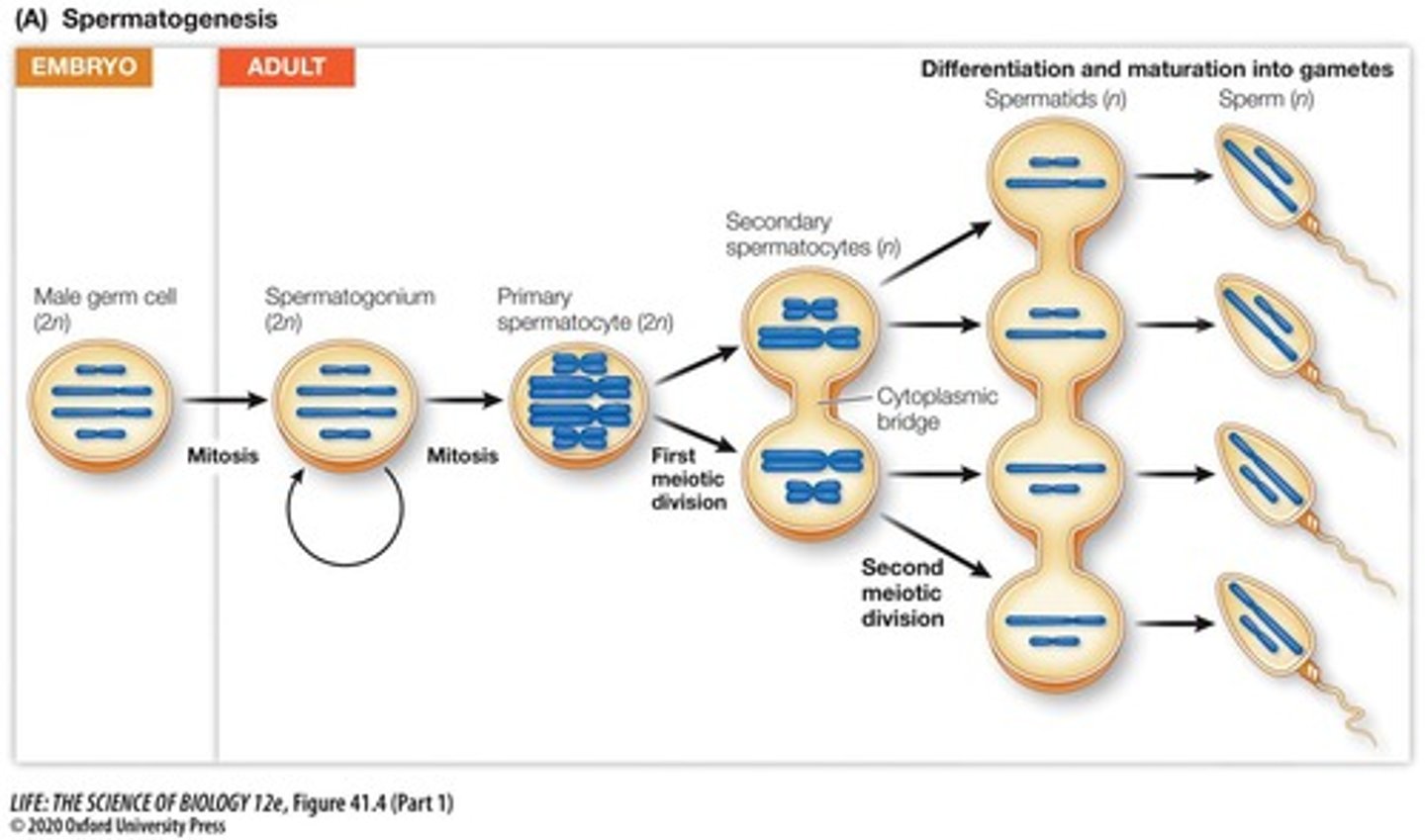
Spermatogenesis
Process of sperm production in seminiferous tubules.
Leydig Cells
Produce testosterone in the testes.
Sertoli Cells
Nourish developing sperm in seminiferous tubules.
Epididymis
Stores and matures sperm after production.
