Ch 23 Questions
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Air entering the body is filtered, warmed, and humidified by the
A) lungs. B) alveoli. C) upper respiratory tract. D) lower respiratory tract. E) bronchioles
upper respiratory tract
Use of the accessory respiratory muscles is characteristic of forced breathing, or
A) eupnea. B) hypoxia. C) apnea. D) hyperpnea. E) dyspnea
hyperpnea.
The volume of air moved in a single respiratory cycle is called
A) alveolar minute volume.
B) respiratory volume.
C) vital capacity.
D) lung volume.
E) tidal volume
tidal volume
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide is greatest in
A) inspired air.
B) alveolar air.
C) venous blood.
D) expired air.
E) arterial blood
venous blood.
_____ pair(s) of salivary glands secrete into the oral cavity.
A) Three B) Two C) Six to Ten D) One E) Four
Three
The airway that connects the larynx to the bronchial tree is the
A) laryngopharynx.
B) trachea.
C) bronchus.
D) bronchiole.
E) alveolar duct
trachea.
Moving air to and from exchange surfaces is called
A) conduction.
B) ventilation.
C) internal respiration.
D) external respiration.
E) compliance.
ventilation.
The respiratory defense system is important because it
A) keeps out pathogens.
B) helps warm the air.
C) keeps out debris. D) helps filter the air.
E) All of the answers are correct.
All of the answers are correct.
The entire array of protective mechanisms in the respiratory system is called the
A) mucus escalator.
B) respiratory immunity.
C) acquired respiratory defense.
D) macrophage complex.
E) respiratory defense system
respiratory defense system
About 70% of carbon dioxide is transported in deoxygenated blood
A) as bicarbonate ions bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
B) combined with hemoglobin as carbaminohemoglobin.
C) as dissolved CO2 in the blood plasma.
D) as bicarbonate ions in the blood plasma.
E) as carbonic acid in the red blood cells.
as bicarbonate ions in the blood plasma.
The larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles all make up the
A) upper respiratory tract.
B) alveoli of the respiratory tract.
C) lower respiratory tract.
D) internal respiratory tract.
E) respiratory mucosa.
lower respiratory tract.
________ is the most common lethal inherited disease affecting individuals of Northern European descent.
A) Congestive heart failure
B) Cystic fibrosis
C) Parkinson's disease
D) Myasthenia gravis
E) MRSA
Cystic fibrosis
Low partial pressure of oxygen in tissues is a condition called
A) hypoxia. B) asthma. C) lung cancer. D) emphysema. E) ischemia
hypoxia.
The normal respiratory rate of a resting adult ranges from ________ breaths each minute, or roughly one for every four heartbeats.
A) 8 - 14
B) 6 - 10
C) 18 - 22
D) 12 - 18
E) 10 - 15
12 - 18
The beating of the cilia of the respiratory passages in the direction of the pharynx forms a(n)
A) respiratory rhythmicity center.
B) mucus escalator.
C) debris filter.
D) increased surface area for gas exchange.
E) sticky surface.
mucus escalator.
The oral mucosa has ________ epithelium.
A) stratified columnar
B) pseudostratified
C) stratified squamous
D) simple squamous
E) transitional
stratified squamous
The respiratory membrane of the gas exchange surfaces consists of A) ciliated squamous epithelium.
B) moist cuboidal epithelium.
C) pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
D) surfactant cells.
E) simple squamous epithelium.
simple squamous epithelium.
The respiratory epithelium of the conducting airways consists of
simple squamous epithelium. |
stratified squamous epithelium. |
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium. |
ciliated squamous epithelium. |
moist cuboidal epithelium. |
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
The respiratory mucosa consists of
ciliated stratified squamous and columnar cells. |
dense regular connective and areolar tissue. |
fibrocartilage and mucous cells. |
dense irregular connective and adipose tissue. |
epithelium and underlying layer of areolar tissue. |
epithelium and underlying layer of areolar tissue (lamina propria)
An important component of the lamina propria in the upper respiratory system is
sweat glands. |
serous glands. |
mucus glands. |
smooth muscle cells. |
ceruminous glands. |
mucus glands.
Inhaling through the nostrils is preferred over the mouth because
A) there is less resistance to air flow.
B) bacteria won't be inhaled from the oral cavity.
C) it allows better conditioning of the inhaled air.
D) it combines olfaction with respiration.
E) it dries out the mouth.
it allows better conditioning of the inhaled air.
Most of the oxygen transported by the blood is
A) dissolved in plasma.
B) carried by white blood cells.
C) in ionic form as solute in the plasma.
D) bound to the same protein as carbon dioxide.
