carbohydrates
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
glucose structural functions
building blocks of molecs, cells, and organisms - make up nucleotides, ATP, cofactors, cell walls, exoskeletons, connective tissue, cartilage, bone
nutritional and information functions of glucose
nut - energy storage, fuels, metabolic intmds
info - give info abt intracellular components like proteins in phospholipid bilayer (that id cells and cell communication)
mono vs oligo vs polysaccharides
m - 1 sugar (3-8C), unbranched C backbone, all Cs connected with 1x bonds, 1 C is a carbonyl (aldose or ketose) and all others have OH
o - di, tri… (2-20C)
p - over 20C
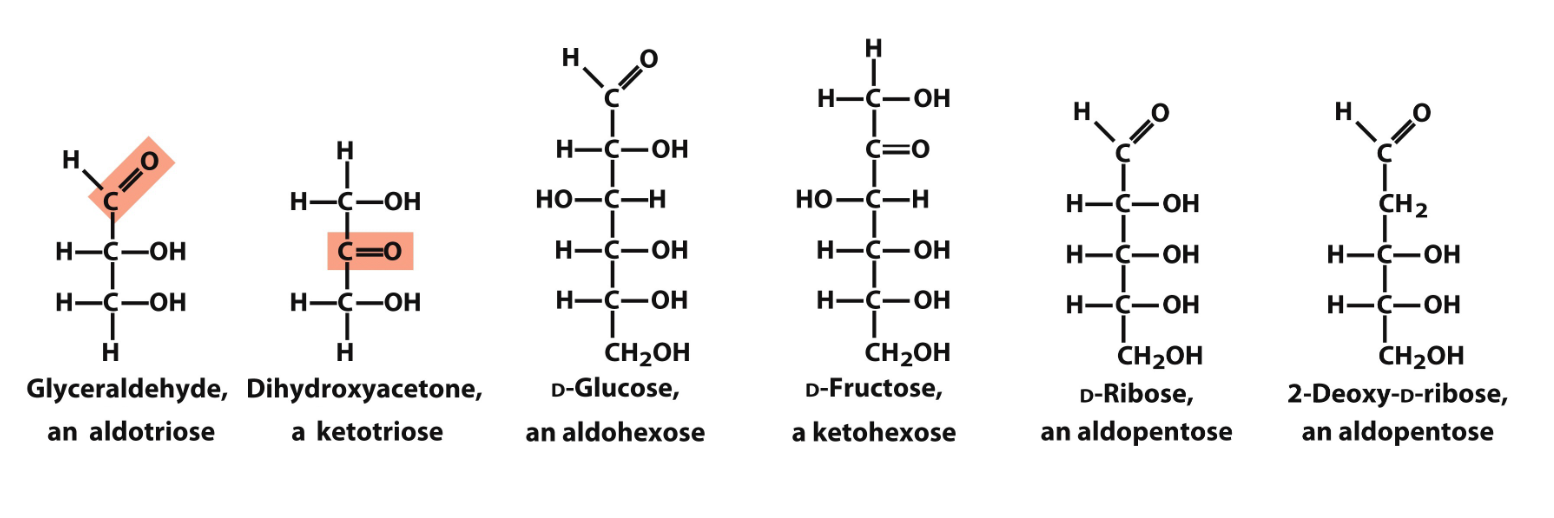
general formula of sugars
(CH2O)n
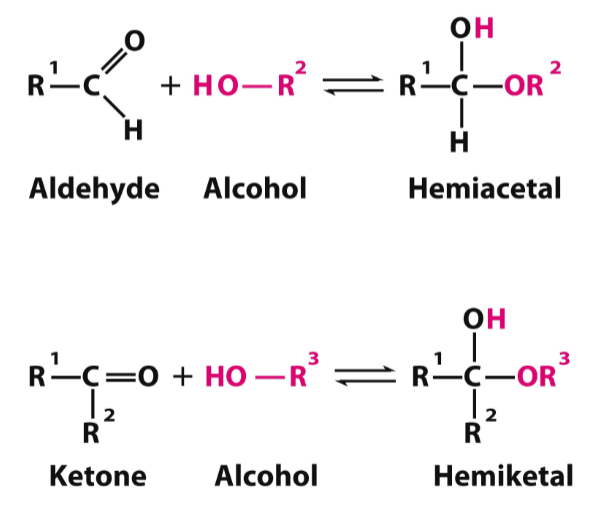
monosaccharides and hemiacetal/ketal
R-OH can interact with aldehyde or ketone to make a new covalent bond, forming a hemiacetal or hemiketal
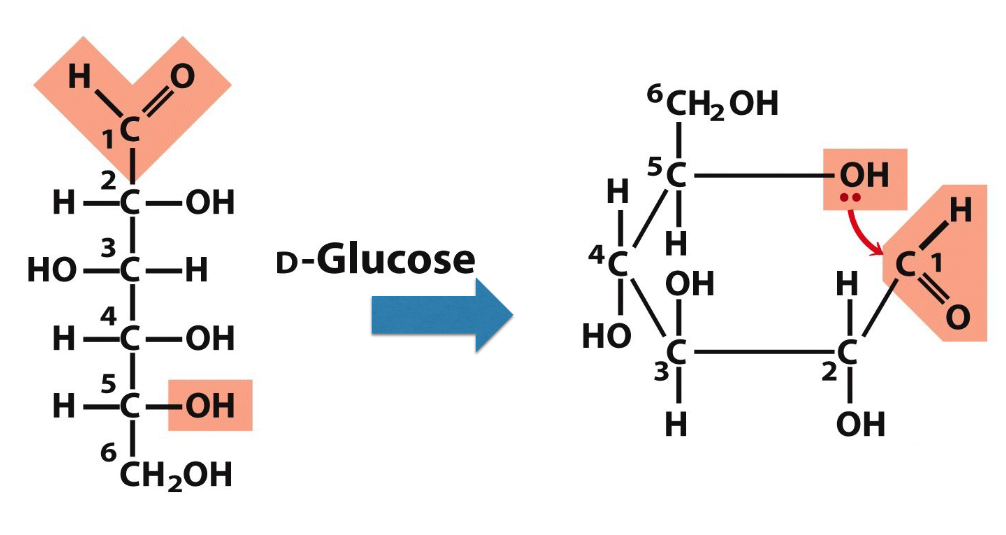
monosaccharide and cyclic structures
