Biology Definitions (Leaving Cert)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/296
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:02 PM on 11/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
297 Terms
1
New cards
Biology
Is the study of living things.
2
New cards
The scientific method
is the process of investigation in which problems are identified and their suggested solutions are tested by carrying out experiments.
3
New cards
An observation
Is when something is noticed.
4
New cards
A hypothesis
Is an educated guess.
5
New cards
An experiment
Is designed to test a hypothesis.
6
New cards
Data
Consists of the MEASUREMENTS, OBSERVATIONS or INFORMATION GATHERED from experiments.
7
New cards
A conclusion
Is a summary of the results of an experiment.
8
New cards
A theory
Is a hypothesis that has been SUPPORTED by many different experiments.
9
New cards
A principle or law
Arises from a theory that has been shown to be VALID when FULLY TESTED over a long period of time.
10
New cards
A variable
Is a factor that may change in an experiment.
11
New cards
A control
is used to provide a comparison against which the actual experiment is being tested.
12
New cards
A replicate
Is a repeat of an experiment, under the same conditions.
13
New cards
Double blind
Means that both the investigator and the participant are unaware of the nature of the treatment the participant is receiving.
14
New cards
Ethics
Relates to whether conduct is right or wrong.
15
New cards
An Organism
Is a living thing.
16
New cards
Metabolism
Is the sum of all chemical reactions in an organism.
17
New cards
Continuity of life
Means that living things arise from other living things of the same type.
18
New cards
Life
Is defined as the possession of these five characteristics: organisation, nutrition, excretion, response, reproduction.
19
New cards
Organisation
Means that living things are composed of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems.
20
New cards
Nutrition
Is the way living things get and use food FOR ENERGY.
21
New cards
Exrection
Is the removal of waste products of METABOLISM.
22
New cards
Response
is the way living things REACT to changes in their environment.
23
New cards
Reproduction
Is the production of new individuals.
24
New cards
Sexual Reproduction
Involves the union of sex cells.
25
New cards
Asexual Reproduction
Dose not involve the union of sex cells.
26
New cards
Biomolecules
Are the chemicals that are made inside a living thing.
27
New cards
Phospholipids
Are fat-like substances in which one of the fatty acids is replaced by a phosphate group or has a phosphate group added to it.
28
New cards
Anabolic reactions
The USE energy to convert smaller molecules into larger molecules.
29
New cards
Catabolic reactions
The RELEASE energy when a complex molecule is broken down to a simpler form.
30
New cards
Cytoplasm
Is the living material in a cell outside the nucleus.
31
New cards
Transmission Electron Microscope
Shows the internal structure of a specimen.
32
New cards
Scanning Electron Microscope
Shows a surface view of a specimen.
33
New cards
Cell ultra-structure
Is the fine detail of a cell as seen with an electron microscope.
34
New cards
Chromatin
Is the name given to chromosomes when they are elongated and not dividing.
35
New cards
Hydrophilic
Water loving.
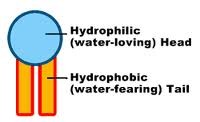
36
New cards
Hydrophobic
Water hating.
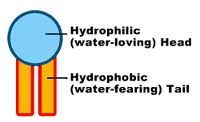
37
New cards
Prokaryotic cells
Do not have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles. e.g. bacteria cells.
38
New cards
Eukaryotic cells
Have a Nucleus and membrane bound organelles. e.g. animal and plant cells.
39
New cards
Tissue
Are groups of similar cells that have the same structure and function.
40
New cards
Micropropogation
Is the growth of new plants from plant cells.
41
New cards
Callus
A group of cells.
42
New cards
Tissue culture
Is the growth of new cells in or on a sterile nutrient medium outside the organism.
43
New cards
Monoclonal antibodies
Cancer treatment antibodies.
44
New cards
In vitro
Outside of the body.
45
New cards
Organ
Is a structure composed of a number of different tissues that work together to carry out one or more functions.
46
New cards
Organ system
Consists of a number of Organs working together to carry out one or more functions.
47
New cards
Organism
A group of organ systems working together to allow life.
48
New cards
Diffusion
Is the spreading of gas molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. (Passive Process)
49
New cards
Osmosis
Is the movement of water molecules from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration across a selectively permeable membrane. (Passive Process)
50
New cards
A selectively permeable membrane
Allows some but not all molecules through.
51
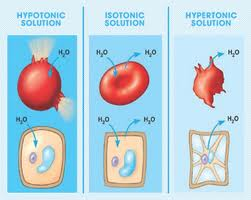
New cards
Hypertonic
Water concentration is higher inside than outside the cell.
