Quiz 4 Anatomy
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
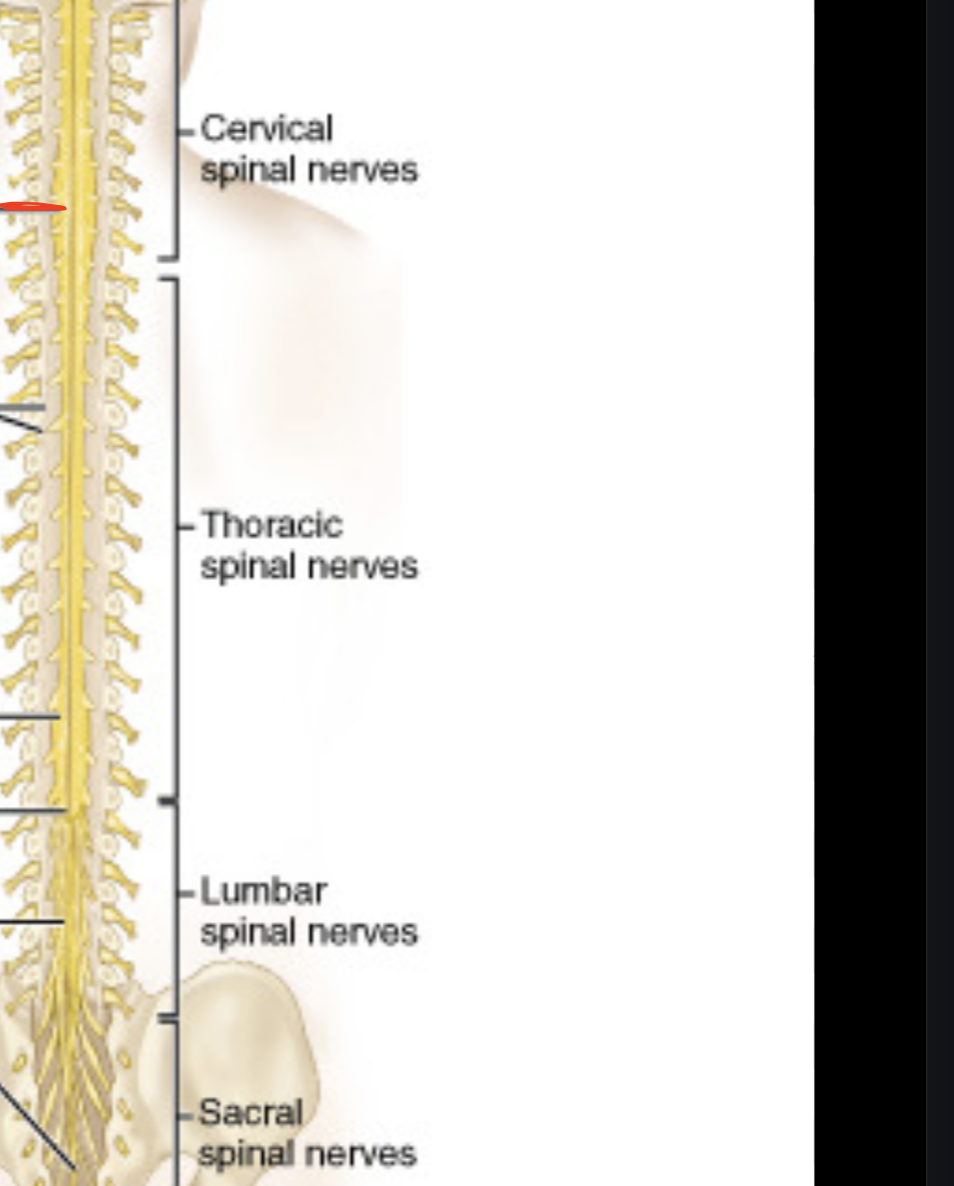
Cervical enlargement
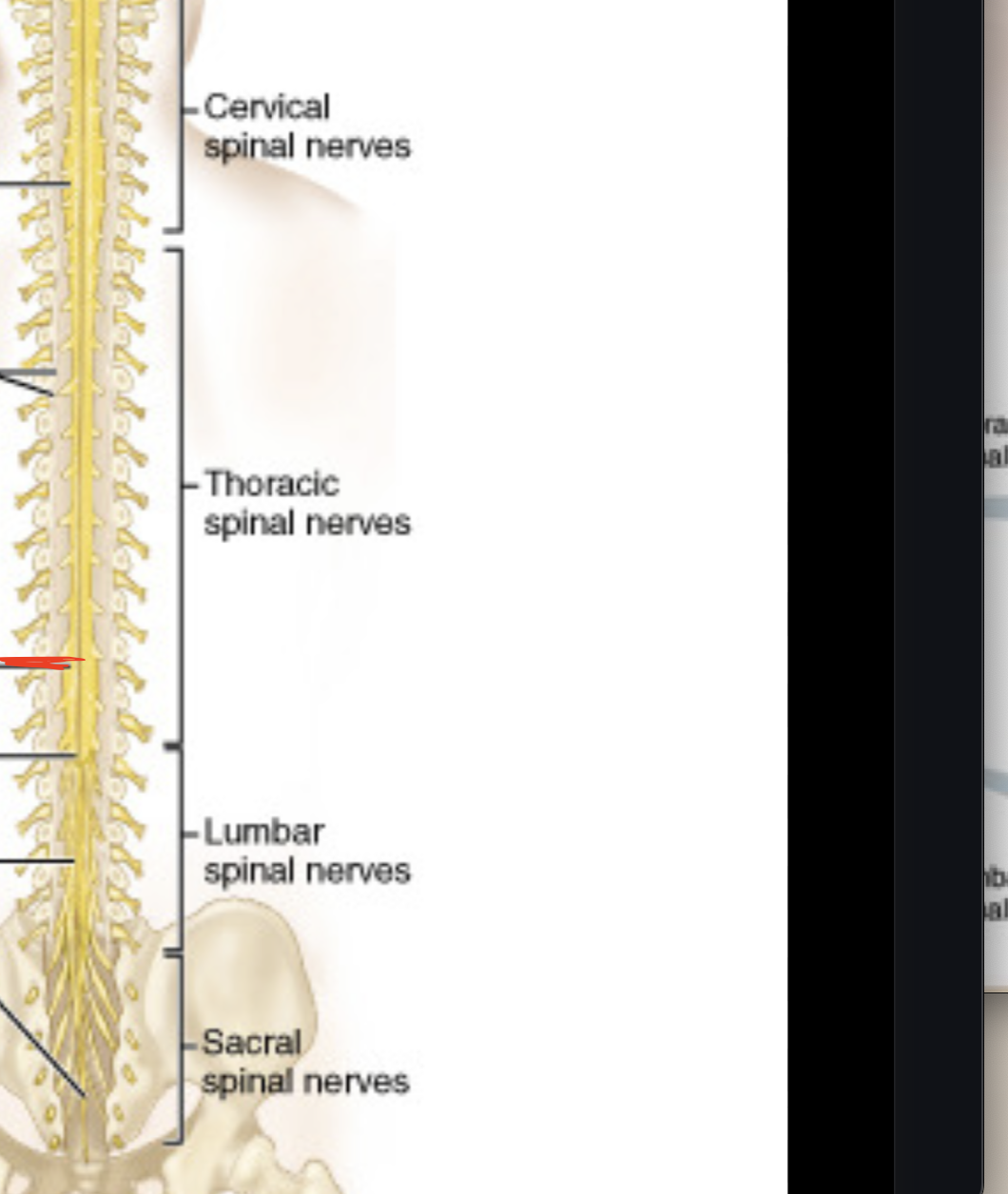
Lumbosacral enlargement
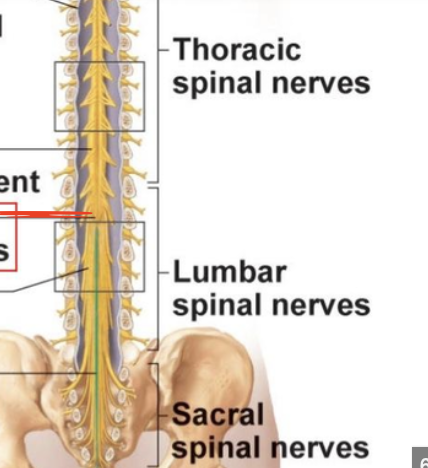
Conus Medullaris
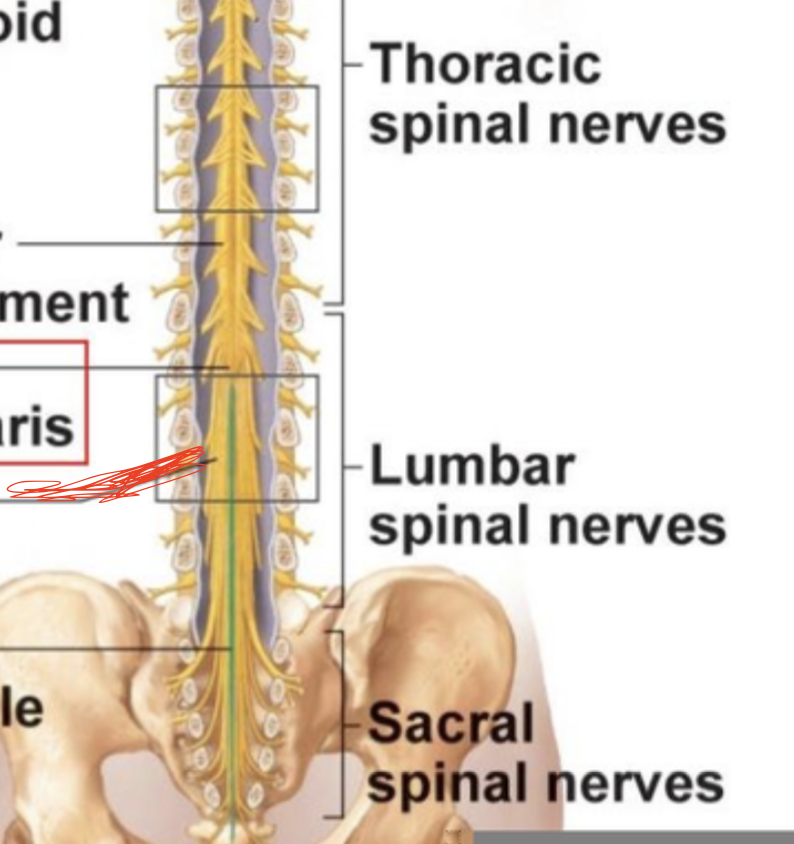
Cauda Equina
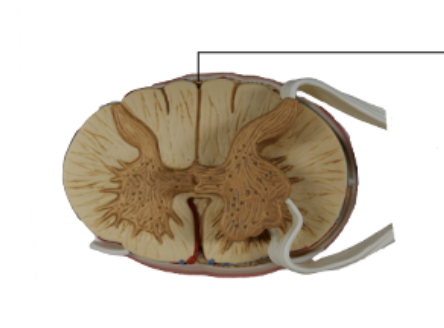
Posterior Median Fissure
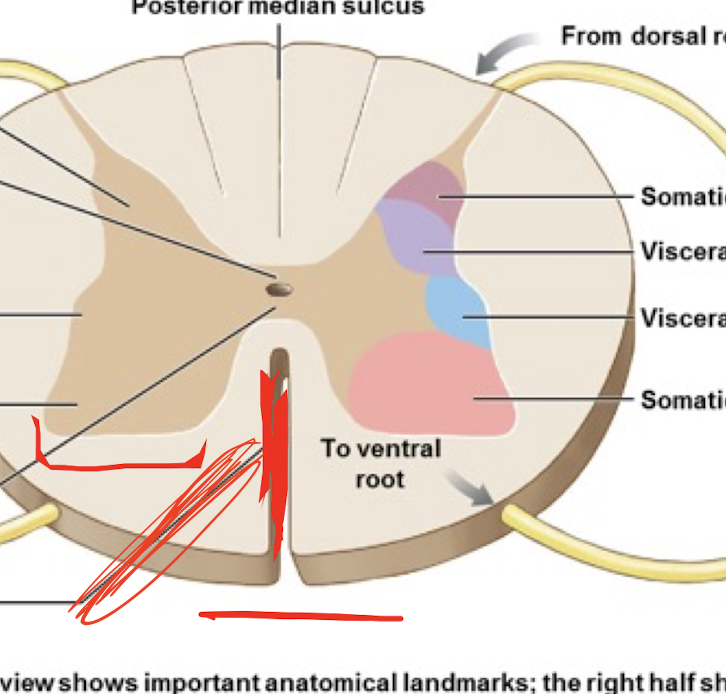
Anterior Median Fissure
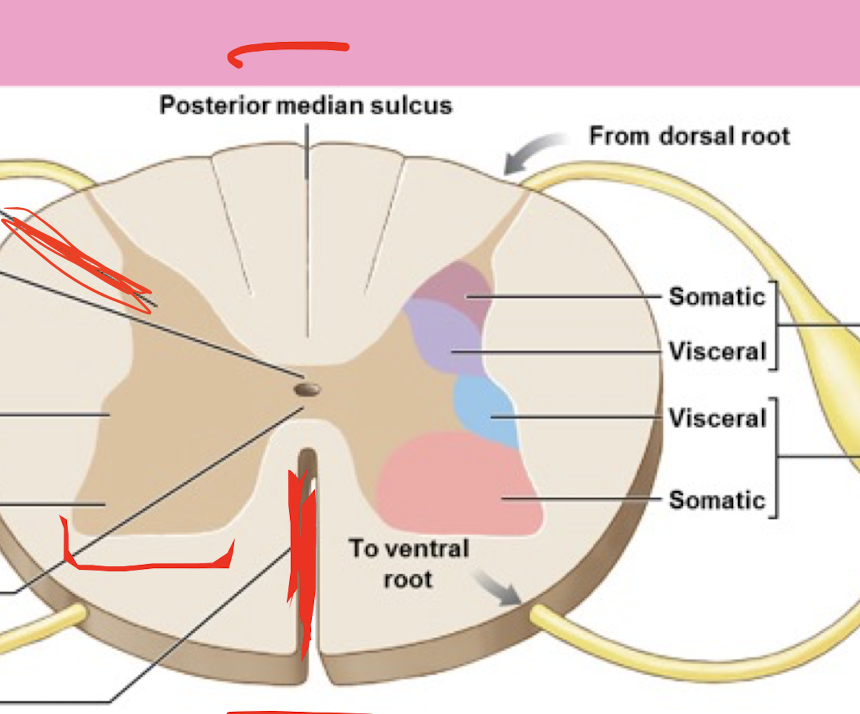
