Genetics, Populations, Evolution, and Ecosystems
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
What is meant by the term genotype?
The genetic constitution of an organism.
What is meant by the term phenotype?
The expression of this genetic constitution and its interaction with the environment.
What are alleles and how do they arise?
Variations of a particular gene → arise by mutation
Homozygous
A pair of homologous chromosomes carrying the same alleles for a single gene.
Heterozygous
A pair of homologous chromosomes carrying two different alleles for a single gene.
How many alleles of a gene can be found in diploid organisms?
2 as diploid organisms have 2 sets of chromosomes
But there may be many alleles of a single gene in a population.
Describe the different types of alleles
Dominant- always expressed in the phenotype(shown in the phenotype)
Recessive- only expressed when 2 copies are present, no dominant allele present- homozygous recessive
Codominant alleles- Both alleles are equally dominant and expressed in the phenotype.
Multiple alleles
More than two alleles for a single gene
Sex -linkage
A gene whose locus is on the X chromosome.
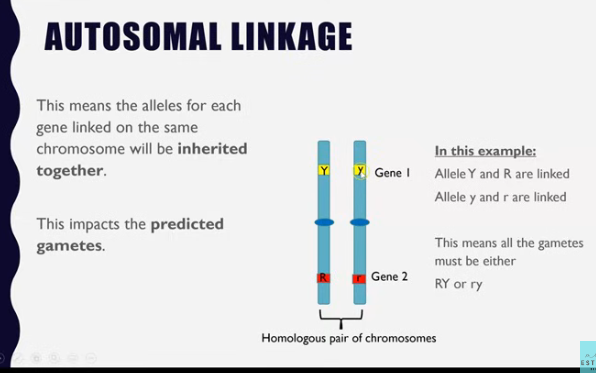
Autosomal linkage
Genes that are located on the same chromosome (not the sex-chromosome).
Epistasis
When one gene modifies or masks the expression of a different gene at a different locus.
Monohybrid
Genetic inheritance cross of a characteristic determined by one gene.
Dihybrid
Genetic inheritance cross for a characteristic determined by two genes.
Sex-linkage
X and Y are sex chromosomes.
Some characteristics are only coded for by genes on the sex chromosomes- sex-linked.
Y chromosome is smaller than the X chromosome so carries fewer genes, so men tend to have only one allele of each sex-linked gene.
This means they express the characteristic of this allele even if it is recessive, meaning they can’t be carriers of X-linked genes and are more likely to have it than females who can be carries and have the disease masked by the dominant allele.
Ally Y chromosomes are inherited by fathers so X chromosomes are always inherited by mothers and x-linked diseases are passed on from mother in sons.
Female carrier and affected male children have 50% chance of producing colour blind child.
Autosomal-linkage
Genes on autosomes can also be linked, meaning they are close together on the same chromosome can can be inherited together.
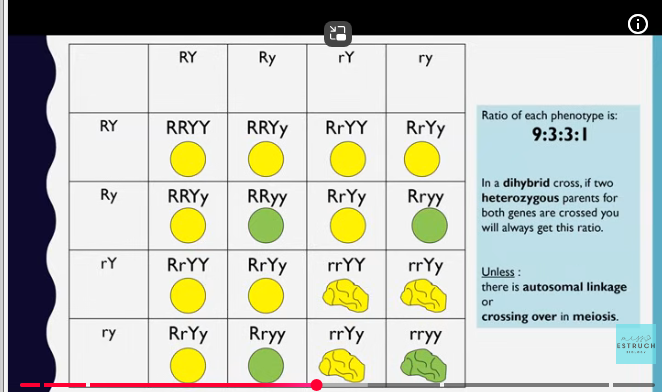
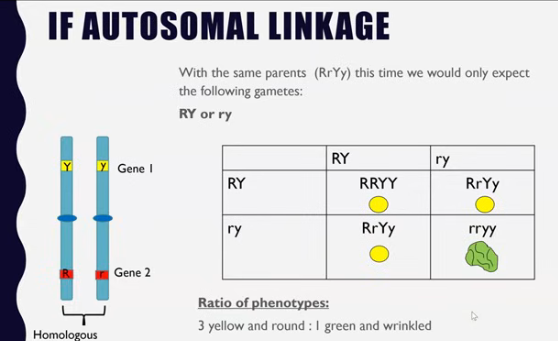
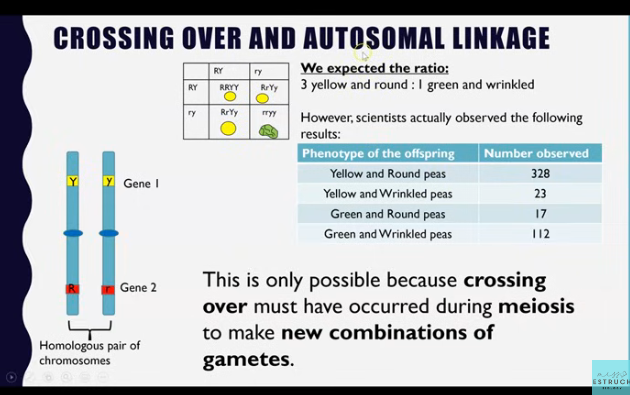
This produced an unexpected ratio, not 1:1:1:1 or 9:3:3:1.