when OH and carbonyl in same molec, form a ring AND hemiacetal/ketal (connection btwn C1 and C5) → happens often in water and is predom form, doesn’t require an enzyme
aldehyde in linear form is readily oxidized - lacking in ring structure
creating a ring generates two different forms
alpha - OH on the bottom of the hemiacetal/ketal C, H on the top
beta - OH on the top of the hemiacetal/ketal C with H on the bottom
glucose naturally occurs in 2/3 beta, 1/3 alpha, and a trace amount in linear form
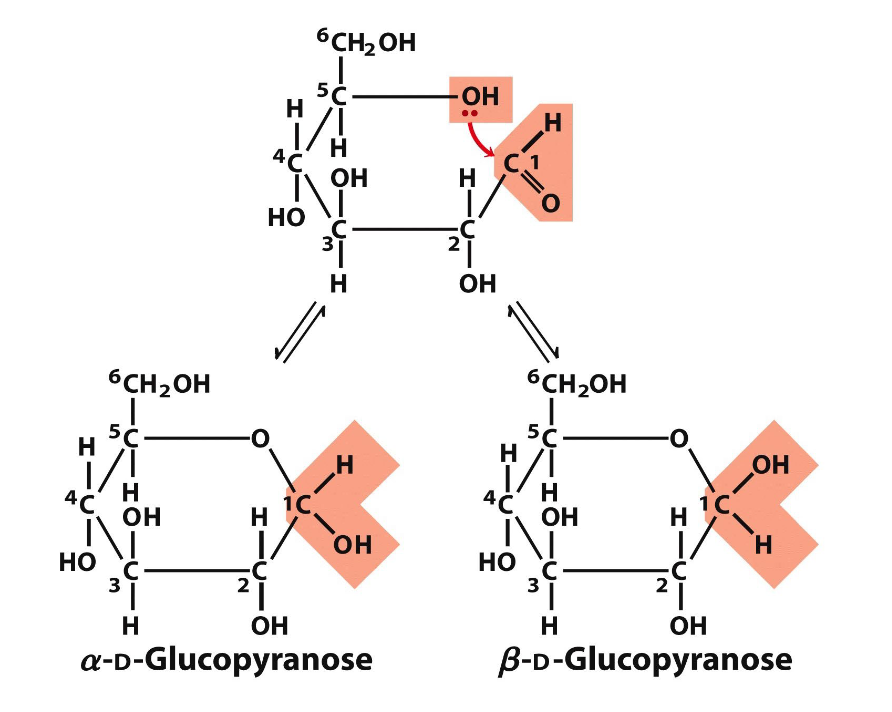
anomers
two forms of a molec that’re only different based on the config of atoms around the hemiacetal/ketal
to convert btwn the two requires ring opening
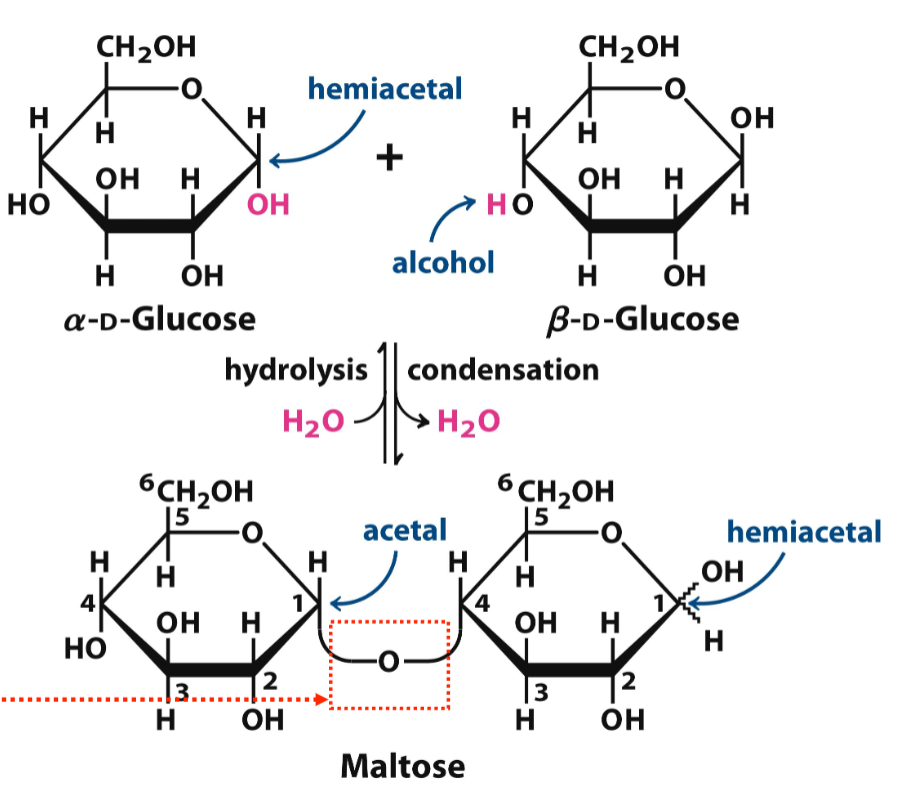
forming glycosidic bonds
requires a condensation rxn that releases H2O - anomeric C of one sugar bonds with the O of C4 of the other glucose (directly opposite of its anomeric C)
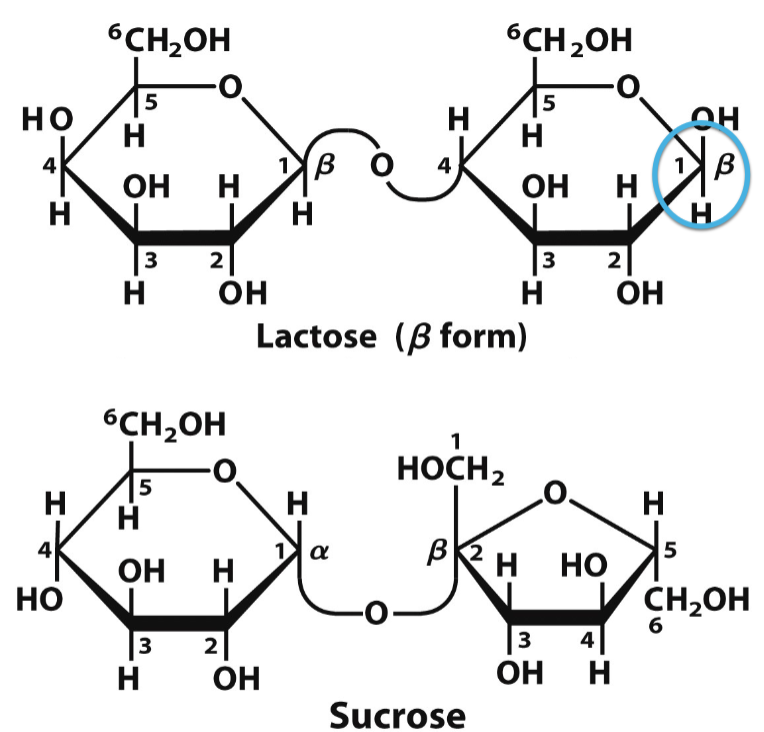