Dorsal Horn
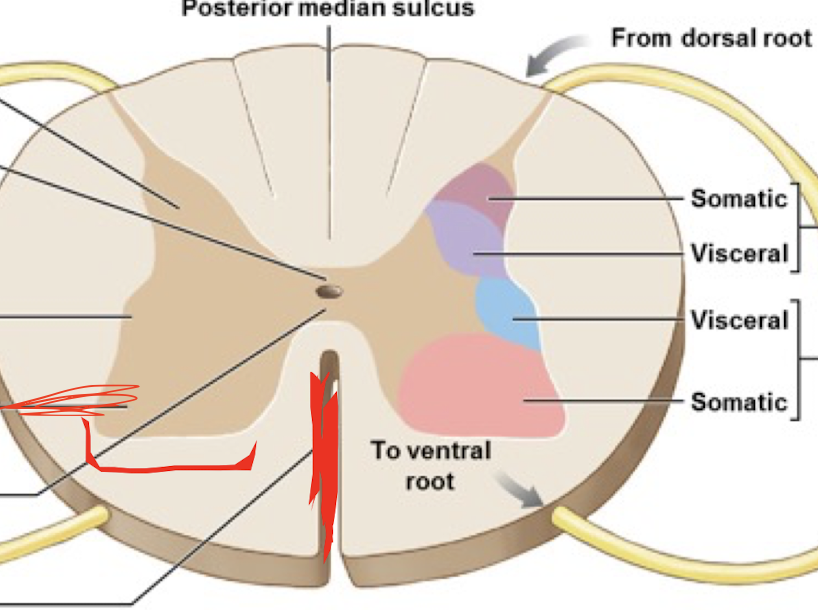
Ventral Horn
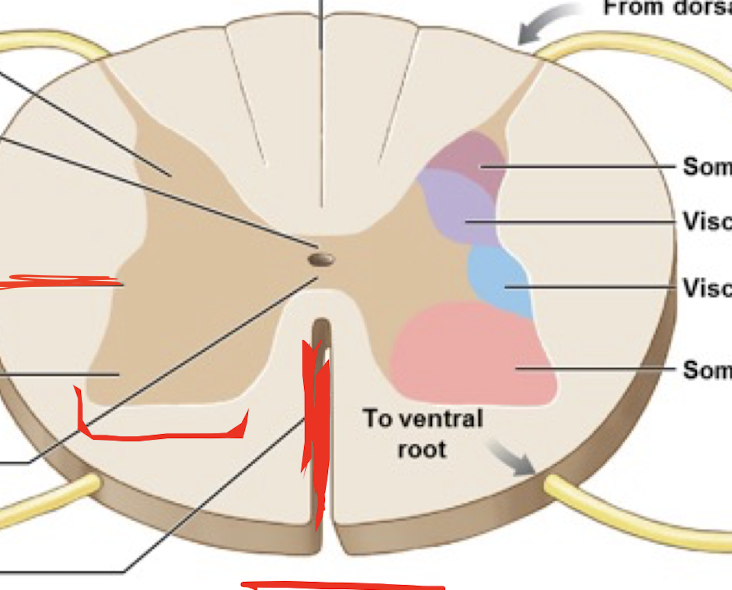
Lateral Horn
Describe the basic procedure of a spinal tap and anesthetic
inserting a needle into the lower back to collect a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for testing, lidocaine or bupivacaine
What level/ region of the spinal chord does a spinal tap occur?
between L3 and L4