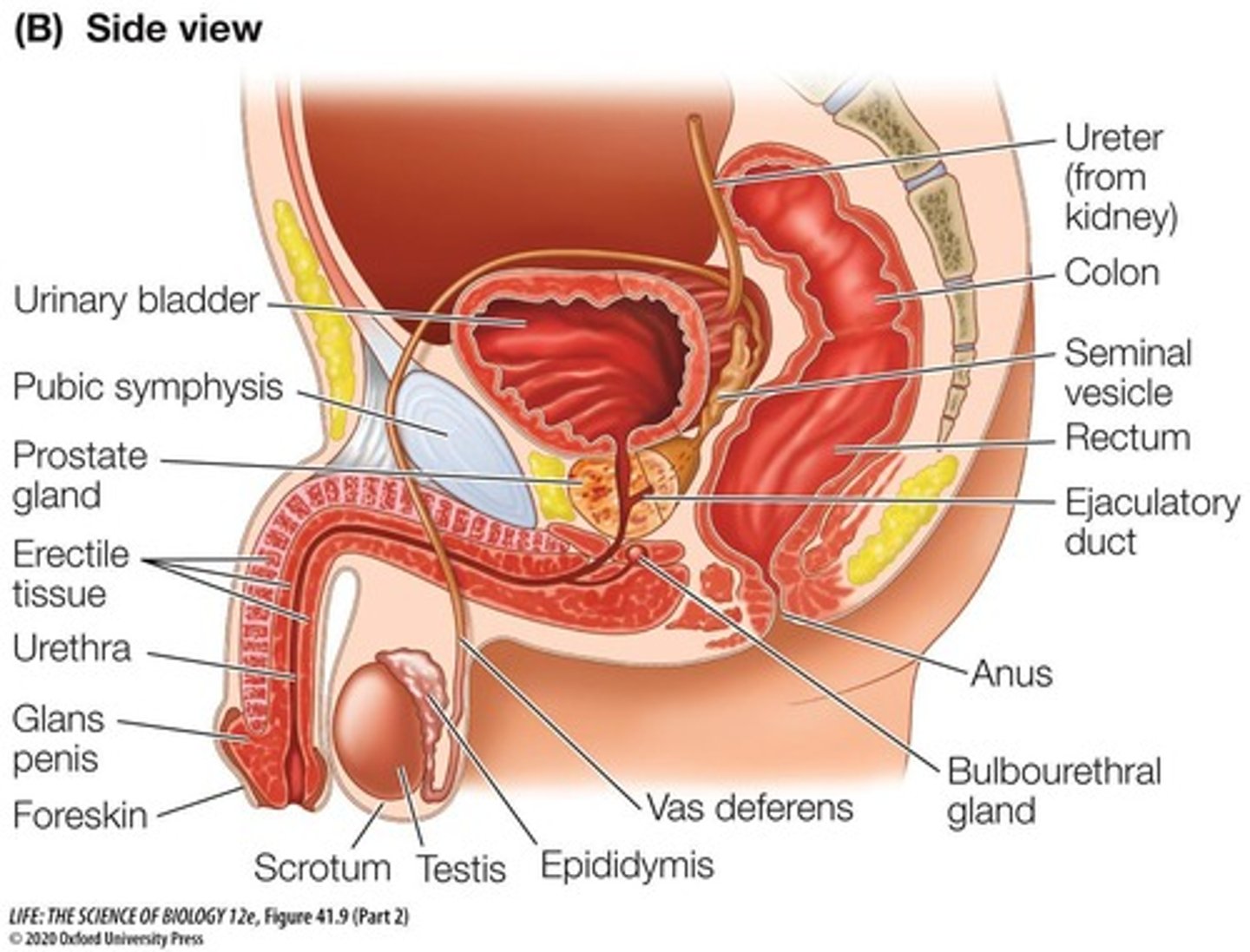
Vas Deferens
Connects epididymis to urethra for sperm transport.
Seminal Vesicles
Secrete seminal fluid components into vas deferens.
Prostate Gland
Produces alkaline fluid to enhance semen.
Bulbourethral Glands
Secrete lubrication for sperm movement during climax.
Penile Erection
Caused by blood vessel dilation from nitric oxide.
cGMP
Molecule causing blood vessel dilation in erection.
Emission
Movement of semen into urethra before ejaculation.
Ejaculation
Muscle contractions force semen out of penis.
GnRH
Hormone stimulating LH and FSH release at puberty.
LH
Luteinizing hormone increasing testosterone production.
FSH
Follicle-stimulating hormone aiding spermatogenesis.
Inhibin
Negative feedback on FSH production by Sertoli cells.
Orgasm
Intense pleasure accompanying emission and ejaculation.
Erectile Dysfunction
Condition treated by drugs inhibiting cGMP breakdown.
Ovary
Organ that releases eggs during ovulation.
