Engines and Power Trains Midterm 3
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Conductors
Substances that are capable of transmitting electric current, heat, or sound. Have less than 4 electrons in outer shell (best are gold, silver, copper)
Insulators
Substances that are poor conductors of electric current (more than 4 electrons in outer shell)
Circuit
Continueous conductor that provides a path for the flow of electrons away from and back to the generator
Volt
Unit in which electrical pressure is measured (electrical generator forces electrons to move from atom to atom, like a pump)
Current
Amount of electrical charges flowing past a point (1 Ampere is equal to 6.28 biliion billion electrons per second)
Resistance
Opposition to flow in an electrical circuit (1 ohm is the amount of electrical resistance overcome by 1 volt to cause 1 amp of current to flow)
How is resistance affected by the size of the wire?
Resistance is proportional to the length and diameter of the wire being used in the circuit.
Large diameter = less resistance; vice versa
Longer wires = more resistance; vice versa
How does temperature affect resistance
Temperature increases = resistance increases
Resistance formula
R = (rho*length)/area
Electrical Power
the work done per time by a current (I) under pressure (V) or E. (unit of measurement = W)
Watts(W)
Watts = Volts(V) * Amps(A)
Horsepower
The power required to raise 33,000 lbs one foot in one minute (1hp = 746 watts)
Alternating Current (AC)
Current that reverses its direction at a given frequency (60 Hz)
Direct Current (DC)
Electric current which flows in only one direction (used in all automotive and mobile equipment electrical systems)
Semi-conductors
Composed of elements with exactly 4 valence electrons in outer shell. Used in devices that control electrical current
Diodes
A device that will allow current to pass in only one direction
Standard diode
Always produce a simple one-way flow of electrons
Zener diodes
reverses the flow of current above a certain voltage
Transistors
Devices that use a small electrical current to control a larger current
Capacitors
Devices that store electrons. Used to protect other components from voltage spikes, and as a filter to smooth out voltage to a constant level
Resistors
Devices that reduce voltage output by resisting the flow of current in the circuit
Static charge
Type of force that causes electrons to leave an atom, this is done by friction
Magnetic fields
A bar magnet generates lines of force which come out of the North pole and enter the south pole
These lines of force are heavily concentrated at the poles
Thus, magnetic force is greatest at the poles
Electromagnetism
Electrical current generates its own magnetic field
As the current flow through the conductor is increased, so is the intensity of the magnetic field
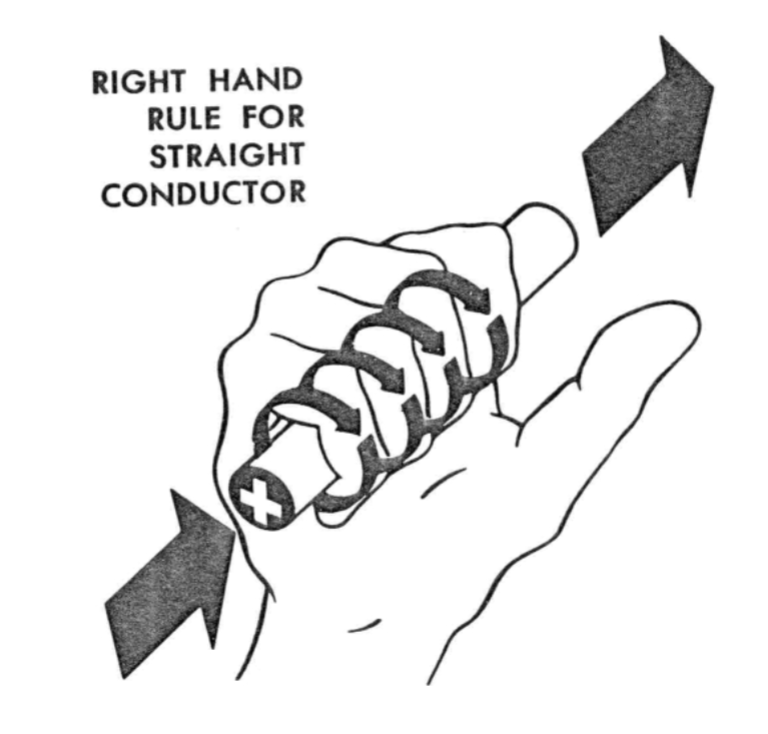
Right Hand Rule
Fingers point at the direction of the electric field and the thumbs point at the direction of the current
Conductors in Magnetic Fields
If two parallel conductors are:
Carrying current in opposite directions, their magnetic field will repel them
Carrying current in the same direction, they will be attracted.