Inheritance genetic diagrams coding
Monohybrid: Single letter: B or b
Codominant: Gene^ allele: both have to be capital
Multiple alleles: Gene^ allele: both have to be capital
Sex-linkage: Chromosome^ allele: alleles can be lower or capital.
Autosomal linkage and epistasis: Single letter: capital or lower case: Aa Bb
Epistasis examples: Dihybrid
Fruit colour
Coat colour in Labradors
Epistasis: Coat colour in Labradors
Controlled by two genes
Gene 1 controls whether pigment will be expressed.
Allele E- dominant and codes or pigment production.
Allele e- recessive and codes for pigment production.
Gene 2: Controls which pigment is expressed
Alleles B- dominant and codes for black dur
Allele b- recessive and codes for brown fur
What is a dihybrid cross?
A genetic cross where the inheritance of two genes is considered at the same time.
Mendel’s peas

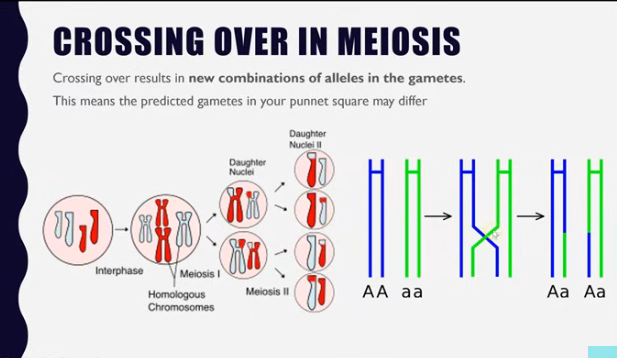
Crossing over in meiosis
Crossing over results in new combinations of alleles in the gametes.
This means the predicted gametes in your punnet square may differ.

Autosomal linkage: autosome means chromosome 1-22
When two genes are locates on the same chromosome (not X or Y).

What is the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
A mathematical model which can be used to predict the allele frequencies within a population.
Gene pool: all of the alleles of the genes within a population at one time.
Population: All the individuals of one species in one area at one time.
Alleles frequency: The proportion of an alleles within the gene pool.
p² +2pq +q²=1
p+q=1
Is Hardy-Weinberg accurate
No because it makes lots of assumptions:
No migration to introduce or remove alleles from the population.
No mutations to create new alleles.
No selection favouring particular alleles.
Mating is random (no inbreeding)
The population is large
What is a niche?
What each species in an ecosystem occupies, including it’s position in the food web and habitat.
Each species occupies it’s own niche governed by adaptation to both biotic and abiotic conditions.
Biotic examples of niches
What it eats and what organisms eat it.
Abiotic examples of niches
The temperature range an organism can tolerate, the time of day that it is active e.g. nocturnal.
What happens if organisms occupy the same niches?
they will compete as if they are the same species because they are sharing resources.
If no interbreeding occurs then the species with the higher birth rate will outcompete the other species and take over the niche UNLESS one can adapt to change their niche e.g. eat a different food source.
Problems with investigating niches
A proper ecosystem can never be replicated because the number of variables are too high.
Taking away variables doesn’t mean that you are controlling them and if these are influential, then they might change you results.
Competition may be forced in experiment e.g. in ecosystem there may be different food sources available.
Also competitive exclusion means they are competing and technically share same niche and resource partitioning means they have separate niches.
Animals become adapted to their niche
An adaptation is a feature that members the same species have the increases their survival chances and reproduction in their habitation, increasing the frequency of advantageous alleles → natural selection over many generations → evolution.