Describe the pathway for tactile information from the peripheries to the cortex of the brain
First Order, second order, third order
Where are the 3 orders of neurons located
First order: Dorsal root ganglia
Second Order: Spinal chord/ brainstem
Third order: Thalamus
1st order neuron from lower limb
Gracile Fasciculus
1st order neuron from upper limb
Cuneate Fasciculus
Describe the relationship between the upper and lower motor neurons
Upper motor neurons synapse on lower motor neurons in ventral horn
Where does crossing over of the motor tract occur?
at the base of the pyramids
What structures of the midbrain and medulla does the corticospinal tract pass through?
cerebral peduncles
list all cranial nerves
What are the sympathetic chain ganglia and where are they located?
Sympathetic motor neuron circuits parallel to the spinal chord
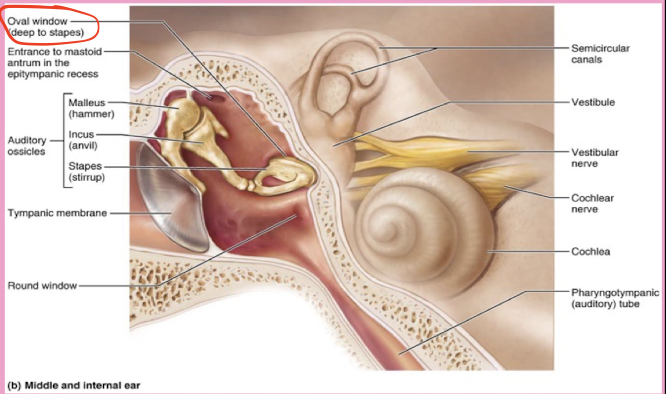
What are the two structures of the external ear? what cartilage is in the auricle?