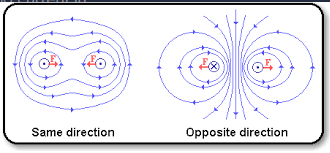
In the case of two or more parallel conductors carrying current in the same direction:
The magneitc field between the conductors is cancled out and the conductors form a single magnetic field of greater strength
If the conductor is formed into a single loop:
It’s magnetic field is the same as a straight conductor
If the conductor is formed into many loops (coil):
It’s magnetic field is the equivalent os the sum of all the loops
Electromagnetic induction
When a conductor is moved across a magnetic field, voltage is induced in the conductor. Because voltage has polarity (direction), it will cause current to flopw in a given direction (electrical generation)
How batteries produce current
Produce current through a chemical reaction between the lead plates (Anodes and Cathodes) in the cell and electrolyte
What are the negative lead plates of a battery?
Anodes (Lead = Pb)
What are the positive plates of a battery
Cathodes (Lead Peroxide = PbO2)
Besides the lead plates, what also produces current in the battery
Electrolytes (H2SO4)
When does the battery become discharged?
When the electrolytes are exhausted and the plates become sulfated
What does it look like for the Anode plate (negative) to become sulfated?
Pb + SO4 = PbSO4 + 2e-
What does it look like for the Cathode plate (positive) to become sulfated?
PbO2 + SO4 + 4H + 2e- → PbSO4 + 2H2O
How are batteries recharged?
Batteries are recharged by passing DC in opposite direction of the dicharge, reversing the process
What is the chemical reaction process of the battery being recharged?
2PbSO4 + 2H2O → Pb + PbO2 + 4H+ + 2SO4
Note how the H2 SO4 electrolyte has been restored during the charging reaction
Each cell in a lead acid battery is composed of:
lead (-) plates; anodes
lead peroxide (+) plates; cathodes
electrolyte, a mixture of 2/3 water and 1/3 sulfuric acid
separators, insulating plates that keep the anode and cathode from shorting out
How do you determeine the amount of voltage produced by a battery?
Batteries are made up of one or more cells in a a plastic or rubber case, connected in a series
[Each cell produces about two volts, so → Voltage = # cells * 2]
Does temperature affect the specific gravity of a battery electrolyte?
Temperature effects the density/specific gravity of all liquids including battery electrolytes
As temperature decreases, the density/specific gravity increases and vice versa
Cold Battery → Greater Charge
Hot Battery → Weaker Charge
What is used to check the specific gravity of each cell in a battery?
Hydrometer; most hydrometers include a thermometer to correct the specific gravity reading to (80 deg F)
Functions of a charging system:
Recharges the battery
During starting: the battery supplies the entire electrical load
During peak operation: the battery helps the generator/alternator supply enough current
Provides the current during operation
During normal operation: the generator/alternator is able to supply all the current that is needed
What is a DC charging system?
Use a generator and a regulator to produce and control electrical power
What are the two major components of a generator?
Armature: a rotating wire conductor loop
Magnetic poles: A stationary magnetic field
When the armature is rotated within the field produced by the magnetic poles, we have:
relative motion between a magnetic field and a conductor, so voltage is generated in the wire loop
What is a commutator?
Used with the generator; a split metal ring, with one hald connected to each side of the wire loop
What do brushes do?
They make contact with the commutator and connect to wires that carry the current to the load and back again
What type of current does a generator produce?
Produced AC current because the flow of the current reverses as it rotates within the fixed magnetic field
What converts the generator’s AC current to DC current
The commutator and brushes
How do brushes contribute to the AC to DC current change
The brushes are fixed relative to the magnetic poles. So, as the current swaps direction in the armature, it also swaps brushes with left = positive and right = negative
What are some factors that affect generator output?
Strength of the magnetic field
The number of wire conductor loops on the armature
The speed of the armature
What are some other generator system components?
Cutout relay
Voltage regulator
Current Regulator
What is a cutout relay?
disconnects the generator when the system is not in operation (to prevent battery discharge)
What is a voltage regulator?
Cuts the power to the field circuit when there is low demand on the generator
What is a current regulator?
cuts power to the field circuit when there is too much demand on the generator
What is an AC charging system?
Uses an alternator and a regulator to produce and control electrical power
What are AC charging systems composed of?
Alternator
Voltage/current regulator (controls voltage and current output by regulating the field circuit)
Bridge rectifier (converts AC to DC using diodes)
Ignition switch
Battery
Load
How does an alternator differ from a generator?
In an alternator, the conductor (stator) is stationary and the magnetic poles (rotor) rotate
An alternator rectifies AC to DC using diodes rather than a commutator
Since the conductors are stationary, how does this benefit the circuit?
It can be connected directly to the charging circuit instead of passing through a commutator and brushes
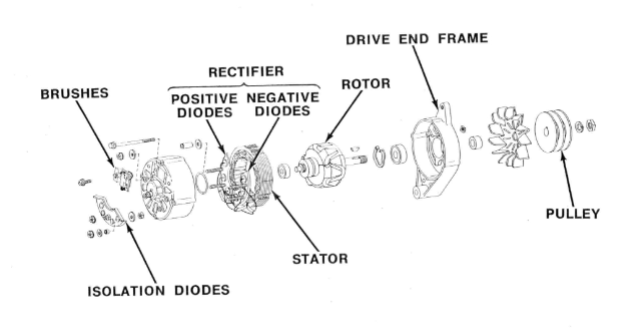
Components of an alternator:
Rotor: consists of a wire coil wrapped around an iron core mounted on a shaft
The ends of the coil are attached to two slip rings on the shaft
DC current flows through the coil via the brushes and slip rings (generating a multi-pole magnetic field)
Stator: is an iron frame that carries three sets of windings (one for each phase)
Recitifier: composed of six diodes connected to each phase in sets of two
What is the purpose of a starting circuit?
