U of U PA School Dehydration, Hypovolemia, and Edema
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is dehydration?
Pure water loss with sodium retained
What does dehydration often coexist with?
Hypovolemia
How do cells change with dehydration?
Decreased in intracellular fluid volume causes decreased cell size
How do sodium and osmolarity levels change with dehydration?
Hyperosmolarity
Hypernatremia
What is hypovolemia?
Loss of water and salt equally
How do cells change size in hypovolemia?
Cells remain same size
What is edema?
Water and sodium retention
Expanding of interstitial fluid compartment
What is tonicity?
Relation of serum/ECF to ICF
What is hypertonic? How does water move?
Increased concentration of ions outside of cell
Water flows out of a cell without ions
What is isotonic?
ECF=ICF
What is hypotonic? How does water move?
Decreased concentration of ions outside cell
Water flows into cell without ions
What is osmolarity? Osmolality?
Osmolarity - Concentration of substance per liter
Osmolality - Concentration of substance per kilogram
Where is the majority of the bodies water?
ICF
What is found in abundance in ICF?
Potassium and proteins
What is found in abundance in ECF?
Sodium
What are the types of fluid in ECF?
Interstitial fluid - space between cells
Intravascular fluid - plasma in vasculature
What is the most important function of the kidney? How is this primarily done?
Volume control
Control of ECF via effective arterial blood volume (EABV)
What is effective arterial blood volume?
The volume of arterial blood that is effectively perfused to tissues and organs. This is not simply the total volume of blood in the body, but rather the portion of it that is effectively participating in the circulatory process to deliver oxygen and nutrients and remove waste products.
How does the kidney control ECF volume? How is it monitored?
Can change the concentration of sodium retained
Sensed with baroreceptors - sense renal perfusion
What do baroreceptors in the kidneys do?
Stimulate renin release via JG apparatus when low pressure to increase sodium conservation via aldosterone
ANP/BNP natriuretic factors release when high pressure to increase sodium excretion in kidney
How is concentration of ECF managed?
Via ADH by increasing water reabsorption and signaling thirst
Osmoreceptors
How do disorders of water reveal themselves? Disorders of sodium?
Disorders of water reveal themselves as sodium abnormalities
Disorders of sodium reveal themselves as volume abnormalities
What controls ICF?
Individual solute concentrations inside the cell managed by the cell and tonicity of ECF
Controls water to either move in or out of cell membrane
Where is most water loss from in dehydration?
ICF since it equilibrates across cell membrane
Backfills lost ECF
How much water can be absorbed via oral intake?
1 L/hr
How does dehydration present?
Thirst
Tachycardia
Decreased JVD and cap refill
Dry mucous membranes
Hypotension
What unique physical exam findings are indicative of dehydration?
+ passive leg raise
IVC collapse with inspiration
What lab findings are common with dehydration?
Hypernatremia
Serum osmolality >295 (280 normal)
What labs can help identify the cause of dehydration? (4)
BMP
UA
Lactic acid - increased in poor perfusion
Bicarb decreases
What is the treatment for dehydration?
Rehydration (oral or IV fluids)
Correcting electrolyte abnormalities
Identify and reverse causes
How fast can rehydration occur in dehydration?
If dehydration happened quickly (<48 hours) it can be corrected with 1-2L in 1st hour
Long-standing dehydration with hypernatremia needs slow correction
When is D5W used of NS?
If hypernatremia
What can be added to an IV once a patient beings urinating?
Potassium
How does hypovolemia present? (4)
Poor cardiac perfusion
AMS
Tachycardia
Thirst
When does hypovolemic shock occur? What is is?
If 30%+ of EABV is lost
Global tissue hypoperfusion leads to cellular hypoxia and dysfunction
What can oliguria reveal? What levels indicate oliguria
Earliest sign of a kidney injury
<20 ml/hr or 500 ml/day
How is hypovolemia treated?
Increase tissue perfusion
If hemorrhagic - FFP, platelets, and RBCs
If non-hemorrhagic - NS/LR.albumin in boluses of 30 ml/kg
What is anasarca?
Edema effecting entire body
What causes edema?
Increases in sodium leads to increases in ECF
Hypoalbuminemia
Mechanical obstruction and local factors
How does increases in sodium leading to increases in ECF lead to edema?
Renal sodium retention due to poor renal perfusion triggering aldosterone leads to increase in intravascular hydrostatic pressure leading to capillary leak and increased interstitial fluid
How does hypoalbuminemia leading to edema? What can cause it?
Decreased intravascular oncotic forces leading to capillary lea interstitial tissues
Cirrhosis
Nephrotic syndrome
Kwashiorkor - severe protein malnutrition and bilateral extremity swelling
How does mechanical obstruction and local factors lead to edema? What can cause it?
