Topic 4 Genetic Code, Meiosis, Biodiversity and Natural selection
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Describe the differences between eukaryotic DNA and Prokaryotic DNA

What is the definition of a ‘gene’
The key is a base sequence of DNA that codes for an amino acid sequence of a polypeptide and functional RNA
What is the definition of a ‘locus’
Location of the gene on a chromosome
What is a triplet code?
A sequence of three DNA bases that codes for a specific amino acid
If I had a polypeptide chain that contains 20 amino acids how many DNA bases where needed to code for it?
3×20=60
What are the three features of the genetic code?
Degenerate
Universal
Non-Overlapping
What does Degenerate mean
There are only 4 dna bases
So three bases are needed to code for one amino acid
4×4×4= 64 different amino acids can be coded for
An amino acid can be coded for by MORE than one amino acid
Why is the degeneracy of the genetic code an advantage?
Of a mutation occurs in one of the DNA bases
it may still code for the same amino acid
Therefore have no effect
what does it mean when the genetic code is Universal?
The same triplet code will code for the same amino acid in ALL organisms
What does Non-Overlapping mean in the genetic code
The triplet code of bases is read as a discrete unit
Why is non-overlapping advantageous?
If a mutation occurs it will only affect one codon
The fore one amino acid
What are introns and exons in DNA?
Introns- non coding sequences of DNA
Exons- sequences of DNA that code for amino acids
What is the definition of a codon?
The three bases on mRNA Thrace code for a specific amino acid
What is the definitions of a start and stop codon?
Start codon- three bases at the start of every gene that initiate translation
Stop codon- three bases at the end of every gene that causes the ribosome to detach and stop translation
What is the definition of a genome
An organisms complete set of DNA in a cell
What is the definition of a proteome
Is the full range of proteins that a cell is able to produce
Where is mRNA found in and how is it made?
Found in the cytoplasm and nucleus
Made in transcription in the nucleus from the DNA sequence
Where is tRNA found in, and what is it involved in?
found in the cytoplasm
Involved in translation, and it has an amino acid binding site
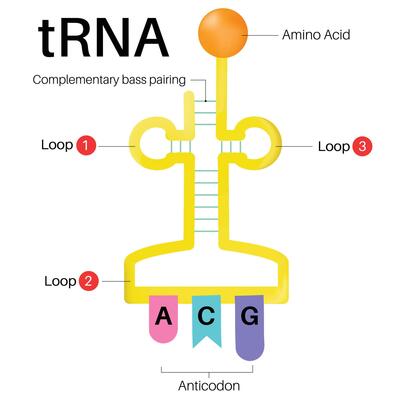
Describe the structure of a tRNA molecule
Has an amino acid binding site that is specific
A single stranded polynucleotide that is folded in a clover leaf shape
It has Hydrogen bonds between base pairs to hold it shape
It has anticodons which are complementary to mRNA codons
What are the 2 stages in protein synthesis?
Transcription and translation
Describe the process of transcription (5 marks)
Hydrogen bonds between the DNA bases break, causing the DNA double helix to separate into two template strands with exposed bases
One DNA strand is used as template
Free RNA nucleotides are attracted to their complimentary bases by complimentary base pairing
RNA Uracil base pairs pair with adenine DNA bases
RNA Polymerase catalases the condensation reaction to form phosphodiester bonds between adjacent RNA nucleotides together
Creating Pre-mRNA which is then spliced (removing introns) to form mRNA
Describe what occurs after transcription in order to turn pre-mRNA into mRNA
pre-mRNA is spliced to remove the introns
Why doesn’t splicing occur in Prokaryotic mRNA?
prokaryotic DNA does not contain introns
Describe the process of translation (6 marks)
mRNA attaches to the ribosome
tRNA anticodons bind to complimentary mRNA codons
tRNA molecules bring specific amino acids coded for by the specific mRNA codons
Adjacent amino acids are joined together by phosphodiester bonds using ATP
tRNA is released after the amino acids join to form a polypeptide
The ribosome moves along the mRNA strand to form a polypeptide
What are the three ways genetic variation can be introduced?
Meiosis
Mutations
Radom fertilisation of gametes
Describe the process of meiosis

What are the differences between meiosis and mitosis?
Meiosis- produces 4 haploid cells, Mitosis creates 2 diploid cells
Meiosis- has 2 nuclear divisions, Mitosis has 1
Meiosis- introduce genetic variation, Mitosis creates genetically identical cells
Describe the process of independent segregation in meiosis 1
Happens in Meiosis 1
When the homologous chromosomes line up opposite each other at the equator
And it is random on which side is the paternal and maternal chromosome lie
What is the formula to work out the different combinations of the homologous pairs.