Auricle/pinna ( Elastic Cartilage)
External Acoustic meatus
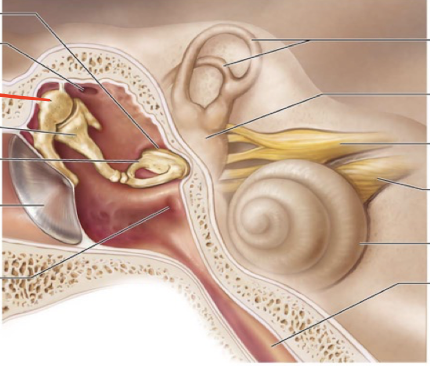
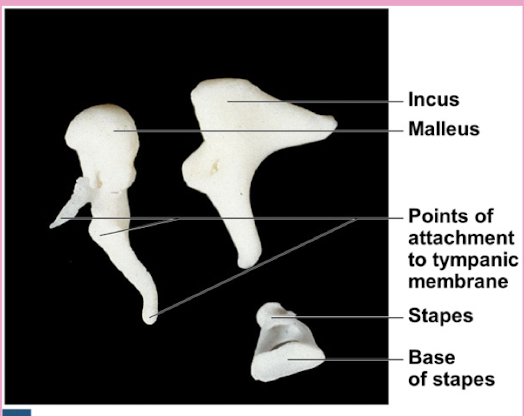
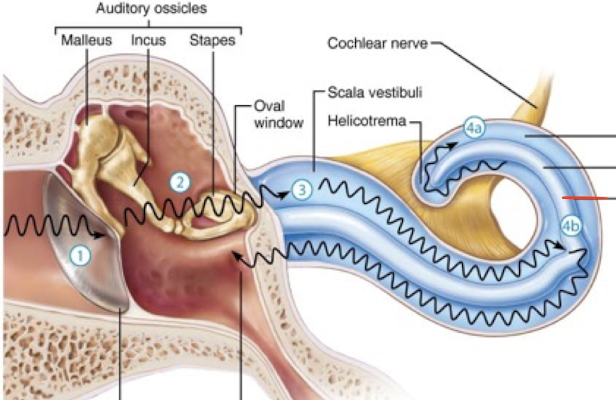
Malleus
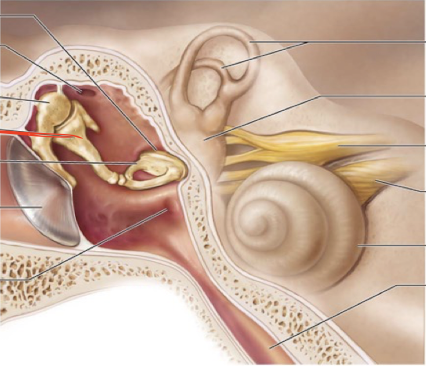
Incus
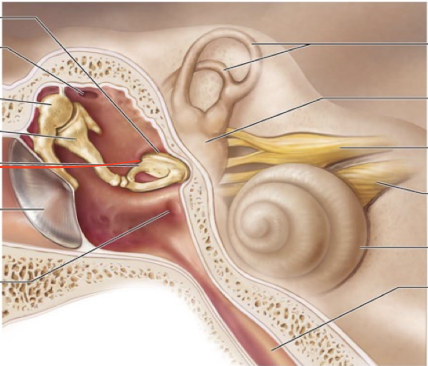
Stapes
What is the oval window in the ear?
a small, oval-shaped opening in the medial wall of the middle ear that serves as a communication pathway between the middle ear and the inner ear's vestibule, specifically where the stapes footplate sits