Obstruction leads to impaired venous flow and increased osmotic forces causing capillary leak
SCV syndrome
DVT
Lymphedema
What are the types of edema? (6)
Peripheral - rarely dangerous
Pulmonary - very dangerous
Ascites
Scleral
Periorbital
Cerebral - very dangerous
What can cause peripheral edema? (4)
CHF
Cirrhosis
Nephrotic syndrome
Amlodipine
Wha is the treatment for peripheral edema? (4)
Leg elevation
Diuretics
Decreased sodium intake
Compression hose
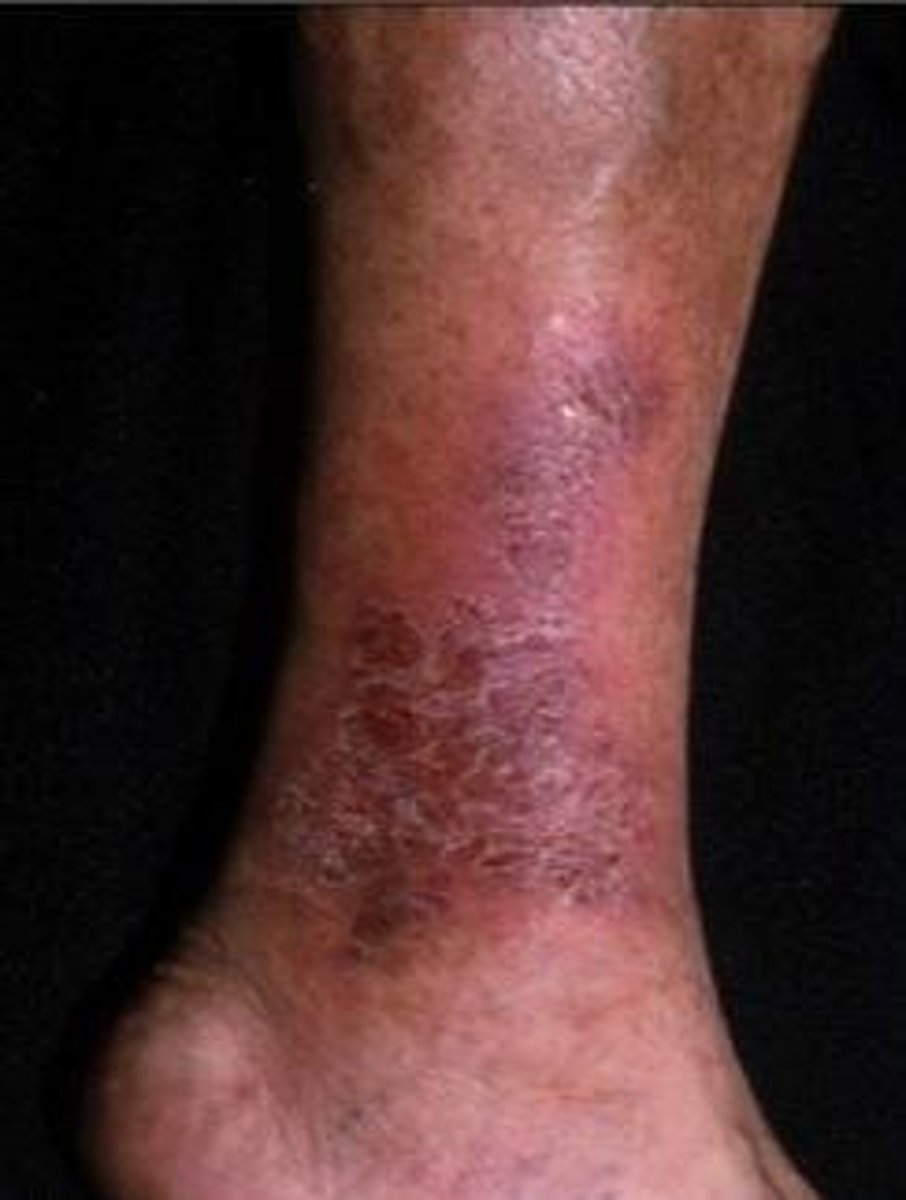
What causes hemosiderin staining?
Heme/iron leaks out of capillary into tissue due to chronic increased venous pressure
What is pulmonary edema?
Fluid back up and collection in alveoli
How does pulmonary edema present?
Dyspnea and orthopnea
Hemosiderin laden macrophages in sputum
What is the treatment for pulmonary edema?
ABCs
Diuretics or dialysis
Therapeutic thoracentesis if moderate to large pleural effusion
What is ascites?
Cirrhosis complication with fluid accumulation in peritoneal cavity
What causes ascites?
Portal venous hypertension plus concurrent inability of liver to synthesize albumin
How does ascites present? (5)
Fluid wave sign
Hemorrhoids
Pleural effusion
Esophageal varicies
Caput medusa
What test can help diagnose ascites?
Peritoneal ultrasound
What is the treatment for ascites?
Paracentesis
Can add IV albumin to stop intravascular shift into peritoneum causing hypotension and cardiac arrest