2^n
n= number of homologous pairs
Describe the process of crossing over in meiosis 1

Definition of a gene mutation
Is the change in the base sequence of DNA, which is random and occurs in DNA replication
What increases the likelihood of a genetic mutation?
Exposure to cancer causing agents
Such as UV, and radiation
What 2 types of genetic mutation are there?
Substitution
Deletion
Why is a deletion of a DNA base worse than a substitution of a base?
Substituting a base may still allow the new codon to still code for the same amino acid due to the genetic code being degenerate
Deleting a base can cause a frame shift. Which changes all the codons to incorrectly code for the wrong amino acids
What mutation can occur in meiosis?
Non-disjunction In meiosis 1
The homologous chromosome do not separate equally
Meiosis 2 the sister chromosomes don’t separate equally
What does non-disjunction cause?
Where the haploid cells receiving extra chromosomes or too few chromosomes
What is the definition of genetic diversity?
The number of different alleles in a population
What is the definition of a gene pool
All the genes and alleles in a population at a particular time
What is the definition of allele frequency?
Is the proportion of organisms within the population carrying a particular allele
Describe the process of natural selection

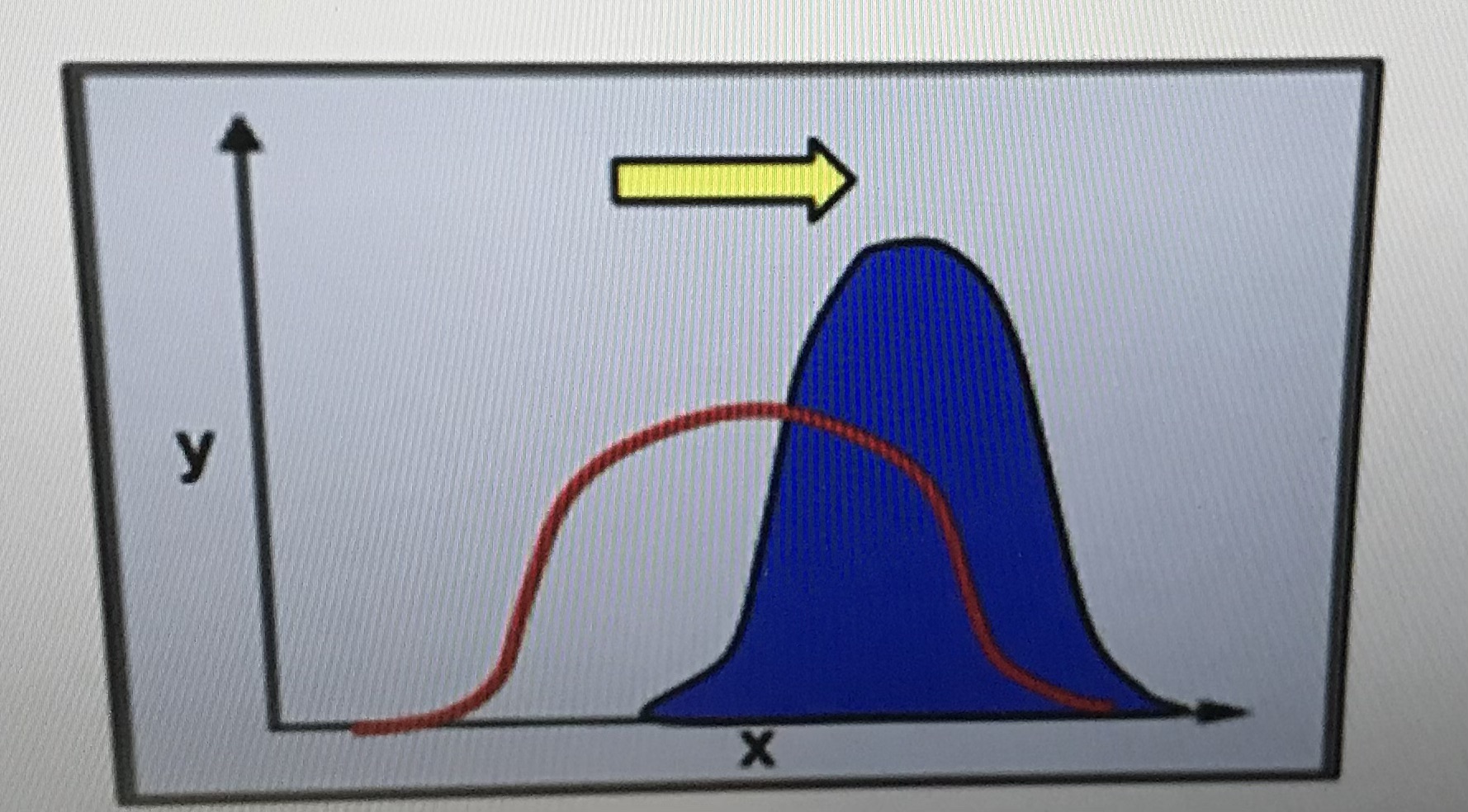
Directional selection
When a change in the environment occurs
Causing the modal trait to move to one extreme
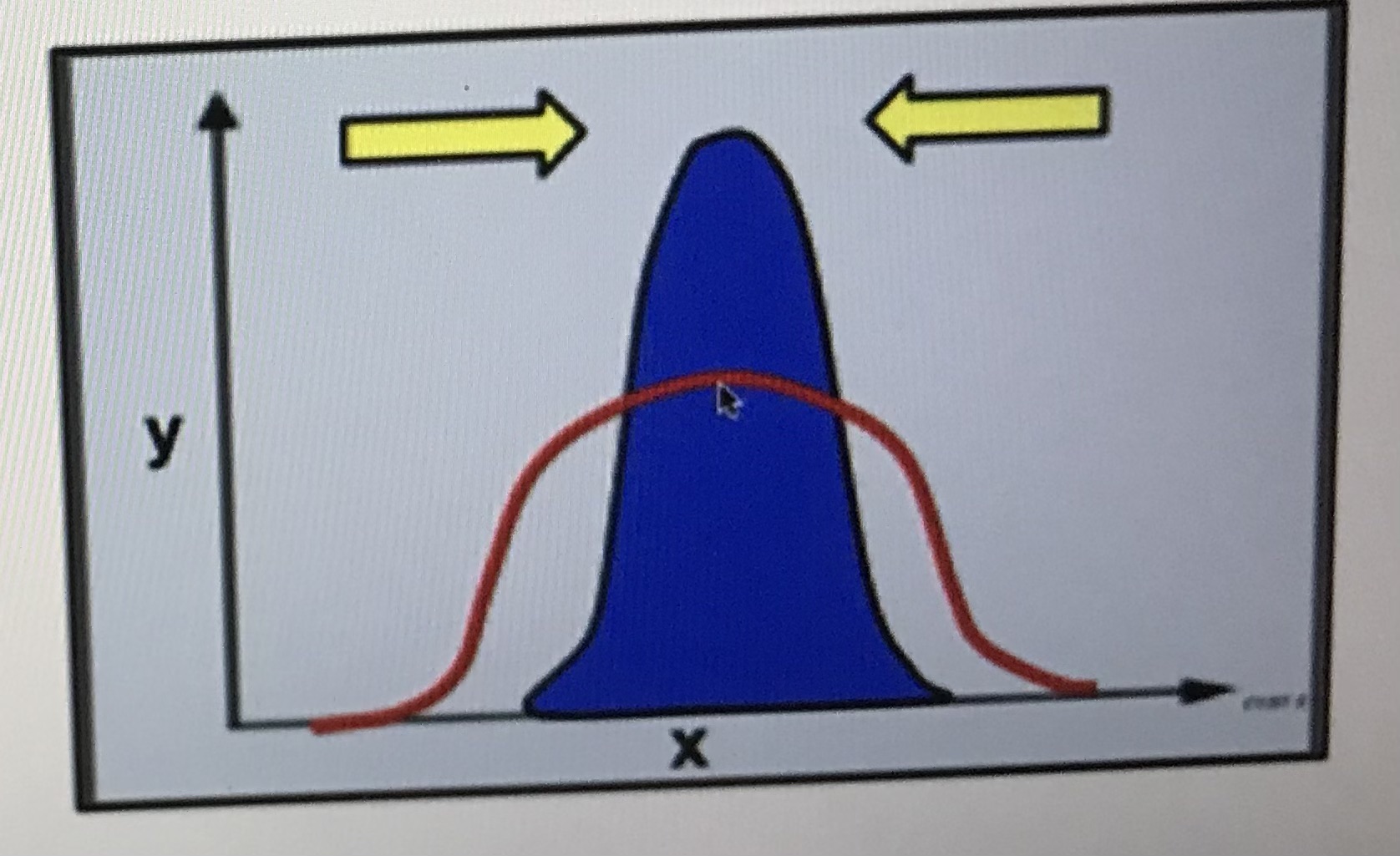
Stabilising selection
No change in the environment
The modal trait has a selective advantage
Individuals which have other traits decrease,
standard deviation decreases

Mutation results in a new allele
Individuals with the allele are able to digest triglycerides
And are more likely to survive and reproduce
Their offspring will inherit the allele
Directional selection occurs over many generations
and the allele frequency increases in the population
Definition of a species
Two organisms that belong to the same species and able to breed and produce fertile offspring
What type of adaption is Courtship behaviour?