Every species has had to adapt to use the ecosystem in a way no other species can in order to occupy their own unique niche.
Organisms are adapted to both the biotic e.g. specific predators (thorns) and abiotic e.g. temperature (thick fur).
Biotic and Abiotic factors
Biotic: Impact of the interactions between organisms.
Abiotic: Non-living conditions of an ecosystem.
What is a habitat?
The part of an ecosystem in which particular organisms live.
What is a population?
Groups of the same species living in the same area at the same time, that can interbreed to make fertile offspring.
What is a community?
The populations of all the different species that live in the same area at the same time.
What is an ecosystem?
Both the biotic and abiotic parts of an environment and how they interact.
Ecosystems can range in sizes from the very small to the very large.
What do plants compete with each other for?
Light
Space
Water
Mineral ions in the soil
What do animals compete with each other for?
Food
Water
Mating partners
Territory
What is interdependence?
Where, in a community, each species depends on other species for things such as food, shelter, pollination and seed dispersal.
What is a stable community?
A community where all the species and environmental factors are in balance, so that the population sizes are roughly constant.
An ecosystem can only support a population size that is stable.
What are the 4 different biotic factors that might affect organisms in an ecosystem?
Availability of food
Arrival of new predator
Competition
New pathogens
What are the 7 different abiotic factors?
Light intensity
Temperature
Water/moisture levels
pH and mineral content of the soil
Wind intensity and direction
Carbon dioxide levels (for plants)
Oxygen levels (for aquatic animals)
Significance of availability of food
If the availability of food falls, then the number of organisms in that community will also fall
Significance of the arrival of a new predator
Can cause the population of a prey species to fall
Can also affect existing predators e.g. if they’re competing for the same prey
Significance of competition (between species)
If a species is outcompeted then it’s population can fall so much that numbers are no longer sufficient to breed and the species may become extinct.
Significance of new pathogens
If an infectious disease emerges and then spreads, it can wipe out a population of a species.
Significance of light intensity
All plants need light to carry out photosynthesis; if the light intensity is too low then the rate of photosynthesis falls and the plants will grow more slowly.
This is significance because if plants grow more slowly, then animals that eat plants may not have enough food
Significance of temperature
If the temperature of an environment changes then this could cause the distribution of species to change
E.g. animals could migrate and plant species might disappear from that area.
Significance of water/ moisture levels
It’s a significance abiotic factor as without water, both plants and animals can’t survive.
Significance of pH and mineral content of the soil
Many plants cannot grown on soil which is too acidic or too alkaline
Plants also require certain minerals in the soil e.g. nitrate which is used to make amino acids for proteins
Significance of wind intensity and direction
Strong winds blowing inland from the sea can cause plants to lose water
Significance of carbon dioxide levels (for plants)
Plants need carbon dioxide to photosynthesise and if carbon dioxide levels fall then the rate of photosynthesis can also decrease, meaning that the plant grows more slowly. If plants grow slower, then animals that feed on plants may not have enough food.
Significance of oxygen (for aquatic animals)
Oxygen is needed for aerobic respiration
The level of dissolved oxygen in water can decrease e.g. on hot days. This is harmful to aquatic organisms such as fish.
What are predators?
Organisms which hunt and kill their food (they are always carnivores).
They are specially adapted to capture and kill their prey.
→ predator-prey relationship builds up.
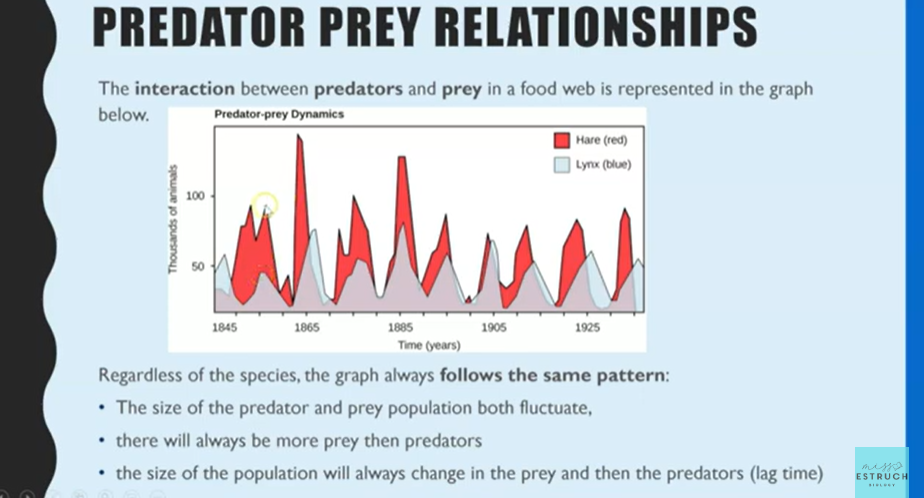
Predator-prey relationships
If conditions favour the prey, such as plentiful food → prey will reproduce and increase in number → creates large supply of food for predator, so it is more successful and breeds, increasing it’s numbers → increases predators causing hunting of prey, reducing their numbers → decreases food supply for predators so their numbers decrease → prey increases because less are being captured.
