Unit 1 Flashcards
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
What are homologous structures?
Parts of the body that are similar in structure but have different functions.
What are vestigial structures?
A structure that has been reduced in size and function but may once have been complete and functional.
What is DNA evidence?
Species that share a closer evolutionary relationship will show a higher similarity in DNA.
What is embryological development?
When embryos of different species develop in very similar ways, suggesting a common ancestor.
What are fossil records?
Fossils that give us time scales on how long evolution takes.
What is gradualism?
Changes that happen slowly over a long period of time.
What is punctuated equilibrium?
Species often experience long periods of little to no change significantly, punctuated by short periods of rapid changes.
What does evolution refer to in allele terms?
Change in the relative frequency of alleles in a populations gene pool
What are alleles?
Variations of a gene
What is an inheritable mutations?
An inheritable change to DNA that occurs in germ cells, like egg or sperm.
What are the 3 factors of mutations?
Beneficial, neutral, and harmful.
What are 3 ways that new inheritable mutations occur?
Radiation, chemicals, and during DNA replication.
What is a beneficial mutation?
Positively impacts the organisms ability to survive in its environment.
What is a harmful mutation?
Negatively impacts the organisms ability to survive in its environment.
What is a neutral mutation?
Doesn’t impact the organisms ability to survive and reproduce in its environment.
What is a gene pool?
Consists of all the alleles in all the individuals that make up a population.
What is a population?
Smallest level of a group of organisms where evolution can occur.
What factors affect the frequency of certain alleles?
Natural selection, genetic drift, genetic flow, and inbreeding.
What is gene flow?
Exchange of alleles between 2 populations of the same species.
What does Gene flow result to?
Increased genetic variation.
What is genetic drift? What are the 2 types?
A change in the populations gene pool due to random chance. Genetic bottleneck, founder effect.
What is genetic bottleneck and what does it result to?
Occurs when an event significantly reduces a populations size and gene pool. Results in decreased genetic variation.
What is the founder effect and what does it result in?
Happens when a small number of individuals move to a new habitat and start a new population. Results in decreased genetic variation.
What does inbreeding mean?
Reproduction of closely related animals over multiple generations.
What are deleterious alleles?
An allele that makes an animal less “fit”.
What is artificial selection?
Happens when humans, rather than the environment, decide which traits are useful.
What is an advantage and disadvantage of artifical selection?
Humans try to establish desired traits that animals will pass onto the next generation. Results in undesirable traits and decreased genetic diversity.
What is another name for artifical selection?
Selective breeding.
Where does photosynthesis occur?
chloroplast within plants
What does photosynthesis do to create glucose?
uses water and carbon dioxide given by animals along with sunlight.
What is the waste from photosynthesis in plants?
oxygen
What is the formula for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O → 6O2 + C6H12O6
Where does cellular respiration occur?
mitochondria within animals and plant cells
What does cellular respiration use, and what does it create?
Uses glucose sugar and oxygen made by plants to create Adenosine Triphosphate.
What does cellular respiration release as waste?
Carbon dioxide and Water.
What is the chemical formula for Cellular respiration?
6O2 + C6H12O6 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
What goes into the chicken, and out of the chicken?
What goes into the plant, and out of the plant?
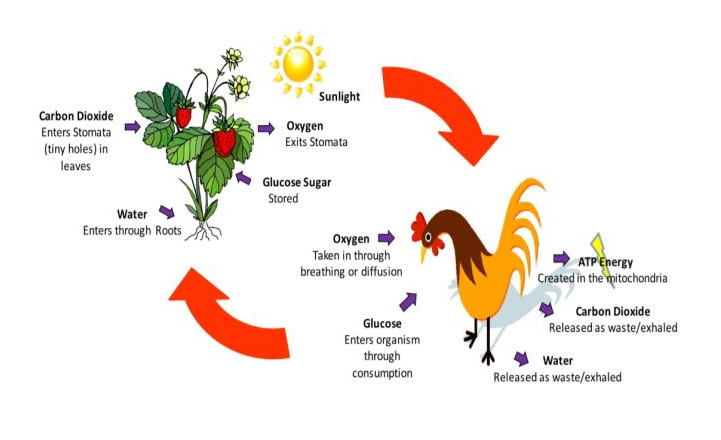
What is the stomata?
tiny openings in the plant that allow carbon dioxide to go in and oxygen to come out.
What is an organism
Any living thing, such as animals, bacteria, or plants.
What do nutrients do for organisms?
They provide them with what they need to grow.
What does space to live provide organisms with?
A place where they can get food, water, and shelter.
What is the difference between internal stimulus and external stimulus?
Internal means response within the body of the organism, while the external means outside of.
What is the cells energy currency?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
What does water do for organisms?
Helps organisms carry out cellular activities.
What does air refer to?
Carbon dioxide and oxygen.
What is maintaining homeostates?
When the body of an organism responds to environmental changes.
Difference between asexual and sexual reproduction?
Asexual requires 1 parent that makes an identical offspring, while sexual requires 2 parents with different genes.