what effect does that the anomeric C being alpha or beta
if the anomeric C is alpha, the glycosidic bond is u shaped with o in middle
if its beta, the glycosidic bond is s shaped with o in the middle
reducing end
monosaccharides with the free anomeric C - next to create a glycosidic bond
reducing vs nonreducing
reducing carbohydrates - have a free anomeric C (lactose)
nonreducing - doesn’t have a free anomeric C (sucrose)
E and glycosidic bonds
creating the glycosidic bond requires an enzyme - e can only make/break specific bonds : an e that makes a alpha 1,4 linkage won’t break an alpha 1,4 linkage or make/break alpha 1,6 linkage; beta 1,4 linkage; or 1,6 linkage
polysaccharides
can be homo or heteropolysaccharides, can be branches or not
1,6 linkages create make branches
type of polysaccharides formed dept on the type of e and its active site
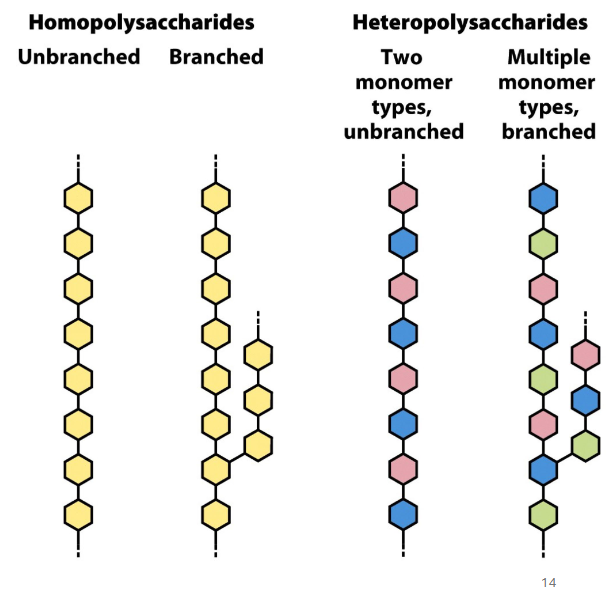
homo vs heteropolysaccharides
homo - polysaccharide chains made of the same type of sugar