E) bound to hemoglobin.
bound to hemoglobin.
The partial pressure of oxygen in atmospheric air at sea level is
A) less than the partial pressure of oxygen in atmospheric air at the top of Mt. Everest.
B) equal to the sum of partial pressures from carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
C) equal to the partial pressure of oxygen in atmospheric air at the top of Mt. Everest.
D) greater than the partial pressure of oxygen in atmospheric air at the top of Mt. Everest.
E) None of the answers is correct.
D) greater than the partial pressure of oxygen in atmospheric air at the top of Mt. Everest.
The right lung is to ________ as the left lung is to ________.
A) three lobes; three lobes
B) two lobes; three lobes
C) two lobes; two lobes
D) four lobes; three lobes
E) three lobes; two lobes
three lobes; two lobes
Gas exchange between air and circulating blood takes place within the
A) alveoli.
B) trachea.
C) bronchi.
D) terminal bronchioles.
E) All of the answers are correct.
alveoli.
The technical term for quiet breathing is
A) eupnea.
B) passive.
C) shallow breathing.
D) hypoventilation.
E) costal breathing
eupnea.
The nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx constitute the ________ portion of the airway.
A) primary B) respiratory C) exchange D) conducting E) sinus
conducting
Harry suffers from cystic fibrosis and has severe breathing difficulties. His problems result from
lack of neural control of respiration. |
reduced mucus secretions in the trachea. |
genetic mutation in cilia production. |
thick secretions that are difficult to transport. |
laryngospasms. |
thick secretions that are difficult to transport
Which of the following statements is true regarding partial pressure and the diffusion of gases in the body?
In internal respiration, the PCO2 in the systemic capillary is 40, while the PCO2 in the interstitial fluid is 45. |
Internal respiration involves the diffusion of oxygen from the alveolus into the pulmonary capillary. |
The partial pressure of oxygen in the pulmonary circulation as it returns to the heart is 95 mm of Hg. |
The partial pressure of oxygen in the systemic capillary is 40 mm of Hg before it moves into the interstitial fluid. |
If the partial pressure of oxygen in the interstitial fluid is lower than the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the interstitial fluid, carbon dioxide will not diffuse from the interstitial fluid into the systemic circulation. |
In internal respiration, the PCO2 in the systemic capillary is 40, while the PCO2 in the interstitial fluid is 45.
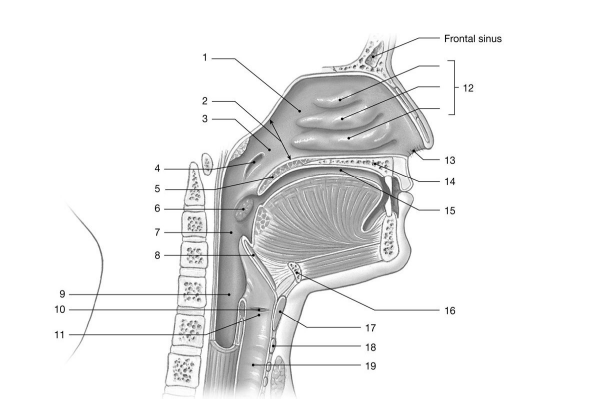
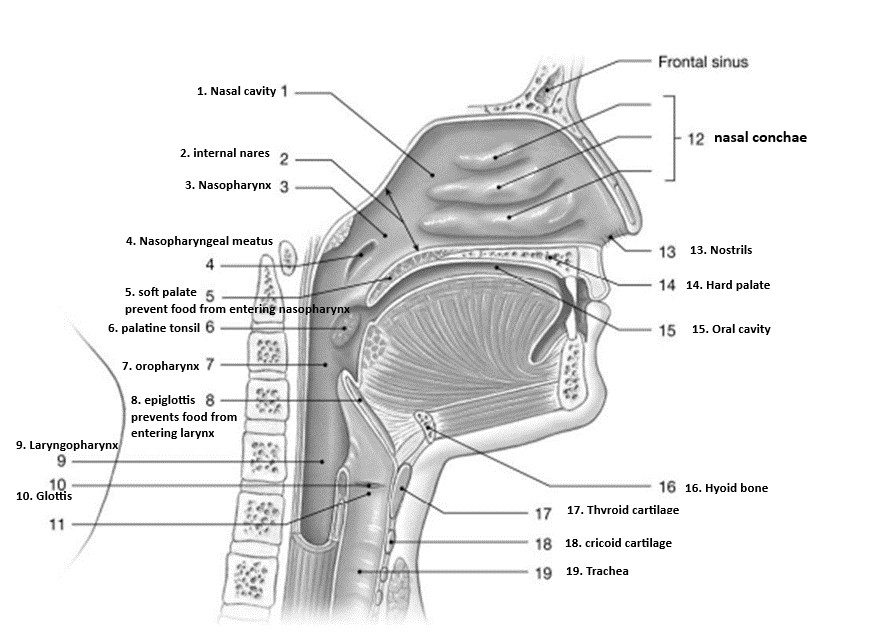
The nasopharynx transitions into the oropharynx at the level of the
internal nares. |
cribriform plate. |
pharyngeal septum. |
hard palate. |
soft palate. |
soft palate.