What gets passed to offspring from parents?
Traits.
Difference between unicellular and multicellular?
Unicellular is a simple single cell, and multicellular is complex and made of cells.
What is the difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs?
Autotrophs are producers like plants, while heterotrophs are consumers like carnivores and herbivores.
What do all organisms need?
Water, nutrients, space to live, oxygen and CO2.
How do organisms change overtime?
Natural Selection, traits best suited for the environment get passed on to offspring.
What are the 8 characteristics of life?
Cells, homeostasis, energy, reproduce, traits, grow, respond, change.
What is evolution?
Process of gradual change that takes place over many generations, where organisms slowly change physically and behaviorally.
What is speciation?
Formation of a new, distinct species due to evolution. 2 different species reproduce infertile offspring, while 2 of the same species reproduce fertile offspring.
What are the 3 types of evolution?
Convergent, Divergent, Coevolution.
What is convergent evolution?
2 or more species share similar traits that did not come from a common ancestor. Happens when different species adapt to similar environments.
What is analogous structures?
Shared structures within organisms, like how whales and sharks have fins, same function, but different origin. Related to convergent evolution.
What is divergent evolution?
2 or more species separating from a common ancestor. Happens when part of a population becomes isolated due to migration or geographic barriers. Ex. Humans and frogs have the same bones so we have a common ancestor, but due to environment separation, our adaptions are different.
What is coevolution?
Occurs when 2 or more species influence each other’s evolution because of their interactions, like predator and prey, or bees and flowers.
Relating to coevolution, how will birds evolve if mimic butterflies evolve to look more like the inedible monarch butterflies?
The birds would evolve to better spot the differences between a mimic and monarch.
Relating to coevolution, how will plants evolve if an insect is depending on it for food, but the plant does not want to be eaten?
The plant would evolve to have some kind of defense, chemical in this case, to defend against the insect population.
What was Aristotle’s theory?
His theory was that all plants and animals had been placed on earth and never changed.
What is Lamark’s theory?
He theorized the law of use and disuse, the more often a body part is used, the more developed it will be. He also theorized inheritance of acquired characteristics, where the more developed or underdeveloped traits get passed on to offspring.
How was Lamark’s theory disproven?
August Weismann cut tails off of 20 generations of mice, and their tails did not change in length or size. This demonstrated that acquired characteristics are not inherited.
What was Darwin’s theory of evolution?
He theorized that evolution happens from Natural Selection.
What is Natural selection?
A phenomenon occurring in the natural world where organisms possessing traits that are highly suited to their environment have a greater likelihood of survival and reproductive success.
What are the 4 key conditions necessary for Natural Selection to occur?
Struggle for survival, inheritable variation, variation of fitness, and lots of time.
What is the struggle for survival and why is it a thing?
Competition between living things to survive, because there are more animals born than the environment can handle.
What is inheritable variation?
Organisms exhibit differences due to variations in the genes, like some giraffes having longer necks than others.
What is an inheritable trait?
Traits that can be passed down to offspring.
How do traits get passed on to offspring?
Through DNA and genes.
What is variation of fitness?
The fitness that is determined by an organisms ability to produce offspring.
How is the fitness determined of organisms?
The greater the number of offspring an organism can produce, the higher its fitness level is.
What is lots of time for natural selection?
Natural selection causes gradual changes in the population, resulting in all organisms acquiring the advantageous traits over many generations.
What is the definition of prokaryote?
Unicellular organisms without a nucleus or organelles, all prokaryotics are bacteria.
What is the definition of eukaryote?
Complex organisms, can be unicellular or multicellular, contains organelles surrounded by membranes.
What are unicellular organisms?
Contains one cell that carries out all the functions required to maintain the life of an organism, can be prokaryotic or eurkaryotic.
What are multicellular organisms? And cell specialization?
Made of more than one cell, cell develops differently through cell differentiaton, therefore has different appearances that suit their function. Cells are specialized to perform certain functions.
What is the function of a Neuron?(nerve cell)
Sends info from one part of the body to another.
What is the function of red blood cells?
Carries oxygen throughout the body.
What is the function of sperm cells?
Fertilizes the egg.
How do cells use DNA?
They use the DNA that they need, as the rest are inactive.
What can stem cells do?
Become any cell in the body because they have not undergone the process of cell differentiation yet.
What is adaptation?
Characteristics that help organisms survive and reproduce in its environment. Includes structural and behavioral.
What is one example of snake adaptations?
Snakes constrict and suffocate their prey, their jaws unhinge to swallow their prey, they can smell using their tongue.
What are behavioral adaptations for?
Finding food, a mate, for protection, and moving from place to place.
What is one adaptations for owls?
Head turning, hairballs, nocturnal.
What is the smallest unit of life?
Cell.
What are tissues?
Groups of cells that are similar in shape and function.
What are organs?
Tissues that are organized into larger structures that have one function.
What is an organ system?
Groups of organs that have related functions.
What is an organism?
An individual animal, plant, or single celled life form.