It is to safely and efficiently crank the IC engine
Modern automative engine simply require much energy. Modern energy systems quickly start engine while keeping operator safe.
What are the starting circuit components?
Battery: Supplies energy
Starter switch: Activates the circuit
Solenoid or magnetic switch: Engages the starter motor
Starter motor: Drives the flywheel to crank the engine
What are the components of a starting motor?
Field frame assembly
Armature
Drive mechanism
Solenoid
How does a starter work?
Coverts electrical energy to mechanical work (it is the reverse of a generator)
The armature forms its own magnetic field when energized by current from the battery
How was the current passed from the battery to the armature?
The current is passed through a commutator and brushes (just like the generator)
So far, what is comprised of the starter motor
The starter motor is comprised of the:
Pole pieces
armature
commutator
brushes
What are the types of motor circuits
Series-wound
Parallel-wound
Series-parallel wound
compound wound
What are the different types of switches?
Magnetic
Manual
Solenoid
Series-parallel
Are manual switches often used?
No, because of the high current hazard and long electrical path
How do magnetic switches work?
Close the circuit between the battery and the starter when an electromagnet and can be mounted on the starter or in some other location
How do solenoid switches work?
Perform the same function as the magnetic switch but also pushes the pinion gear into mesh with the flywheel so they have to be mounted on the starter
What do the starter drives do?
Connects the starting motor to the flywheel so that the crankshaft can be turned
Accomplished by moving the starter pinion gear into mesh with the flywheel when the starter motor is engaged
What are the types of starter drives
Inertia drives
electromagnetic drives
What is inertia drive?
Utilizes the weighed pinion gear on a spiral shaft to engage the flywheel
What is electromagnetic drive?
Use the action of the solenoid plunger to engage the pinion gear with the flywheel (Overrunning Clutch Drive)
What is the purpose of an ignition system
To create (high voltage) spark to ignite the air/fuel mixture in the spark ignition engines
What are the ignition circuit components
Ignition coil
Condensor
Distributor and breaker points
Spark plugs
What are the two parts of an ignition circuit?
Primary circuit: low voltage from battery
Secondary voltage: high voltage used to fire the spark plugs
What is expected from an ignition system
Must convert the low voltage to high voltage to fire engine
Accurately time the high voltage sources
Deliver the voltage to the correct spark plug at the appropriate time
What are the components of the primary circuit?
Ignition switch
Coil primary winding
Distributor contact/breaker point
Condenser
What are the components of a secondary circuit?
Coil secondary winding
Distributor rotor
Distributor cap
Spark plugs
What happens in the primary circuit
The current flow is stopped and is absorbed by the condensor instead of going to ground through the points
What happens on the secondary circuit?
Secondary winding is composed of many more turns of wire than the primary thus more voltage
High voltage runs from the coil to the distributor, where it is directed to ground through the appropriate spark plug
Types of Ignition advance systems:
Mechanical/centrifugal advance
Vacuum advance
Modern solid-state ignition systems
What is a centrifugal/mechanical advanced system
the most common type, used to increase advance as the engine speeds up
composed of counterweights and springs pinned to the breaker cam
as the engine speed increases, the weights are pulled and the breaker cam and rotor are moved forward
What is a vacuum advanced system?
Under high manifold vacuum conditions, less fuel and air are being delivered to the cylinder
The lean mixture burn slower than rich full load mixtures thus efficiency is improved with increase advance
Uses diaphragm connected to manifold vacuum
Describe a modern solid state ignition system
There has been a steady reduction in the number of moving parts in ignition systems
This has sharply reduced the need to service (tune up) the ignition on IC engines
First to be replaced was the breaker points and afterwards the distributors all together
The next step is to eliminate the distributor all together
Ignition switch
Controls opens/closes the primary circuit
Coil primary winding
Composed of a few turns of heavy wire; it generates a magnetic field in the coil
Distributor contact/breaker points
Opens and closes the primary circuit during operation
Condenser
Prevents arcing at the points and helps collapse the magnetic field in the coil rapidly.
Coil secondary winding
Composes of many turns of fine wire multiples the voltage induced by the magnetic field of the primary winding
Distributor rotor
Transfers the high secondary voltage to the distributor cap
Distributor cap
Distributes the high voltage to the correct spark plug
Spark plugs
Ignites the air fuel mixture in the cylinder
The heat range of a plug refers to it’s ability to transfer heat to the engine cooling system
By varying the length and shape of the insulator, the distance traveled by heat is also varied
Long path = hot plug
Short path = cold plug