The conchae
divide the nasal cavity into a right and a left side. |
provide a increase in surface area for the sense of smell. |
create turbulence in the air to trap particulate matter in mucus. |
provide an opening into the pharynx. |
provide an opening to paranasal sinuses. |
create turbulence in the air to trap particulate matter in mucus
Functions of the nasal cavity include all of the following except
warming the air. |
filtering the air. |
housing tonsils. |
humidifying the air. |
housing olfactory receptors. |
housing tonsils.
The nasal cavity opens into the nasopharynx through a connection known as the
oropharynx. |
internal nares. |
auditory canal. |
nasal vestibule. |
nasal meatus. |
internal nares.
The superior region of the pharynx is called the
nasal cavity. |
nasopharynx. |
laryngopharynx. |
oropharynx. |
superior nasal conchae. |
nasopharynx.
The larynx contains ________ cartilages.
2 |
5 |
9 |
6 |
14 |
9
The ring-shaped cartilage just inferior to the thyroid cartilage is the ________ cartilage.
cuneiform |
cricoid |
arytenoid |
epiglottis |
corniculate |
cricoid
The elastic cartilage that covers the opening to the larynx during swallowing is the
epiglottis. |
cricoid cartilage. |
corniculate cartilage. |
cuneiform cartilage. |
thyroid cartilage. |
epiglottis.
The largest cartilage of the larynx is the ________ cartilage.
cricoid |
thyroid |
epiglottic |
arytenoid |
cuneiform |
thyroid
Thyroid cartilage (rings of trachea) made of
Hyaline cartilage (most abundant type)
How many lobes does each lung have, and which lung has a cardiac notch? (Figure 23-9)
right lung has 3 lobes, the left lung has 2 lobes; the left lung has a cardiac notch |
right lung has 2 lobes, the left lung has 3 lobes; the right lung has a cardiac notch |
right lung has 3 lobes, the left lung has 2 lobes; the right lung has a cardiac notch |
right lung has 2 lobes, the left lung has 3 lobes; the left lung has a cardiac notch |
both lungs have 3 lobes, the left lung has a cardiac notch |
right lung has 3 lobes, the left lung has 2 lobes; the left lung has a cardiac notch
In which direction does carbon dioxide move during internal respiration?
from the blood into the lungs |
from the blood into the tissue cells |
from the lungs into the blood |
from the lungs into the atmosphere |
from the tissue cells into the blood |
from the tissue cells into the blood
Low partial pressure of oxygen in tissues is a condition called
ischemia. |
hypoxia. |
asthma. |
emphysema. |
lung cancer. |
hypoxia.
Complete lack of oxygen in tissues
Anoxia
The physical movement of air into and out of lungs is termed
cellular respiration. |
external respiration. |
pulmonary ventilation. |
internal respiration. |
gas diffusion. |
pulmonary ventilation
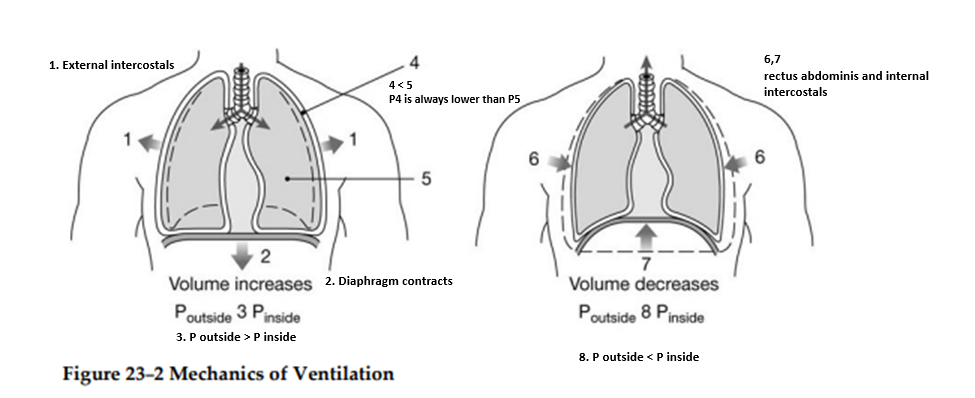
Name the primary muscles of inspiration. (Figure 23-14)
diaphragm and internal intercostal muscles |
serratus anterior and rectus abdominus |
rectus abdominis and transversus thoracis |
diaphragm and external intercostal muscles |
internal intercostal muscles and external intercostal muscles |
diaphragm and external intercostal muscles
Accessory Respiratory Muscles inspiration
Sternocleidomastoid
Scalenes
Pectoralis minor
Serratus anterior
Accessory Respiratory Muscles (exhalation)
Transversus thoracis
Internal intercostal muscle
Rectus abdominis
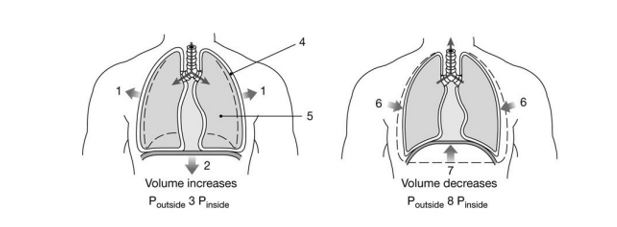
If the volume of the lungs increases, what happens to the air pressure inside the lungs?