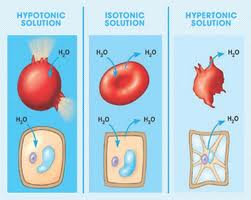
52
New cards
Isotonic
Water concentration is the same inside and outside the cell.
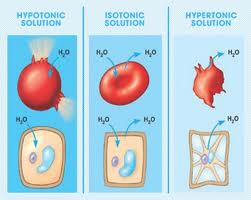
53
New cards
Hypotonic
Water concentration is higher outside the cell than inside the cell.
54
New cards
Protoplasm
Is all the living parts of a cell.
55
New cards
Turgor or Turgor pressure
Is the OUTWARD pressure of the cytoplasm and vacuole AGAINST the cell wall of the plant.
56
New cards
Cell continuity
Means that cells develop from pre-existing cells.
57
New cards
Chromosomes
Are COILED THREADS of DNA and protein.
58
New cards
A gene
Is a section of DNA that contains the instructions to make a protein.
59
New cards
A diploid Cell
Has two sets of chromosomes, one from the mother and one from the father. (2n)
60
New cards
A homologous Pair
is two chromosomes of similar size, with the same sequence of genes.
61
New cards
Haploid cells
Have one set of chromosomes. (n)
62
New cards
Interphase
Is the phase in the cell cycle when the cell is not dividing.
63
New cards
A centromere
Is the point where chromosomes attach.
64
New cards
Mitosis
Is a form of nuclear division in which one nucleus divides into two nuclei, each containing identical sets of chromosomes.
65
New cards
Cancer
Is a group of disorders in which certain cells lose their ability to control both the rate of mitosis and the number of times it happens.
66
New cards
Meosis
Is the form of nuclear division in which 4 daughter nuclei contain half the number of parent chromosomes.
67
New cards
Micro-organisms
Are small living things.
68
New cards
Autotrophic
Means an organism makes its own food.
69
New cards
Chemosynthesis
Is the production of food using energy released from chemical reactions.
70
New cards
Photosynthetic
Describes bacteria that make their own food using light energy.
71
New cards
Heterotrophic
Means an organism takes in food made by other organisms.
72
New cards
Saprophytes
Are organisms that take in food from dead organic matter.
73
New cards
Parasites
Are organisms that take in food from a live host and usually cause harm.
74
New cards
Pathogenic Bacteria
Are bacteria that cause disease.
75
New cards
Antibiotics
Are chemicals produced by micro-organisms that stop the growth of, or kill other micro-organisms without damaging human tissue.
76
New cards
Batch Culture
Is the cell growth of cells in a sealed container, or bioreactor, over a short period of time under ideal conditions until all the nutrients are used up.
77
New cards
A Bioreactor
Is a vessel or container in which living cells or their products are used to make a product.
78
New cards
Continuous Flow
Food processing is the growth of cells in an open container, or bioreactor, where nutrients are added and the end products are removed all the time at a rate that maintains the volume of liquid and the number of cells.
79
New cards
Aerobic Bacteria
Use oxygen
80
New cards
Anaerobic Bacteria
Do not use oxygen
81
New cards
Hypha
Is a tube or filament in a fungus.
82
New cards
Mycelium
Is a visible mass of hyphae.
83
New cards
Obligate parasite
Can only take it's food from a live host.
84
New cards
Facultative parasite
Can get its food from a live or dead host.
85
New cards
Sporulation
Is the process of making spores.
86
New cards
Meristem
Is a plant tissue capable of mitosis.
87
New cards
Herbaceous plants
do not contain wood (lignin)
88
New cards
Woody plants
contain wood (lignin)
89
New cards
Node
Is the point of a stem at which the leaf is attached
90
New cards
internode
is the region on a stem between two nodes
91
New cards
bud
is a potential growth point which may develop into a shoot, a leaf or flower
92
New cards
lenticel
is an opening on a stem for gas exchange
93
New cards
venation
is the pattern of veins in a leaf
94
New cards
Lignin
is a strengthening material found in some plant cell walls
95
New cards
cotyledon
is a seed leaf
96
New cards
Plasma
Is the liquid part of the blood
97
New cards
Serum
Is plasma with the blood clotting proteins removed.
98
New cards
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells
99
New cards
Lymphocytes
White blood cells that produce antibodies
100
New cards
Monocytes
White blood cells that engulf pathogens.