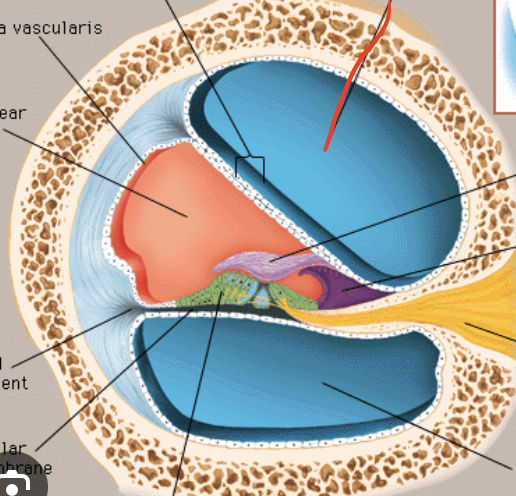
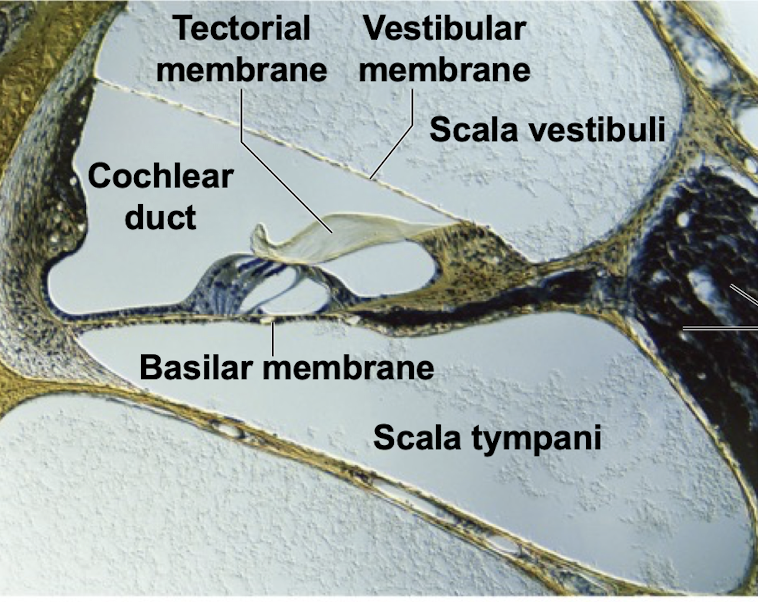
Scala Vestibuli
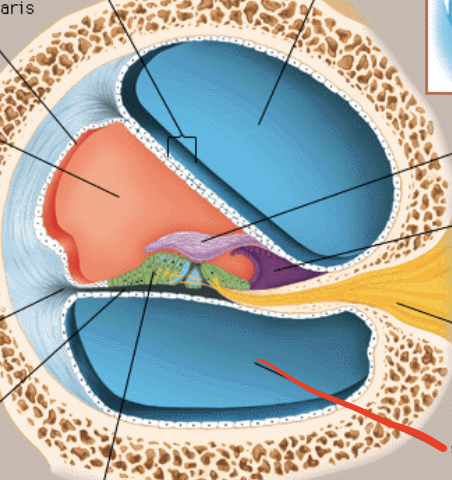
Scala tymphani
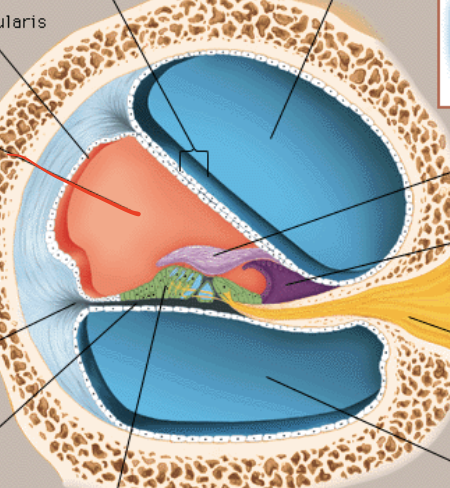
Scala Media
Stereocilia
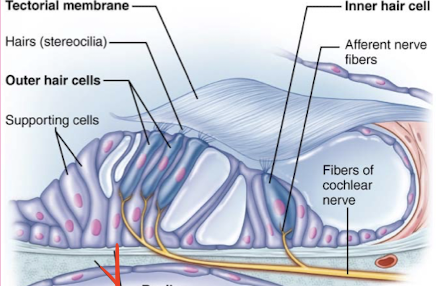
Basilar membrane
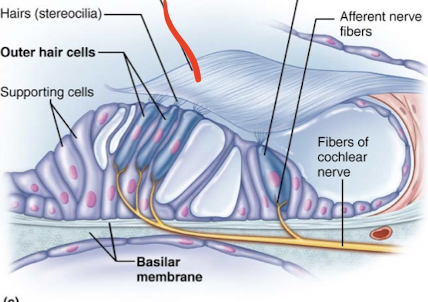
Tectorial membrane
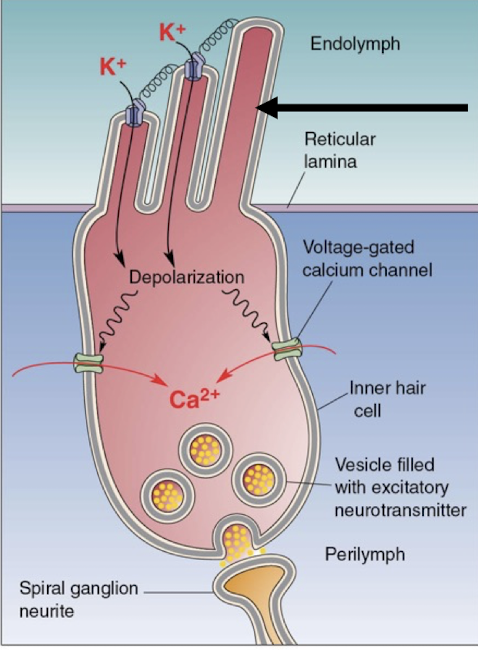
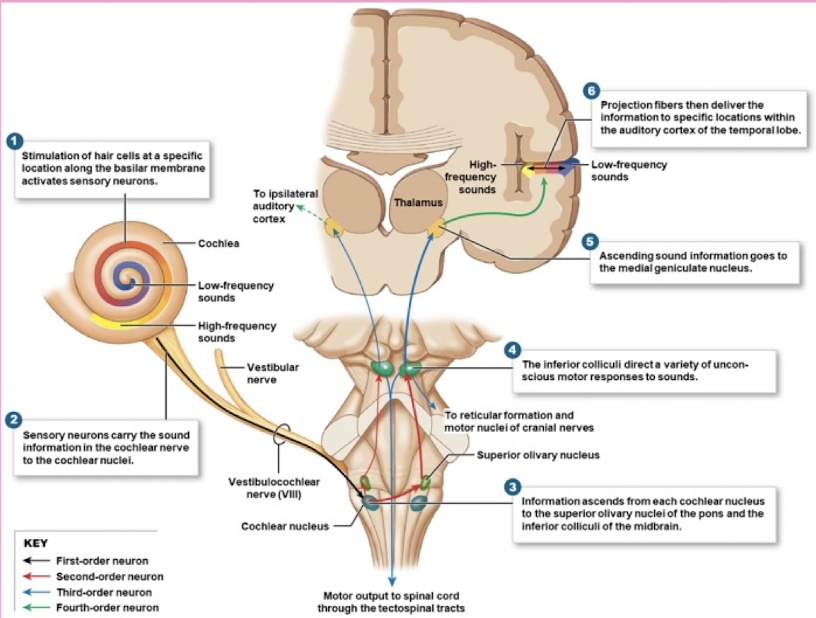
Identify structures of auditory circuit