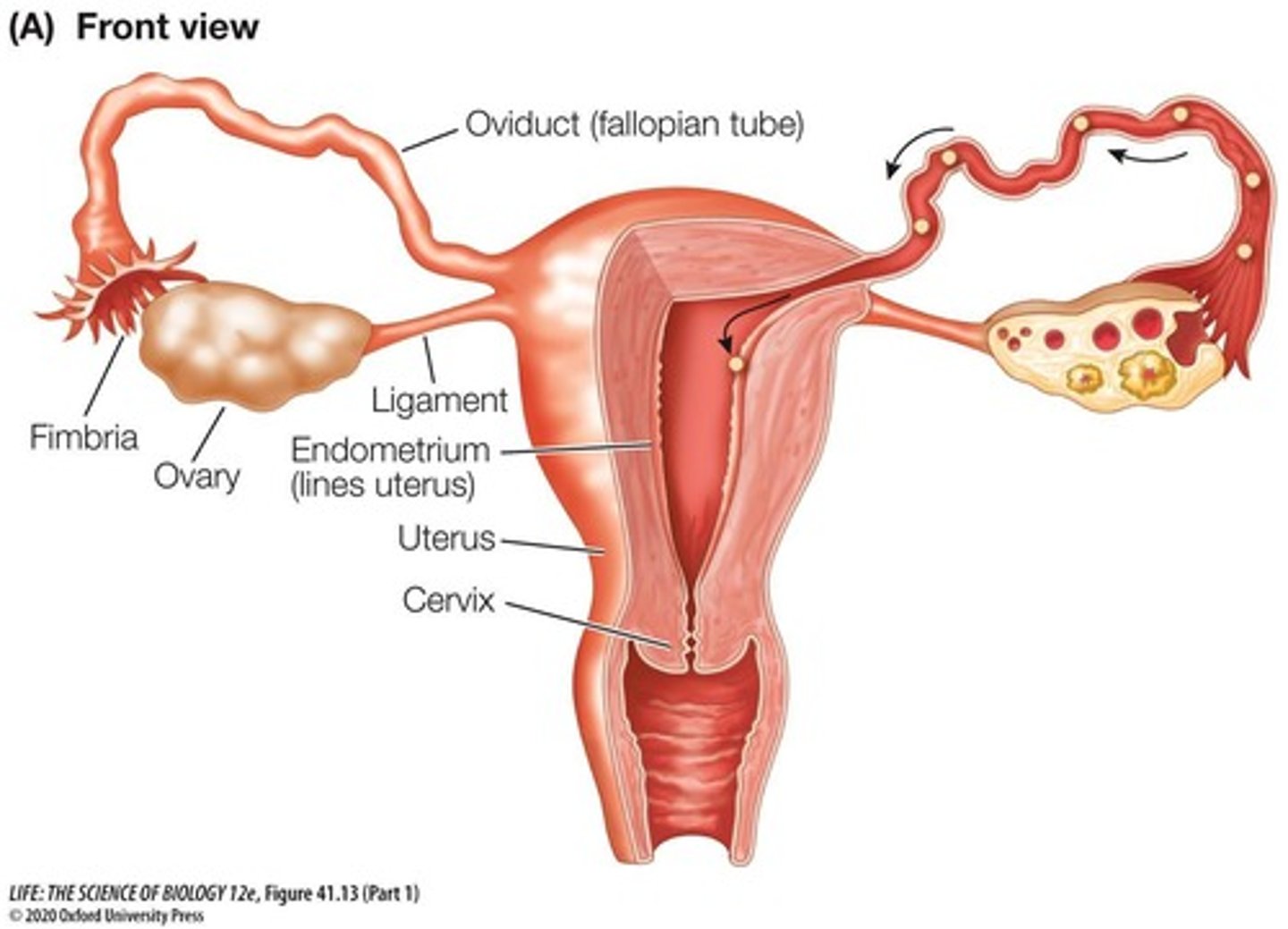
Oviduct
Tube where fertilization occurs and eggs travel.