Behavioural adaptation
That is essential for successful mating and species recognition
For survival
Describe what courtship behaviour is
The different behaviours that animals demonstrate to attract a mate. Each species demonstrates it own unique behaviour
This is essential for successful mating
What is an advantage of Courtship?
To recognise members of the same species and opposite sex
Only occurs when both males and females are sexually mature.
Males will only dance when releasing gametes
Females will only respond to the males when releasing eggs
Why can courtship rituals ensure the survival of the offspring?
Form a pair bond between the parents
Choose a strong and healthy mate
How are organisms named using the Binomial Naming System?
genus species
Phylogenetic trees
Arranges species into groups according to evolutionary origin and relationships
What can phylogeny tell us?
How closely related species are. And if they share a common ancestor
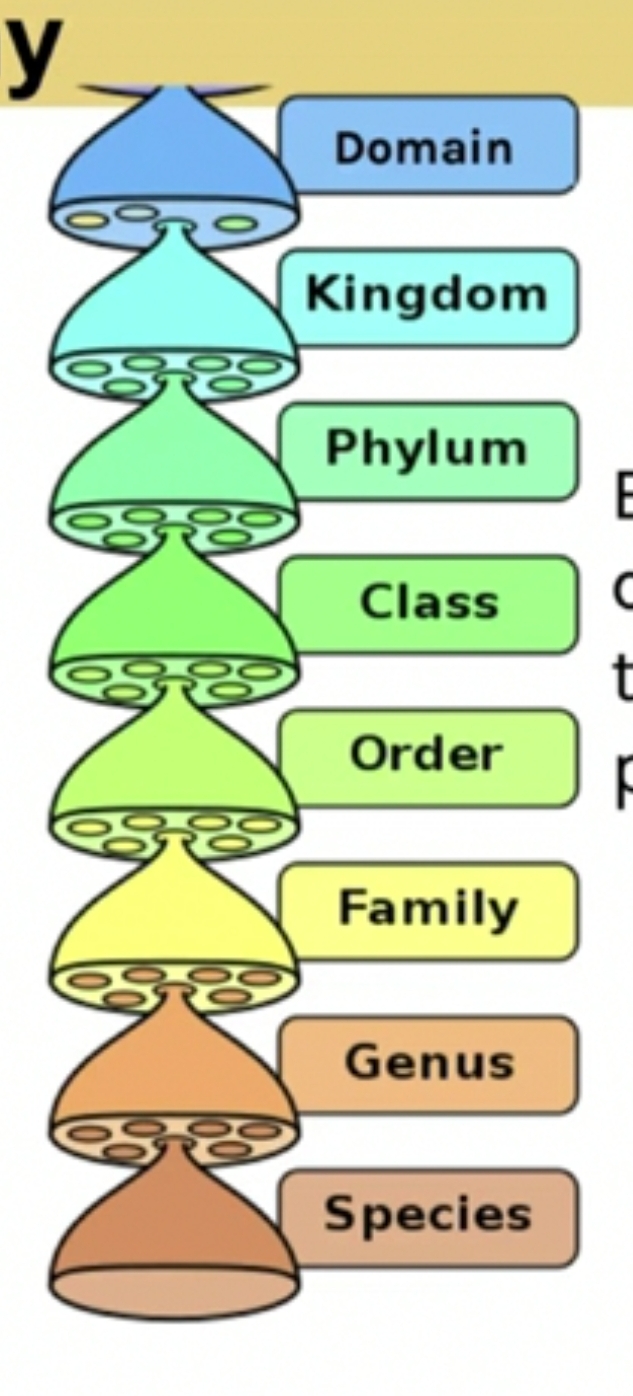
What is the order in classification
Definition for species richness
The number of different species in a community
Definition of index of diveristy
The number of different species and the number of individuals in each species
Explain how allopathic speciation can form a new species
Physical barrier,
No gene flow
Mutation occurs causing genetic variation
Different environments causes different selection pressures
The mutation causes an advantageous allele to occur, which is then passed on the next generation
Overtime the two groups of species cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring anymore