hetero - chains made of different types of sugars
starch and glycogen
in plant and animal (respectively) - store glycose, can be branches or unbranched homops of glucose - glycogen is more branched and starch is less, more linear
have alpha 1,4 and 1,6 linkages
mostly in liver and some in muscle
why is glycogen more branches
it makes the structure more compact with more free ends so the sugars can be easily popped on and off and more easily used
cellulose
homops of d-glucose units, parallel cellulose chains form h bonds btwn each other to make straight fibers w/ strong connection
the o in the ring can h bond with nearby OH in glucose
why can’t we digest cellulose
bc its linked by beta 1,4 glycosidic bonds and we don’t have the e’s to break those bonds - cows have multiple stomachs and let it sit for a long time and have the right e
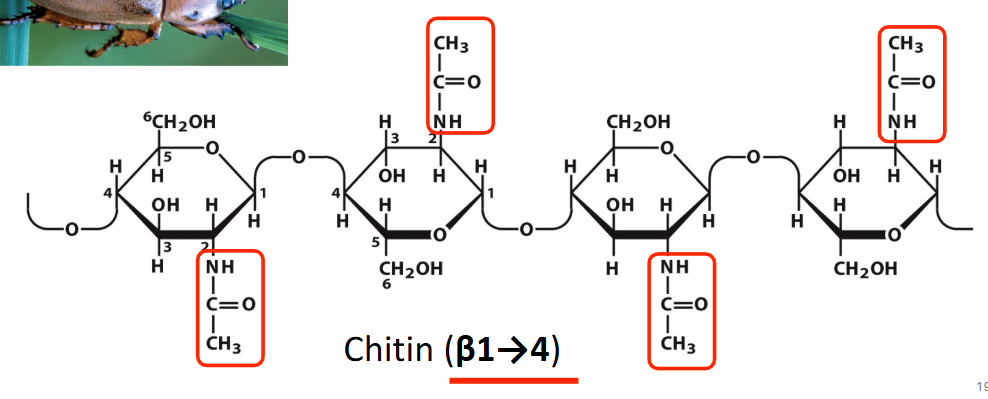
chitin
has an acetylated amino group on C2, has beta 1,4 linkage, primary component of insect and crustacean exoskeletons