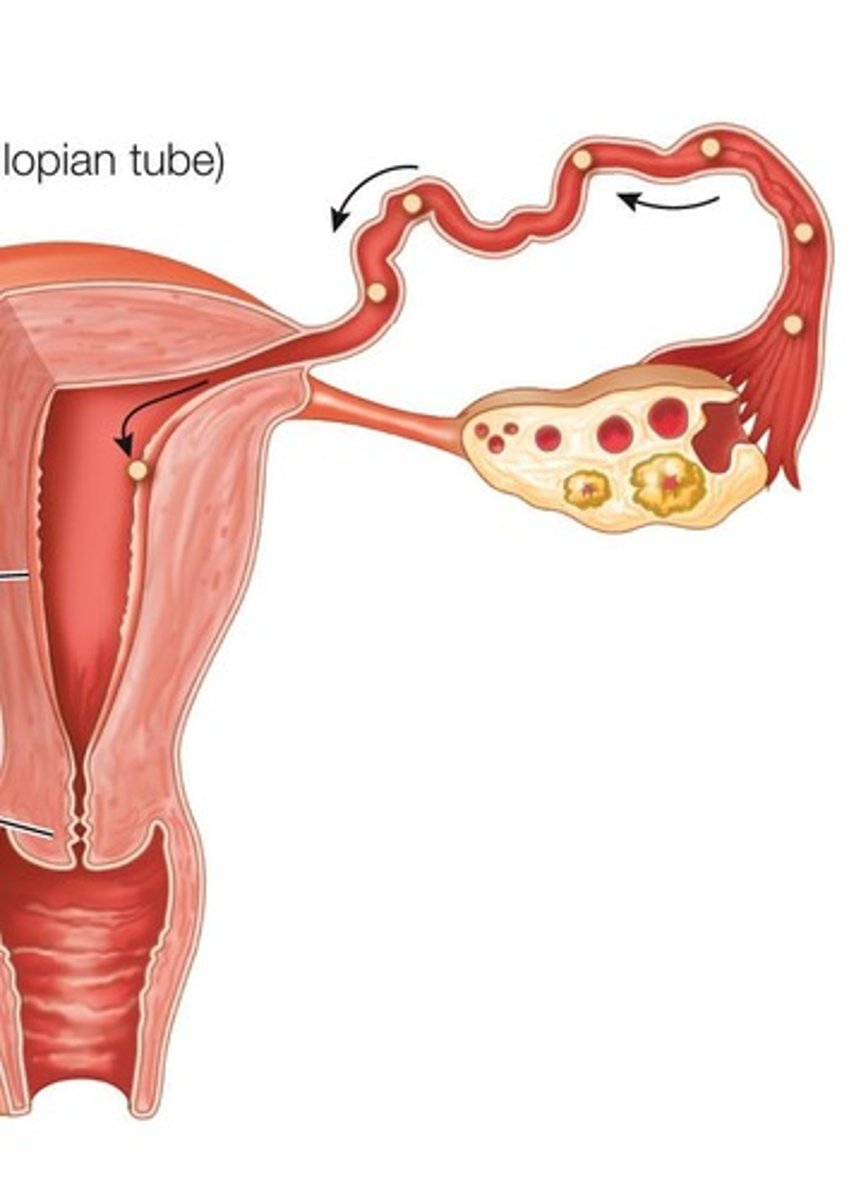
Fimbria
Finger-like projections guiding the egg to oviduct.
Cilia
Hair-like structures moving the egg toward uterus.
Uterus
Organ where fertilized egg develops into embryo.
Cervix
Narrow passage connecting uterus to vagina.
Vagina
Canal through which the baby exits during birth.
Fertilization
Fusion of sperm and egg nuclei forming zygote.
Zygote
Diploid cell resulting from sperm-egg fusion.
Blastocyst
Stage of development after zygote undergoes division.
Endometrium
Uterine lining where blastocyst implants.
Placenta
Organ formed from blastocyst interaction with endometrium.
Ovarian Cycle
Cycle producing eggs and hormones in females.
Uterine Cycle
Cycle preparing endometrium for potential implantation.
Menstruation
Sloughing off of endometrium if no implantation occurs.
Primary Oocytes
Immature eggs present in ovaries at birth.
Follicle
Structure containing a primary oocyte and surrounding cells.
Corpus Luteum
Endocrine gland formed from leftover follicle cells.
Estrogen
Hormone promoting development of female secondary characteristics.
Progesterone
Hormone maintaining endometrium for potential pregnancy.
GnRH
Hormone stimulating FSH and LH production at puberty.
FSH
Hormone stimulating follicle growth and estrogen production.
LH
Hormone triggering ovulation and corpus luteum formation.
Negative Feedback
Inhibition of hormone release to regulate reproductive cycles.
hCG
Hormone secreted by blastocyst after implantation.
Corpus Luteum
Produces estrogen and progesterone during early pregnancy.
Endometrium
Uterine lining maintained by estrogen and progesterone.
Pregnancy Testing
Detects hCG presence in urine or blood.
Placenta
Nourishes embryo and produces hormones during pregnancy.
Gonadotropins
Hormones that stimulate ovarian function, inhibited during pregnancy.
Birth Control Pills
Maintain high estrogen and progesterone levels to prevent ovulation.