Cochlea, Cochlear nerve, cochlear nuclei, superior olivary complex, lateral lemniscus, inferior colliculus, medial geniculate body, and auditory cortex
facial nerve innervates what?
anterior 2/3 of tongue
Glossopharyngeal innervates what?
posterior 1/3 of tongue
Vagus nerve innervates what?
surface of epiglottis
Which nucleus of the medulla do the taste nerves project to?
solitary nucleus
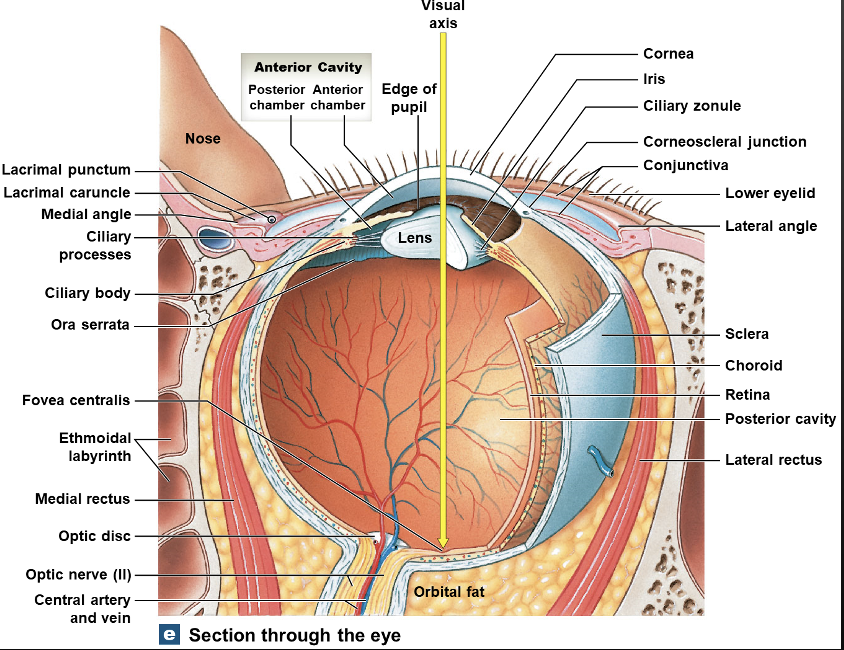
what does the fibrous layer consist of?