This occurs in very specific habitats when the food chain is very small.
Always more prey than predators.

Carrying Capacity
An ecosystem can only support a stable population size.
The carrying capacity is the maximum, stable population size of a species that an ecosystem can support.
Affected by biotic and abiotic factors as they affect population sizes.
Represented on a map as the point where population growth levels off and stabilises.
What is intraspecific competition?
Competition between organisms of the same species.
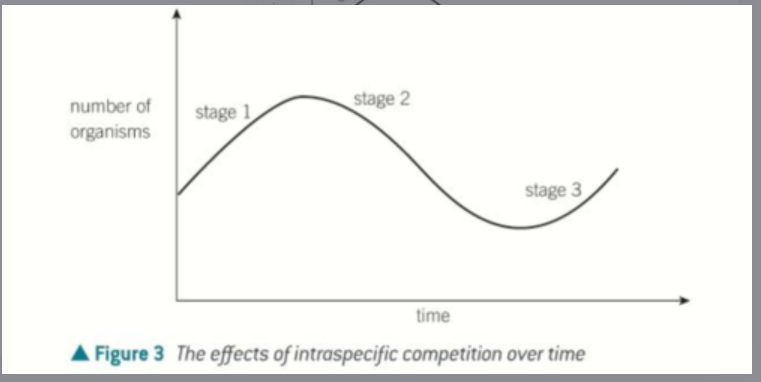
First resources are plentiful so all organisms grow in populations size.
This means resources per individual has fallen so population sizes shrink.
Then resources per individual has increased.
What is interspecific competition?
Competition between organisms of different species.
Leads to a fall in resources available to both populations, meaning there’s less energy for growth.
When does interspecific competition occur?
When different populations compete for the same resources e.g food.
If one species becomes better adapted to the surroundings e.g. more able to catch food, it can outcompete the other → population will decline and could be wiped from the habitat.
More on intraspecific and interspecific competition
Intraspecific: Competing for mate→ links to courtship rituals, individuals that are fitter will have more energy to perform a more impressive courtship ritual, or may have better fur or feathers in a a better condition to attract a mate.
Interspecific: Competing for food, habitat or water
What does predation mean?
An organism killing and eating another source of food.
Evaluation of collecting data and interpreting graphs based on observations of predator-prey relationships
Advantages: Real interactions in an ecosystem are investigated and higher organisms can be tracked more easily.
Disadvantages: Causal relationships can only be inferred.
What happens when the population size is below the carrying capacity?
The number of individuals will rise exponentially until the carrying capacity is reached.
In many systems, this results in overshoot and a further decline in population.
Fluctuations will flatten out with a very fixed carrying capacity.

Top line is biological carrying capacity and bottom line is cultural carrying capacity.
Shows there may be different carrying capacities in an ecosystem depending on human interactions with the environment.
Graph C
Shows a dynamic carrying capacity in an ecosystem changing due to the consumption of a resource by the species being monitored.
Why are samples carried out?
Time efficient way to estimate a population size.
Also can be more accurate than counting every individual organism → recount
How to ensure samples are accurate?
Random sampling- eliminate bias
Large number of samples (30+)
Why: To ensure you are accurately representing the information
Why are line transects used?