It remains constant. |
It decreases. |
It increases and possibly damages the lungs. |
It increases. |
It increases twice the amount of the increase in volume. |
It decreases.
What occurs if intrapulmonic pressure is 763 mm Hg?
apnea |
exhalation |
hyperventilation |
inhalation |
pause in breathing |
exhalation
Alveolar ventilation refers to the
utilization of oxygen by alveolar cells to support metabolism. |
movement of dissolved gases from the alveoli to the blood. |
movement of air into and out of the lungs. |
movement of air into and out of the alveoli. |
movement of dissolved gases from the blood to the alveoli. |
movement of air into and out of the alveoli.
The function of pulmonary ventilation is to
supply oxygen to the blood. |
remove carbon dioxide from the blood. |
remove air from dead air space. |
maintain adequate alveolar ventilation. |
prevent gas exchange in the bronchioles. |
maintain adequate alveolar ventilation.
The ________ extends from the sixth cervical vertebra to the fifth thoracic vertebra.
A) lungs
B) primary bronchi
C) secondary bronchi
D) trachea
E) tertiary bronchi
trachea
If a patient inhales as deeply as possible and then exhales as much as possible, the volume of air expelled would be the patient's
reserve volume. |
vital capacity. |
tidal volume. |
inspiratory reserve volume. |
expiratory reserve volume. |
vital capacity.
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
Additional amount of air capable of being exhaled
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
Additional amount of air that can be inhaled
The following is a list of some airways.
1. secondary bronchus
2. bronchioles
3. alveolar ducts
4. primary bronchus
5. respiratory bronchiole
6. alveoli
7. terminal bronchiole
The order in which air passes through is
4, 1, 2, 7, 5, 3, 6
When the inspiratory muscles relax, the rib cage returns to its original position as a result of
gravity. |
elastic rebound. |
accessory muscle contraction. |
partial pressure difference. |
exhalation. |
elastic rebound.
The ________ of the lungs is an indication of their expandability, how easily the lungs expand and contract.
intrapulmonary pressure |
cellular respiration |
volume |
ventilation |
compliance |
compliance
A typical respiratory minute volume is
2 liters. |
500 mL. |
10 liters. |
6 liters. |
1 liter. |
6 liters.
Air that remains in conducting passages and doesn't participate in gas exchange is termed
minimal volume. |
vital capacity. |
functional residual capacity. |
residual volume. |
anatomic dead space. |
anatomic dead space.
Lungs are held tightly to the wall of the thorax due to
pulmonary ligaments that anchor the lungs. |
atmospheric pressure pushing on the lungs. |
tight junctions between the lungs and the thorax. |
surface tension of the pleural fluid and negative pressure in the cavity. |
the diaphragm and intercostal muscle contractions. |
surface tension of the pleural fluid and negative pressure in the cavity.
Functionally, which is more important to respiratory efficiency?
respiratory minute volume |
Functional residual capacity |
Alveolar ventilation rate |
tidal volume |
Alveolar ventilation rate
The partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood is approximately
100 mm Hg.
The partial pressure of oxygen in the interstitial space of peripheral tissues is approximately
40 mm Hg
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide in venous blood is approximately
45 mm Hg
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the interstitial space of peripheral tissues is approximately
45 mm Hg
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide is greatest in
venous blood
Decompression sickness is a painful condition that develops when a person is exposed to a sudden drop in atmospheric pressure. Bubbles of ____ gas are responsible for the problem.