Sclera and Cornea
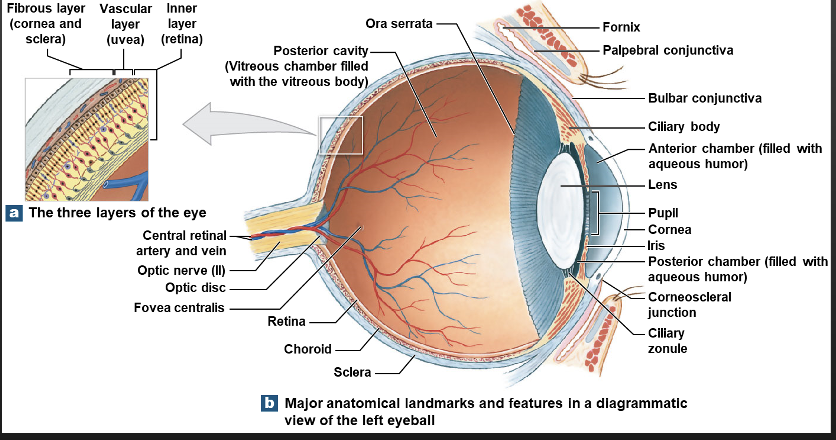
Vascular layer
Iris, Ciliary Body( Ciliary muscles and Zonules), Choroid
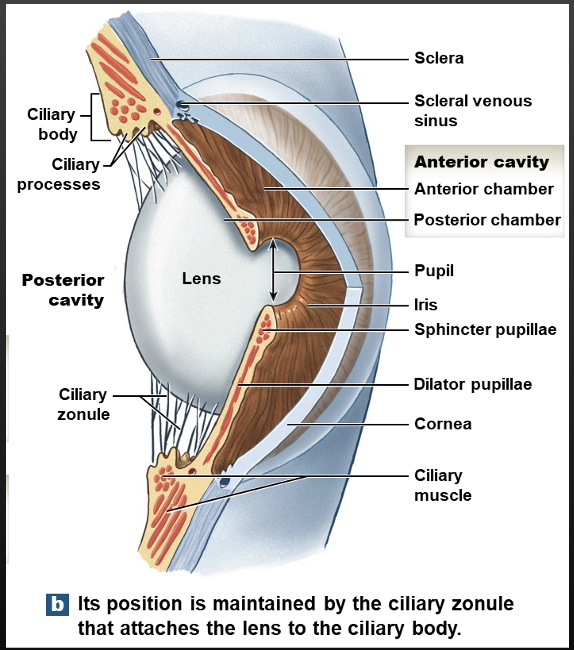
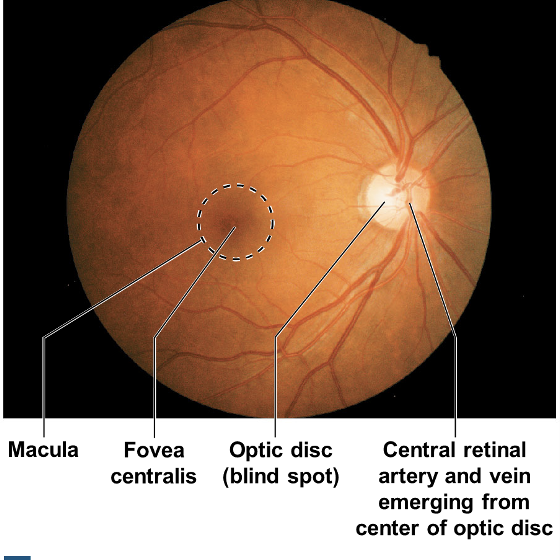
Inner layer
Retina( Macula; fovea centralis, optic disc)
Anterior cavity
Anterior chamber, Posterior chamber, Aqueous humor
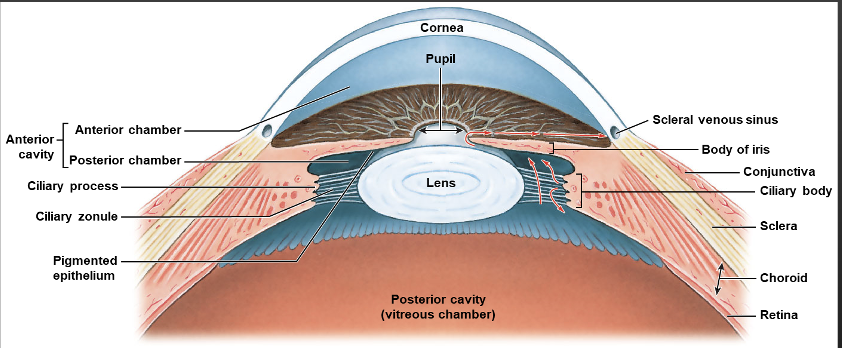
What drains the Aqueous humor fluid
scleral venous sinus
What Causes glaucoma?
When Aqueous humor cannot be drained thru scleral venous sinus so pressure builds up
Focuses the image on the photoreceptors of the retina
Consists of concentric layers of cells
Changes shape due to:
•Tension in suspensory ligaments
•Contraction and relaxation of ciliary muscles
lens
Posterior Cavity
Vitreous humor
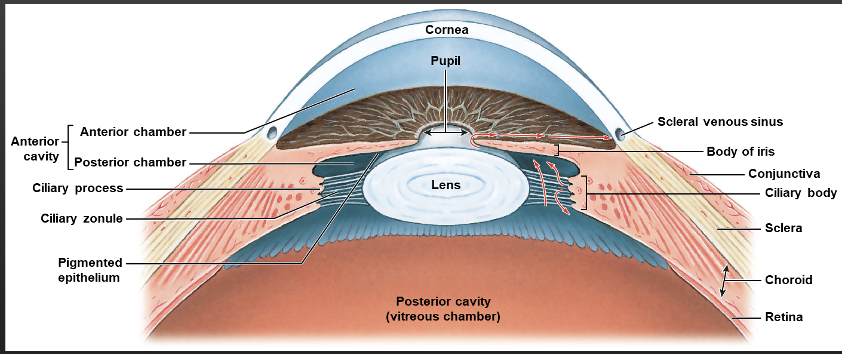
identify all the structures of the visual circuit