To examine a change over distance
Sampling summary
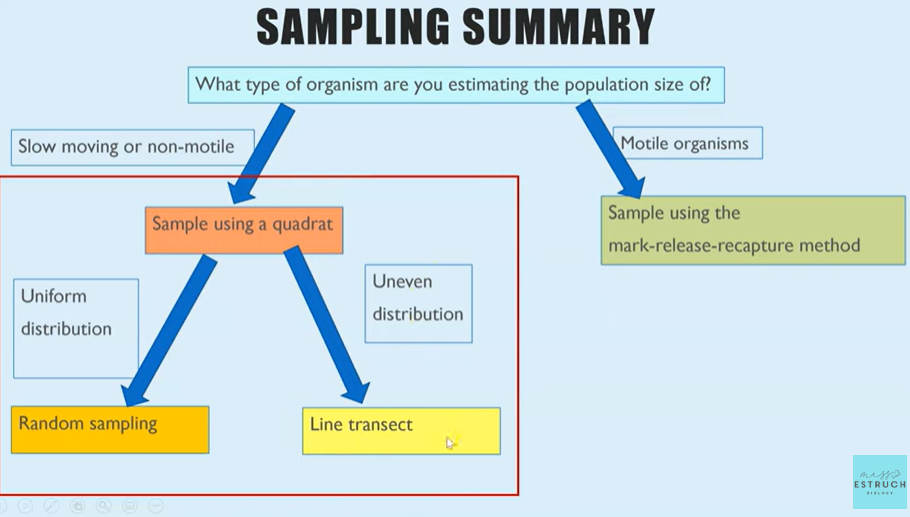

Random Sampling Methods
Used to estimate population sizes that are evenly distributed.
Lie 2 tape measures at a right angle to create a gridded area.
Use a random number generator to generate two coordinates.
Place the quadrat and collect the data ( density/ percentage cover/ frequency)
Repeat at least 30 times and calculate a mean.
Line Transects
Use to estimate population sizes when they are unevenly distributed e.g. populations which change over distance.
Examples: Sandy shore/rocky shore, path or river impact
Can be belt or interrupted belt transect.
Belt- Placed at every position along tape measure.
Interrupted belt transect- Quadrat is placed at uniform intervals along the tape measure e.g. every 5 metres.
Place the tape measure at a right angle to the shore line.
Place the quadrat every 5 metres/ every position.
Collect the data (density/percentage cover/local frequency).
Repeat by placing at least another 30 transects along the beach at right angles to the shore line.
Methods to estimate the abundance of a species
Local frequency- % of squares in the quadrat with the species present.
Density- The number of one species in a given area.
Percentage cover (proportion of the ground occupied by the species).
Local frequency
Quick method to sample a large area
Useful if too difficult to identify individual organism e.g. moss or if too many to count e.g. grass.
Poor accuracy and doesn’t consider overlapping plants or the size of the plant.
Density
More accurate if you can easily distinguish an individual plant and there are not too many to count.
Can be used to estimate species richness (count number of different species present).
More time-consuming
Percentage cover
Quicker than density
Useful if too difficult to identify individual organisms e.g. moss or if too many to count e.g. grass.
Subjective, limiting accuracy
Doesn’t consider overlapping plants or the size of the plants.
What is succession?
The change in an ecological community over time.
A seral stage is when you see a notable difference in the community.
Changes can be plotted on a graph.
Climax community is final seral stage (forest and type varies e.g. deciduous forest with oaks vs pine trees)- no more changes in overall combination of species.
What is primary succession?
A primary succession starts with a pioneer species colonising bare sand or rock (rock can be from new land being created from volcano or Earthquake).
Pioneer species, such as lichen are adapted to survive in harsh abiotic factors and through their death and decomposition change the abiotic factors to become lass harsh (nutrients) and form a thin layer of soil, humus.
(They also reproduce)
As a result of thus humus, reducing the harshness of the conditions, mosses and smaller plants can now survive, and they further increase the depth and nutrient content of the soil (can hold more water → larger plants).
This pattern continues and as the abiotic factors continue to be less harsh, larger plants can survive and change the environment further.
Each new species may change the environment in such a way that it becomes less suitable for the previous species. Therefore each existing species is outcompeted by a new species colonising.
Changes that organisms produce in their abiotic environment can result in a less hostile environment and increases biodiversity.
The final stage in a succession is known as the climax community and this is dominated by trees.
What is the pioneer species?
The first species to colonise the new land, at the beginning of primary succession.
Why can lichen survive in harsh conditions?
Because it’s two different species (algae and fungus) co-existing together, with each bringing a mutual benefit (symbiotic relationship).
Algae can photosynthesis (slightly green)- glucose is created that’s shared with fungus.
Fungus can absorb water ( from rainfall) and release enzymes outside of cells (extracellular) which begins to break down the rock to release minerals.