Nitrogen
Which of the following factors would increase the amount of oxygen discharged by hemoglobin to peripheral tissues?
decreased amounts of BPG |
increased tissue PO2 |
decreased temperature and decreased amounts of BPG |
decreased pH |
decreased temperature |
decreased pH
Most of the carbon dioxide in the blood is transported as
carbaminohemoglobin. |
solute dissolved in the cytoplasm of red blood cells. |
bicarbonate ions. |
carbonic acid. |
solute dissolved in the plasma. |
bicarbonate ions.
Low pH alters hemoglobin structure so that oxygen binds less strongly to hemoglobin at low PO2. This increases the effectiveness of
hemoglobin synthesis. |
carbon dioxide transport. |
acid-base balance. |
internal respiration. |
external respiration. |
internal respiration.
If PO2 increases
saturation goes down and hemoglobin gives away oxygen. |
hemoglobin gives away oxygen. |
saturation goes up and hemoglobin stores oxygen. |
saturation goes up. |
hemoglobin stores oxygen. |
saturation goes up and hemoglobin stores oxygen.
In which of the conditions would oxygen release from hemoglobin be increased?
During a round of golf on a cool, cloudy day. |
During the run of a triathlon on a hot, humid day. |
Relaxing and reading a book |
Taking a leisurely walk through a park. |
During the run of a triathlon on a hot, humid day.
If the hemoglobin molecules in a blood sample each had a single oxygen molecule bound to them, on average, the saturation would be __________.
10 percent |
25 percent |
50 percent |
100 percent |
25 percent
When levels of CO2 rise in the blood, which of the following changes will occur?
pH levels decrease. |
Levels of HCO3- increase. |
Hemoglobin releases O2. |
All of the above changes will occur with an increase in CO2. |
All of the above changes will occur with an increase in CO2.
The most important chemical regulator of respiration is
bicarbonate ion. |
hemoglobin. |
carbon dioxide. |
oxygen. |
sodium ion. |
carbon dioxide.
A 10 percent increase in the level of carbon dioxide in the blood will
decrease the vital capacity. |
decrease the alveolar ventilation rate. |
decrease the rate of breathing. |
double the respiratory rate. |
decrease pulmonary ventilation. |
double the respiratory rate.
The term hypercapnia refers to
elevated PO2. |
elevated PCO2. |
labored breathing. |
the cessation of breathing. |
an increase in pH. |
elevated PCO2.
Hypocapnia
Abnormally low PCO2
Apnea
A period of suspended respiration
Glossopharyngeal nerves (IX)
Changes in blood pH or PO2 at carotid bodies
Vagus nerves (X)
Changes in blood pH or PO2 at aortic bodies
The apneustic centers of the pons
alter chemoreceptor sensitivity. |
inhibit the pneumotaxic and inspiratory centers. |
generate the gasp reflex. |
monitor blood gas levels. |
provide stimulation to the inspiratory center. |
provide stimulation to the inspiratory center.
The pneumotaxic center of the pons
modifies the rate and depth of breathing
All of the following provide chemoreceptor input to the respiratory centers of the medulla oblongata except the
carotid body. |
aortic body. |
central chemoreceptors. |
olfactory epithelium. |
medullary chemoreceptors. |
olfactory epithelium.
Damage to the type II pneumocytes of the lungs would result in
a loss of surfactant
–Caused by sympathetic activation
–Enlarges luminal diameter of airway
Bronchodilation
Caused by Parasympathetic activation
–Reduces luminal diameter of airway
Bronchoconstriction
Sympathetic input to the smooth muscle tissue in bronchioles causes all of these EXCEPT
bronchoconstriction
Wall of alveoli, Simple squamous, gas exchange
Pneumocyte type I
Surfactant (Allows alveoli to expand)
Pneumocyte type II
white blood cells
Engulf small particles that reach lungs
Alveolar macrophages
Blockage of pulmonary blood flow by a clot or similar obstruction is
pulmonary embolism
A blocked branch of pulmonary artery that stops blood flow to lobules or alveoli
Pulmonary embolism
A pulmonary embolism can be caused by ________ becoming trapped in a pulmonary artery.
blood clots
circulating objects in the blood
masses of fat
air bubbles
all of the above
all of the above
process involved in exchange of O2 and CO2 with external environment
diffusion of gases between the alveoli and the circulating blood
external respiration
The process by which dissolved gases are exchanged between blood and interstitial fluids is
11 to 12 mins
Internal respiration
Normal blood temp
38 C, binding of oxygen and hemoglobin