These minerals can then be absorbed by algae and fungi
Secondary succession
The succession is disrupted and plants are destroyed.
Succession starts again, but the soil is already created, so it does not start from the bare rock seral stage.
Minerals in soil provide less harsh conditions so species richness and number of organisms increase/biodiversity so a climax community can be reached (potentially again).
Succession summary

This complex food web is what makes the community stable as even if one species is affected, the rest of the community can recover.

What is conservation?
Preventing succession from proceeding.
This is to prevent a climax community and conserve a greater range of species.
This is because human activity has destructed many habitats, resulting in a loss of food and space for organisms → can lead to extinction.
There needs to be management though between the conflict between human needs (increasing population means more space for housing and higher demand for food) and conservation in order to maintain the sustainability of natural resources.
For example, forests can be coppiced to provide timber for fuel and furniture, allowing the tree to survive.
Coppicing a tree
Provides timber for fuel and furniture → human needs.
Tree still survives- conservation.
Species that would’ve been outcompeted in climax community can also be conserved e.g. if tree blocked sunlight → other seral stages maintained.
Mark-Release-Recapture
Used to estimate the size of populations of motile animals (moving animals).
An initial sample of the population is captured.
These individuals are marked (weather resistant mark) and then released back into the wild, and the number caught is recorded.
These individuals are released and left for a period of time to allow them to be randomly dispersed throughout the habitat.
Then a second sample is captured.
The total number captured and the number recaptured, with the marking, is recorded.
The size of the population is then estimated on the principle that the proportion marked in the second sample, marks the proportion of individuals in the population as a whole.
I alr know the calculation
The more you do the more reliable
Catching must be ethical
How to ensure capturing and marking is ethical?
Non toxic
Must not increase chances of predation
Must not reduce chances of reproduction
Assumptions regarding capture-recapture
Assumes population size is constant ignoring potential births, deaths or migration.
Assumes animals always redistribute evenly, when this may not be the case eg. they may all huddle near food.
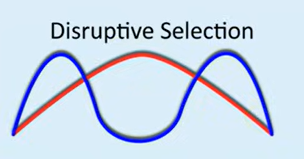
What is disruptive selection?
Could be due to physical separation, changes in environment, new predator, disease etc.
When individuals which contain the alleles coding for either extreme trait are more likely to survive and pass on their alleles.
As a result, the allele frequency changes and more individuals possess the allele for the extreme trait and the middling trait becomes less frequent.
Continued disruptive selection can ultimately lead to speciation.

What is speciation?
The process that results in the creation of new species.
This occurs when one original population of the same species becomes reproductively isolated.
This isolation means that there are now two populations of the same species, but they cannot breed together.
This can result in the accumulation of differences in their gene pool to the extent that the two populations would be unable to interbreed to make fertile offspring, and are therefore classed as two different species.
There are two different ways that populations can become reproductively isolated, either geographically (allopatric), or because of changes in reproductive mechanisms (sympatric).
Allopatric speciation
Populations can become separated geographically leading to reproductive isolation.
Within all populations there is genetic variation due to random mutations.
A population could become geographically isolated over time by new mountain ranges or new bodies of water separating land masses.
This separated the original population into two, meaning they can no longer reproduce with one another.
Both separate populations will continue to accumulate different beneficial mutations over time to help them survive in their environments, which are likely to vary.
Due to this accumulation of DNA differences, over time, the two populations becomes so genetically different that they would be unable to interbreed to create fertile offspring.
They are therefore classed as two different species.
Sympatric speciation
Populations can become reproductively isolated due to differences their behaviour.
Individuals of the same species may not be separated by geographical barriers , but are still unable to reproduce.
This could be because of a random mutation within the population, which could impact reproductive behaviour, for example, it may cause individuals to perform a different courtship ritual or individuals to be fertile at different times of the year.
Due to this, these individuals will not reproduce together and there will be no gene flow between the two groups within the populations.
Overtime, these reproductively isolated populations will accumulate different mutations to the extent that their DNA is so different that they cannot interbreed to create fertile offspring.
They are therefore classed as two different species.
Genetic drift
This is the change in the allele frequency within a population between generations.
There will always be genetic drift from one generation to the next, but continual, substantial genetic drift results in evolution.
The smaller a population is, the bigger the impact of allele frequency changes have proportionally, and this is why evolution occurs more rapidly in smaller populations.